2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Power locks
[x] Cancel search: Power locksPage 1226 of 2199

8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER DISTRIBUTION
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS.........2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CIGAR LIGHTER
OUTLET.............................2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET DOOR SPRING
REMOVAL.............................3
INSTALLATION..........................3
IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................4
REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................4
JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION..........................5
OPERATION............................5
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................6
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................8
REMOVAL.............................8
DISASSEMBLY
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
DISASSEMBLY........................9ASSEMBLY
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
ASSEMBLY..........................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION - FRONT POWER OUTLET....12
OPERATION - FRONT POWER OUTLET......12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER OUTLET . 12
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
POWER OUTLET RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER OUTLET
RELAY..............................14
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
IOD WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
FUSE COVER
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
REAR POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION - REAR POWER OUTLET.....16
OPERATION - REAR POWER OUTLET.......17
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR POWER
OUTLET............................17
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................18
POWER DISTRIBUTION
DESCRIPTION
This group covers the various standard and
optional power distribution components used on this
model. The power distribution system for this vehicle
consists of the following components:
²Power Distribution Center (PDC)
²Junction Block (JB)
²Power Outlets
The power distribution system also incorporates
various types of circuit control and protection fea-
tures, including:
²Automatic resetting circuit breakers
²Blade-type fuses
²Bus bars
²Cartridge fuses²Circuit splice blocks
²Flashers
²Fusible links
²Standard and Micro-Relays
Following are general descriptions of the major
components in the power distribution system. See the
owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for more
information on the features and use of all of the
power distribution system components. Refer to Wir-
ing Diagrams for complete circuit diagrams.
OPERATION
The power distribution system for this vehicle is
designed to provide safe, reliable, and centralized dis-
tribution points for the electrical current required to
operate all of the standard and optional factory-in-
stalled electrical and electronic powertrain, chassis,
safety, security, comfort and convenience systems. At
WJ8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 1
Page 1464 of 2199

The PCM uses the IAC motor to control idle speed
(along with timing) and to reach a desired MAP dur-
ing decel (keep engine from stalling).
The IAC motor has 4 wires with 4 circuits. Two of
the wires are for 12 volts and ground to supply elec-
trical current to the motor windings to operate the
stepper motor in one direction. The other 2 wires are
also for 12 volts and ground to supply electrical cur-
rent to operate the stepper motor in the opposite
direction.
To make the IAC go in the opposite direction, the
PCM just reverses polarity on both windings. If only
1 wire is open, the IAC can only be moved 1 step
(increment) in either direction. To keep the IAC
motor in position when no movement is needed, the
PCM will energize both windings at the same time.
This locks the IAC motor in place.
In the IAC motor system, the PCM will count
every step that the motor is moved. This allows the
PCM to determine the motor pintle position. If the
memory is cleared, the PCM no longer knows the
position of the pintle. So at the first key ON, the
PCM drives the IAC motor closed, regardless of
where it was before. This zeros the counter. From
this point the PCM will back out the IAC motor and
keep track of its position again.
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following:
²Off-idle dashpot (throttle blade will close quickly
but idle speed will not stop quickly)
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
²Power steering load control
The PCM can control polarity of the circuit to con-
trol direction of the stepper motor.
IAC Stepper Motor Program:The PCM is also
equipped with a memory program that records the
number of steps the IAC stepper motor most recently
advanced to during a certain set of parameters. For
example: The PCM was attempting to maintain a
1000 rpm target during a cold start-up cycle. The last
recorded number of steps for that may have been
125. That value would be recorded in the memory
cell so that the next time the PCM recognizes the
identical conditions, the PCM recalls that 125 steps
were required to maintain the target. This program
allows for greater customer satisfaction due to
greater control of engine idle.
Another function of the memory program, which
occurs when the power steering switch (if equipped),
or the A/C request circuit, requires that the IAC step-
per motor control engine rpm, is the recording of the
last targeted steps into the memory cell. The PCMcan anticipate A/C compressor loads. This is accom-
plished by delaying compressor operation for approx-
imately 0.5 seconds until the PCM moves the IAC
stepper motor to the recorded steps that were loaded
into the memory cell. Using this program helps elim-
inate idle-quality changes as loads change. Finally,
the PCM incorporates a9No-Load9engine speed lim-
iter of approximately 1800 - 2000 rpm, when it rec-
ognizes that the TPS is indicating an idle signal and
IAC motor cannot maintain engine idle.
