2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Intake air temperature sensor
[x] Cancel search: Intake air temperature sensorPage 1466 of 2199

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
The Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) sensor
is installed into the intake manifold plenum near the
front of the throttle body (Fig. 27).
(1) Install sensor into intake manifold. Tighten
sensor to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
INSTALLATION - 4.7L
Threaded Type Sensor
(1) Install sensor (Fig. 28) into intake manifold.
Tighten sensor to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
Snap-In Type Sensor
(1) Check condition of sensor o-ring (Fig. 30).
(2) Clean sensor mounting hole in intake manifold.(3) Position sensor (Fig. 29) into intake manifold
and rotate clockwise until past release tab.
(4) Install electrical connector.
Fig. 28 IAT - 4.7L (THREADED TYPE)
1 - THROTTLE BODY
2 - TPS
3 - IAC MOTOR
4 - IAT SENSOR (THREADED TYPE)
5 - MOUNTING SCREWS
Fig. 29 IAT SENSOR - 4.7L (SNAP-IN TYPE)
1 - LEFT SIDE OF THROTTLE BODY
2 - ELEC. CONNECT.
3 - IAT SENSOR
4 - RELEASE TAB
Fig. 30 IAT SENSOR TAB / O-RING - 4.7L (SNAP-IN
TYPE)
1 - IAT SENSOR
2 - SENSOR O-RING
3 - RELEASE TAB
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 47
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1467 of 2199

MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
On the 4.0L six-cylinder engine the MAP sensor is
mounted to the engine throttle body. On the 4.7L V-8
engine the MAP sensor is mounted to front of the
intake manifold.
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
intake manifold. An o-ring seals the sensor to the
intake manifold.
OPERATION
The MAP sensor is used as an input to the Power-
train Control Module (PCM). It contains a silicon
based sensing unit to provide data on the manifold
vacuum that draws the air/fuel mixture into the com-
bustion chamber. The PCM requires this information
to determine injector pulse width and spark advance.
When manifold absolute pressure (MAP) equals
Barometric pressure, the pulse width will be at max-
imum.
A 5 volt reference is supplied from the PCM and
returns a voltage signal to the PCM that reflects
manifold pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V
and full scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of 0±15
psi, the voltage changes 4.0V. To operate the sensor,
it is supplied a regulated 4.8 to 5.1 volts. Ground is
provided through the low-noise, sensor return circuit
at the PCM.
The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to fuel injector pulse width. The most important
function of the MAP sensor is to determine baromet-
ric pressure. The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is
at sea level or at a higher altitude, because the air
density changes with altitude. It will also help to cor-
rect for varying barometric pressure. Barometric
pressure and altitude have a direct inverse correla-
tion; as altitude goes up, barometric goes down. At
key-on, the PCM powers up and looks at MAP volt-
age, and based upon the voltage it sees, it knows the
current barometric pressure (relative to altitude).
Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at the voltage
again, continuously every 12 milliseconds, and com-
pares the current voltage to what it was at key-on.
The difference between current voltage and what it
was at key-on, is manifold vacuum.
During key-on (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring a known good sensor.
As the altitude increases, the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to avery different altitude than where it was at key-on,
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open Throttle (WOT), based
upon Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) angle and RPM,
it will update barometric pressure in the MAP mem-
ory cell. With periodic updates, the PCM can make
its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor input to aid in cal-
culating the following:
²Manifold pressure
²Barometric pressure
²Engine load
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (certain automatic trans-
missions only)
²Idle speed
²Decel fuel shutoff
The MAP sensor signal is provided from a single
piezoresistive element located in the center of a dia-
phragm. The element and diaphragm are both made
of silicone. As manifold pressure changes, the dia-
phragm moves causing the element to deflect, which
stresses the silicone. When silicone is exposed to
stress, its resistance changes. As manifold vacuum
increases, the MAP sensor input voltage decreases
proportionally. The sensor also contains electronics
that condition the signal and provide temperature
compensation.
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; meaning as
pressure changes, voltage changes proportionately.
The range of voltage output from the sensor is usu-
ally between 4.6 volts at sea level to as low as 0.3
volts at 26 in. of Hg. Barometric pressure is the pres-
sure exerted by the atmosphere upon an object. At
sea level on a standard day, no storm, barometric
pressure is approximately 29.92 in Hg. For every 100
feet of altitude, barometric pressure drops .10 in. Hg.
