2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Diffe
[x] Cancel search: DiffePage 2156 of 2199

EMISSIONS CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM.............................1
DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST
MODE...............................2
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE...............................2
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES..............................2DESCRIPTION - TASK MANAGER.........17
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED SYSTEMS . . . 17
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION........19
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS . . 19
DESCRIPTION - NON-MONITORED
CIRCUITS...........................20
DESCRIPTION - HIGH AND LOW LIMITS . . . 20
DESCRIPTION - LOAD VALUE...........20
OPERATION - TASK MANAGER............21
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS................24
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
many different circuits in the fuel injection, ignition,
emission and engine systems. If the PCM senses a prob-
lem with a monitored circuit often enough to indicate an
actual problem, it stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) in the PCM's memory. If the code applies to a
non-emissions related component or system, and the
problem is repaired or ceases to exist, the PCM cancels
the code after 40 warm-up cycles. Diagnostic trouble
codes that affect vehicle emissions illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator (check engine) Lamp. Refer to Mal-
function Indicator Lamp in this section.
Certain criteria must be met before the PCM
stores a DTC in memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine RPM, engine temperature,
and/or input voltage to the PCM.
The PCM might not store a DTC for a monitored cir-
cuit even though a malfunction has occurred. This may
happen because one of the DTC criteria for the circuit
has not been met.For example
,assume the diagnostic
trouble code criteria requires the PCM to monitor the
circuit only when the engine operates between 750 and
2000 RPM. Suppose the sensor's output circuit shorts to
ground when engine operates above 2400 RPM (result-
ing in 0 volt input to the PCM). Because the condition
happens at an engine speed above the maximum thresh-
old (2000 rpm), the PCM will not store a DTC.
There are several operating conditions for which
the PCM monitors and sets DTC's. Refer to Moni-
tored Systems, Components, and Non-Monitored Cir-
cuits in this section.Technicians must retrieve stored DTC's by connect-
ing the DRB scan tool (or an equivalent scan tool) to
the 16±way data link connector (Fig. 1).
NOTE: Various diagnostic procedures may actually
cause a diagnostic monitor to set a DTC. For
instance, pulling a spark plug wire to perform a
spark test may set the misfire code. When a repair
is completed and verified, connect the DRB scan
tool to the 16±way data link connector to erase all
