2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE rain sensor
[x] Cancel search: rain sensorPage 1799 of 2199
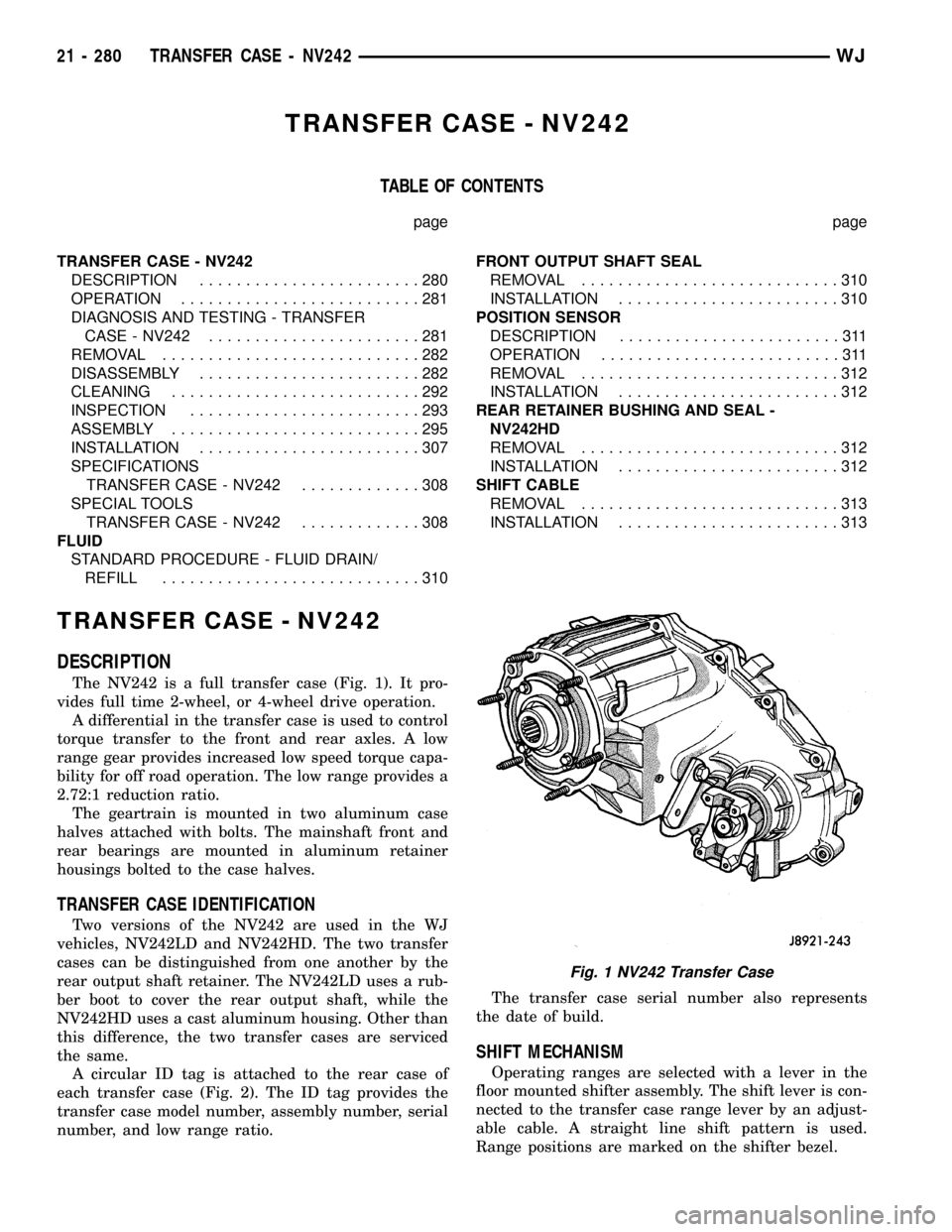
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION........................280
OPERATION..........................281
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV242.......................281
REMOVAL............................282
DISASSEMBLY........................282
CLEANING...........................292
INSPECTION.........................293
ASSEMBLY...........................295
INSTALLATION........................307
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN/
REFILL............................310FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................310
INSTALLATION........................310
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................311
OPERATION..........................311
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
REAR RETAINER BUSHING AND SEAL -
NV242HD
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL............................313
INSTALLATION........................313
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION
The NV242 is a full transfer case (Fig. 1). It pro-
vides full time 2-wheel, or 4-wheel drive operation.
