2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE turn sign
[x] Cancel search: turn signPage 1865 of 2199
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRES
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle's requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:
²Rapid acceleration
²Severe brake applications
²High speed driving
²Excessive speeds on turns
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
Radial-ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation.(Refer to 22
- TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE),
This will help to achieve a greater tread life.
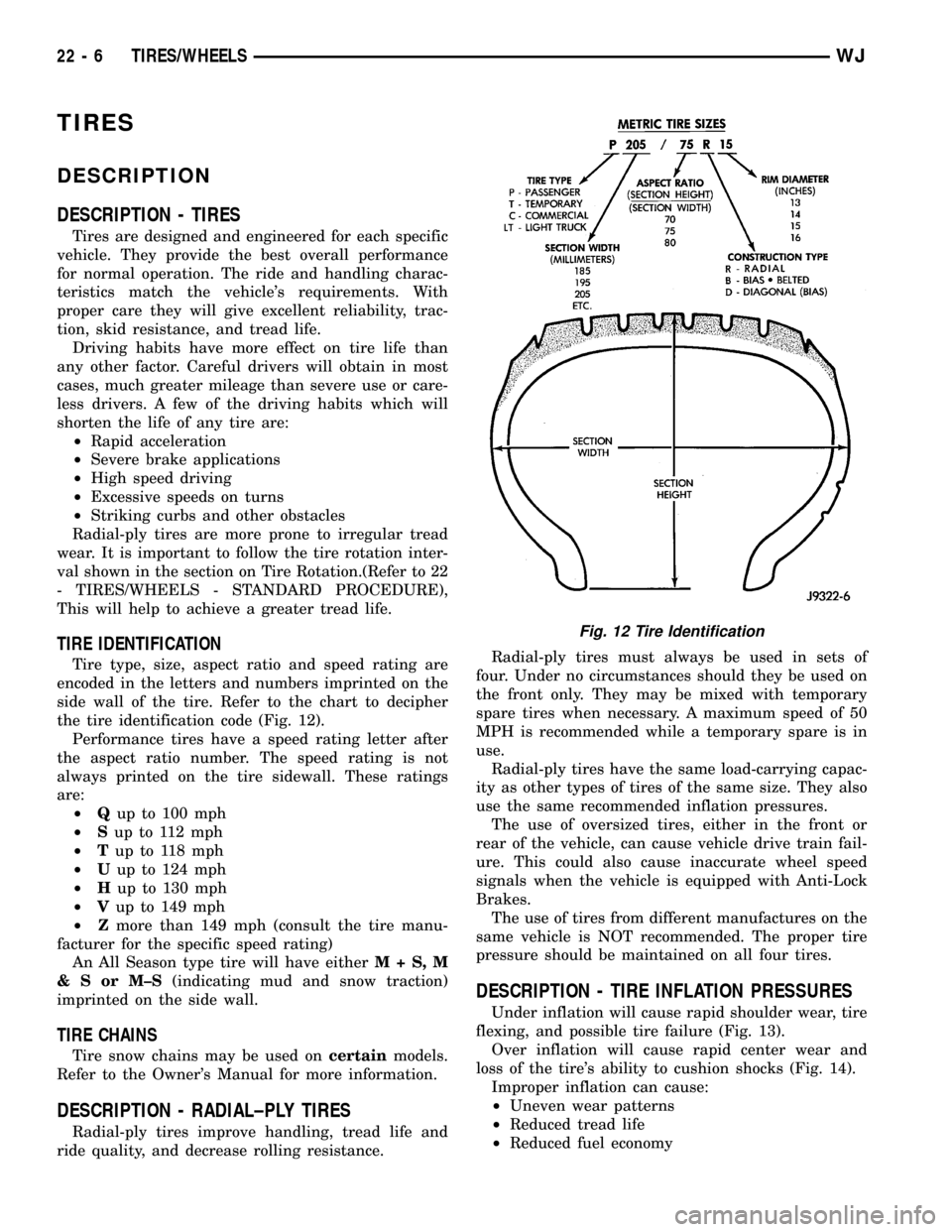
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 12).