DTC's and extinguish the MIL (check engine lamp).Fig. 1 Data Link (Diagnostic) Connector Location
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER/LEFT EDGE
2 - DATA LINK CONNECTOR
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 1
Page 2157 of 2199

DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. Connect
the DRB scan tool to the data link connector and
access the state display screen. Then access either
State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display
Sensors.
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly. Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector and access the Actuators screen.
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0030 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0031 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0032 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0036 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0037 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0038 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0043 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0044 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0051 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0052 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2167 of 2199
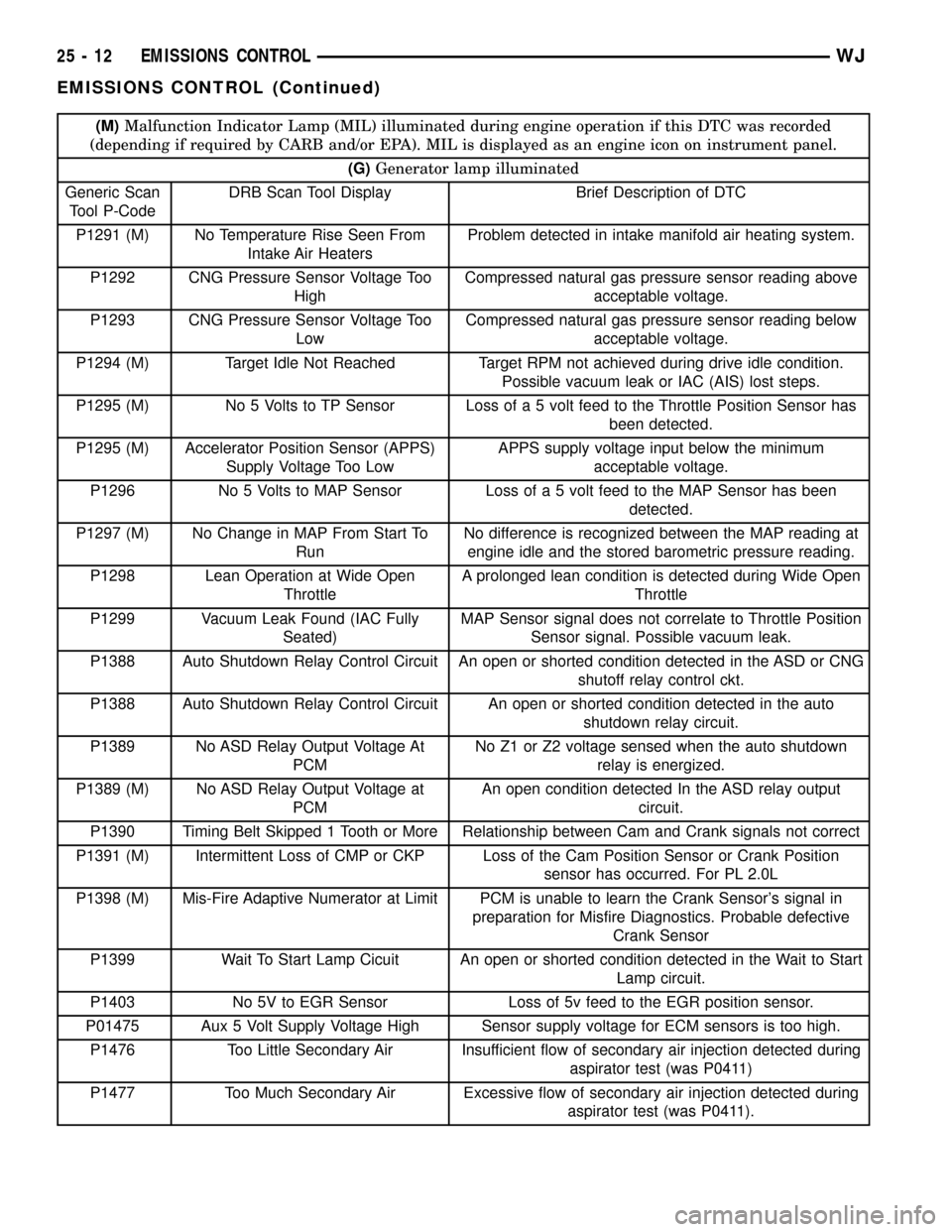
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1291 (M) No Temperature Rise Seen From
Intake Air HeatersProblem detected in intake manifold air heating system.
P1292 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
HighCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading above
acceptable voltage.
P1293 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
LowCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading below
acceptable voltage.
P1294 (M) Target Idle Not Reached Target RPM not achieved during drive idle condition.
Possible vacuum leak or IAC (AIS) lost steps.
P1295 (M) No 5 Volts to TP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the Throttle Position Sensor has
been detected.
P1295 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Supply Voltage Too LowAPPS supply voltage input below the minimum
acceptable voltage.
P1296 No 5 Volts to MAP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the MAP Sensor has been
detected.
P1297 (M) No Change in MAP From Start To
RunNo difference is recognized between the MAP reading at
engine idle and the stored barometric pressure reading.
P1298 Lean Operation at Wide Open
ThrottleA prolonged lean condition is detected during Wide Open
Throttle
P1299 Vacuum Leak Found (IAC Fully
Seated)MAP Sensor signal does not correlate to Throttle Position
Sensor signal. Possible vacuum leak.
P1388 Auto Shutdown Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the ASD or CNG
shutoff relay control ckt.
P1388 Auto Shutdown Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the auto
shutdown relay circuit.
P1389 No ASD Relay Output Voltage At
PCMNo Z1 or Z2 voltage sensed when the auto shutdown
relay is energized.