A differential in the transfer case is used to control
torque transfer to the front and rear axles. A low
range gear provides increased low speed torque capa-
bility for off road operation. The low range provides a
2.72:1 reduction ratio.
The geartrain is mounted in two aluminum case
halves attached with bolts. The mainshaft front and
rear bearings are mounted in aluminum retainer
housings bolted to the case halves.
TRANSFER CASE IDENTIFICATION
Two versions of the NV242 are used in the WJ
vehicles, NV242LD and NV242HD. The two transfer
cases can be distinguished from one another by the
rear output shaft retainer. The NV242LD uses a rub-
ber boot to cover the rear output shaft, while the
NV242HD uses a cast aluminum housing. Other than
this difference, the two transfer cases are serviced
the same.
A circular ID tag is attached to the rear case of
each transfer case (Fig. 2). The ID tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a lever in the
floor mounted shifter assembly. The shift lever is con-
nected to the transfer case range lever by an adjust-
able cable. A straight line shift pattern is used.
Range positions are marked on the shifter bezel.
Fig. 1 NV242 Transfer Case
21 - 280 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
Page 1801 of 2199

REMOVAL
(1) Shift transfer case into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove transfer case drain plug and drain
transfer case lubricant.
(4) Mark front and rear propeller shaft yokes for
alignment reference.
(5) Support transmission with jack stand.
(6) Remove rear crossmember and skid plate, if
equipped (Fig. 3).
(7) Disconnect front/rear propeller shafts at trans-
fer case. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIV-
ELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(8) Disconnect transfer case cable from range
lever.
(9) Disconnect transfer case vent hose (Fig. 4) and
transfer case position sensor.
(10) Support transfer case with transmission jack.
(11) Secure transfer case to jack with chains.
(12) Remove nuts attaching transfer case to trans-
mission.(13) Pull transfer case and jack rearward to disen-
gage transfer case.
(14) Remove transfer case from under vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
REAR RETAINER - NV242LD
(1) Remove output shaft boot. Spread band clamp
that secures boot on slinger with a suitable awl.
Then slide boot off shaft (Fig. 5).
Fig. 3 Crossmember Removal
1 - CROSSMEMBER
2 - REAR TRANSMISSION MOUNT
Fig. 4 Transfer Case Mounting
1 - NV242 TRANSFER CASE
Fig. 5 Output Boot - Typical
1 - SLINGER
2 - BOOT
3-AWL
4 - TRANSFER CASE
21 - 282 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1830 of 2199
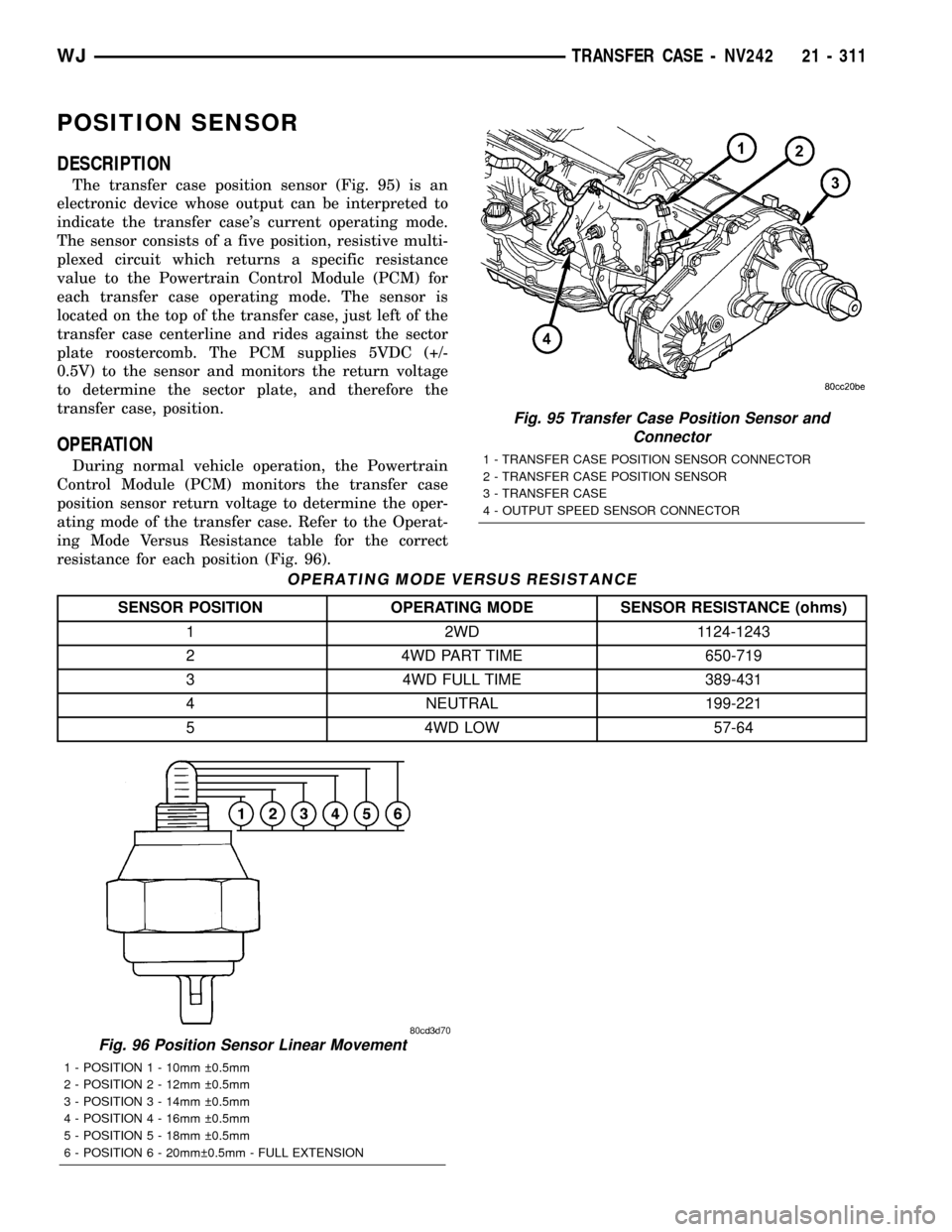
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transfer case position sensor (Fig. 95) is an
electronic device whose output can be interpreted to
