2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Gear
[x] Cancel search: GearPage 1658 of 2199
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
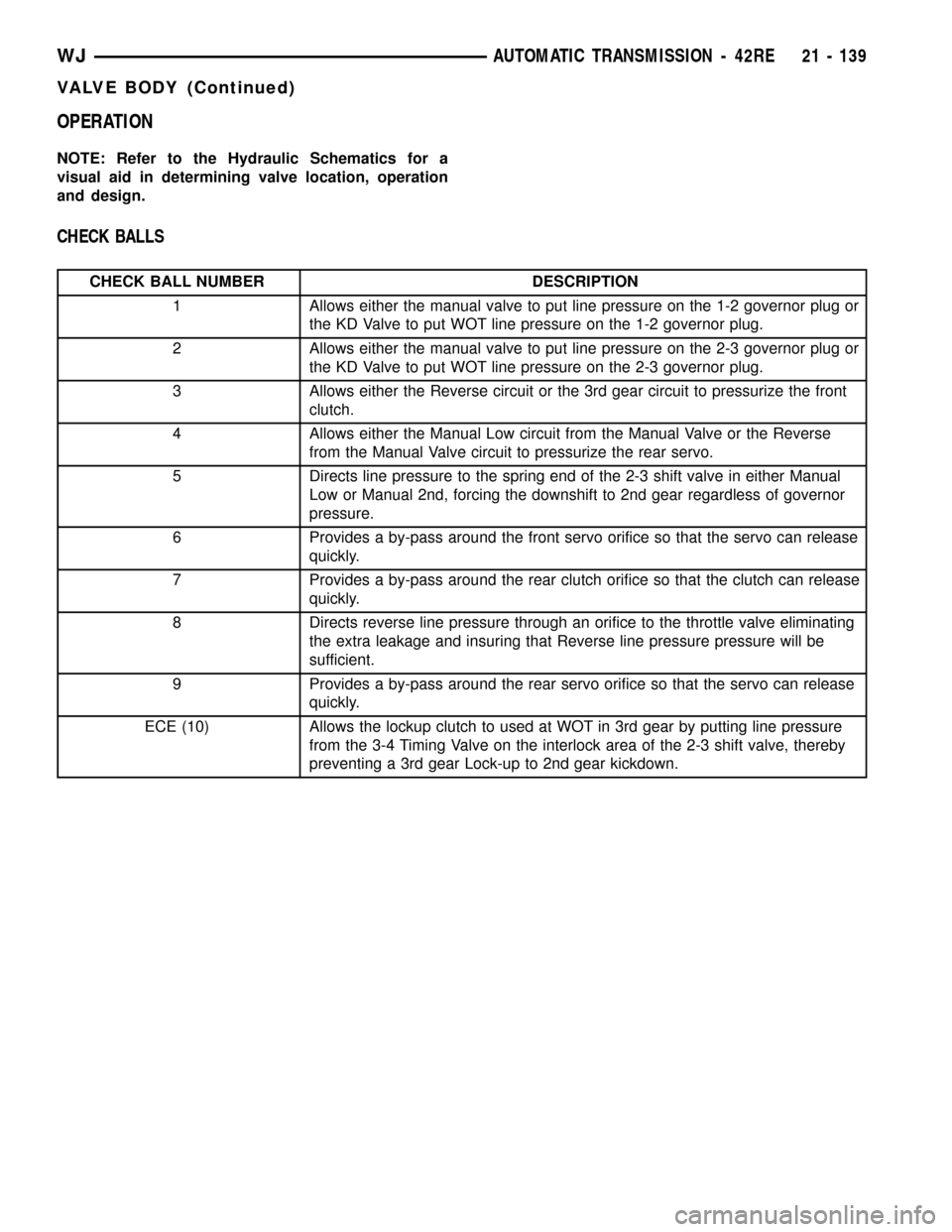
CHECK BALLS
CHECK BALL NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 Allows either the manual valve to put line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug or
the KD Valve to put WOT line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug.
2 Allows either the manual valve to put line pressure on the 2-3 governor plug or
the KD Valve to put WOT line pressure on the 2-3 governor plug.
3 Allows either the Reverse circuit or the 3rd gear circuit to pressurize the front
clutch.
4 Allows either the Manual Low circuit from the Manual Valve or the Reverse
from the Manual Valve circuit to pressurize the rear servo.
5 Directs line pressure to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve in either Manual
Low or Manual 2nd, forcing the downshift to 2nd gear regardless of governor
pressure.
6 Provides a by-pass around the front servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
7 Provides a by-pass around the rear clutch orifice so that the clutch can release
quickly.
8 Directs reverse line pressure through an orifice to the throttle valve eliminating
the extra leakage and insuring that Reverse line pressure pressure will be
sufficient.