P1389 (M) No ASD Relay Output Voltage at
PCMAn open condition detected In the ASD relay output
circuit.
P1390 Timing Belt Skipped 1 Tooth or More Relationship between Cam and Crank signals not correct
P1391 (M) Intermittent Loss of CMP or CKP Loss of the Cam Position Sensor or Crank Position
sensor has occurred. For PL 2.0L
P1398 (M) Mis-Fire Adaptive Numerator at Limit PCM is unable to learn the Crank Sensor's signal in
preparation for Misfire Diagnostics. Probable defective
Crank Sensor
P1399 Wait To Start Lamp Cicuit An open or shorted condition detected in the Wait to Start
Lamp circuit.
P1403 No 5V to EGR Sensor Loss of 5v feed to the EGR position sensor.
P01475 Aux 5 Volt Supply Voltage High Sensor supply voltage for ECM sensors is too high.
P1476 Too Little Secondary Air Insufficient flow of secondary air injection detected during
aspirator test (was P0411)
P1477 Too Much Secondary Air Excessive flow of secondary air injection detected during
aspirator test (was P0411).
25 - 12 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2171 of 2199
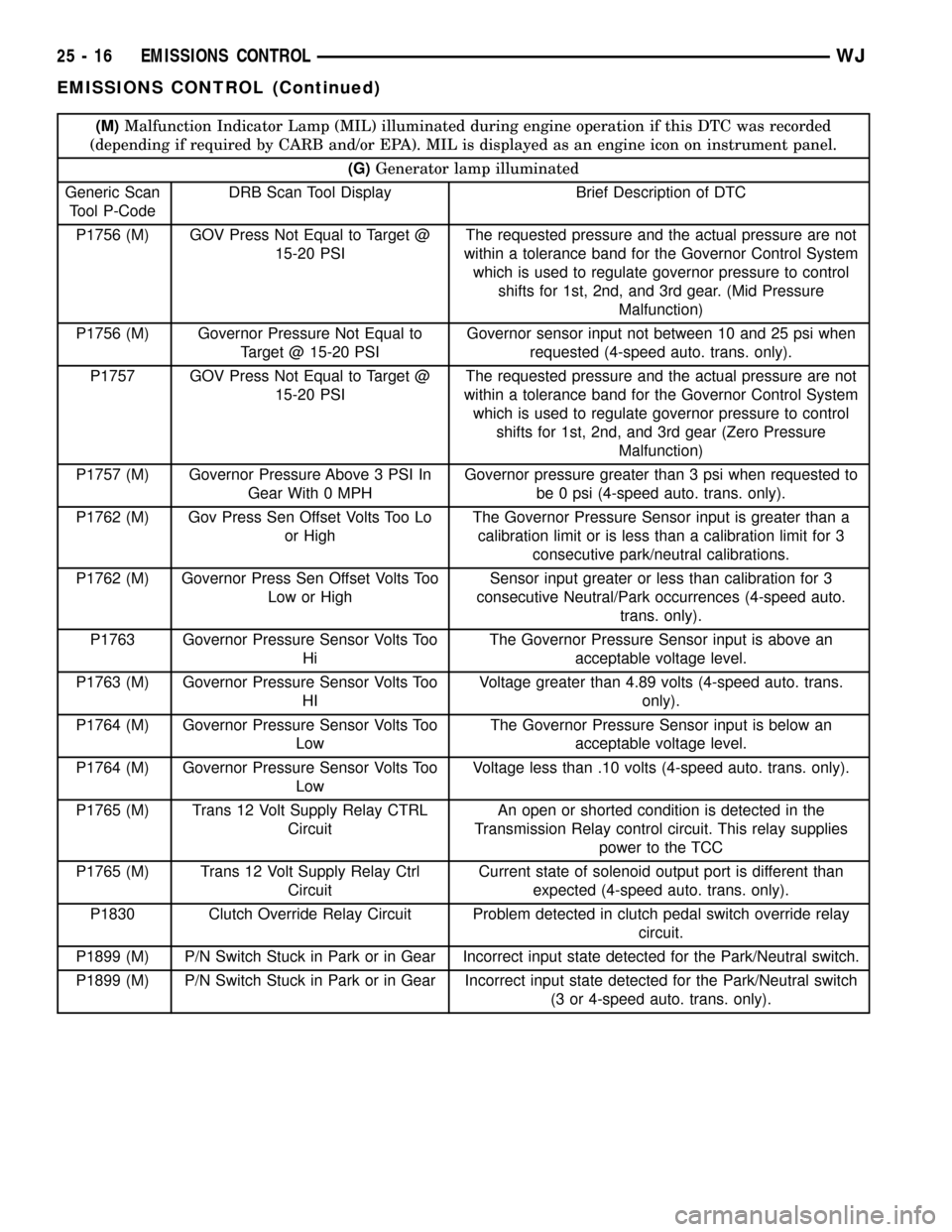
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1756 (M) GOV Press Not Equal to Target @
15-20 PSIThe requested pressure and the actual pressure are not
within a tolerance band for the Governor Control System
which is used to regulate governor pressure to control
shifts for 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gear. (Mid Pressure
Malfunction)
P1756 (M) Governor Pressure Not Equal to
Target @ 15-20 PSIGovernor sensor input not between 10 and 25 psi when
requested (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P1757 GOV Press Not Equal to Target @
15-20 PSIThe requested pressure and the actual pressure are not
within a tolerance band for the Governor Control System
which is used to regulate governor pressure to control
shifts for 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gear (Zero Pressure
Malfunction)
P1757 (M) Governor Pressure Above 3 PSI In
Gear With 0 MPHGovernor pressure greater than 3 psi when requested to
be 0 psi (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P1762 (M) Gov Press Sen Offset Volts Too Lo
or HighThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is greater than a
calibration limit or is less than a calibration limit for 3
consecutive park/neutral calibrations.
P1762 (M) Governor Press Sen Offset Volts Too
Low or HighSensor input greater or less than calibration for 3
consecutive Neutral/Park occurrences (4-speed auto.
trans. only).