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the IAC motor through the PCM.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The IAC motor is located on the throttle body.
(1) Remove air duct and air resonator box at throt-
tle body.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor
(Fig. 40).
(3) Remove two mounting bolts (screws) (Fig. 26).
(4) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
REMOVAL - 4.7L
(1) Remove air duct and air resonator box at throt-
tle body.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor
(Fig. 36).
(3) Remove two mounting bolts (screws) (Fig. 42).
(4) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
Fig. 26 Mounting Bolts (Screws)ÐIAC
1 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
2 - MOUNTING SCREWS
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 45
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1519 of 2199

INSTALLATION
NOTE: The pulley is marked front for installation.
CAUTION: On vehicles equipped with the 4.0L or
4.7L, Do not reuse the old power steering pump
pulley it is not intended for reuse. A new pulley
must be installed if removed.
(1) Replace pulley if bent, cracked, or loose.
(2) Install pulley on pump with Installer C-4063-B
or equivalent installer (Fig. 15). The front edge of the
pulley hub must be flush with the end of the shaft.
Ensure the tool and pulley are aligned with the
pump shaft.(3) Install pump assembly.
(4) With Serpentine Belt, run engine until warm (5
min.) and note any belt chirp. If chirp exists, move
pulley outward approximately 0.5 mm (0.020 in.). If
noise increases, press on 1.0 mm (0.040 in.).Be
careful that pulley does not contact mounting
bolts.
RESERVOIR
REMOVAL
(1) Remove power steering pump.
(2) Clean exterior of pump.
(3) Clamp the pump body in a soft jaw vice.
NOTE: Use new retaining clips for installation.
(4) Pry up tab and slide the retaining clips off (Fig.
16).
(5) Remove fluid reservoir from pump body.
Remove and discard O-ring seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate new O-ring Seal with Mopar Power
Steering Fluid or equivalent.
(2) Install O-ring seal in housing.
(3) Install reservoir onto housing.
(4) Slide and tap innewreservoir retainer clips
until tab locks to housing.
(5) Install power steering pump.
(6) Add power steering fluid,(Refer to 19 - STEER-
ING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 14 Pulley Removal
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP DRIVE PULLEY
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4333
Fig. 15 Pulley Installation
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP DRIVE PULLEY
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4063±B
Fig. 16 Pump Reservoir Clips
1 - RESERVOIR
2 - RETAINING CLIPS
19 - 42 PUMPWJ
PULLEY (Continued)
Page 1525 of 2199

PARK POWERFLOW
As the engine is running and the crankshaft is
rotating, the flexplate and torque converter, which
are also bolted to it, are all rotating in a clockwise
direction as viewed from the front of the engine. The
notched hub of the torque converter is connected to
the oil pump's internal gear, supplying the transmis-
sion with oil pressure. As the converter turns, it
turns the input shaft in a clockwise direction. As the
input shaft is rotating, the front clutch hub-rear
clutch retainer and all their associated parts are also
rotating, all being directly connected to the input
shaft. The power flow from the engine through the
front clutch hub and rear clutch retainer stops at the
rear clutch retainer. Therefore, no power flow to the
output shaft occurs because no clutches are applied.
The only mechanism in use at this time is the park-
ing sprag (Fig. 3), which locks the parking gear on
the output shaft to the transmission case.
NEUTRAL POWERFLOW
With the gear selector in the NEUTRAL position
(Fig. 4), the power flow of the transmission is essen-
tially the same as in the park position. The only
operational difference is that the parking sprag has
been disengaged, unlocking the output shaft from the
transmission case and allowing it to move freely.
Fig. 3 Park Powerflow
1 - LEVER ENGAGED FOR PARK
2 - PARK SPRAG
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT
Fig. 4 Neutral Powerflow
1 - PAWL DISENGAGED FOR NEUTRAL
2 - PARK SPRAG
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT
4 - CAM
5-PAWL
21 - 6 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1917 of 2199

(23) Reconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connectors to the following floor panel transmission
tunnel components:
²the Airbag Control Module (ACM) connector
receptacle
²the park brake switch terminal
²the transmission shifter connector receptacle.
