2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Transfer case shifter
[x] Cancel search: Transfer case shifterPage 1782 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Place the floor shifter lever in PARK position.
(2) Loosen the adjustment screw on the shift cable.
(3) Verify that the park lock cable adjustment tab
is pulled upward to the unlocked position.
(4) Install wiring harness to the shifter assembly
bracket. Engage any wire connectors removed from
the shifter assembly.
(5) Install the transfer case shift cable to the
shifter assembly bracket. Install clip to hold cable to
the bracket.
(6) Snap the transfer case shift cable, if equipped,
onto the transfer case shift lever pin.
(7) Install the park lock cable into the shifter
assembly bracket and into the shifter BTSI lever.(Re-
fer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC/SHIFT INTERLOCK MECHANISM -
ADJUSTMENTS)
(8) Install the shift cable to the shifter assembly
bracket. Push cable into the bracket until secure.
(9) Install shifter assembly onto the shifter assem-
bly studs on the floor pan.
(10) Install the nuts to hold the shifter assembly
onto the floor pan. Tighten nuts to 28 N´m (250
in.lbs.).
(11) Snap the shift cable onto the shift lever pin.
(12) Verify that the shift lever is in the PARK posi-
tion.
(13) Tighten the adjustment screw to 7 N´m (65
in.lbs.).
(14) Place the key in the accessory position.
(15) Push downward on the park lock cable adjust-
ment tab to lock the adjustment.
(16) Verify correct shifter, park lock, and BTSI
operation.
(17) Install any console parts removed for access to
shift lever assembly and shift cables. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLA-
TION)
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) is located in the
valve body and controls the direction of the transmis-
sion fluid when the L/R-TCC solenoid is energized.
OPERATION
The Solenoid Switch Valve controls line pressure
from the LR-TCC solenoid. In 1st gear, the SSV will
be in the downshifted position, thus directing fluid to
the L/R clutch circuit. In 2nd, 3rd, 4th,and 5th gears,
the solenoid switch valve will be in the upshifted
position and directs the fluid into the torque con-
verter clutch (TCC) circuit.When shifting into 1st gear, a special hydraulic
sequence is performed to ensure SSV movement into
the downshifted position. The L/R pressure switch is
monitored to confirm SSV movement. If the move-
ment is not confirmed (the L/R pressure switch does
not close), 2nd gear is substituted for 1st. A DTC will
be set after three unsuccessful attempts are made to
get into 1st gear in one given key start.
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION
The typical electrical solenoid used in automotive
applications is a linear actuator. It is a device that
produces motion in a straight line. This straight line
motion can be either forward or backward in direc-
tion, and short or long distance.
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that uses
a magnetic force to perform work. It consists of a coil
of wire, wrapped around a magnetic core made from
steel or iron, and a spring loaded, movable plunger,
which performs the work, or straight line motion.
The solenoids used in transmission applications
are attached to valves which can be classified asnor-
mally openornormally closed. Thenormally
opensolenoid valve is defined as a valve which
allows hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is
applied to the solenoid. Thenormally closedsole-
noid valve is defined as a valve which does not allow
hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is applied
to the solenoid. These valves perform hydraulic con-
trol functions for the transmission and must there-
fore be durable and tolerant of dirt particles. For
these reasons, the valves have hardened steel pop-
pets and ball valves. The solenoids operate the valves
directly, which means that the solenoids must have
very high outputs to close the valves against the siz-
able flow areas and line pressures found in current
transmissions. Fast response time is also necessary
to ensure accurate control of the transmission.
The strength of the magnetic field is the primary
force that determines the speed of operation in a par-
ticular solenoid design. A stronger magnetic field will
cause the plunger to move at a greater speed than a
weaker one. There are basically two ways to increase
the force of the magnetic field:
1. Increase the amount of current applied to the
coil or
2. Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil.
The most common practice is to increase the num-
ber of turns by using thin wire that can completely
fill the available space within the solenoid housing.