If a storm goes through it can change barometric
pressure from what should be present for that alti-
tude. You should know what the average pressure
and corresponding barometric pressure is for your
area.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The MAP sensor is mounted to the side of the
throttle body (Fig. 40). An L-shaped rubber fitting is
used to connect the MAP sensor to throttle body (Fig.
31).
(1) Remove air cleaner duct and air resonator box
at throttle body.
14 - 48 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
Page 2095 of 2199

Both the manual A/C Heater control panel and the
AZC control panel are serviced only as complete
units and cannot be repaired. If faulty or damaged,
the entire control panel unit must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC ZONE
CONTROL SYSTEM
The Automatic Zone Control (AZC) control module
has a system self-diagnostic mode which continuously
monitors various parameters during normal system
operation. If a system fault is detected, a current and
historical fault is recorded. When the current fault is
cleared, the historical fault remains until reset (man-
ually or automatically). Both the current and histor-
ical fault codes can be accessed through either the
front panel, or over the Programmable Communica-
tions Interface (PCI) bus using a DRBIIItscan tool,
and the appropriate diagnostic information.
The AZC control module is capable of three differ-
ent types of self-diagnostic tests, as follows:
²Fault Code Tests
²Input Circuit Tests
²Output Circuit/Actuator Tests
The information that follows describes:
²How to read the self-diagnostic display
²How to enter the AZC control module self-diag-
nostic test mode
²How to select the self-diagnostic test types
²How to perform the different tests
ENTERING THE AZC SELF-DIAGNOSTIC MODE
To enter the AZC self-diagnostic mode, perform the
following:
(1) Depress the a/c and recirc buttons at the same
time and hold. Rotate the left temperature control
knob clockwise (CW) one detent.
(2) If you continue to keep the a/c and recirc but-
tons depressed, the AZC control module will perform
a Segment Test of the Vacuum Fluorescent (VF) dis-
play. In the Segment Test you should see all of the
display segments illuminate as long as both buttons
are held. If a display segment fails to illuminate, the
vacuum fluorescent display is faulty and the a/c
heater control must be replaced.
(3) After viewing the Segment Test, release the
A/C and Recirc buttons and the display will clear
momentarily.Ifa0isdisplayed, then no faults
are set in the system.Should there be any faults,
either9current9or9historical9, all fault codes will be
displayed in ascending numerical sequence (note no
effort is made to display fault codes in chronological
order). Each fault code is displayed for one second
before the next code is displayed. Once all fault codes
have been displayed, the system will then repeat the
fault code numbers. This will continue until the left
side set temperature control is moved at least onedetent position in the CW direction or the ignition is
turned9OFF9.
FAULT CODE TESTS
Fault codes are two-digit numbers that identify a
circuit that is malfunctioning. There are two differ-
ent kinds of fault codes.
1.Current Fault Codes- Current means the
fault is present right now. There are two types of cur-
rent faults: input faults, and system faults.
2.Historical Fault Codes- Historical or stored
means that the fault occurred previously, but is not
present right now. A majority of historical fault codes
are caused by intermittent wire harness or wire har-
ness connector problems.
