2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Park
[x] Cancel search: ParkPage 1949 of 2199
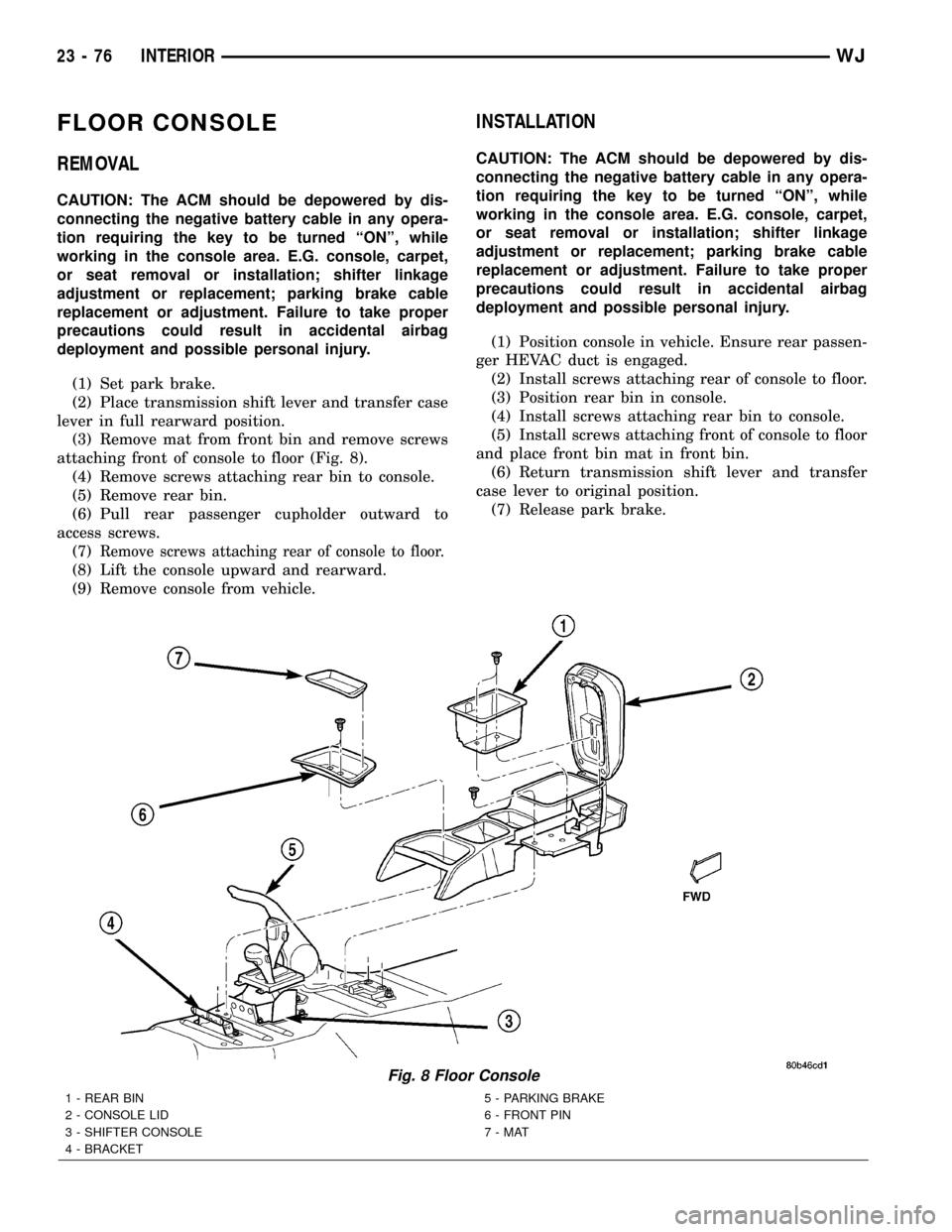
FLOOR CONSOLE
REMOVAL
CAUTION: The ACM should be depowered by dis-
connecting the negative battery cable in any opera-
tion requiring the key to be turned ªONº, while
working in the console area. E.G. console, carpet,
or seat removal or installation; shifter linkage
adjustment or replacement; parking brake cable
replacement or adjustment. Failure to take proper
precautions could result in accidental airbag
deployment and possible personal injury.