P1763 Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
HiThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is above an
acceptable voltage level.
P1763 (M) Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
HIVoltage greater than 4.89 volts (4-speed auto. trans.
only).
P1764 (M) Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
LowThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is below an
acceptable voltage level.
P1764 (M) Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
LowVoltage less than .10 volts (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P1765 (M) Trans 12 Volt Supply Relay CTRL
CircuitAn open or shorted condition is detected in the
Transmission Relay control circuit. This relay supplies
power to the TCC
P1765 (M) Trans 12 Volt Supply Relay Ctrl
CircuitCurrent state of solenoid output port is different than
expected (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P1830 Clutch Override Relay Circuit Problem detected in clutch pedal switch override relay
circuit.
P1899 (M) P/N Switch Stuck in Park or in Gear Incorrect input state detected for the Park/Neutral switch.
P1899 (M) P/N Switch Stuck in Park or in Gear Incorrect input state detected for the Park/Neutral switch
(3 or 4-speed auto. trans. only).
25 - 16 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2172 of 2199

DESCRIPTION - TASK MANAGER
The PCM is responsible for efficiently coordinating
the operation of all the emissions-related compo-
nents. The PCM is also responsible for determining if
the diagnostic systems are operating properly. The
software designed to carry out these responsibilities
is referred to as the 'Task Manager'.
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED SYSTEMS
There are new electronic circuit monitors that
check fuel, emission, engine and ignition perfor-
mance. These monitors use information from various
sensor circuits to indicate the overall operation of the
fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems and thus
the emissions performance of the vehicle.
The fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems
monitors do not indicate a specific component prob-
lem. They do indicate that there is an implied prob-
lem within one of the systems and that a specific
problem must be diagnosed.
If any of these monitors detect a problem affecting
vehicle emissions, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) will be illuminated. These monitors generate
Diagnostic Trouble Codes that can be displayed with
the MIL or a scan tool.