Performance tires have a speed rating letter after
the aspect ratio number. The speed rating is not
always printed on the tire sidewall. These ratings
are:
²Qup to 100 mph
²Sup to 112 mph
²Tup to 118 mph
²Uup to 124 mph
²Hup to 130 mph
²Vup to 149 mph
²Zmore than 149 mph (consult the tire manu-
facturer for the specific speed rating)
An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
&SorM±S(indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall.
TIRE CHAINS
Tire snow chains may be used oncertainmodels.
Refer to the Owner's Manual for more information.
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL±PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life and
ride quality, and decrease rolling resistance.Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary. A maximum speed of 50
MPH is recommended while a temporary spare is in
use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or
rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train fail-
ure. This could also cause inaccurate wheel speed
signals when the vehicle is equipped with Anti-Lock
Brakes.
The use of tires from different manufactures on the
same vehicle is NOT recommended. The proper tire
pressure should be maintained on all four tires.
DESCRIPTION - TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
Under inflation will cause rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and possible tire failure (Fig. 13).
Over inflation will cause rapid center wear and
loss of the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 14).
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
Fig. 12 Tire Identification
22 - 6 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
Page 2098 of 2199

(2)If there are no fault codes, the ª00º dis-
play value will remain in the VF window.Should
there be any codes, each will be displayed for one
second in ascending numerical sequence (note: no
effort is made to display faults in the order they
occurred). The left side set temperature display will
be blanked and the right side set temperature dis-
play will indicate current and historical codes (8 his-
torical max) presently active. Once all codes have
been displayed, the system will repeat the fault code
numbers. This will continue until the left side set
temperature control is moved at least one detent
position in either direction, by pressing both the A/C
and Recirc buttons at the same time, or the ignition
is turned off. Record all of the fault codes, then see
the Current and Historical Fault Code charts for the
descriptions.
CLEARING FAULT CODES
Current faults cannot be electronically cleared.
Repair must be made to the system to eliminate the
fault causing code. Historical fault codes can be
cleared manually, or automatically. To clear a histor-
ical fault manually, depress and hold either the A/C
or Recirc button for at least three seconds while the
display is in the fault code mode of operation. Histor-
ical fault codes are cleared automatically when the
corresponding current fault code has been cleared,
and has remained cleared for a number of ignition
cycles. The faults have been cleared when two hori-
zontal bars appear in the Test Selector display.
EXITING SELF-DIAGNOSTIC MODE
The self-diagnostic mode can be exited by pressing
both the A/C and Recirc buttons at the same time, or
turning off the ignition.
MONITOR CURRENT PARAMETERS
While in the display fault code mode of operation,
current system parameters can also be monitored
and/or forced. Rotating the left side set temperature
control clockwise will increase the pointer number
while rotating the control counter clockwise will
decrease the pointer number. Rotating the right set
temperature control will have no impact on pointer
value or the value of the parameter being monitored.
Once the desired pointer number has been selected,
pressing either the AC or Recirc buttons will display
the current value of the selected parameter.The
right side set temperature display is only capa-
ble of displaying only values ranging from 0 to
99, the left side set temperature display is used
for values greater than 99. If the value is less
than 99, the left side set temperature display
remains blanked.While a parameter is being over-
ridden, the system will continue to function normallyexcept for the parameter which is being manually
controlled.
For values < 0, the9G9segment in the left side set
temperature Most Significant Digit (MSD)(or left-
most number in the pair) will be used to indicate a
negative number. For values between -01 to -99 the
Least Significant Digit (LSD)(or right-most number
of the pair) in the left side set temperature will
remain blank. System control of parameter being dis-
played can be overridden by rotating the right set
temperature control in either direction. Rotating the
right temperature control in the CW direction, the
selected parameter value is overridden and incre-
mented beginning at the value which was being dis-
played. Rotating the right temperature control in the
CCW direction, the selected parameter value is over-
ridden and decremented beginning at the value
which was being displayed. The rate at which incre-
menting and decrement occurs is one unit value per
set temperature detent position.