(1) Set park brake.
(2) Place transmission shift lever and transfer case
lever in full rearward position.
(3) Remove mat from front bin and remove screws
attaching front of console to floor (Fig. 8).
(4) Remove screws attaching rear bin to console.
(5) Remove rear bin.
(6) Pull rear passenger cupholder outward to
access screws.
(7)
Remove screws attaching rear of console to floor.
(8) Lift the console upward and rearward.
(9) Remove console from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The ACM should be depowered by dis-
connecting the negative battery cable in any opera-
tion requiring the key to be turned ªONº, while
working in the console area. E.G. console, carpet,
or seat removal or installation; shifter linkage
adjustment or replacement; parking brake cable
replacement or adjustment. Failure to take proper
precautions could result in accidental airbag
deployment and possible personal injury.
(1) Position console in vehicle. Ensure rear passen-
ger HEVAC duct is engaged.
(2) Install screws attaching rear of console to floor.
(3) Position rear bin in console.
(4) Install screws attaching rear bin to console.
(5) Install screws attaching front of console to floor
and place front bin mat in front bin.
(6) Return transmission shift lever and transfer
case lever to original position.
(7) Release park brake.
Fig. 8 Floor Console
1 - REAR BIN
2 - CONSOLE LID
3 - SHIFTER CONSOLE
4 - BRACKET5 - PARKING BRAKE
6 - FRONT PIN
7-MAT
23 - 76 INTERIORWJ
Page 1974 of 2199

CONTROL MODULE
REMOVAL
(1) Move the glass panel to the fully closed posi-
tion.
(2) Remove the A-pillar trim. (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/A-PILLAR TRIM - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove the sun visors. (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/SUN VISOR - REMOVAL)
(4) Remove the overhead console. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CONSOLE - REMOVAL)
(5) Lower headliner as necessary to gain access to
the sunroof express module.
(6) Disconnect the express module wire harness
connectors.
(7) Remove express module screw.
(8) Remove express module from the keyway by
sliding module towards the center of the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Insert sunroof express module in the keyway
located in the sunroof module and slide the module
outward to lock it into position.
(2) Install the sunroof express module screw.
(3) Connect the wire connectors to the sunroof
express module.
(4) Install the headliner into position.
(5) Install the overhead console. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CONSOLE - INSTALLA-
TION)
(6) Install the sun visors. (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
TERIOR/SUN VISOR - INSTALLATION)
(7) Install the A-pillar trim. (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/A-PILLAR TRIM - INSTALLATION)
(8) Test sunroof operation, adjust if necessary.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/SUNROOF/GLASS PANEL -
ADJUSTMENTS)
DRIVE MOTOR
REMOVAL
CAUTION: The sunroof system is timed from the
factory so that the motor shuts off automatically
when the sunroof window reaches a certain posi-
tion. Extreme care must be taken when removing
the motor, timing may be thrown off causing possi-
ble damage to the sunroof system. Anytime the
motor is removed from the sunroof assembly the
sunroof glass panel must be in the FULLY CLOSED
POSITION or the unit will be out of timing. The drive
motor cannot be reset to the park position after
being removed.CAUTION: The sunroof motor should only be pow-
ered through the vehicle battery and sunroof wire
harness. Applying power to the sunroof motor leads
will cause failure of the control module.
(1) Move glass panel to the fully closed position.
(2) Remove the A-pillar trim. (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/A-PILLAR TRIM - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove the B-pillar upper trim. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/B-PILLAR UPPER TRIM -
REMOVAL)
(4) Remove the C-pillar trim. (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/C-PILLAR TRIM - REMOVAL)
(5) Remove the D-pillar trim. (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/D-PILLAR TRIM - REMOVAL)
(6) Remove the sunvisors. (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
TERIOR/SUN VISOR - REMOVAL)
(7) Remove the overhead console. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CONSOLE - REMOVAL)
(8) Disconnect the control switch wire connector.