indicate the transfer case's current operating mode.
The sensor consists of a five position, resistive multi-
plexed circuit which returns a specific resistance
value to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) for
each transfer case operating mode. The sensor is
located on the top of the transfer case, just left of the
transfer case centerline and rides against the sector
plate roostercomb. The PCM supplies 5VDC (+/-
0.5V) to the sensor and monitors the return voltage
to determine the sector plate, and therefore the
transfer case, position.
OPERATION
During normal vehicle operation, the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) monitors the transfer case
position sensor return voltage to determine the oper-
ating mode of the transfer case. Refer to the Operat-
ing Mode Versus Resistance table for the correct
resistance for each position (Fig. 96).
OPERATING MODE VERSUS RESISTANCE
SENSOR POSITION OPERATING MODE SENSOR RESISTANCE (ohms)
1 2WD 1124-1243
2 4WD PART TIME 650-719
3 4WD FULL TIME 389-431
4 NEUTRAL 199-221
5 4WD LOW 57-64
Fig. 96 Position Sensor Linear Movement
1 - POSITION 1 - 10mm 0.5mm
2 - POSITION 2 - 12mm 0.5mm
3 - POSITION 3 - 14mm 0.5mm
4 - POSITION 4 - 16mm 0.5mm
5 - POSITION 5 - 18mm 0.5mm
6 - POSITION 6 - 20mm 0.5mm - FULL EXTENSION
Fig. 95 Transfer Case Position Sensor and
Connector
1 - TRANSFER CASE POSITION SENSOR CONNECTOR
2 - TRANSFER CASE POSITION SENSOR
3 - TRANSFER CASE
4 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 311
Page 2094 of 2199

open circuit to the fuse in the junction block as
required.
(5) The coil ground terminal cavity (85) is switched
to ground through the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). There should be continuity between this cav-
ity and the A/C compressor clutch relay control cir-
cuit cavity of the PCM wire harness connector C
(gray) at all times. If not OK, repair the open circuit
as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 11).
(3) Refer to the label on the PDC for compressor
clutch relay identification and location.
(4) Unplug the compressor clutch relay from the
PDC.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the compressor clutch relay by aligning
the relay terminals with the cavities in the PDC and
pushing the relay firmly into place.
(2) Install the PDC cover.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
(4) Test the relay operation.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
The manual temperature control HVAC system
uses a combination of electrical, and vacuum con-trols. The Automatic Zone Control (AZC) HVAC sys-
tem uses only electrical controls. These controls
provide the vehicle operator with a number of setting
options to help control the climate and comfort
within the vehicle. Refer to the owner's manual in
the vehicle glove box for more information on the
suggested operation and use of these controls.