The strength of the spring and the length of the
plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 263
SHIFT MECHANISM (Continued)
Page 1799 of 2199
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION........................280
OPERATION..........................281
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV242.......................281
REMOVAL............................282
DISASSEMBLY........................282
CLEANING...........................292
INSPECTION.........................293
ASSEMBLY...........................295
INSTALLATION........................307
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN/
REFILL............................310FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................310
INSTALLATION........................310
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................311
OPERATION..........................311
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
REAR RETAINER BUSHING AND SEAL -
NV242HD
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL............................313
INSTALLATION........................313
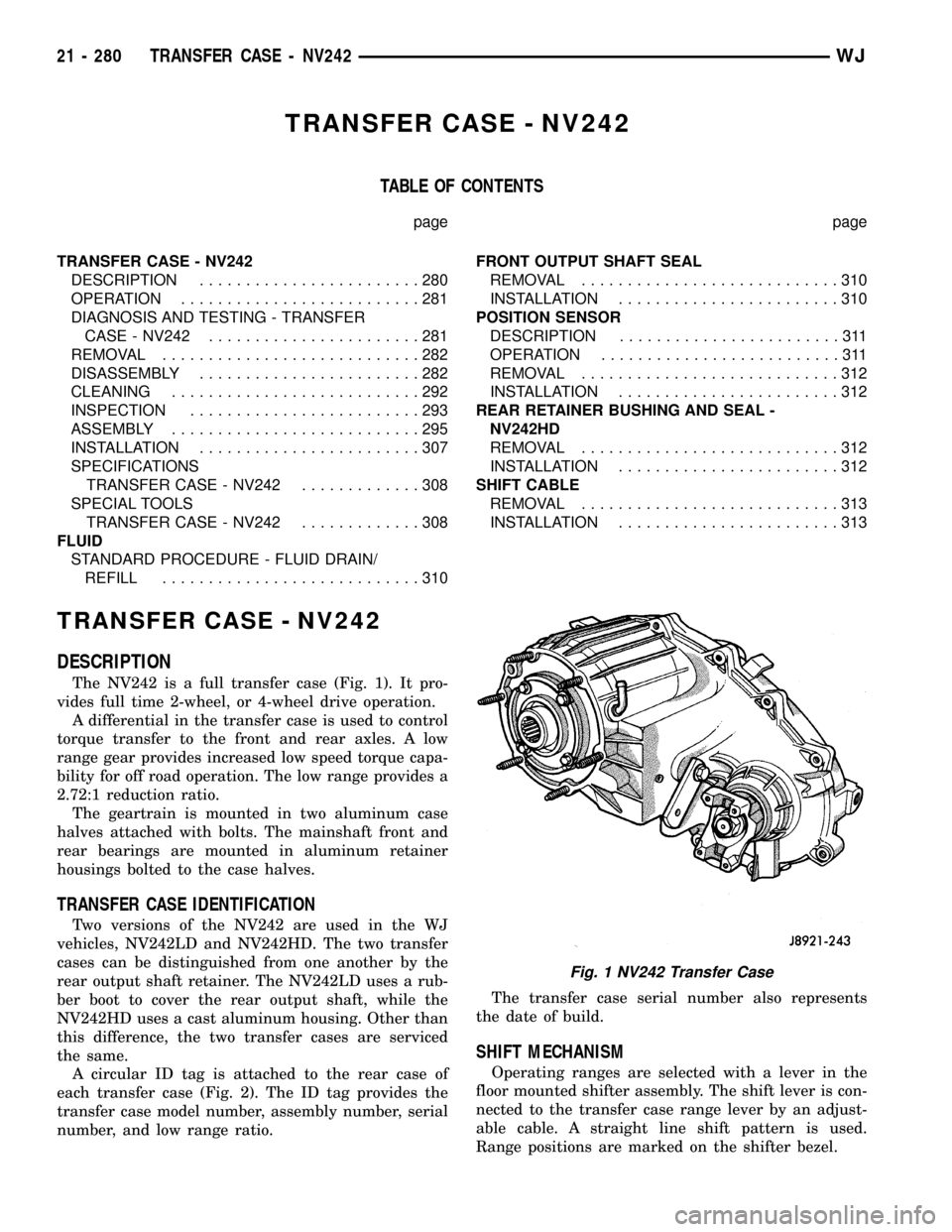
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION
The NV242 is a full transfer case (Fig. 1). It pro-
vides full time 2-wheel, or 4-wheel drive operation.