(9) Remove headliner as necessary to gain access
to sunroof drive motor. Refer to Headliner Removal
and Installation for proper procedures.
(10) Disconnect the drive motor wire harness con-
nectors (Fig. 3).
(11) Remove drive motor fasteners and remove
motor from the sunroof housing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Ensure that the window is in the fully closed
position before mounting the motor. If motor fails
with the window in the open position the sunroof
glass panel timing will have to be timed. The new
motor comes in the fully closed position and with a
gage for setting cable timing. (Refer to 23 - BODY/
SUNROOF/GLASS PANEL - ADJUSTMENTS - TIM-
ING)
(2) Place drive motor into position on the sunroof
housing and install fasteners.
Fig. 3 Sunroof Drive Motor and Express Module
1 - EXPRESS MODULE
2 - SCREW
WJSUNROOF 23 - 101
Page 2156 of 2199

EMISSIONS CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM.............................1
DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST
MODE...............................2
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE...............................2
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES..............................2DESCRIPTION - TASK MANAGER.........17
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED SYSTEMS . . . 17
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION........19
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS . . 19
DESCRIPTION - NON-MONITORED
CIRCUITS...........................20
DESCRIPTION - HIGH AND LOW LIMITS . . . 20
DESCRIPTION - LOAD VALUE...........20
OPERATION - TASK MANAGER............21
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS................24
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
many different circuits in the fuel injection, ignition,
emission and engine systems. If the PCM senses a prob-
lem with a monitored circuit often enough to indicate an
actual problem, it stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) in the PCM's memory. If the code applies to a
non-emissions related component or system, and the
problem is repaired or ceases to exist, the PCM cancels
the code after 40 warm-up cycles. Diagnostic trouble
codes that affect vehicle emissions illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator (check engine) Lamp. Refer to Mal-
function Indicator Lamp in this section.
Certain criteria must be met before the PCM
stores a DTC in memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine RPM, engine temperature,
and/or input voltage to the PCM.
The PCM might not store a DTC for a monitored cir-
cuit even though a malfunction has occurred. This may
happen because one of the DTC criteria for the circuit
has not been met.For example
,assume the diagnostic
trouble code criteria requires the PCM to monitor the
circuit only when the engine operates between 750 and
2000 RPM. Suppose the sensor's output circuit shorts to
ground when engine operates above 2400 RPM (result-
ing in 0 volt input to the PCM). Because the condition
happens at an engine speed above the maximum thresh-
old (2000 rpm), the PCM will not store a DTC.
There are several operating conditions for which
the PCM monitors and sets DTC's. Refer to Moni-
tored Systems, Components, and Non-Monitored Cir-
cuits in this section.Technicians must retrieve stored DTC's by connect-
ing the DRB scan tool (or an equivalent scan tool) to
the 16±way data link connector (Fig. 1).