HVAC SYSTEM POINTER
Pointer
NumberDESCRIPTION Value
Displayed
01 A/C Enable 0 or 1
0=
disabled
1=
enabled
02 Final fan PWM duty cycle 0 to 255
While the value of this pointer
is being displayed, turning the
right set temperature control
either direction will manually
control the value. CW =
increase; CCW = decrease
03 Left NPRG * 0 to 255
* NPRG equals a calculated number based on outside
and in-vehicle conditions. This value is used by the
AZC to position the Mode motor, Air Inlet motor, and
control blower motor speed.
While the value of this pointer
is being displayed, turning the
right set temperature control
either direction will manually
control the value. CW =
increase; CCW = decrease
04 Right NPRG 0 to 255
WJCONTROLS 24 - 21
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2102 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Plug the wire harness and/or vacuum harness
connectors into the back of the a/c heater control.
(2) Position the a/c heater control in the instru-
ment panel and secure it with 4 screws. Tighten the
screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Reinstall the center upper, and center lower
bezels onto the instrument panel. Refer to Instru-
ment Panel System for the procedures.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
DESCRIPTION
The A/C pressure transducer is installed on a fit-
ting located on the refrigerant discharge line near
the condenser. An internally threaded hex fitting on
the transducer connects it to the externally threaded
Schrader-type fitting on the discharge line. A rubber
O-ring seals the connection between the transducer
and the discharge line fitting. Three terminals within
a molded plastic connector receptacle on the top of
the transducer connect it to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem through a take out and connector of the head-
lamp and dash wire harness.
The A/C pressure transducer cannot be adjusted or
repaired and if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The A/C pressure transducer monitors the pres-
sures in the high side of the refrigerant system
through its connection to a fitting on the discharge
line. The transducer will change its internal resis-
tance in response to the pressures it monitors. The
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) provides a five
volt reference signal and a sensor ground to the
transducer, then monitors the output voltage of the
transducer on a sensor return circuit to determine
refrigerant pressure. The PCM is preporgrammed to
respond to this and other sensor inputs by controlling
the operation of the air conditioning compressor
clutch and the radiator cooling fan to help optimize
air conditioning system performance and to protect
the system components from damage. The A/C pres-
sure transducer input to the PCM will also prevent
the air conditioning compressor clutch from engaging
when the ambient temperatures are below about
0.556É C (33É F) due to the pressure/temperature
relationship of the refrigerant. The Schrader-type
valve in the liquid line fitting permits the A/C pres-
sure transducer to be removed or installed without
distrubing the refrigerant in the system. The A/C
pressure transducer is diagnosed using the DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation.
Fig. 13 A/C HEATER CONTROL REMOVE/INSTALL
1 - MOUNTING SCREW TABS
Fig. 14 A/C HEATER CONTROL CONNECTIONS
1 - MODE SWITCH
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
3 - VACUUM HARNESS
WJCONTROLS 24 - 25
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2131 of 2199

ready. The refrigerant system should not be left open
to the atmosphere any longer than necessary. Cap or
plug all lines and fittings as soon as they are opened
to prevent the entrance of dirt and moisture. All lines
and components in parts stock should be capped or
sealed until they are to be installed.
All tools, including the refrigerant recycling equip-
ment, the manifold gauge set, and test hoses should
be kept clean and dry. All tools and equipment must
be designed for R-134a refrigerant.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM LEAKS
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
If the air conditioning system is not cooling prop-
erly, determine if the refrigerant system is fully-
charged. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
A/C PERFORMANCE)
An electronic leak detector designed for R-134a
refrigerant is recommended for locating and confirm-
ing refrigerant system leaks. Refer to the operating
instructions supplied by the equipment manufacturer
for proper care and use of this equipment.
An oily residue on or near refrigerant system lines,
connector fittings, components, or component seals
can indicate the general location of a possible refrig-
erant leak. However, the exact leak location should
be confirmed with an electronic leak detector prior to
component repair or replacement.
To detect a leak in the refrigerant system, perform
one of the following procedures:
SYSTEM EMPTY
(1) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(2) Connect and dispense 0.283 kilograms (0.625
pounds or 10 ounces) of R-134a refrigerant into the
evacuated refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
CHARGE)
(3) Position the vehicle in a wind-free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks.