Both a/c heater control panels are located on the
instrument panel inboard of the steering column and
below the radio (Fig. 12). Both control panels contain
rotary-type temperature control knob(s), a rotary-
type mode control switch knob, a rotary-type blower
motor speed switch knob and an air conditioning
compressor push button switch. The rear window
defogger push button switch is also located on a/c
heater control panel. The AZC control panel also fea-
tures a recirculation push button switch and a vac-
uum fluorescent display area.
OPERATION
The AZC control module uses infrared sensing
technology to control occupant comfort levels, not the
actual passenger compartment air temperature. Dual
infrared sensors mounted in the face of the control
unit independently measure the surface temperature
to maintain customer-perceived comfort temperature
under changing conditions. Dual Zone temperature
control provides wide side-to-side variation in comfort
temperature to exceed the needs of either front seat
occupant. This sensing system replaces interior air
temperature and solar sensors used to approximate
direct sensing control through complex control pro-
grams.
Fig. 11 POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
2 - NEGATIVE CABLE
3 - POSITIVE CABLE
4 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
Fig. 12 A/C HEATER CONTROL PANELS
WJCONTROLS 24 - 17
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
Page 2102 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Plug the wire harness and/or vacuum harness
connectors into the back of the a/c heater control.
(2) Position the a/c heater control in the instru-
ment panel and secure it with 4 screws. Tighten the
screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Reinstall the center upper, and center lower
bezels onto the instrument panel. Refer to Instru-
ment Panel System for the procedures.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
DESCRIPTION
The A/C pressure transducer is installed on a fit-
ting located on the refrigerant discharge line near
the condenser. An internally threaded hex fitting on
the transducer connects it to the externally threaded
Schrader-type fitting on the discharge line. A rubber
O-ring seals the connection between the transducer
and the discharge line fitting. Three terminals within
a molded plastic connector receptacle on the top of
the transducer connect it to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem through a take out and connector of the head-
lamp and dash wire harness.
The A/C pressure transducer cannot be adjusted or
repaired and if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The A/C pressure transducer monitors the pres-
sures in the high side of the refrigerant system
through its connection to a fitting on the discharge
line. The transducer will change its internal resis-
tance in response to the pressures it monitors. The
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) provides a five
volt reference signal and a sensor ground to the
transducer, then monitors the output voltage of the
transducer on a sensor return circuit to determine
refrigerant pressure. The PCM is preporgrammed to
respond to this and other sensor inputs by controlling
the operation of the air conditioning compressor
clutch and the radiator cooling fan to help optimize
air conditioning system performance and to protect
the system components from damage. The A/C pres-
sure transducer input to the PCM will also prevent
the air conditioning compressor clutch from engaging
when the ambient temperatures are below about
0.556É C (33É F) due to the pressure/temperature
relationship of the refrigerant. The Schrader-type
valve in the liquid line fitting permits the A/C pres-
sure transducer to be removed or installed without
distrubing the refrigerant in the system. The A/C
pressure transducer is diagnosed using the DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation.
Fig. 13 A/C HEATER CONTROL REMOVE/INSTALL
1 - MOUNTING SCREW TABS
Fig. 14 A/C HEATER CONTROL CONNECTIONS
1 - MODE SWITCH
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
3 - VACUUM HARNESS
WJCONTROLS 24 - 25
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2103 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
The A/C pressure transducer is tested using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information. Before testing the A/C pressure
transducer, be certain that the transducer wire har-
ness connection is clean of corrosion and properly
connected. For the air conditioning system to operate,
an A/C pressure transducer voltage reading between0.7 and 4.56 volts is required. Voltage outside this
range indicate a low or high refrigerant system pres-
sure condition to the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM is programmed to respond to a low
or high refrigerant system pressure by suppressing
operation of the compressor. Refer to the A/C Pres-
sure Transducer Voltage table for the possible condi-
tion indicated by the transducer voltage readings.
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER VOLTAGE
VOLTAGE POSSIBLE INDICATION
0.0 1. NO SENSOR SUPPLY VOLTAGE FROM PCM.
2. SHORTED SENSOR CIRCUIT.
3. FAULTY TRANSDUCER
0.150 TO 0.450 1. AMBIENT TEMPERATURE BELOW 10É c (50É F).
2. LOW REFRIGERANT SYSTEM PRESSURE.
0.451 TO 4.519 1. NORMAL REFRIGERANT SYSTEM PRESSURE.
4.520 TO 4.850 1. HIGH REFRIGERANT SYSTEM PRESSURE.
5.0 1. OPEN SENSOR CIRCUIT.