9 Provides a by-pass around the rear servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
ECE (10) Allows the lockup clutch to used at WOT in 3rd gear by putting line pressure
from the 3-4 Timing Valve on the interlock area of the 2-3 shift valve, thereby
preventing a 3rd gear Lock-up to 2nd gear kickdown.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 139
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1659 of 2199
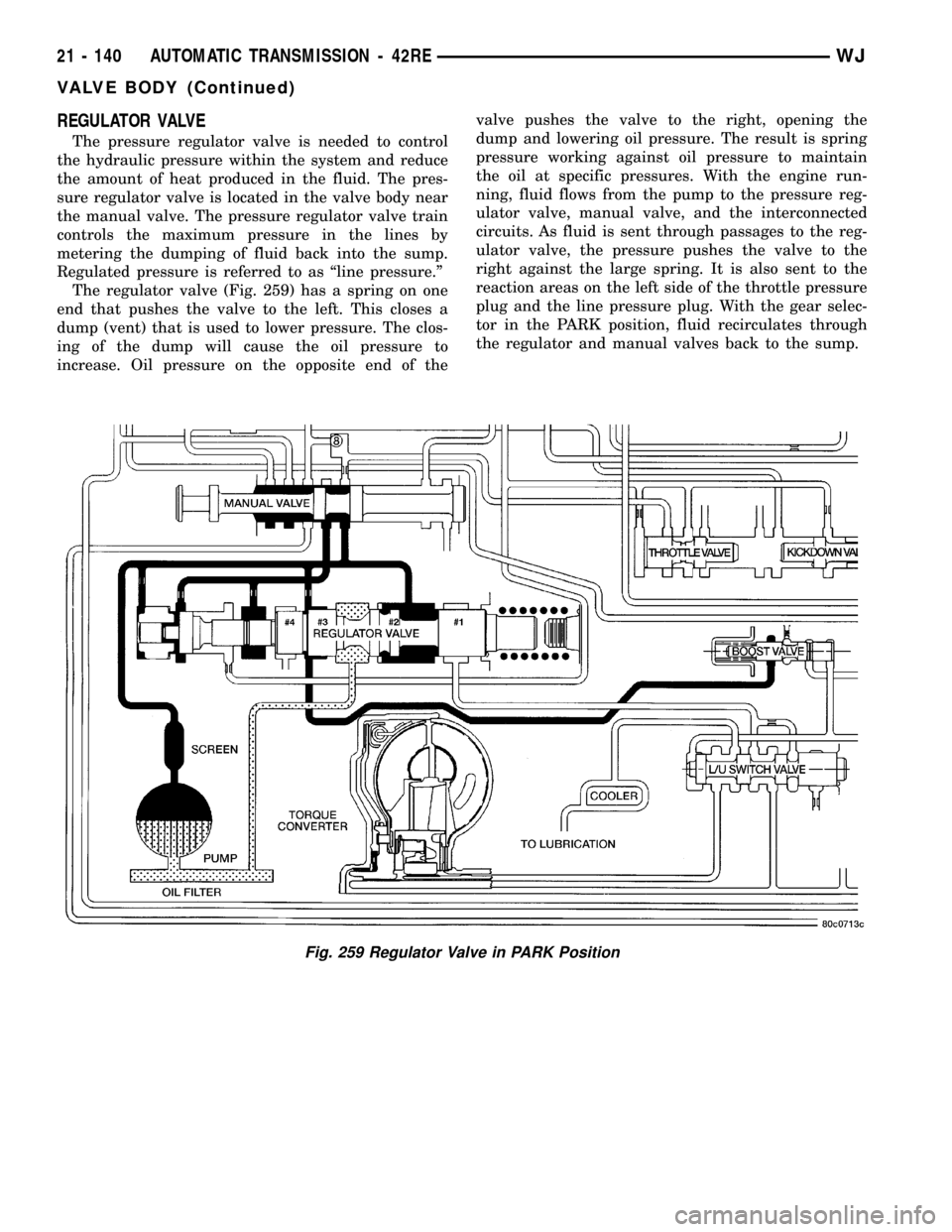
REGULATOR VALVE
The pressure regulator valve is needed to control
the hydraulic pressure within the system and reduce
the amount of heat produced in the fluid. The pres-
sure regulator valve is located in the valve body near
the manual valve. The pressure regulator valve train
controls the maximum pressure in the lines by
metering the dumping of fluid back into the sump.
Regulated pressure is referred to as ªline pressure.º
The regulator valve (Fig. 259) has a spring on one
end that pushes the valve to the left. This closes a
dump (vent) that is used to lower pressure. The clos-
ing of the dump will cause the oil pressure to
increase. Oil pressure on the opposite end of thevalve pushes the valve to the right, opening the
dump and lowering oil pressure. The result is spring
pressure working against oil pressure to maintain
the oil at specific pressures. With the engine run-
ning, fluid flows from the pump to the pressure reg-
ulator valve, manual valve, and the interconnected
circuits. As fluid is sent through passages to the reg-
ulator valve, the pressure pushes the valve to the
right against the large spring. It is also sent to the
reaction areas on the left side of the throttle pressure
plug and the line pressure plug. With the gear selec-
tor in the PARK position, fluid recirculates through
the regulator and manual valves back to the sump.