CURRENT FAULT CODES
Input faults 01 = IR thermister circuit
open
02 = IR thermister circuit
shorted
03 = Fan pot shorted
04 = Fan pot open
05 = Mode pot shorted
06 = Mode pot open
07 = IR sensor delta too
large
08 = Reserved
09 = Reserved
10 = One of four motor
drivers has drive9A9
shorted to ground
11 = Engine air intake
temperature Buss
message missing
12 = Country code Buss
message missing
24 - 18 CONTROLSWJ
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2097 of 2199

HISTORICAL FAULT CODES
Input faults 33 = IR thermister circuit was open
34 = IR thermister circuit was shorted
35 = Fan pot was shorted
36 = Fan pot was open
37 = Mode pot was shorted
38 = Mode pot was open
39 = IR sensor delta was too large
40 = Reserved
41 = Reserved
42 = One of four motor drivers had drive9A9shorted to
ground
43 = Engine air intake temperature Buss message
missing
44 = Country code Buss message missing
System Faults 45 = Mode motor was not responding
46 = AI (Recirc) motor was not responding
47 = Left temperature door was not responding
48 = Right temperature door was not responding
49 = Mode door travel range too small
50 = Mode door travel range too large
51 = AI (Recirc) door travel range too small
52 = AI (Recirc) door travel range too large
53 = Left temperature door travel too small
54 = Left temperature door travel too large
55 = Right temperature door travel too small
56 = Right temperature door travel too large
57 = Calibration check sum error
58 = Engine coolant temp bus message missing
59 = Vehicle speed bus message missing
60 = Engine RPM bus message missing
61 = OAT bus message missing
62 = Display intensity bus message missing
63 = VIN number bus message missing
64 = Raw OAT bus message was missing
65 = Reserved
66 = Reserved
67 = Reserved
NOTE: A battery disconnect will erase all faults
stored in Random Access Memory (RAM) of the
AZC control module. It is recommended that all
faults be recorded before they are erased.RETRIEVING FAULT CODES
(1) To begin the fault code tests, depress the A/C
and Recirc buttons at the same time and rotate the
left temperature control knob clockwise (CW) one
detent, then release the push-button.
24 - 20 CONTROLSWJ
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2101 of 2199
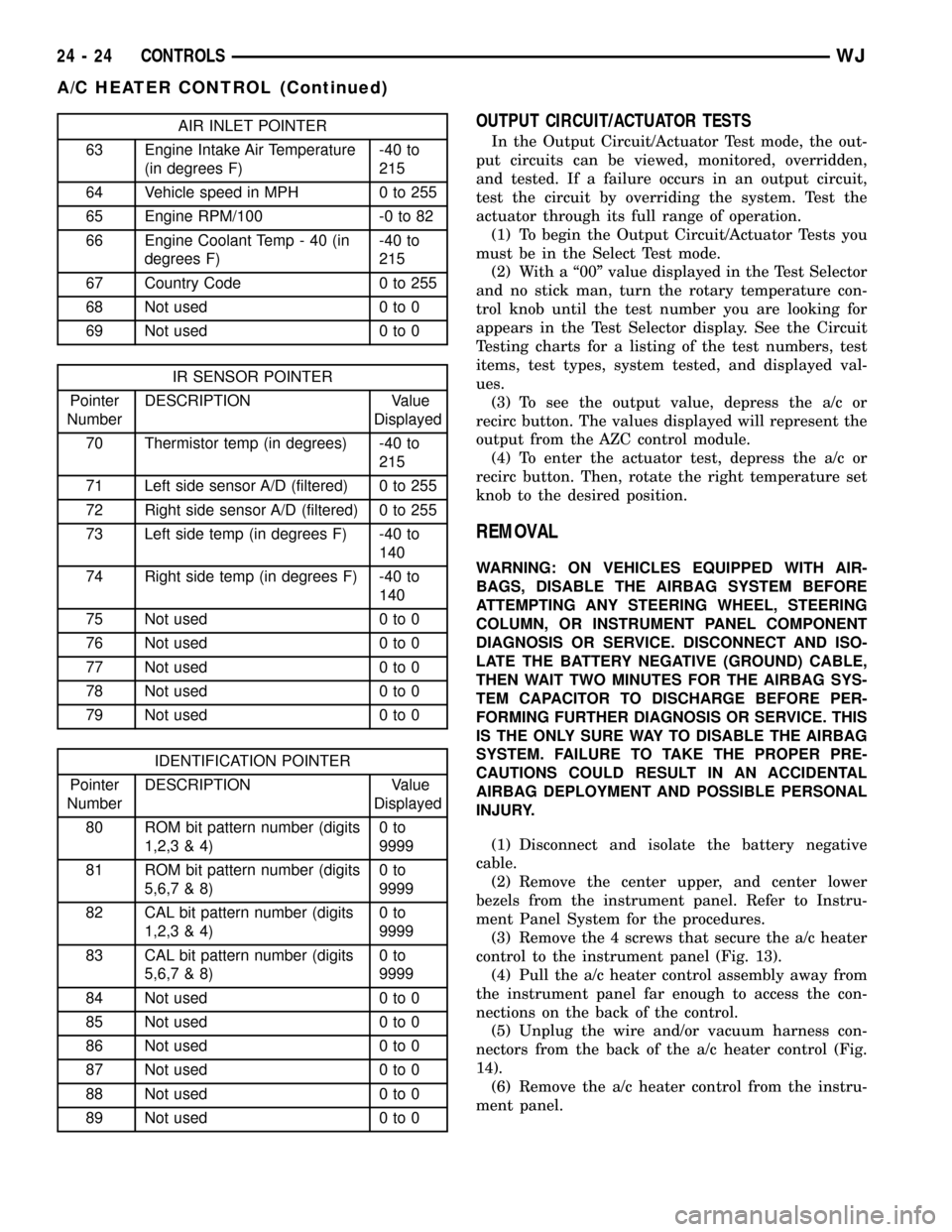
AIR INLET POINTER
63 Engine Intake Air Temperature
(in degrees F)-40 to
215
64 Vehicle speed in MPH 0 to 255
65 Engine RPM/100 -0 to 82
66 Engine Coolant Temp - 40 (in
degrees F)-40 to
215
67 Country Code 0 to 255
68 Not used 0 to 0
69 Not used 0 to 0
IR SENSOR POINTER
Pointer
NumberDESCRIPTION Value
Displayed
70 Thermistor temp (in degrees) -40 to
215
71 Left side sensor A/D (filtered) 0 to 255
72 Right side sensor A/D (filtered) 0 to 255
73 Left side temp (in degrees F) -40 to
140
74 Right side temp (in degrees F) -40 to
140
75 Not used 0 to 0
76 Not used 0 to 0
77 Not used 0 to 0
78 Not used 0 to 0
79 Not used 0 to 0
IDENTIFICATION POINTER
Pointer
NumberDESCRIPTION Value
Displayed
80 ROM bit pattern number (digits
1,2,3 & 4)0to
9999
81 ROM bit pattern number (digits
5,6,7 & 8)0to
9999
82 CAL bit pattern number (digits