(24) Reconnect the left and right body wire har-
ness connectors, the Ignition Off Draw (IOD) wire
harness connector and the fused B(+) wire harness
connector to the connector receptacles of the Junction
Block (JB) and tighten the connector screws (Fig. 5).
Tighten the screws to 4 N´m (36 in. lbs.).
(25) Engage the lower steering column shaft with
the steering shaft coupler and position the steering
column to the mounting studs on the instrument
panel steering column support bracket (Fig. 4).
(26) Install and tighten the four nuts that secure
the steering column to the studs on the instrument
panel steering column support bracket. Tighten the
nuts to 11.8 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(27) Install and tighten the bolt that secures the
coupler to the lower steering column shaft. Tighten
the bolt to 49 N´m (36 ft. lbs.).
(28) Turn the ignition switch to the On position,
then install the shifter interlock cable connector into
the ignition lock housing receptacle.
(29) Reconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connectors to the following steering column compo-
nents (Fig. 3):
²the two lower clockspring connector receptacles
²the left multi-function switch connector recepta-
cle
²the right multi-function switch connector recep-
tacle
²the two ignition switch connector receptacles
²the shifter interlock solenoid connector recepta-
cle
²if the vehicle is so equipped, the Sentry Key
Immobilizer Module (SKIM) connector receptacle.
(30) Position the lower tilting steering column
shroud to the steering column multi-function switchmounting housing, then install and tighten the screw
that secures the shroud to the housing (Fig. 2).
Tighten the screw to 1.9 N´m (17 in. lbs.).
(31) Position the upper tilting steering column
shroud over the steering column. Align the upper and
lower shrouds with each other and snap the two
halves together.
(32) Reinstall the steering column bracket onto the
instrument panel steering column support bracket.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/IP
STEERING COLUMN BRACKET - INSTALLA-
TION).
(33) Reinstall the steering column opening cover
onto the instrument panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN OPEN-
ING COVER - INSTALLATION).
(34) Reinstall the cluster bezel onto the instru-
ment panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT
PANEL/CLUSTER BEZEL - INSTALLATION).
(35) Reinstall the fuse cover onto the Junction
Block (JB). (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER DIS-
TRIBUTION/FUSE COVER - INSTALLATION).
(36) Reinstall the console onto the floor panel
transmission tunnel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERI-
OR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLATION).
(37) Reinstall the trim panels onto the right and
left inner cowl sides. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERI-
OR/COWL TRIM - INSTALLATION).
(38) Reinstall the scuff plates onto the right and
left front door sills. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/
DOOR SILL SCUFF PLATE - INSTALLATION).
(39) Reinstall the top cover onto the instrument
panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
INSTRUMENT PANEL TOP COVER - INSTALLA-
TION).
(40) Reinstall the trim onto the right and left
A-pillars. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/A-PILLAR
TRIM - INSTALLATION).