Fig. 259 Regulator Valve in PARK Position
21 - 140 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1660 of 2199
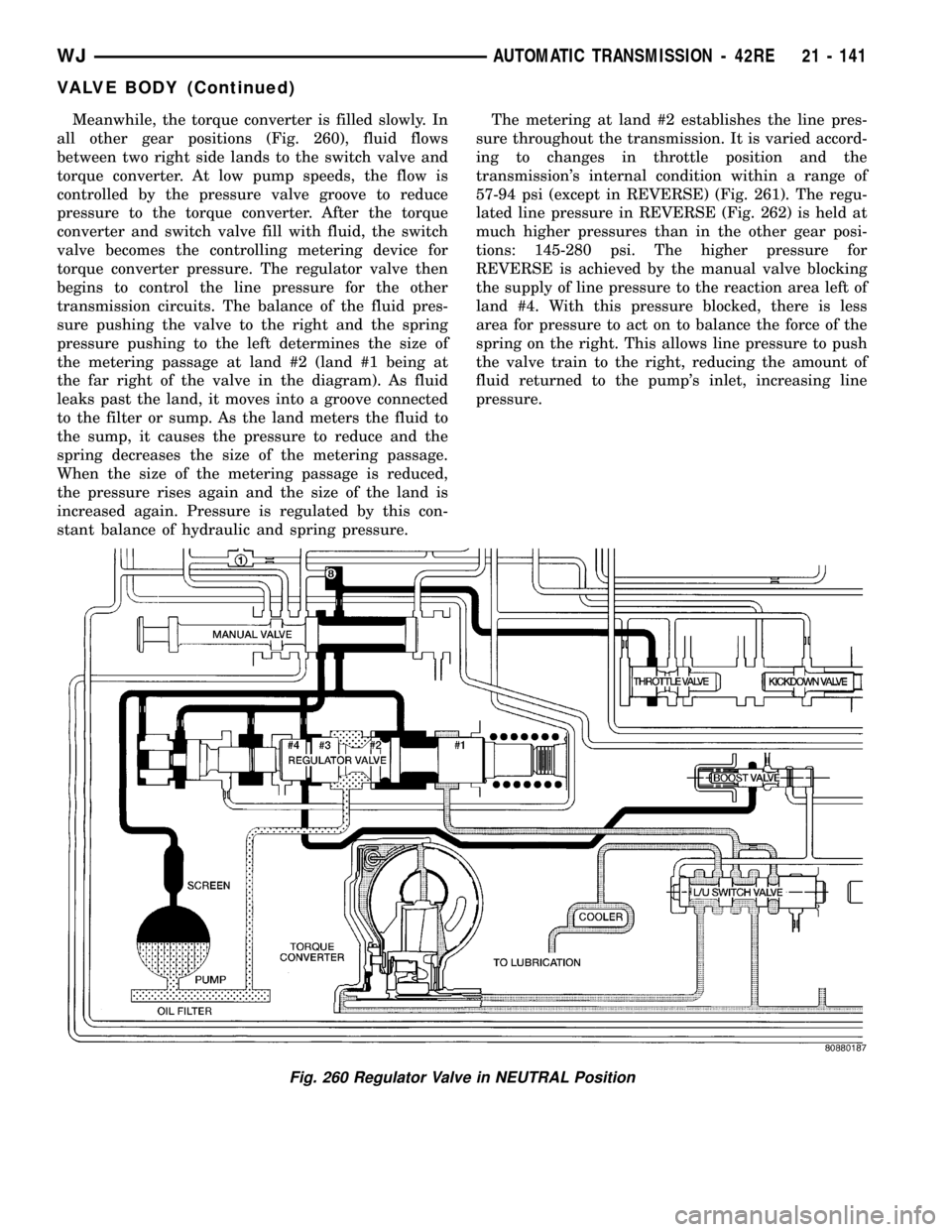
Meanwhile, the torque converter is filled slowly. In
all other gear positions (Fig. 260), fluid flows
between two right side lands to the switch valve and
torque converter. At low pump speeds, the flow is
controlled by the pressure valve groove to reduce
pressure to the torque converter. After the torque
converter and switch valve fill with fluid, the switch
valve becomes the controlling metering device for
torque converter pressure. The regulator valve then
begins to control the line pressure for the other
transmission circuits. The balance of the fluid pres-
sure pushing the valve to the right and the spring
pressure pushing to the left determines the size of
the metering passage at land #2 (land #1 being at
the far right of the valve in the diagram). As fluid
leaks past the land, it moves into a groove connected
to the filter or sump. As the land meters the fluid to
the sump, it causes the pressure to reduce and the
spring decreases the size of the metering passage.
When the size of the metering passage is reduced,
the pressure rises again and the size of the land is
increased again. Pressure is regulated by this con-
stant balance of hydraulic and spring pressure.The metering at land #2 establishes the line pres-
sure throughout the transmission. It is varied accord-
ing to changes in throttle position and the
transmission's internal condition within a range of
57-94 psi (except in REVERSE) (Fig. 261). The regu-
lated line pressure in REVERSE (Fig. 262) is held at
much higher pressures than in the other gear posi-
tions: 145-280 psi. The higher pressure for
REVERSE is achieved by the manual valve blocking
the supply of line pressure to the reaction area left of
land #4. With this pressure blocked, there is less
area for pressure to act on to balance the force of the
spring on the right. This allows line pressure to push
the valve train to the right, reducing the amount of
fluid returned to the pump's inlet, increasing line
pressure.