The following is a list of the system monitors:
²Misfire Monitor
²Fuel System Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
All these system monitors require two consecutive
trips with the malfunction present to set a fault.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnos-
tics Procedures manual for diagnostic proce-
dures.
The following is an operation and description of
each system monitor:
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S) MONITOR
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
Catalyst and Fuel Monitors.The O2S can fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²slow response rate
²reduced output voltage
²dynamic shift
²shorted or open circuits
Response rate is the time required for the sensor to
switch from lean to rich once it is exposed to a richer
than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As the sen-
sor starts malfunctioning, it could take longer to
detect the changes in the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas.
The output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1
volt. A good sensor can easily generate any output
voltage in this range as it is exposed to different con-
centrations of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F
mixture (lean or rich), the output voltage has to
change beyond a threshold value. A malfunctioning
sensor could have difficulty changing beyond the
threshold value.
OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER MONITOR
If there is an oxygen sensor (O2S) shorted to volt-
age DTC, as well as a O2S heater DTC, the O2S
fault MUST be repaired first. Before checking the
O2S fault, verify that the heater circuit is operating
correctly.
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572 É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The voltage readings taken from the O2S sensor
are very temperature sensitive. The readings are not
accurate below 300ÉC. Heating of the O2S sensor is
done to allow the engine controller to shift to closed
loop control as soon as possible. The heating element
used to heat the O2S sensor must be tested to ensure
that it is heating the sensor properly.
The O2S sensor circuit is monitored for a drop in
voltage. The sensor output is used to test the heater
by isolating the effect of the heater element on the
O2S sensor output voltage from the other effects.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP MONITOR (IF EQUIPPED)
The leak detection assembly incorporates two pri-
mary functions: it must detect a leak in the evapora-
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 17
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2174 of 2199

and deteriorate engine performance, driveability and
fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2S's sensor strategy is based on the fact that
as a catalyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity
and its efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring
the oxygen storage capacity of a catalyst, its effi-
ciency can be indirectly calculated. The upstream
O2S is used to detect the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gas before the gas enters the catalytic con-
verter. The PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the
output of the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxy-
gen content (lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a
low content of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL will be illu-
minated.
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION
The term ªTripº has different meanings depending
on what the circumstances are. If the MIL (Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp) is OFF, a Trip is defined as
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst
Monitor have been completed in the same drive cycle.
When any Emission DTC is set, the MIL on the
dash is turned ON. When the MIL is ON, it takes 3
good trips to turn the MIL OFF. In this case, itdepends on what type of DTC is set to know what a
ªTripº is.
For the Fuel Monitor or Mis-Fire Monitor (contin-
uous monitor), the vehicle must be operated in the
ªSimilar Condition Windowº for a specified amount of
time to be considered a Good Trip.
If a Non-Contiuous OBDII Monitor fails twice in a
row and turns ON the MIL, re-running that monitor
which previously failed, on the next start-up and
passing the monitor, is considered to be a Good Trip.
These will include the following:
²Oxygen Sensor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Purge Flow Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
²EGR Monitor (if equipped)
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
If any other Emission DTC is set (not an OBDII
Monitor), a Good Trip is considered to be when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Monitor have
been completed; or 2 Minutes of engine run time if
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor or Catalyst Monitor have
been stopped from running.
It can take up to 2 Failures in a row to turn on the
MIL. After the MIL is ON, it takes 3 Good Trips to
turn the MIL OFF. After the MIL is OFF, the PCM
will self-erase the DTC after 40 Warm-up cycles. A
Warm-up cycle is counted when the ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature Sensor) has crossed 160ÉF and
has risen by at least 40ÉF since the engine has been
started.
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum if
the TPS indicates a small throttle opening.