(41) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
23 - 44 INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMWJ
INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1971 of 2199
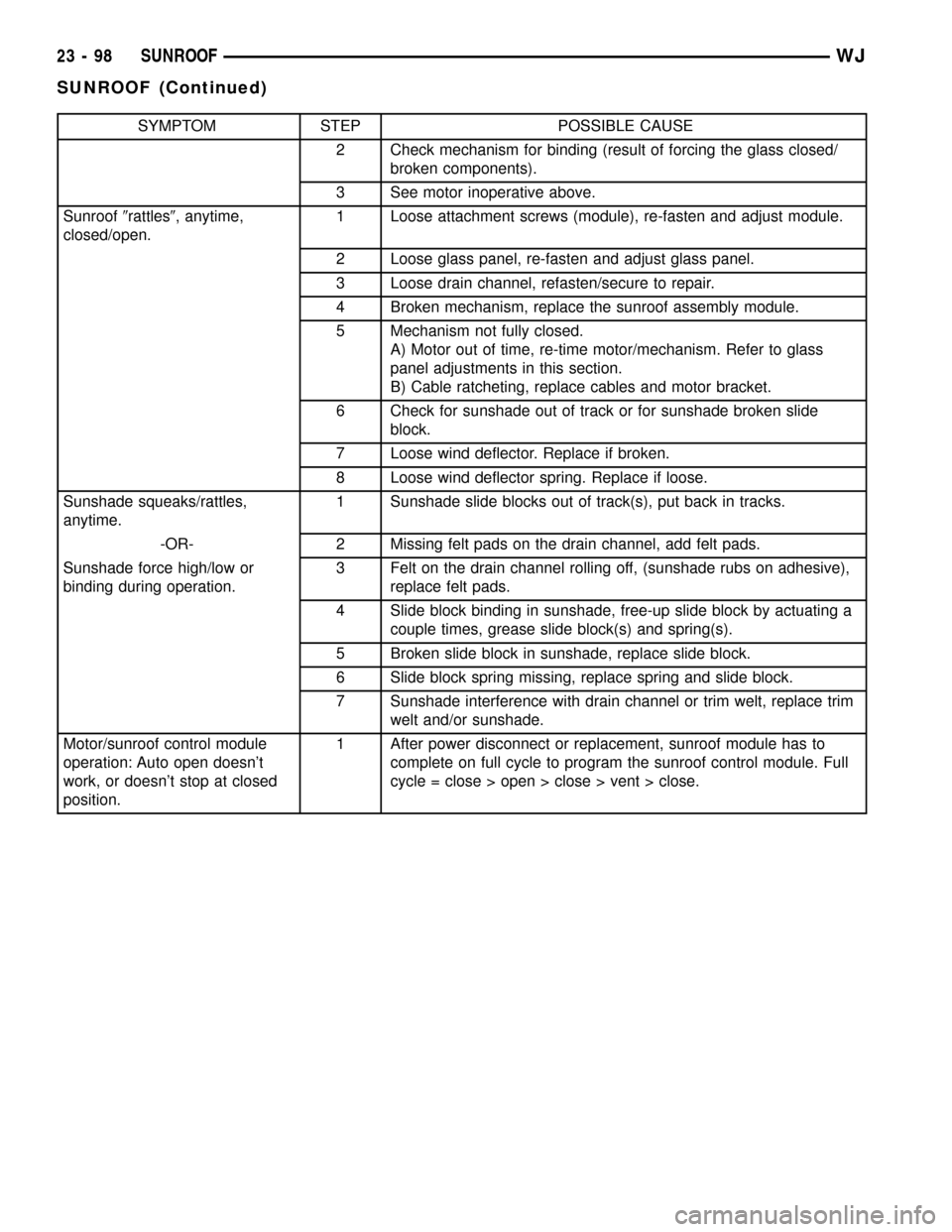
SYMPTOM STEP POSSIBLE CAUSE
2 Check mechanism for binding (result of forcing the glass closed/
broken components).
3 See motor inoperative above.
Sunroof9rattles9, anytime,
closed/open.1 Loose attachment screws (module), re-fasten and adjust module.
2 Loose glass panel, re-fasten and adjust glass panel.
3 Loose drain channel, refasten/secure to repair.
4 Broken mechanism, replace the sunroof assembly module.
5 Mechanism not fully closed.
A) Motor out of time, re-time motor/mechanism. Refer to glass
panel adjustments in this section.
B) Cable ratcheting, replace cables and motor bracket.
6 Check for sunshade out of track or for sunshade broken slide
block.
7 Loose wind deflector. Replace if broken.
8 Loose wind deflector spring. Replace if loose.
Sunshade squeaks/rattles,
anytime.1 Sunshade slide blocks out of track(s), put back in tracks.
-OR- 2 Missing felt pads on the drain channel, add felt pads.
Sunshade force high/low or
binding during operation.3 Felt on the drain channel rolling off, (sunshade rubs on adhesive),
replace felt pads.
4 Slide block binding in sunshade, free-up slide block by actuating a
couple times, grease slide block(s) and spring(s).
5 Broken slide block in sunshade, replace slide block.
6 Slide block spring missing, replace spring and slide block.
7 Sunshade interference with drain channel or trim welt, replace trim
welt and/or sunshade.