Fig. 260 Regulator Valve in NEUTRAL Position
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 141
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1662 of 2199
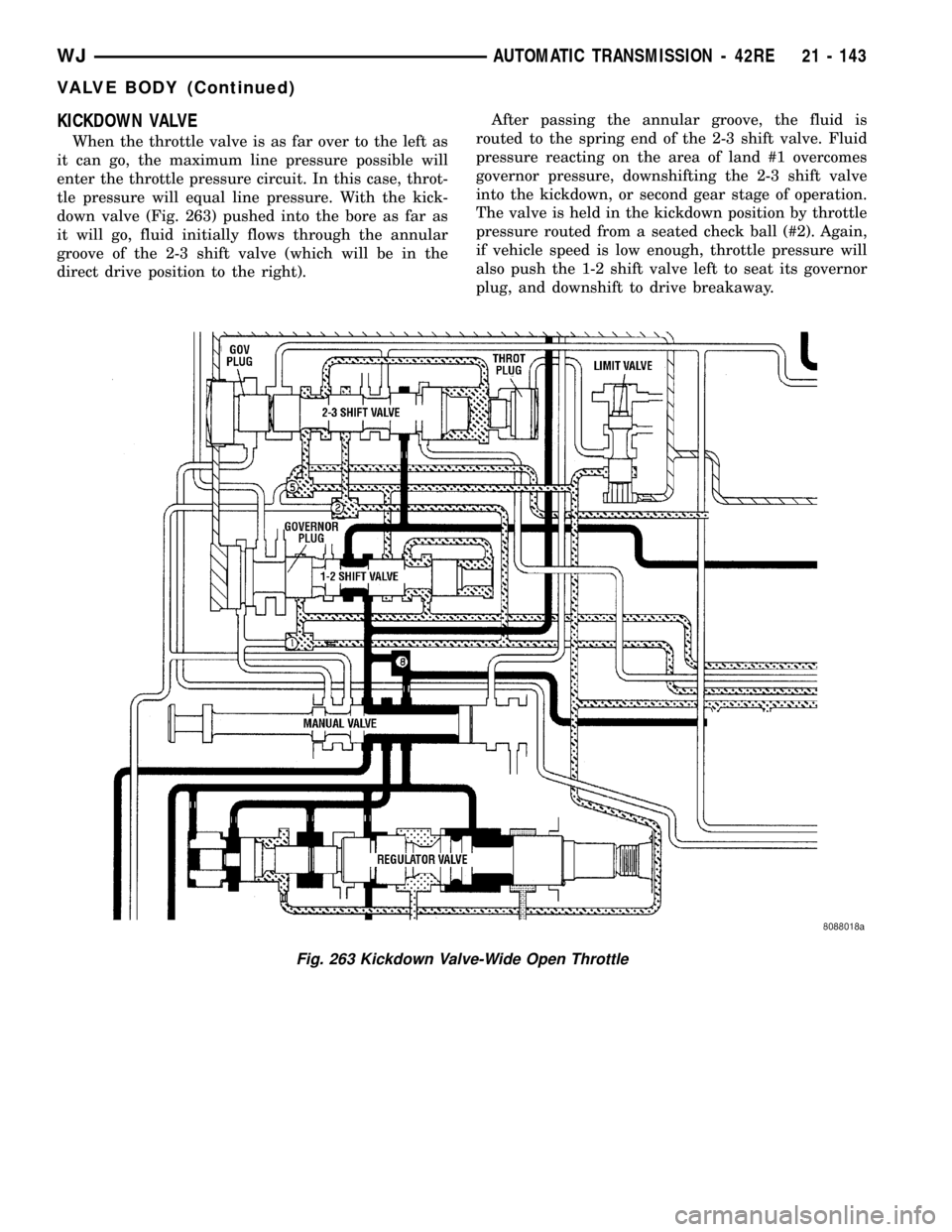
KICKDOWN VALVE
When the throttle valve is as far over to the left as
it can go, the maximum line pressure possible will
enter the throttle pressure circuit. In this case, throt-
tle pressure will equal line pressure. With the kick-
down valve (Fig. 263) pushed into the bore as far as
it will go, fluid initially flows through the annular
groove of the 2-3 shift valve (which will be in the
direct drive position to the right).After passing the annular groove, the fluid is
routed to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve. Fluid
pressure reacting on the area of land #1 overcomes
governor pressure, downshifting the 2-3 shift valve
into the kickdown, or second gear stage of operation.
The valve is held in the kickdown position by throttle
pressure routed from a seated check ball (#2). Again,
if vehicle speed is low enough, throttle pressure will
also push the 1-2 shift valve left to seat its governor
plug, and downshift to drive breakaway.