(4) With the engine not running, use a electronic
R-134a leak detector and search for leaks. Because
R-134a refrigerant is heavier than air, the leak detec-tor probe should be moved slowly along the bottom
side of all refrigerant lines, connector fittings and
components.
(5) To inspect the evaporator coil for leaks, insert
the electronic leak detector probe into the center
instrument panel outlet. Set the blower motor switch
to the lowest speed position, the A/C button in the
On position, and select the Recirculation Mode.
SYSTEM LOW
(1) Position the vehicle in a wind-free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks.
(2) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
the engine to run with the air conditioning system
turned on for five minutes.
(3) With the engine not running, use a electronic
R-134a leak detector and search for leaks. Because
R-134a refrigerant is heavier than air, the leak detec-
tor probe should be moved slowly along the bottom
side of all refrigerant lines, connector fittings and
components.
(4) To inspect the evaporator coil for leaks, insert
the electronic leak detector probe into the center
instrument panel outlet. Set the blower motor switch
to the lowest speed position, the A/C button in the
On position, and select the Recirculation Mode.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM SERVICE EQUIPMENT
WARNING: EYE PROTECTION MUST BE WORN
WHEN SERVICING AN AIR CONDITIONING REFRIG-
ERANT SYSTEM. TURN OFF (ROTATE CLOCKWISE)
ALL VALVES ON THE EQUIPMENT BEING USED,
BEFORE CONNECTING TO OR DISCONNECTING
FROM THE REFRIGERANT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO
OBSERVE THESE WARNINGS MAY RESULT IN PER-
SONAL INJURY.
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
When servicing the air conditioning system, a
R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging sta-
tion that meets SAE Standard J2210 must be used.
Contact an automotive service equipment supplier for
refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging equipment.
Refer to the operating instructions supplied by the
24 - 54 PLUMBINGWJ
PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 2175 of 2199

an associated limp in will take two trips to illumi-
nate the MIL.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
DESCRIPTION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems and conditions that could have malfunctions
causing driveability problems. The PCM might not
store diagnostic trouble codes for these conditions.
However, problems with these systems may cause the
PCM to store diagnostic trouble codes for other sys-
tems or components. For example, a fuel pressure
problem will not register a fault directly, but could
cause a rich/lean condition or misfire. This could
cause the PCM to store an oxygen sensor or misfire
diagnostic trouble code
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor or fuel system diag-
nostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system, although it may set a fuel
system fault.
FUEL INJECTOR MECHANICAL MALFUNCTIONS
The PCM cannot determine if a fuel injector is
clogged, the needle is sticking or if the wrong injectoris installed. However, these could result in a rich or
lean condition causing the PCM to store a diagnostic
trouble code for either misfire, an oxygen sensor, or
the fuel system.
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION
Although the PCM monitors engine exhaust oxygen
content when the system is in closed loop, it cannot
determine excessive oil consumption.
THROTTLE BODY AIRFLOW
The PCM cannot detect a clogged or restricted air
cleaner inlet or filter element.
VACUUM ASSIST
The PCM cannot detect leaks or restrictions in the
vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control
system devices. However, these could cause the PCM
to store a MAP sensor diagnostic trouble code and
cause a high idle condition.
PCM SYSTEM GROUND
The PCM cannot determine a poor system ground.
However, one or more diagnostic trouble codes may
be generated as a result of this condition. The mod-
ule should be mounted to the body at all times, also
during diagnostic.
PCM CONNECTOR ENGAGEMENT
The PCM may not be able to determine spread or
damaged connector pins. However, it might store
diagnostic trouble codes as a result of spread connec-
tor pins.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The PCM compares input signal voltages from each
input device with established high and low limits for
the device. If the input voltage is not within limits
and other criteria are met, the PCM stores a diagnos-
tic trouble code in memory. Other diagnostic trouble
code criteria might include engine RPM limits or
input voltages from other sensors or switches that
must be present before verifying a diagnostic trouble
code condition.