NOTE: Various diagnostic procedures may actually
cause a diagnostic monitor to set a DTC. For
instance, pulling a spark plug wire to perform a
spark test may set the misfire code. When a repair
is completed and verified, connect the DRB scan
tool to the 16±way data link connector to erase all
DTC's and extinguish the MIL (check engine lamp).Fig. 1 Data Link (Diagnostic) Connector Location
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER/LEFT EDGE
2 - DATA LINK CONNECTOR
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 1
Page 2171 of 2199
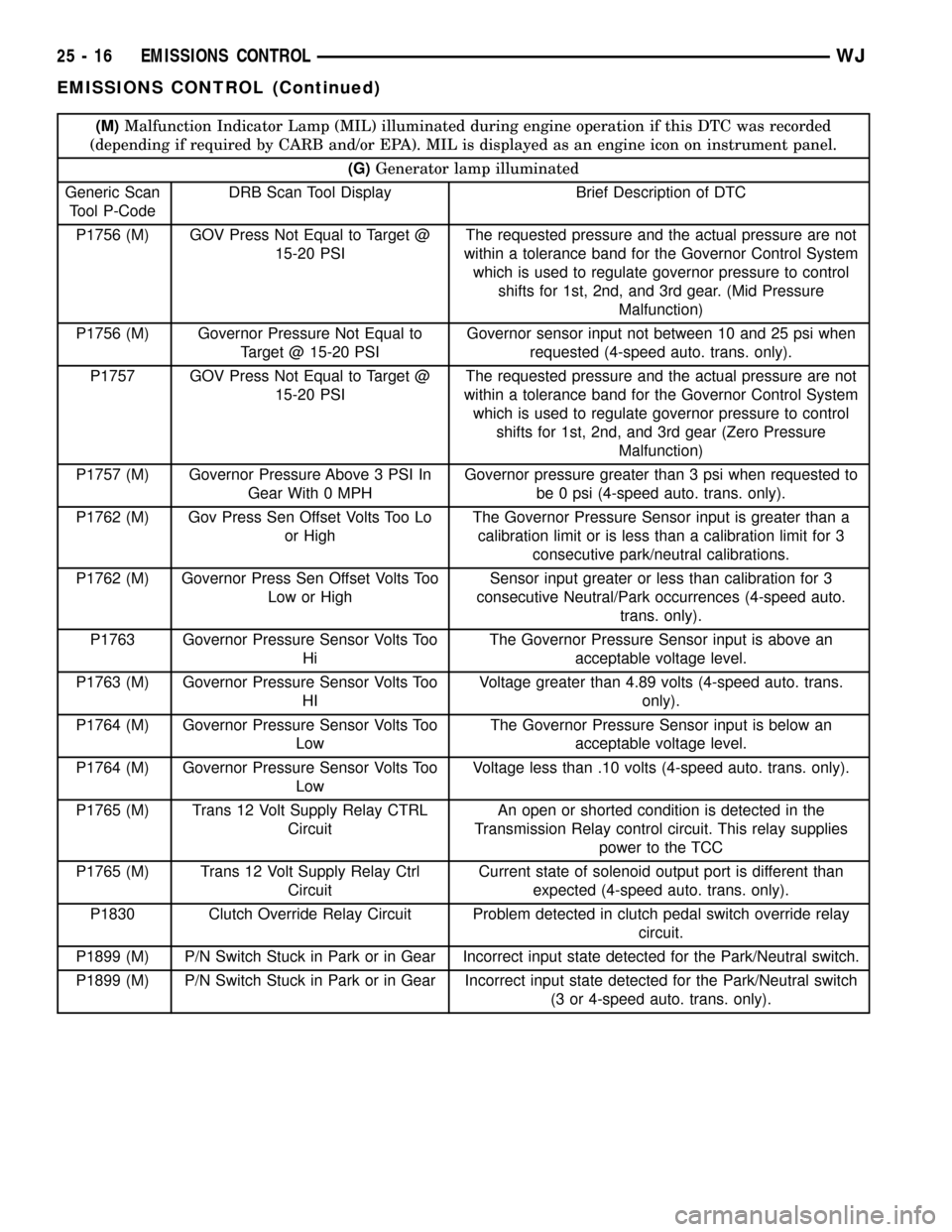
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1756 (M) GOV Press Not Equal to Target @
15-20 PSIThe requested pressure and the actual pressure are not
within a tolerance band for the Governor Control System
which is used to regulate governor pressure to control
shifts for 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gear. (Mid Pressure
Malfunction)
P1756 (M) Governor Pressure Not Equal to
Target @ 15-20 PSIGovernor sensor input not between 10 and 25 psi when
requested (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P1757 GOV Press Not Equal to Target @
15-20 PSIThe requested pressure and the actual pressure are not
within a tolerance band for the Governor Control System
which is used to regulate governor pressure to control
shifts for 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gear (Zero Pressure
Malfunction)
P1757 (M) Governor Pressure Above 3 PSI In
Gear With 0 MPHGovernor pressure greater than 3 psi when requested to
be 0 psi (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P1762 (M) Gov Press Sen Offset Volts Too Lo
or HighThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is greater than a
calibration limit or is less than a calibration limit for 3
consecutive park/neutral calibrations.