All open/short circuit checks or any component that
has an associated limp in will set a fault after 1 trip
with the malfunction present. Components without
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 19
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2176 of 2199

OPERATION - TASK MANAGER
The Task Manager determines which tests happen
when and which functions occur when. Many of the
diagnostic steps required by OBD II must be per-
formed under specific operating conditions. The Task
Manager software organizes and prioritizes the diag-
nostic procedures. The job of the Task Manager is to
determine if conditions are appropriate for tests to be
run, monitor the parameters for a trip for each test,
and record the results of the test. Following are the
responsibilities of the Task Manager software:
²Test Sequence
²MIL Illumination
²Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
²Trip Indicator
²Freeze Frame Data Storage
²Similar Conditions Window
Test Sequence
In many instances, emissions systems must fail
diagnostic tests more than once before the PCM illu-
minates the MIL. These tests are know as 'two trip
monitors.' Other tests that turn the MIL lamp on
after a single failure are known as 'one trip moni-
tors.' A trip is defined as 'start the vehicle and oper-
ate it to meet the criteria necessary to run the given
monitor.'
Many of the diagnostic tests must be performed
under certain operating conditions. However, there
are times when tests cannot be run because another
test is in progress (conflict), another test has failed
(pending) or the Task Manager has set a fault that
may cause a failure of the test (suspend).
²Pending
Under some situations the Task Manager will not
run a monitor if the MIL is illuminated and a fault is
stored from another monitor. In these situations, the
Task Manager postpones monitorspendingresolu-
tion of the original fault. The Task Manager does not
run the test until the problem is remedied.
For example, when the MIL is illuminated for an
Oxygen Sensor fault, the Task Manager does not run
the Catalyst Monitor until the Oxygen Sensor fault is
remedied. Since the Catalyst Monitor is based on sig-
nals from the Oxygen Sensor, running the test would
produce inaccurate results.
²Conflict
There are situations when the Task Manager does
not run a test if another monitor is in progress. In
these situations, the effects of another monitor run-
ning could result in an erroneous failure. If thiscon-
flictis present, the monitor is not run until the
conflicting condition passes. Most likely the monitor
will run later after the conflicting monitor has
passed.
For example, if the Fuel System Monitor is inprogress, the Task Manager does not run the EGR
Monitor. Since both tests monitor changes in air/fuel
ratio and adaptive fuel compensation, the monitors
will conflict with each other.
²Suspend
Occasionally the Task Manager may not allow a two
trip fault to mature. The Task Manager willsus-
pendthe maturing of a fault if a condition exists
that may induce an erroneous failure. This prevents
illuminating the MIL for the wrong fault and allows
more precis diagnosis.
For example, if the PCM is storing a one trip fault
for the Oxygen Sensor and the EGR monitor, the
Task Manager may still run the EGR Monitor but
will suspend the results until the Oxygen Sensor
Monitor either passes or fails. At that point the Task
Manager can determine if the EGR system is actu-
ally failing or if an Oxygen Sensor is failing.MIL Illumination
The PCM Task Manager carries out the illumina-
tion of the MIL. The Task Manager triggers MIL illu-
mination upon test failure, depending on monitor
failure criteria.
The Task Manager Screen shows both a Requested
MIL state and an Actual MIL state. When the MIL is
illuminated upon completion of a test for a third trip,
the Requested MIL state changes to OFF. However,
the MIL remains illuminated until the next key
cycle. (On some vehicles, the MIL will actually turn
OFF during the third key cycle) During the key cycle
for the third good trip, the Requested MIL state is
OFF, while the Actual MIL state is ON. After the
next key cycle, the MIL is not illuminated and both
MIL states read OFF.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
With OBD II, different DTC faults have different
priorities according to regulations. As a result, the
priorities determine MIL illumination and DTC era-
sure. DTCs are entered according to individual prior-
ity. DTCs with a higher priority overwrite lower
priority DTCs.
Priorities
²Priority 0 ÐNon-emissions related trouble codes
²Priority 1 Ð One trip failure of a two trip fault
for non-fuel system and non-misfire.
²Priority 2 Ð One trip failure of a two trip fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) or misfire.
²Priority3ÐTwotrip failure for a non-fuel sys-
tem and non-misfire or matured one trip comprehen-
sive component fault.