DESCRIPTION - LOAD VALUE
ENGINE IDLE/NEUTRAL 2500 RPM/NEUTRAL
All Engines 2% to 8% of Maximum Load 9% to 17% of Maximum Load
25 - 20 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2186 of 2199

OPERATION
The main purpose of the LDP is to pressurize the
fuel system for leak checking. It closes the EVAP sys-
tem vent to atmospheric pressure so the system can
be pressurized for leak testing. The diaphragm is
powered by engine vacuum. It pumps air into the
EVAP system to develop a pressure of about 7.59
H2O (1/4) psi. A reed switch in the LDP allows the
PCM to monitor the position of the LDP diaphragm.
The PCM uses the reed switch input to monitor how
fast the LDP is pumping air into the EVAP system.
This allows detection of leaks and blockage. The LDP
assembly consists of several parts (Fig. 12). The sole-
noid is controlled by the PCM, and it connects the
upper pump cavity to either engine vacuum or atmo-
spheric pressure. A vent valve closes the EVAP sys-
tem to atmosphere, sealing the system during leak
testing. The pump section of the LDP consists of a
diaphragm that moves up and down to bring air in
through the air filter and inlet check valve, and
pump it out through an outlet check valve into the
EVAP system. The diaphragm is pulled up by engine
vacuum, and pushed down by spring pressure, as the
LDP solenoid turns on and off. The LDP also has a
magnetic reed switch to signal diaphragm position to
the PCM. When the diaphragm is down, the switch is
closed, which sends a 12 V (system voltage) signal to
the PCM. When the diaphragm is up, the switch is
open, and there is no voltage sent to the PCM. This
allows the PCM to monitor LDP pumping action as it
turns the LDP solenoid on and off.
LDP AT REST (NOT POWERED)
When the LDP is at rest (no electrical/vacuum) the
diaphragm is allowed to drop down if the internal
(EVAP system) pressure is not greater than the
return spring. The LDP solenoid blocks the engine
vacuum port and opens the atmospheric pressure
port connected through the EVAP system air filter.
The vent valve is held open by the diaphragm. This
allows the canister to see atmospheric pressure (Fig.
13).
DIAPHRAGM UPWARD MOVEMENT
When the PCM energizes the LDP solenoid, the
solenoid blocks the atmospheric port leading through
the EVAP air filter and at the same time opens the
engine vacuum port to the pump cavity above the
diaphragm. The diaphragm moves upward when vac-
uum above the diaphragm exceeds spring force. This
upward movement closes the vent valve. It also
causes low pressure below the diaphragm, unseating
the inlet check valve and allowing air in from the
EVAP air filter. When the diaphragm completes its
upward movement, the LDP reed switch turns from
closed to open (Fig. 14).
DIAPHRAGM DOWNWARD MOVEMENT
Based on reed switch input, the PCM de-energizes
the LDP solenoid, causing it to block the vacuum
port, and open the atmospheric port. This connects
the upper pump cavity to atmosphere through the
EVAP air filter. The spring is now able to push the
diaphragm down. The downward movement of the
diaphragm closes the inlet check valve and opens the
outlet check valve pumping air into the evaporative
system. The LDP reed switch turns from open to
closed, allowing the PCM to monitor LDP pumping
(diaphragm up/down) activity (Fig. 15). During the
pumping mode, the diaphragm will not move down
far enough to open the vent valve. The pumping cycle
is repeated as the solenoid is turned on and off.
When the evaporative system begins to pressurize,
the pressure on the bottom of the diaphragm will
begin to oppose the spring pressure, slowing the
pumping action. The PCM watches the time from
when the solenoid is de-energized, until the dia-
phragm drops down far enough for the reed switch to
Fig. 12 EVAP LEAK DETECTION SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
1 - Reed Switch
2 - Solenoid
3 - Spring
4 - Pump Cavity
5 - Diaphragm
6 - Inlet Check Valve
7 - Vent Valve
8 - From Air Filter
9 - To Canister
10 - Outlet Check Valve
11 - Engine Vacuum
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 31
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2189 of 2199

MIL will illuminate, and the remaining EVAP Leak
Detection Test is canceled.