2. FAULTY TRANSDUCER.
REMOVAL
WARNING: Transducer can be removed without
recoverying the system, but some loss of refriger-
ant can be expected(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) and (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION).
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Disconnect the headlamp and dash wire har-
ness connector for the A/C pressure transducer from
the transducer connector receptacle.
(3) Using an open end wrench, unscrew the A/C
pressure transducer from the fitting on the discharge
line.
(4) Remove the seal from the A/C pressure trans-
ducer fitting and discard.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate a new O-ring seal with clean refrig-
erant oil and install it on the A/C pressure trans-
ducer fitting.
(2) Using an open end wrench, install and tighten
the A/C pressure transducer onto the fitting on the
discharge line.
(3) Reconnect the headlamp and dash wire harness
connector for the A/C pressure transducer to the
transducer connector receptacle.(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
BLOWER MOTOR
CONTROLLER
DESCRIPTION
Models equipped with the optional Automatic Zone
Control (AZC) system have a blower motor controller.
The controller allows the selection of almost infi-
nitely variable blower motor speeds. The controller is
mounted to the HVAC housing, under the instrument
panel and just inboard of the blower motor, in the
same location used for the blower motor resistor on
manual temperature control systems. It can be
accessed without removing any other components.
OPERATION
The blower motor controller output to the blower
motor can be adjusted by the blower motor speed
switch knob on the AZC A/C Heater control panel, or
it can be adjusted automatically by the logic circuitry
and programming of the AZC control module. In
either case, the AZC control module sends the correct
pulse width modulated signal to the blower motor
controller to obtain the selected or programmed
blower motor speed.
The blower motor controller cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
24 - 26 CONTROLSWJ
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER (Continued)
Page 2156 of 2199

EMISSIONS CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM.............................1
DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST
MODE...............................2
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE...............................2
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES..............................2DESCRIPTION - TASK MANAGER.........17
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED SYSTEMS . . . 17
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION........19
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS . . 19
DESCRIPTION - NON-MONITORED
CIRCUITS...........................20
DESCRIPTION - HIGH AND LOW LIMITS . . . 20
DESCRIPTION - LOAD VALUE...........20
OPERATION - TASK MANAGER............21
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS................24
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
many different circuits in the fuel injection, ignition,
emission and engine systems. If the PCM senses a prob-
lem with a monitored circuit often enough to indicate an
actual problem, it stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) in the PCM's memory. If the code applies to a
non-emissions related component or system, and the
problem is repaired or ceases to exist, the PCM cancels
the code after 40 warm-up cycles. Diagnostic trouble
codes that affect vehicle emissions illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator (check engine) Lamp. Refer to Mal-
function Indicator Lamp in this section.
Certain criteria must be met before the PCM
stores a DTC in memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine RPM, engine temperature,
and/or input voltage to the PCM.
The PCM might not store a DTC for a monitored cir-
cuit even though a malfunction has occurred. This may
happen because one of the DTC criteria for the circuit
has not been met.For example
,assume the diagnostic
trouble code criteria requires the PCM to monitor the
circuit only when the engine operates between 750 and
2000 RPM. Suppose the sensor's output circuit shorts to
ground when engine operates above 2400 RPM (result-
ing in 0 volt input to the PCM). Because the condition
happens at an engine speed above the maximum thresh-
old (2000 rpm), the PCM will not store a DTC.
There are several operating conditions for which
the PCM monitors and sets DTC's. Refer to Moni-
tored Systems, Components, and Non-Monitored Cir-
cuits in this section.Technicians must retrieve stored DTC's by connect-
ing the DRB scan tool (or an equivalent scan tool) to
the 16±way data link connector (Fig. 1).
NOTE: Various diagnostic procedures may actually
cause a diagnostic monitor to set a DTC. For
instance, pulling a spark plug wire to perform a
spark test may set the misfire code. When a repair
is completed and verified, connect the DRB scan
tool to the 16±way data link connector to erase all
DTC's and extinguish the MIL (check engine lamp).Fig. 1 Data Link (Diagnostic) Connector Location
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER/LEFT EDGE
2 - DATA LINK CONNECTOR
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 1
Page 2157 of 2199

DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. Connect
the DRB scan tool to the data link connector and
access the state display screen. Then access either
State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display
Sensors.
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly. Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector and access the Actuators screen.
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0030 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0031 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0032 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0036 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0037 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0038 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0043 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0044 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0051 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0052 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)