A differential in the transfer case is used to control
torque transfer to the front and rear axles. A low
range gear provides increased low speed torque capa-
bility for off road operation. The low range provides a
2.72:1 reduction ratio.
The geartrain is mounted in two aluminum case
halves attached with bolts. The mainshaft front and
rear bearings are mounted in aluminum retainer
housings bolted to the case halves.
TRANSFER CASE IDENTIFICATION
Two versions of the NV242 are used in the WJ
vehicles, NV242LD and NV242HD. The two transfer
cases can be distinguished from one another by the
rear output shaft retainer. The NV242LD uses a rub-
ber boot to cover the rear output shaft, while the
NV242HD uses a cast aluminum housing. Other than
this difference, the two transfer cases are serviced
the same.
A circular ID tag is attached to the rear case of
each transfer case (Fig. 2). The ID tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a lever in the
floor mounted shifter assembly. The shift lever is con-
nected to the transfer case range lever by an adjust-
able cable. A straight line shift pattern is used.
Range positions are marked on the shifter bezel.
Fig. 1 NV242 Transfer Case
21 - 280 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
Page 1832 of 2199

(5) Install the rear propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(6) Verify proper fluid level.
(7) Lower vehicle.
SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transfer case into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Disconnect the shift cable eyelet from the
transfer case shift lever (Fig. 101).
(4) Remove shift cable from the cable support
bracket.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Remove any necessary console parts for access
to shift lever assembly and shift cable.(7) Disconnect cable at shift lever and shifter
assembly bracket (Fig. 102).
(8) Remove the nuts holding the shift cable seal
plate to the floor pan (Fig. 103).
(9) Pull cable through floor panel opening.
(10) Remove transfer case shift cable from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Route cable through hole in floor pan.
(2) Install seal plate to studs in floor pan.
(3) Install nuts to hold seal plate to floor pan (Fig.
103). Tighten nuts to 7 N´m (65 in.lbs.).
Fig. 100 Install Rear Retainer Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3995-A
Fig. 101 Transfer Case Shift Cable at Transfer Case
1 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT LEVER
2 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CABLE
Fig. 102 Transfer Case Shift Cable at Shifter
1 - CLIP
2 - SHIFTER
3 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT LEVER PIN
4 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CABLE
Fig. 103 Shift Cables at Floor Pan
1 - SEAL PLATES
2 - TRANSMISSION SHIFT CABLE
3 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CABLE
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 313
REAR RETAINER BUSHING AND SEAL - NV242HD (Continued)
Page 1833 of 2199

(4) Install the transfer case shift cable to the
shifter assembly bracket. Seat cable in bracket and
install clip (Fig. 102).
(5) Verify the transfer case shift lever (at console)
is in the NEUTRAL position.
(6) Snap the cable onto the shift lever pin (Fig.
102).
(7) Raise the vehicle.
(8) Install the shift cable to the shift cable support
bracket and install clip (Fig. 101).(9) Verify that the transfer case is still in the
NEUTRAL position.
(10) Snap the shift cable onto the transfer case
shift lever (Fig. 101).
(11) Lower vehicle.
(12) Verify correct transfer case operation in all
ranges.
(13) Install any console parts removed for access to
transfer case shift cable.