1,2,3 & 4)0to
9999
83 CAL bit pattern number (digits
5,6,7 & 8)0to
9999
84 Not used 0 to 0
85 Not used 0 to 0
86 Not used 0 to 0
87 Not used 0 to 0
88 Not used 0 to 0
89 Not used 0 to 0
OUTPUT CIRCUIT/ACTUATOR TESTS
In the Output Circuit/Actuator Test mode, the out-
put circuits can be viewed, monitored, overridden,
and tested. If a failure occurs in an output circuit,
test the circuit by overriding the system. Test the
actuator through its full range of operation.
(1) To begin the Output Circuit/Actuator Tests you
must be in the Select Test mode.
(2) With a ª00º value displayed in the Test Selector
and no stick man, turn the rotary temperature con-
trol knob until the test number you are looking for
appears in the Test Selector display. See the Circuit
Testing charts for a listing of the test numbers, test
items, test types, system tested, and displayed val-
ues.
(3) To see the output value, depress the a/c or
recirc button. The values displayed will represent the
output from the AZC control module.
(4) To enter the actuator test, depress the a/c or
recirc button. Then, rotate the right temperature set
knob to the desired position.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the center upper, and center lower
bezels from the instrument panel. Refer to Instru-
ment Panel System for the procedures.
(3) Remove the 4 screws that secure the a/c heater
control to the instrument panel (Fig. 13).
(4) Pull the a/c heater control assembly away from
the instrument panel far enough to access the con-
nections on the back of the control.
(5) Unplug the wire and/or vacuum harness con-
nectors from the back of the a/c heater control (Fig.
14).
(6) Remove the a/c heater control from the instru-
ment panel.
24 - 24 CONTROLSWJ
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2158 of 2199

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0057 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0058 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0071 (M) Amb/Bat Temp Sensor Performance
P0106 Barometric Pressure Out of Range MAP sensor input voltage out of an acceptable range
detected during reading of barometric pressure at key-on.
P0107 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
P0108 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor input above maximum acceptable voltage.
PO111 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Performance
P0112 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage Low Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0113 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage High Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0116 Coolant Temp Sensor Performance A rationatilty error has been detected in the coolant temp
sensor.
P0117 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too Low Engine coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0118 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too High Engine coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0121 (M) TPS Voltage Does Not Agree With
MAPTPS signal does not correlate to MAP sensor signal.