Fig. 263 Kickdown Valve-Wide Open Throttle
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 143
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1664 of 2199
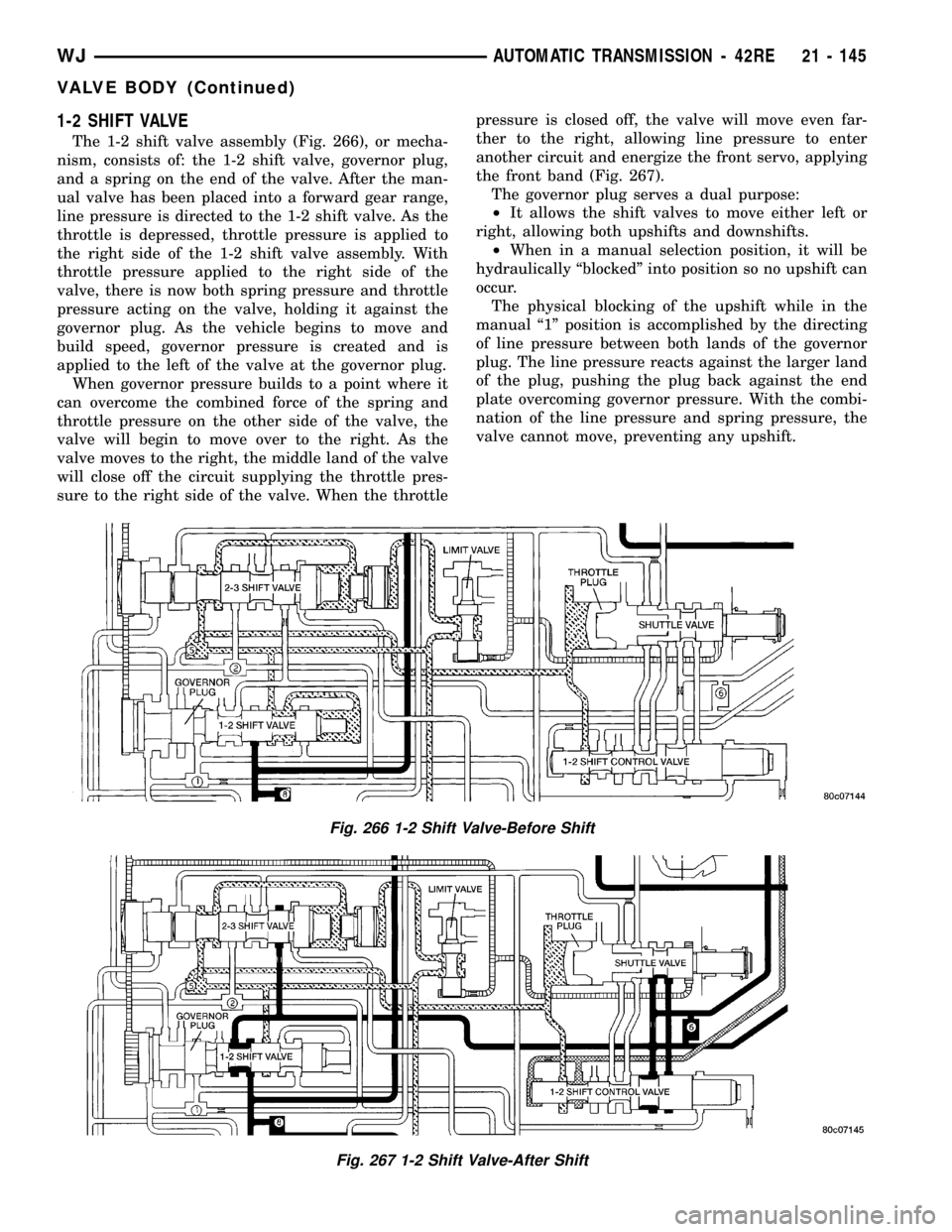
1-2 SHIFT VALVE
The 1-2 shift valve assembly (Fig. 266), or mecha-
nism, consists of: the 1-2 shift valve, governor plug,
and a spring on the end of the valve. After the man-
ual valve has been placed into a forward gear range,
line pressure is directed to the 1-2 shift valve. As the
throttle is depressed, throttle pressure is applied to
the right side of the 1-2 shift valve assembly. With
throttle pressure applied to the right side of the
valve, there is now both spring pressure and throttle
pressure acting on the valve, holding it against the
governor plug. As the vehicle begins to move and
build speed, governor pressure is created and is
applied to the left of the valve at the governor plug.
When governor pressure builds to a point where it
can overcome the combined force of the spring and
throttle pressure on the other side of the valve, the
valve will begin to move over to the right. As the
valve moves to the right, the middle land of the valve
will close off the circuit supplying the throttle pres-
sure to the right side of the valve. When the throttlepressure is closed off, the valve will move even far-
ther to the right, allowing line pressure to enter
another circuit and energize the front servo, applying
the front band (Fig. 267).
The governor plug serves a dual purpose:
²It allows the shift valves to move either left or
right, allowing both upshifts and downshifts.
²When in a manual selection position, it will be
hydraulically ªblockedº into position so no upshift can
occur.
The physical blocking of the upshift while in the
manual ª1º position is accomplished by the directing
of line pressure between both lands of the governor
plug. The line pressure reacts against the larger land
of the plug, pushing the plug back against the end
plate overcoming governor pressure. With the combi-
nation of the line pressure and spring pressure, the
valve cannot move, preventing any upshift.