21 - 314 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
SHIFT CABLE (Continued)
Page 1835 of 2199
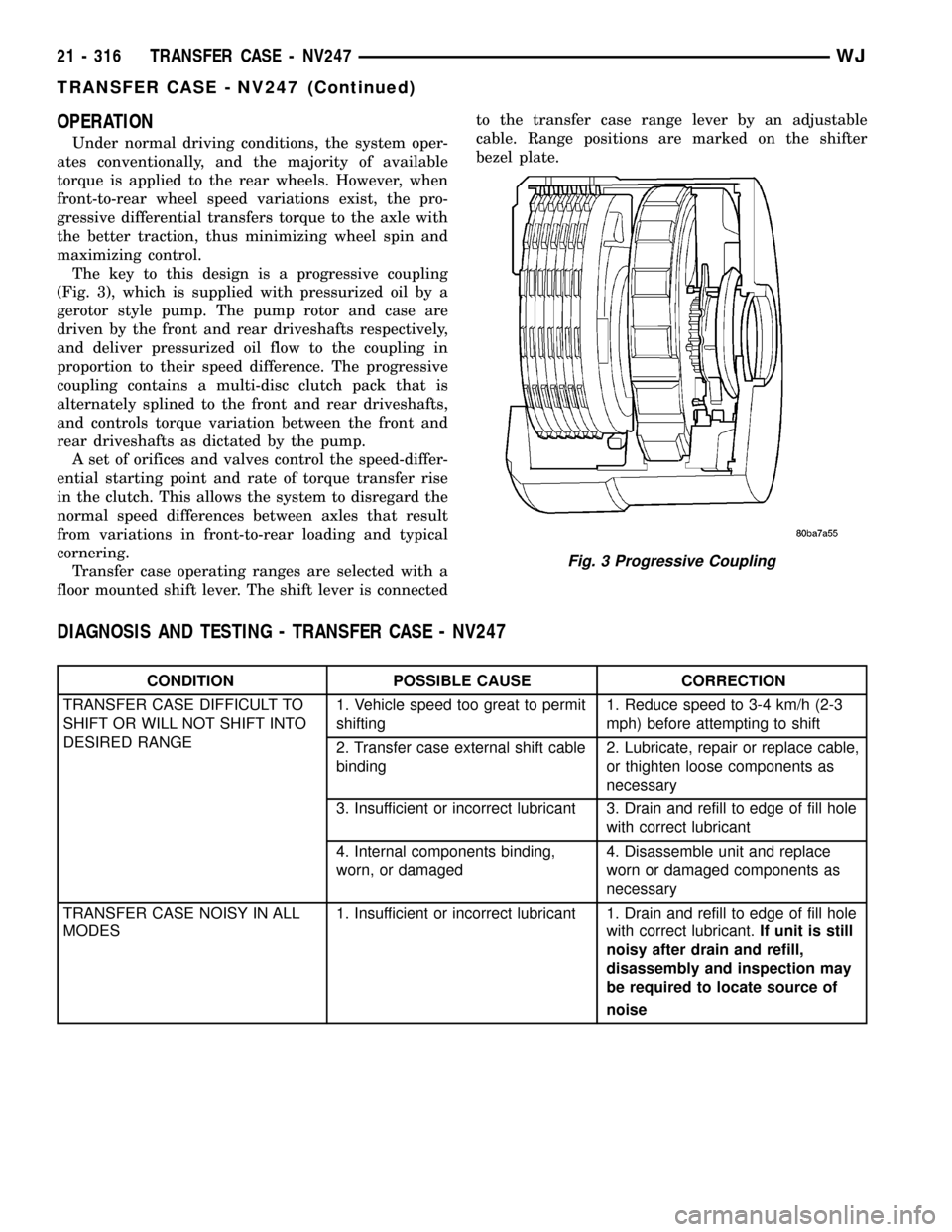
OPERATION
Under normal driving conditions, the system oper-
ates conventionally, and the majority of available
torque is applied to the rear wheels. However, when
front-to-rear wheel speed variations exist, the pro-
gressive differential transfers torque to the axle with
the better traction, thus minimizing wheel spin and
maximizing control.
The key to this design is a progressive coupling
(Fig. 3), which is supplied with pressurized oil by a
gerotor style pump. The pump rotor and case are
driven by the front and rear driveshafts respectively,
and deliver pressurized oil flow to the coupling in
proportion to their speed difference. The progressive
coupling contains a multi-disc clutch pack that is
alternately splined to the front and rear driveshafts,
and controls torque variation between the front and
rear driveshafts as dictated by the pump.
A set of orifices and valves control the speed-differ-
ential starting point and rate of torque transfer rise
in the clutch. This allows the system to disregard the
normal speed differences between axles that result
from variations in front-to-rear loading and typical
cornering.