P0121 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0122 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage Low Throttle position sensor input below the acceptable
voltage range.
P0122 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0123 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
P0123 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too HighAPPS voltage input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
P0125 (M) Closed Loop Temp Not Reached Time to enter Closed Loop Operation (Fuel Control) is
excessive.
P0125 (M) Engine is Cold Too Long Engine does not reach operating temperature.
P0130 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionOxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0131 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0132 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0133 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0134 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor input.
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 3
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2166 of 2199
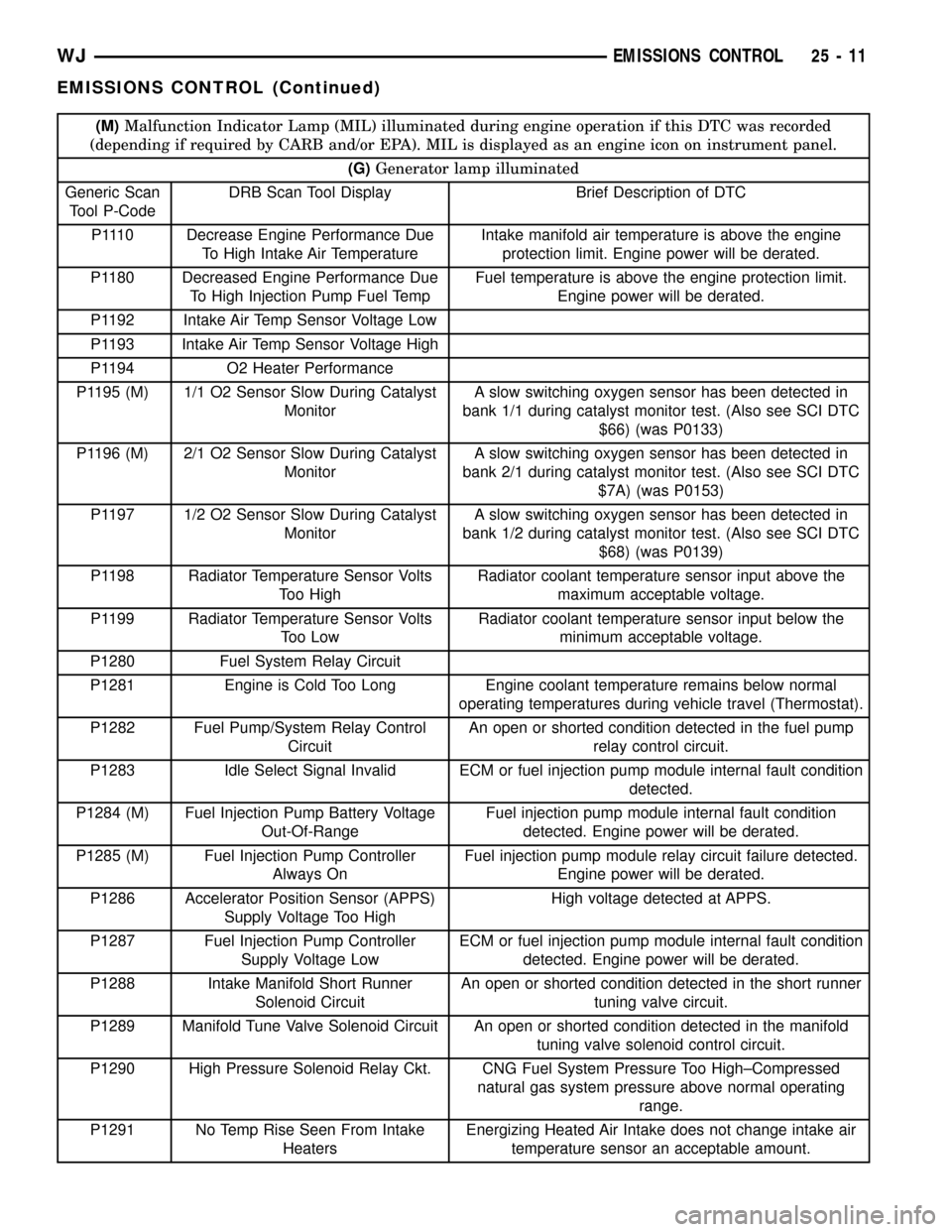
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1110 Decrease Engine Performance Due
To High Intake Air TemperatureIntake manifold air temperature is above the engine
protection limit. Engine power will be derated.