Fig. 266 1-2 Shift Valve-Before Shift
Fig. 267 1-2 Shift Valve-After Shift
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 145
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1665 of 2199
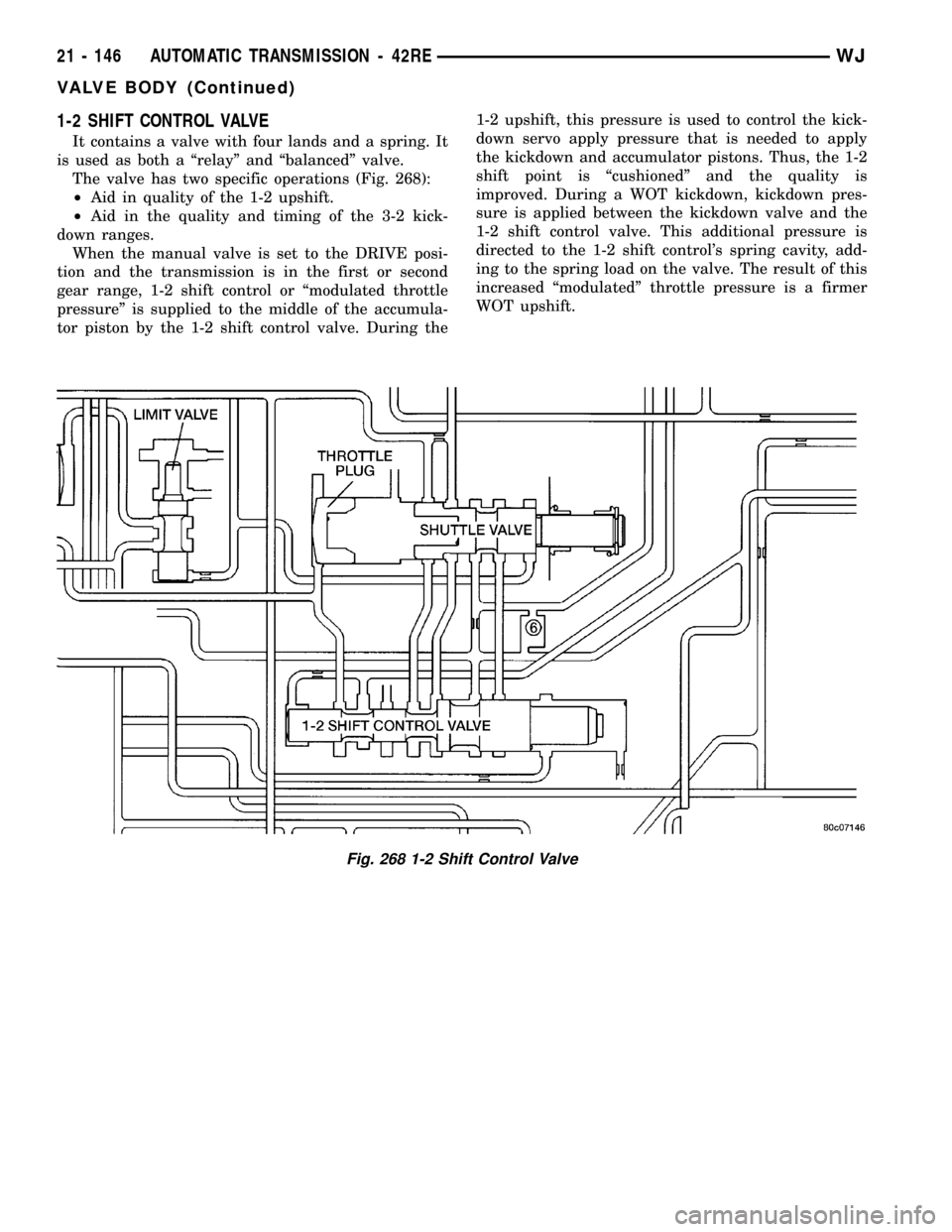
1-2 SHIFT CONTROL VALVE
It contains a valve with four lands and a spring. It
is used as both a ªrelayº and ªbalancedº valve.
The valve has two specific operations (Fig. 268):
²Aid in quality of the 1-2 upshift.
²Aid in the quality and timing of the 3-2 kick-
down ranges.
When the manual valve is set to the DRIVE posi-
tion and the transmission is in the first or second
gear range, 1-2 shift control or ªmodulated throttle
pressureº is supplied to the middle of the accumula-
tor piston by the 1-2 shift control valve. During the1-2 upshift, this pressure is used to control the kick-
down servo apply pressure that is needed to apply
the kickdown and accumulator pistons. Thus, the 1-2
shift point is ªcushionedº and the quality is
improved. During a WOT kickdown, kickdown pres-
sure is applied between the kickdown valve and the
1-2 shift control valve. This additional pressure is
directed to the 1-2 shift control's spring cavity, add-
ing to the spring load on the valve. The result of this
increased ªmodulatedº throttle pressure is a firmer
WOT upshift.