P1762 (M) Governor Press Sen Offset Volts Too
Low or HighSensor input greater or less than calibration for 3
consecutive Neutral/Park occurrences (4-speed auto.
trans. only).
P1763 Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
HiThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is above an
acceptable voltage level.
P1763 (M) Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
HIVoltage greater than 4.89 volts (4-speed auto. trans.
only).
P1764 (M) Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
LowThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is below an
acceptable voltage level.
P1764 (M) Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
LowVoltage less than .10 volts (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P1765 (M) Trans 12 Volt Supply Relay CTRL
CircuitAn open or shorted condition is detected in the
Transmission Relay control circuit. This relay supplies
power to the TCC
P1765 (M) Trans 12 Volt Supply Relay Ctrl
CircuitCurrent state of solenoid output port is different than
expected (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P1830 Clutch Override Relay Circuit Problem detected in clutch pedal switch override relay
circuit.
P1899 (M) P/N Switch Stuck in Park or in Gear Incorrect input state detected for the Park/Neutral switch.
P1899 (M) P/N Switch Stuck in Park or in Gear Incorrect input state detected for the Park/Neutral switch
(3 or 4-speed auto. trans. only).
25 - 16 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2175 of 2199

an associated limp in will take two trips to illumi-
nate the MIL.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
DESCRIPTION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems and conditions that could have malfunctions
causing driveability problems. The PCM might not
store diagnostic trouble codes for these conditions.
However, problems with these systems may cause the
PCM to store diagnostic trouble codes for other sys-
tems or components. For example, a fuel pressure
problem will not register a fault directly, but could
cause a rich/lean condition or misfire. This could
cause the PCM to store an oxygen sensor or misfire
diagnostic trouble code
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor or fuel system diag-
nostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system, although it may set a fuel
system fault.
FUEL INJECTOR MECHANICAL MALFUNCTIONS
The PCM cannot determine if a fuel injector is
clogged, the needle is sticking or if the wrong injectoris installed. However, these could result in a rich or
lean condition causing the PCM to store a diagnostic
trouble code for either misfire, an oxygen sensor, or
the fuel system.
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION
Although the PCM monitors engine exhaust oxygen
content when the system is in closed loop, it cannot
determine excessive oil consumption.
THROTTLE BODY AIRFLOW
The PCM cannot detect a clogged or restricted air
cleaner inlet or filter element.
VACUUM ASSIST
The PCM cannot detect leaks or restrictions in the
vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control
system devices. However, these could cause the PCM
to store a MAP sensor diagnostic trouble code and
cause a high idle condition.
PCM SYSTEM GROUND
The PCM cannot determine a poor system ground.
However, one or more diagnostic trouble codes may
be generated as a result of this condition. The mod-
ule should be mounted to the body at all times, also
during diagnostic.
PCM CONNECTOR ENGAGEMENT
The PCM may not be able to determine spread or
damaged connector pins. However, it might store
diagnostic trouble codes as a result of spread connec-
tor pins.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The PCM compares input signal voltages from each
input device with established high and low limits for
the device. If the input voltage is not within limits
and other criteria are met, the PCM stores a diagnos-
tic trouble code in memory. Other diagnostic trouble
code criteria might include engine RPM limits or
input voltages from other sensors or switches that
must be present before verifying a diagnostic trouble
code condition.
DESCRIPTION - LOAD VALUE
ENGINE IDLE/NEUTRAL 2500 RPM/NEUTRAL
All Engines 2% to 8% of Maximum Load 9% to 17% of Maximum Load
25 - 20 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)