P1180 Decreased Engine Performance Due
To High Injection Pump Fuel TempFuel temperature is above the engine protection limit.
Engine power will be derated.
P1192 Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage Low
P1193 Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage High
P1194 O2 Heater Performance
P1195 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 1/1 during catalyst monitor test. (Also see SCI DTC
$66) (was P0133)
P1196 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 2/1 during catalyst monitor test. (Also see SCI DTC
$7A) (was P0153)
P1197 1/2 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 1/2 during catalyst monitor test. (Also see SCI DTC
$68) (was P0139)
P1198 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too HighRadiator coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P1199 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too LowRadiator coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P1280 Fuel System Relay Circuit
P1281 Engine is Cold Too Long Engine coolant temperature remains below normal
operating temperatures during vehicle travel (Thermostat).
P1282 Fuel Pump/System Relay Control
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the fuel pump
relay control circuit.
P1283 Idle Select Signal Invalid ECM or fuel injection pump module internal fault condition
detected.
P1284 (M) Fuel Injection Pump Battery Voltage
Out-Of-RangeFuel injection pump module internal fault condition
detected. Engine power will be derated.
P1285 (M) Fuel Injection Pump Controller
Always OnFuel injection pump module relay circuit failure detected.
Engine power will be derated.
P1286 Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Supply Voltage Too HighHigh voltage detected at APPS.
P1287 Fuel Injection Pump Controller
Supply Voltage LowECM or fuel injection pump module internal fault condition
detected. Engine power will be derated.
P1288 Intake Manifold Short Runner
Solenoid CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the short runner
tuning valve circuit.
P1289 Manifold Tune Valve Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the manifold
tuning valve solenoid control circuit.
P1290 High Pressure Solenoid Relay Ckt. CNG Fuel System Pressure Too High±Compressed
natural gas system pressure above normal operating
range.
P1291 No Temp Rise Seen From Intake
HeatersEnergizing Heated Air Intake does not change intake air
temperature sensor an acceptable amount.
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 11
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2167 of 2199
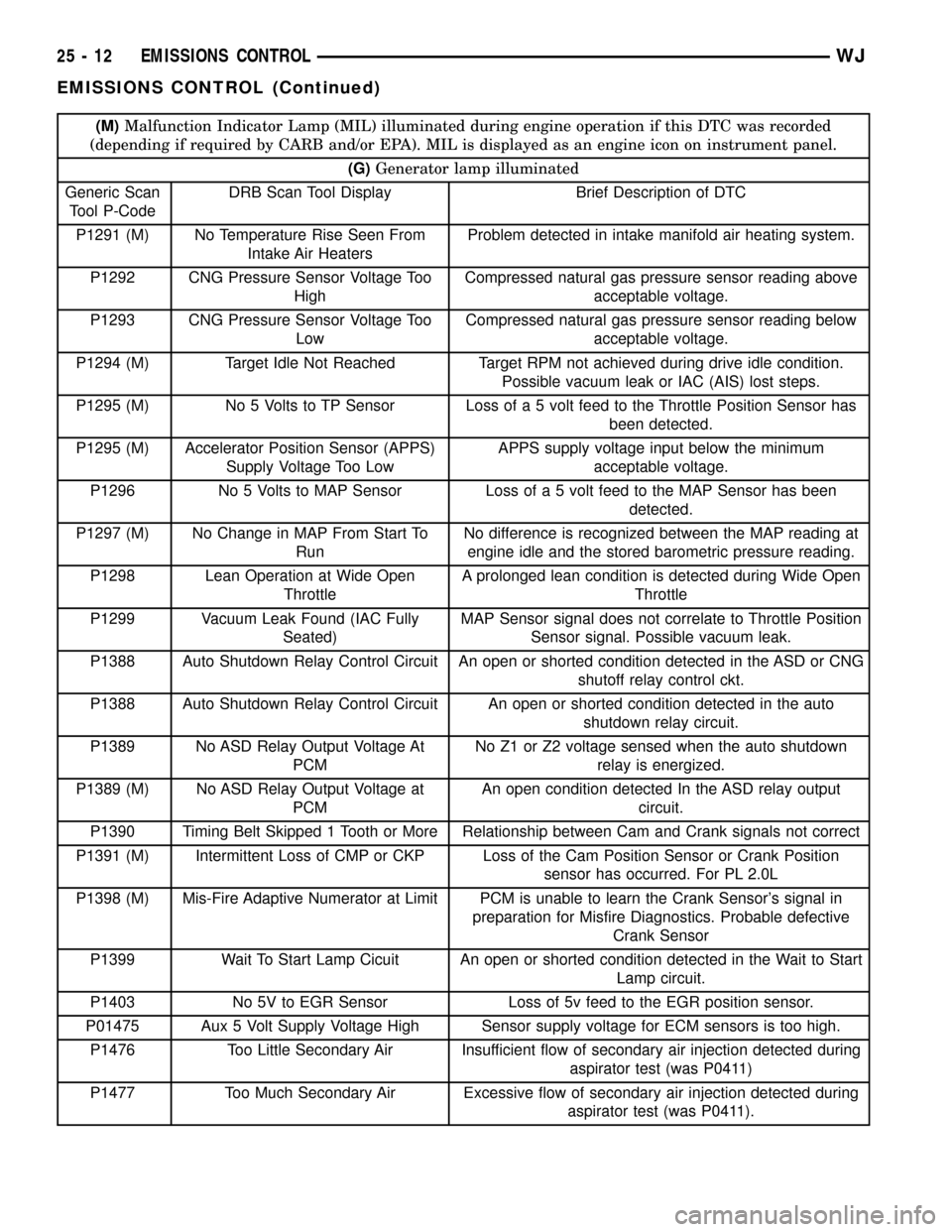
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1291 (M) No Temperature Rise Seen From