Fig. 268 1-2 Shift Control Valve
21 - 146 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1667 of 2199
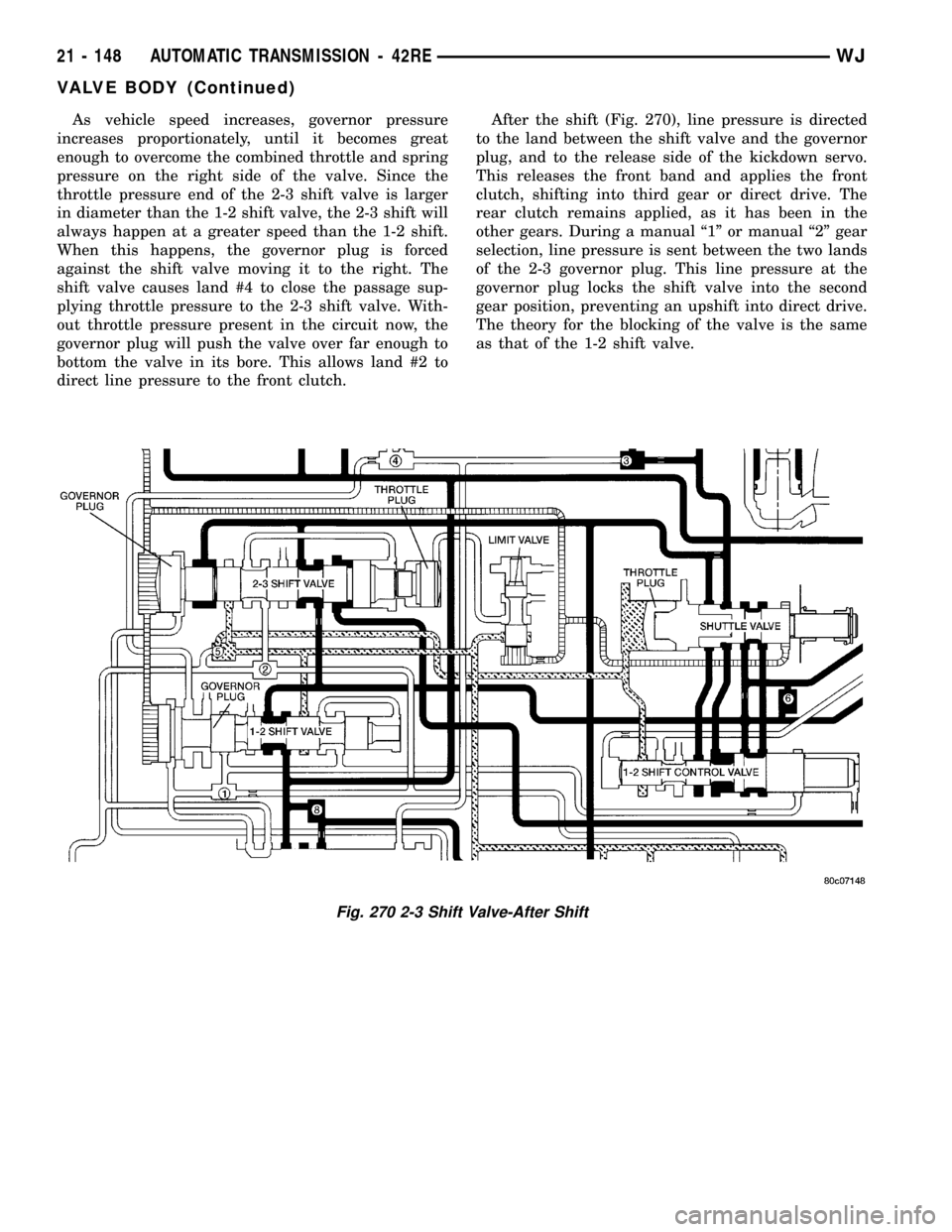
As vehicle speed increases, governor pressure
increases proportionately, until it becomes great
enough to overcome the combined throttle and spring
pressure on the right side of the valve. Since the
throttle pressure end of the 2-3 shift valve is larger
in diameter than the 1-2 shift valve, the 2-3 shift will
always happen at a greater speed than the 1-2 shift.
When this happens, the governor plug is forced
against the shift valve moving it to the right. The
shift valve causes land #4 to close the passage sup-
plying throttle pressure to the 2-3 shift valve. With-
out throttle pressure present in the circuit now, the
governor plug will push the valve over far enough to
bottom the valve in its bore. This allows land #2 to
direct line pressure to the front clutch.After the shift (Fig. 270), line pressure is directed
to the land between the shift valve and the governor
plug, and to the release side of the kickdown servo.
This releases the front band and applies the front
clutch, shifting into third gear or direct drive. The
rear clutch remains applied, as it has been in the
other gears. During a manual ª1º or manual ª2º gear
selection, line pressure is sent between the two lands
of the 2-3 governor plug. This line pressure at the
governor plug locks the shift valve into the second
gear position, preventing an upshift into direct drive.
The theory for the blocking of the valve is the same
as that of the 1-2 shift valve.