SECTION 2 - P1494 Leak Detection Pump
Switch or Mechanical Fault-If DTC P1495 is not
set, the PCM will check for DTC P1494. If the LDP
reed switch was closed when the key was turned to
9ON9, the PCM energizes the LDP solenoid for up to
8 seconds and monitors the LDP switch. As the LDP
diaphragm is pulled up by engine vacuum, the LDP
reed switch should change from closed to open. If it
does not, the PCM sets a temporary fault (P1494) in
memory, and waits until the next time the Enabling
Conditions are met to run the test again. If this is
again detected, P1494 is stored and the MIL is illu-
minated. If the problem is not detected during the
next enabling cycle, the temporary fault will be
cleared.
However, if the PCM detects the reed switch open
when the key is turned to9ON9, the PCM must deter-
mine if this condition is due to residual pressure in
the EVAP system, or an actual fault. The PCM stores
information in memory on EVAP system purging
from previous engine run or drive cycles.
If little or no purging took place, residual pressure
could be holding the LDP diaphragm up, causing the
LDP switch to be open. Since this is not a malfunc-
tion, the PCM cancels the EVAP Leak Detection Test
without setting the temporary fault.
If there was sufficient purging during the previous
cycle to eliminate EVAP system pressure, the PCM
judges that this is a malfunction and sets a tempo-
rary fault in memory. The next time that the
Enabling Conditions are met, the test will run again.
If the fault is again detected, the MIL will illuminate
and DTC P1494 will be stored. If the fault is not
detected, the temporary fault will be cleared.
SECTION 3 - P1486 EVAP Leak Monitor
Pinched Hose Found-If no fault has been detected
so far, the PCM begins testing for possible blockage
in the EVAP system between the LDP and the fuel
tank. This is done by monitoring the time required
for the LDP to pump air into the EVAP system dur-
ing two to three pump cycles. If no blockage is
present, the LDP diaphragm is able to quickly pump
air out of the LDP each time the PCM turns off the
LDP solenoid. If a blockage is present, the PCM
detects that the LDP takes longer to complete each
pump cycle. If the pump cycles take longer than
expected (approximately 6 to 10 seconds) the PCM
will suspect a blockage. On the next drive when
Enabling Conditions are met, the test will run again.
If blockage is again detected, P1486 is stored, and
the MIL is illuminated.
SECTION4-NoDTCCanBeSetDuring This
Time-After the LDP blockage tests are completed,
the PCM then tests for EVAP system leakage. First,the PCM commands the LDP to rapidly pump for 20
to 50 seconds (depending on fuel level) to build pres-
sure in the EVAP system. This evaluates the system
J18-24-0 to see if it can be sufficiently pressurized.
This evaluation (rapid pump cycling) may occur sev-
eral times prior to leak checking. The LDP reed
switch does not close and open during rapid pumping
because the diaphragm does not travel through its
full range during this part of the test.
SECTION 5 - P0456, P0442, P0455 EVAP Leak
Monitor and Leak Detected-Next, the PCM per-
forms one or more test cycles by monitoring the time
required for the LDP reed switch to close (diaphragm
to drop) after the LDP solenoid is turned off.
If the switch does not close, or closes after a long
delay, it means that the system does not have any
significant leakage and the EVAP Leak Detection
Test is complete.
However, if the LDP reed switch closes quickly,
there may be a leak or the fuel level may be low
enough that the LDP must pump more to finish pres-
surizing the EVAP system. In this case, the PCM will
rapidly pump the LDP again to build pressure in the
EVAP system, and follow that by monitoring the time
needed for several LDP test cycles. This process of
rapid pumping followed by several LDP test cycles
may repeat several times before the PCM judges that
a leak is present.
When leaks are present, the LDP test cycle time
will be inversely proportional to the size of the leak.
The larger the leak, the shorter the test cycle time.
The smaller the leak, the longer the test cycle time.
DTC's may be set when a leak as small as 0.5 mm
(0.0209) diameter is present.
If the system detects a leak, a temporary fault will
be stored in PCM memory. The time it takes to detect
a .020, .040, or Large leak is based on calibrations
that vary from model to model. The important point
to remember is if a leak is again detected on the next
EVAP Leak Detection Test, the MIL will illuminate
and a DTC will be stored based on the size of leak
detected. If no leak is detected during the next test,
the temporary fault will be cleared.