Intake Air HeatersProblem detected in intake manifold air heating system.
P1292 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
HighCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading above
acceptable voltage.
P1293 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
LowCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading below
acceptable voltage.
P1294 (M) Target Idle Not Reached Target RPM not achieved during drive idle condition.
Possible vacuum leak or IAC (AIS) lost steps.
P1295 (M) No 5 Volts to TP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the Throttle Position Sensor has
been detected.
P1295 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Supply Voltage Too LowAPPS supply voltage input below the minimum
acceptable voltage.
P1296 No 5 Volts to MAP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the MAP Sensor has been
detected.
P1297 (M) No Change in MAP From Start To
RunNo difference is recognized between the MAP reading at
engine idle and the stored barometric pressure reading.
P1298 Lean Operation at Wide Open
ThrottleA prolonged lean condition is detected during Wide Open
Throttle
P1299 Vacuum Leak Found (IAC Fully
Seated)MAP Sensor signal does not correlate to Throttle Position
Sensor signal. Possible vacuum leak.
P1388 Auto Shutdown Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the ASD or CNG
shutoff relay control ckt.
P1388 Auto Shutdown Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the auto
shutdown relay circuit.
P1389 No ASD Relay Output Voltage At
PCMNo Z1 or Z2 voltage sensed when the auto shutdown
relay is energized.
P1389 (M) No ASD Relay Output Voltage at
PCMAn open condition detected In the ASD relay output
circuit.
P1390 Timing Belt Skipped 1 Tooth or More Relationship between Cam and Crank signals not correct
P1391 (M) Intermittent Loss of CMP or CKP Loss of the Cam Position Sensor or Crank Position
sensor has occurred. For PL 2.0L
P1398 (M) Mis-Fire Adaptive Numerator at Limit PCM is unable to learn the Crank Sensor's signal in
preparation for Misfire Diagnostics. Probable defective
Crank Sensor
P1399 Wait To Start Lamp Cicuit An open or shorted condition detected in the Wait to Start
Lamp circuit.
P1403 No 5V to EGR Sensor Loss of 5v feed to the EGR position sensor.
P01475 Aux 5 Volt Supply Voltage High Sensor supply voltage for ECM sensors is too high.
P1476 Too Little Secondary Air Insufficient flow of secondary air injection detected during
aspirator test (was P0411)
P1477 Too Much Secondary Air Excessive flow of secondary air injection detected during
aspirator test (was P0411).
25 - 12 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)