Fig. 270 2-3 Shift Valve-After Shift
21 - 148 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1669 of 2199
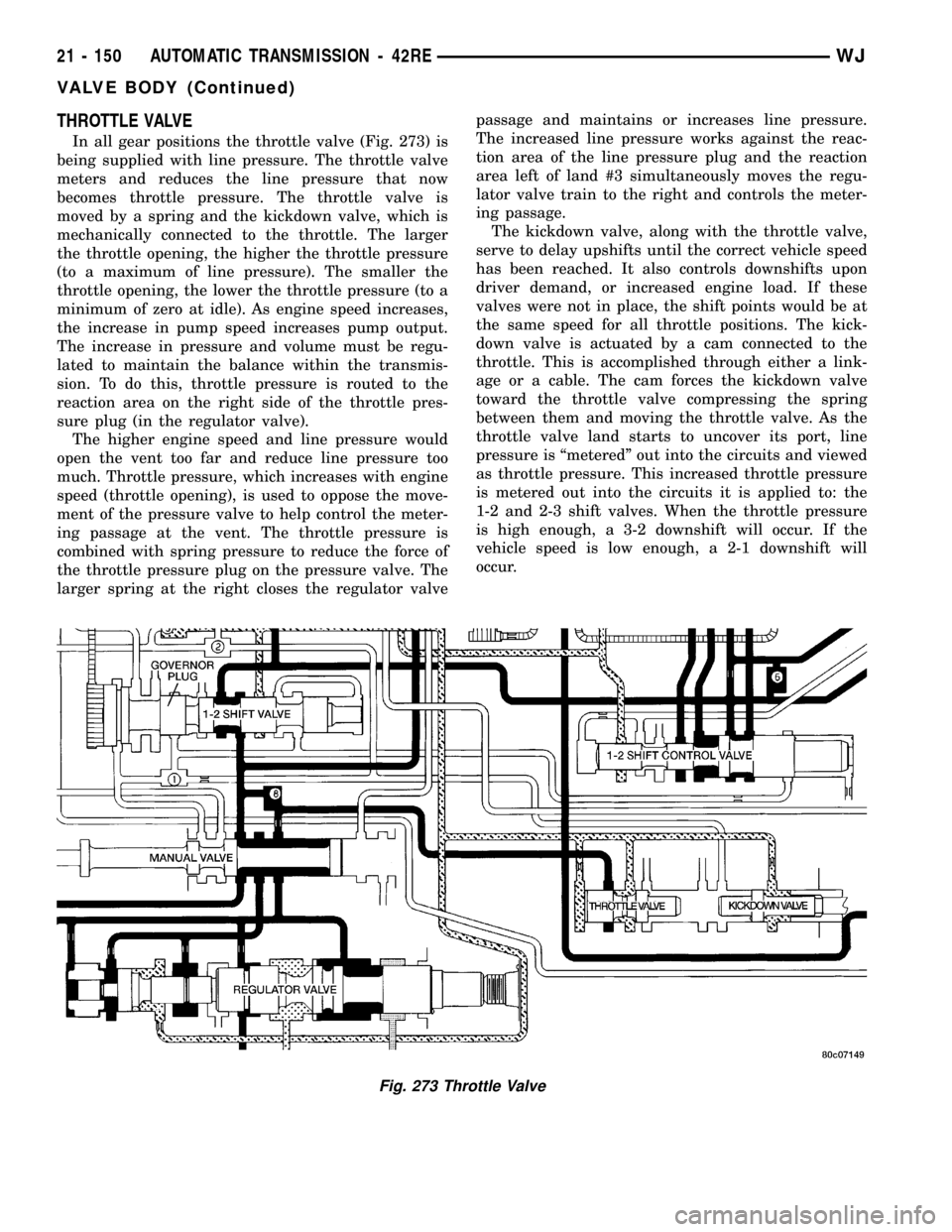
THROTTLE VALVE
In all gear positions the throttle valve (Fig. 273) is
being supplied with line pressure. The throttle valve
meters and reduces the line pressure that now
becomes throttle pressure. The throttle valve is
moved by a spring and the kickdown valve, which is
mechanically connected to the throttle. The larger
the throttle opening, the higher the throttle pressure
(to a maximum of line pressure). The smaller the
throttle opening, the lower the throttle pressure (to a
minimum of zero at idle). As engine speed increases,
the increase in pump speed increases pump output.
The increase in pressure and volume must be regu-
lated to maintain the balance within the transmis-
sion. To do this, throttle pressure is routed to the
reaction area on the right side of the throttle pres-
sure plug (in the regulator valve).
The higher engine speed and line pressure would
open the vent too far and reduce line pressure too
much. Throttle pressure, which increases with engine
speed (throttle opening), is used to oppose the move-
ment of the pressure valve to help control the meter-
ing passage at the vent. The throttle pressure is
combined with spring pressure to reduce the force of
the throttle pressure plug on the pressure valve. The
larger spring at the right closes the regulator valvepassage and maintains or increases line pressure.
The increased line pressure works against the reac-
tion area of the line pressure plug and the reaction
area left of land #3 simultaneously moves the regu-
lator valve train to the right and controls the meter-
ing passage.
The kickdown valve, along with the throttle valve,
serve to delay upshifts until the correct vehicle speed
has been reached. It also controls downshifts upon
driver demand, or increased engine load. If these
valves were not in place, the shift points would be at
the same speed for all throttle positions. The kick-
down valve is actuated by a cam connected to the
throttle. This is accomplished through either a link-
age or a cable. The cam forces the kickdown valve
toward the throttle valve compressing the spring
between them and moving the throttle valve. As the
throttle valve land starts to uncover its port, line
pressure is ªmeteredº out into the circuits and viewed
as throttle pressure. This increased throttle pressure
is metered out into the circuits it is applied to: the
1-2 and 2-3 shift valves. When the throttle pressure
is high enough, a 3-2 downshift will occur. If the
vehicle speed is low enough, a 2-1 downshift will
occur.
Fig. 273 Throttle Valve
21 - 150 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)