Transfer case operating ranges are selected with a
floor mounted shift lever. The shift lever is connectedto the transfer case range lever by an adjustable
cable. Range positions are marked on the shifter
bezel plate.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER CASE - NV247
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
TRANSFER CASE DIFFICULT TO
SHIFT OR WILL NOT SHIFT INTO
DESIRED RANGE1. Vehicle speed too great to permit
shifting1. Reduce speed to 3-4 km/h (2-3
mph) before attempting to shift
2. Transfer case external shift cable
binding2. Lubricate, repair or replace cable,
or thighten loose components as
necessary
3. Insufficient or incorrect lubricant 3. Drain and refill to edge of fill hole
with correct lubricant
4. Internal components binding,
worn, or damaged4. Disassemble unit and replace
worn or damaged components as
necessary
TRANSFER CASE NOISY IN ALL
MODES1. Insufficient or incorrect lubricant 1. Drain and refill to edge of fill hole
with correct lubricant.If unit is still
noisy after drain and refill,
disassembly and inspection may
be required to locate source of
noise
Fig. 3 Progressive Coupling
21 - 316 TRANSFER CASE - NV247WJ
TRANSFER CASE - NV247 (Continued)
Page 1859 of 2199

SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transfer case into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Disconnect the shift cable eyelet from the
transfer case shift lever (Fig. 78).
(4) Remove shift cable from the cable support
bracket.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Remove any necessary console parts for access
to shift lever assembly and shift cable.
(7) Disconnect cable at shift lever and shifter
assembly bracket (Fig. 79).
(8) Remove the nuts holding the shift cable seal
plate to the floor pan (Fig. 80).
(9) Pull cable through floor panel opening.
(10) Remove transfer case shift cable from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Route cable through hole in floor pan.
(2) Install seal plate to studs in floor pan.
(3) Install nuts to hold seal plate to floor pan (Fig.
80). Tighten nuts to 7 N´m (65 in.lbs.).
(4) Install the transfer case shift cable to the
shifter assembly bracket. Seat cable in bracket and
install clip (Fig. 79).
(5) Verify the transfer case shift lever (at console)
is in the NEUTRAL position.
(6) Snap the cable onto the shift lever pin (Fig.
79).
(7) Raise the vehicle.(8) Install the shift cable to the shift cable support
bracket and install clip (Fig. 78).
(9) Verify that the transfer case is still in the
NEUTRAL position.
(10) Snap the shift cable onto the transfer case
shift lever (Fig. 78).
(11) Lower vehicle.