²Priority4ÐTwotrip failure or matured fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) and misfire or one trip cat-
alyst damaging misfire.
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 21
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2177 of 2199

Non-emissions related failures have no priority.
One trip failures of two trip faults have low priority.
Two trip failures or matured faults have higher pri-
ority. One and two trip failures of fuel system and
misfire monitor take precedence over non-fuel system
and non-misfire failures.
DTC Self Erasure
With one trip components or systems, the MIL is
illuminated upon test failure and DTCs are stored.
Two trip monitors are components requiring failure
in two consecutive trips for MIL illumination. Upon
failure of the first test, the Task Manager enters a
maturing code. If the component fails the test for a
second time the code matures and a DTC is set.
After three good trips the MIL is extinguished and
the Task Manager automatically switches the trip
counter to a warm-up cycle counter. DTCs are auto-
matically erased following 40 warm-up cycles if the
component does not fail again.
For misfire and fuel system monitors, the compo-
nent must pass the test under a Similar Conditions
Window in order to record a good trip. A Similar Con-
ditions Window is when engine RPM is within 375
RPM and load is within 10% of when the fault
occurred.
NOTE: It is important to understand that a compo-
nent does not have to fail under a similar window of
operation to mature. It must pass the test under a
Similar Conditions Window when it failed to record
a Good Trip for DTC erasure for misfire and fuel
system monitors.
DTCs can be erased anytime with a DRB III. Eras-
ing the DTC with the DRB III erases all OBD II
information. The DRB III automatically displays a
warning that erasing the DTC will also erase all
OBD II monitor data. This includes all counter infor-
mation for warm-up cycles, trips and Freeze Frame.
Trip Indicator
TheTripis essential for running monitors and
extinguishing the MIL. In OBD II terms, a trip is a
set of vehicle operating conditions that must be met
for a specific monitor to run. All trips begin with a
key cycle.
Good Trip
The Good Trip counters are as follows:
²Specific Good Trip
²Fuel System Good Trip
²Misfire Good Trip
²Alternate Good Trip (appears as a Global Good
Trip on DRB III)
²Comprehensive Components
²Major Monitor
²Warm-Up CyclesSpecific Good Trip
The term Good Trip has different meanings
depending on the circumstances:
²If the MIL is OFF, a trip is defined as when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst Monitor
have been completed in the same drive cycle.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by the Fuel
Monitor or Misfire Monitor (both continuous moni-
tors), the vehicle must be operated in the Similar
Condition Window for a specified amount of time.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by a Task
Manager commanded once-per-trip monitor (such as
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Catalyst Monitor, Purge
Flow Monitor, Leak Detection Pump Monitor, EGR
Monitor or Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor), a good
trip is when the monitor is passed on the next start-
up.
²If the MIL is ON and any other emissions DTC
was set (not an OBD II monitor), a good trip occurs
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Mon-
itor have been completed, or two minutes of engine
run time if the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst
Monitor have been stopped from running.
Fuel System Good Trip
To count a good trip (three required) and turn off
the MIL, the following conditions must occur:
²Engine in closed loop
²Operating in Similar Conditions Window
²Short Term multiplied by Long Term less than
threshold
²Less than threshold for a predetermined time
If all of the previous criteria are met, the PCM will
count a good trip (three required) and turn off the
MIL.
Misfire Good Trip
If the following conditions are met the PCM will
count one good trip (three required) in order to turn
off the MIL:
²Operating in Similar Condition Window
²1000 engine revolutions with no misfire
Warm-Up Cycles
Once the MIL has been extinguished by the Good
Trip Counter, the PCM automatically switches to a
Warm-Up Cycle Counter that can be viewed on the
DRB III. Warm-Up Cycles are used to erase DTCs
and Freeze Frames. Forty Warm-Up cycles must
occur in order for the PCM to self-erase a DTC and
Freeze Frame. A Warm-Up Cycle is defined as fol-
lows:
²Engine coolant temperature must start below
and rise above 160É F
²Engine coolant temperature must rise by 40É F
²No further faults occur
25 - 22 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)