DIAGNOSTIC TIPS During diagnosis, you can
compare the LDP solenoid activity with the monitor
sequence in Figure 6. If the PCM detects a problem
that could set a DTC, the testing is halted and LDP
solenoid activity will stop. As each section of the test
begins, it indicates that the previous section passed
successfully. By watching to see which tests complete,
you can see if any conditions are present that the
PCM considers abnormal.
For example, if the LDP solenoid is energized for
the test cycles to test for blockage (P1486), it means
that the LDP has already passed its test for P1494.
Then, if the PCM detects a possible blockage, it will
25 - 34 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2190 of 2199

set a temporary fault without turning on the MIL
and continue the leak portion of the test. However,
the PCM will assume that the system is already
pressurized and skip the rapid pump cycles.
Always diagnose leaks, if possible, before discon-
necting connections. Disconnecting connections may
mask a leak condition.
Keep in mind that if the purge solenoid seat is
leaking, it could go undetected since the leak would
end up in the intake manifold. Disconnect the purge
solenoid at the manifold when leak checking. In addi-
tion, a pinched hose fault (P1486) could set if the
purge solenoid does not purge the fuel system prop-
erly (blocked seat). The purge solenoid must vent the
fuel system prior to the LDP system test. If the
purge solenoid cannot properly vent the system the
LDP cannot properly complete the test for P1486 and
this fault can set due to pressure being in the EVAP
system during the test sequence.
Multiple actuation's of the DRB IIItLeak Detec-
tion Pump (LDP) Monitor Test can hide a 0.020 leak
because of excess vapor generation. Additionally, any
source for additional vapor generation can hide a
small leak in the EVAP system. Excess vapor gener-
ation can delay the fall of the LDP diaphragm thus
hiding the small leak. An example of this condition
could be bringing a cold vehicle into a warm shop for
testing or high ambient temperatures.
Fully plugged and partially plugged underhood
vacuum lines have been known to set MIL condi-
tions. P1494 and P0456 can be set for this reason.
Always, thoroughly, check plumbing for pinches or
blockage before condemning components.
TEST EQUIPMENT The Evaporative Emission
Leak Detector (EELD) Miller Special Tool 8404 is
capable of visually detecting leaks in the evaporative
system and will take the place of the ultrasonic leak
detector 6917A. The EELD utilizes shop air and a
smoke generator to visually detect leaks down to
0.020 or smaller. The food grade oil used to make the
smoke includes an UV trace dye that will leave tell-
tale signs of the leak under a black light. This is
helpful when components have to be removed to
determine the exact leak location. For detailed test
instructions, follow the operators manual packaged
with the EELD.
NOTE: Be sure that the PCM has the latest software
update. Reprogram as indicated by any applicable
Technical Service Bulletin. After LDP repairs are
completed, verify the repair by running the DRB IIIT
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) Monitor Test as
described in Technical Service Bulletin 18-12-99.REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is located under
the left quarter panel behind the left/rear wheel (Fig.
16). It is attached to a two-piece support bracket
(Fig. 17). The LDP and LDP filter are replaced (ser-
viced) as one unit.
(1) Remove stone shield behind left/rear wheel
(Fig. 18). Drill out plastic rivets for removal.
(2) Remove 3 LDP mounting bolts (Fig. 19).
(3) Remove support bracket brace bolt (Fig. 17).
(4) Loosen, but do not remove 2 support bracket
nuts at frame rail (Fig. 19).
(5) To separate and lower front section of two-piece
support bracket, remove 3 attaching bolts on bottom
of support bracket (Fig. 17). While lowering support
bracket, disconnect LDP wiring clip (Fig. 20).
(6) Disconnect electrical connector at LDP (Fig.
20).
(7) Carefully remove vapor/vacuum lines at LDP
(Fig. 20).
(8) Remove LDP.
INSTALLATION
The LDP is located in the left quarter panel behind
the left/rear wheel. It is attached to a two-piece sup-
port bracket (Fig. 17). The LDP and LDP filter are
replaced (serviced) as one unit.
(1) Position LDP and carefully install vapor/vac-
uum lines to LDP and LDP filter.The vapor/vac-
uum lines and hoses must be firmly connected.
Fig. 16 LOCATION, LDP / EVAP CANISTER
1 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
2 - EVAP CANISTER
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 35
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)