(12) Verify correct transfer case operation in all
ranges.
(13) Install any console parts removed for access to
transfer case shift cable.
Fig. 78 Transfer Case Shift Cable at Transfer Case
1 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT LEVER
2 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CABLE
Fig. 79 Transfer Case Shift Cable at Shifter
1 - CLIP
2 - SHIFTER
3 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT LEVER PIN
4 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CABLE
Fig. 80 Shift Cables at Floor Pan
1 - SEAL PLATES
2 - TRANSMISSION SHIFT CABLE
3 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CABLE
21 - 340 TRANSFER CASE - NV247WJ
Page 1949 of 2199
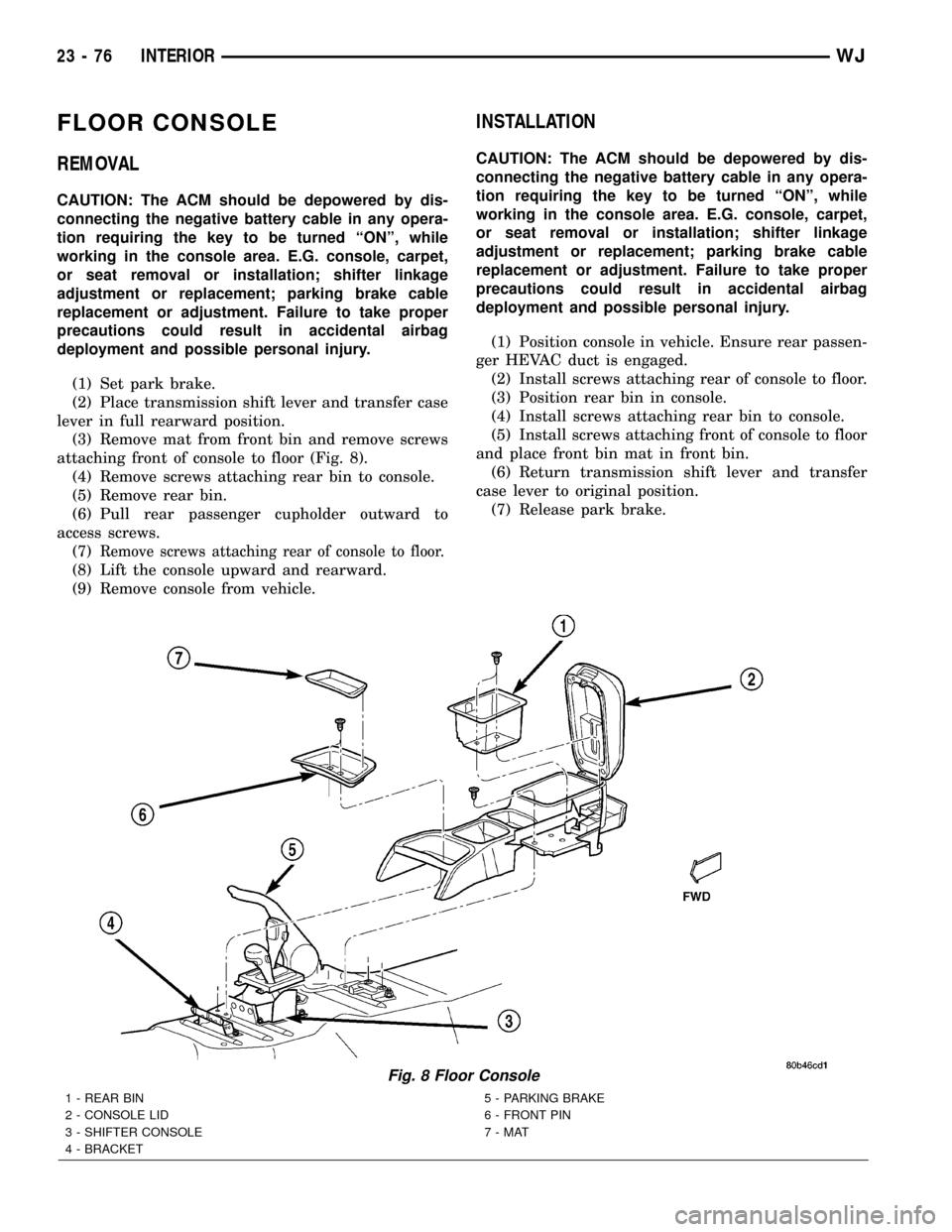
FLOOR CONSOLE
REMOVAL
CAUTION: The ACM should be depowered by dis-
connecting the negative battery cable in any opera-
tion requiring the key to be turned ªONº, while
working in the console area. E.G. console, carpet,
or seat removal or installation; shifter linkage
adjustment or replacement; parking brake cable
replacement or adjustment. Failure to take proper
precautions could result in accidental airbag
deployment and possible personal injury.
(1) Set park brake.
(2) Place transmission shift lever and transfer case
lever in full rearward position.
(3) Remove mat from front bin and remove screws
attaching front of console to floor (Fig. 8).
(4) Remove screws attaching rear bin to console.
(5) Remove rear bin.
(6) Pull rear passenger cupholder outward to
access screws.
(7)
Remove screws attaching rear of console to floor.
(8) Lift the console upward and rearward.
(9) Remove console from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The ACM should be depowered by dis-
connecting the negative battery cable in any opera-
tion requiring the key to be turned ªONº, while
working in the console area. E.G. console, carpet,
or seat removal or installation; shifter linkage
adjustment or replacement; parking brake cable
replacement or adjustment. Failure to take proper
precautions could result in accidental airbag
deployment and possible personal injury.
(1) Position console in vehicle. Ensure rear passen-
ger HEVAC duct is engaged.
(2) Install screws attaching rear of console to floor.
(3) Position rear bin in console.
(4) Install screws attaching rear bin to console.
(5) Install screws attaching front of console to floor
and place front bin mat in front bin.
(6) Return transmission shift lever and transfer
case lever to original position.
(7) Release park brake.
Fig. 8 Floor Console
1 - REAR BIN
2 - CONSOLE LID
3 - SHIFTER CONSOLE
4 - BRACKET5 - PARKING BRAKE
6 - FRONT PIN
7-MAT
23 - 76 INTERIORWJ