Motor/sunroof control module
operation: Auto open doesn't
work, or doesn't stop at closed
position.1 After power disconnect or replacement, sunroof module has to
complete on full cycle to program the sunroof control module. Full
cycle = close > open > close > vent > close.
23 - 98 SUNROOFWJ
SUNROOF (Continued)
Page 2186 of 2199

OPERATION
The main purpose of the LDP is to pressurize the
fuel system for leak checking. It closes the EVAP sys-
tem vent to atmospheric pressure so the system can
be pressurized for leak testing. The diaphragm is
powered by engine vacuum. It pumps air into the
EVAP system to develop a pressure of about 7.59
H2O (1/4) psi. A reed switch in the LDP allows the
PCM to monitor the position of the LDP diaphragm.
The PCM uses the reed switch input to monitor how
fast the LDP is pumping air into the EVAP system.
This allows detection of leaks and blockage. The LDP
assembly consists of several parts (Fig. 12). The sole-
noid is controlled by the PCM, and it connects the
upper pump cavity to either engine vacuum or atmo-
spheric pressure. A vent valve closes the EVAP sys-
tem to atmosphere, sealing the system during leak
testing. The pump section of the LDP consists of a
diaphragm that moves up and down to bring air in
through the air filter and inlet check valve, and
pump it out through an outlet check valve into the
EVAP system. The diaphragm is pulled up by engine
vacuum, and pushed down by spring pressure, as the
LDP solenoid turns on and off. The LDP also has a
magnetic reed switch to signal diaphragm position to
the PCM. When the diaphragm is down, the switch is
closed, which sends a 12 V (system voltage) signal to
the PCM. When the diaphragm is up, the switch is
open, and there is no voltage sent to the PCM. This
allows the PCM to monitor LDP pumping action as it
turns the LDP solenoid on and off.
LDP AT REST (NOT POWERED)
When the LDP is at rest (no electrical/vacuum) the
diaphragm is allowed to drop down if the internal
(EVAP system) pressure is not greater than the
return spring. The LDP solenoid blocks the engine
vacuum port and opens the atmospheric pressure
port connected through the EVAP system air filter.
The vent valve is held open by the diaphragm. This
allows the canister to see atmospheric pressure (Fig.
13).
DIAPHRAGM UPWARD MOVEMENT
When the PCM energizes the LDP solenoid, the
solenoid blocks the atmospheric port leading through
the EVAP air filter and at the same time opens the
engine vacuum port to the pump cavity above the
diaphragm. The diaphragm moves upward when vac-
uum above the diaphragm exceeds spring force. This
upward movement closes the vent valve. It also
causes low pressure below the diaphragm, unseating
the inlet check valve and allowing air in from the
EVAP air filter. When the diaphragm completes its
upward movement, the LDP reed switch turns from
closed to open (Fig. 14).
DIAPHRAGM DOWNWARD MOVEMENT
Based on reed switch input, the PCM de-energizes
the LDP solenoid, causing it to block the vacuum
port, and open the atmospheric port. This connects
the upper pump cavity to atmosphere through the
EVAP air filter. The spring is now able to push the
diaphragm down. The downward movement of the
diaphragm closes the inlet check valve and opens the
outlet check valve pumping air into the evaporative
system. The LDP reed switch turns from open to
closed, allowing the PCM to monitor LDP pumping
(diaphragm up/down) activity (Fig. 15). During the
pumping mode, the diaphragm will not move down
far enough to open the vent valve. The pumping cycle
is repeated as the solenoid is turned on and off.
When the evaporative system begins to pressurize,
the pressure on the bottom of the diaphragm will
begin to oppose the spring pressure, slowing the
pumping action. The PCM watches the time from
when the solenoid is de-energized, until the dia-
phragm drops down far enough for the reed switch to
Fig. 12 EVAP LEAK DETECTION SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
1 - Reed Switch
2 - Solenoid
3 - Spring
4 - Pump Cavity
5 - Diaphragm
6 - Inlet Check Valve
7 - Vent Valve
8 - From Air Filter
9 - To Canister
10 - Outlet Check Valve
11 - Engine Vacuum
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 31
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)