2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Emissions
[x] Cancel search: EmissionsPage 439 of 2199

instrument cluster logic circuit, and that logic will
only allow this indicator to operate when the instru-
ment cluster receives a battery current input on the
fused ignition switch output (run-start) circuit.
Therefore, the indicator will always be off when the
ignition switch is in any position except On or Start.
The bulb only illuminates when it is provided a path
to ground by the instrument cluster transistor. The
instrument cluster will turn on the MIL for the fol-
lowing reasons:
²Bulb Test- Each time the ignition switch is
turned to the On position the MIL is illuminated for
about three seconds as a bulb test.
²MIL Lamp-On Message- Each time the clus-
ter receives a MIL lamp-on message from the PCM,
the indicator will be illuminated. The indicator can
be flashed on and off, or illuminated solid, as dic-
tated by the PCM message. For some DTC's, if a
problem does not recur, the PCM will send a MIL
lamp-off message automatically. Other DTC's may
require that a fault be repaired and the PCM be
reset before a MIL lamp-off message will be sent. For
more information on the PCM and the DTC set and
reset parameters, (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CON-
TROL - OPERATION).
²Communication Error- If the cluster receives
no MIL lamp-on or lamp-off messages from the PCM
for twenty consecutive seconds, the MIL is illumi-
nated by the instrument cluster. The indicator
remains controlled and illuminated by the cluster
until a valid MIL lamp-on or lamp-off message is
received from the PCM.
²Actuator Test- Each time the cluster is put
through the actuator test, the MIL will be turned on
for the duration of the test to confirm the functional-
ity of the bulb and the cluster control circuitry.
The PCM continually monitors each of the many
fuel and emissions system circuits and sensors to
decide whether the system is in good operating con-
dition. The PCM then sends the proper MIL lamp-on
or lamp-off messages to the instrument cluster. If the
MIL fails to light during the bulb test, replace the
bulb with a known good unit. For further diagnosis of
the MIL or the instrument cluster circuitry that con-
trols the indicator, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IN-
STRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). If the instrument cluster turns on the
MIL after the bulb test, it may indicate that a mal-
function has occurred and that the fuel and emis-
sions system may require service. For proper
diagnosis of the fuel and emissions systems, the
PCM, the PCI data bus, or the electronic message
inputs to the instrument cluster that control the
MIL, a DRBIIItscan tool is required. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.ODOMETER
DESCRIPTION
An odometer and trip odometer are standard
equipment in all instrument clusters. The odometer
and trip odometer information are displayed in a
common electronic, blue-green Vacuum-Fluorescent
Display (VFD), which is located in the lower edge of
the speedometer dial face in the instrument cluster
and, when illuminated, is visible through a small
window cutout in the gauge overlay. However, the
odometer and trip odometer information are not dis-
played simultaneously. The trip odometer reset
switch on the instrument cluster electronic circuit
board toggles the display between odometer and trip
odometer modes by depressing the odometer/trip
odometer switch button that extends through the
lower edge of the cluster lens to the right of the
speedometer.
All odometer and trip odometer distance informa-
tion is stored in the instrument cluster memory. This
distance information can be increased when the
proper inputs are provided to the instrument cluster,
but the distance information cannot be decreased.
The odometer can display values up to 999,999 kilo-
meters (999,999 miles). The odometer will not roll
over, but will latch at the maximum value. The trip
odometer can display values up to 999.9 kilometers
(999.9 miles) before it rolls over to zero. The odome-
ter display does not have a decimal point and will
not show values less than a full unit (kilometer or
mile), the trip odometer display does have a decimal
point and will show tenths of a unit (kilometer or
mile).
The unit of measure for the odometer and trip
odometer display is not shown in the VFD. The unit
of measure for the odometer/trip odometer is selected
at the time that the instrument cluster is manufac-
tured, and cannot be changed. If the instrument clus-
ter has a kilometers-per-hour primary speedometer
scale, the odometer/trip odometer registers kilome-
ters; and, if the cluster features a miles-per-hour pri-
mary speedometer scale, the odometer/trip odometer
registers miles.
During daylight hours (exterior lamps Off) the
VFD is illuminated at full brightness for clear visibil-
ity. At night (exterior lamps are On) the instrument
cluster converts an electronic dimming level message
received from the Body Control Module (BCM) over
the Programmable Communications Interface (PCI)
data bus to a digital dimming level signal for control-
ling the lighting level of the VFD. However, a
ªParadeº mode position of the panel lamps dimmer
control ring on the control stalk of the left (lighting)
multi-function switch allows the VFD to be illumi-
8J - 24 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERWJ
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL) (Continued)
Page 1250 of 2199
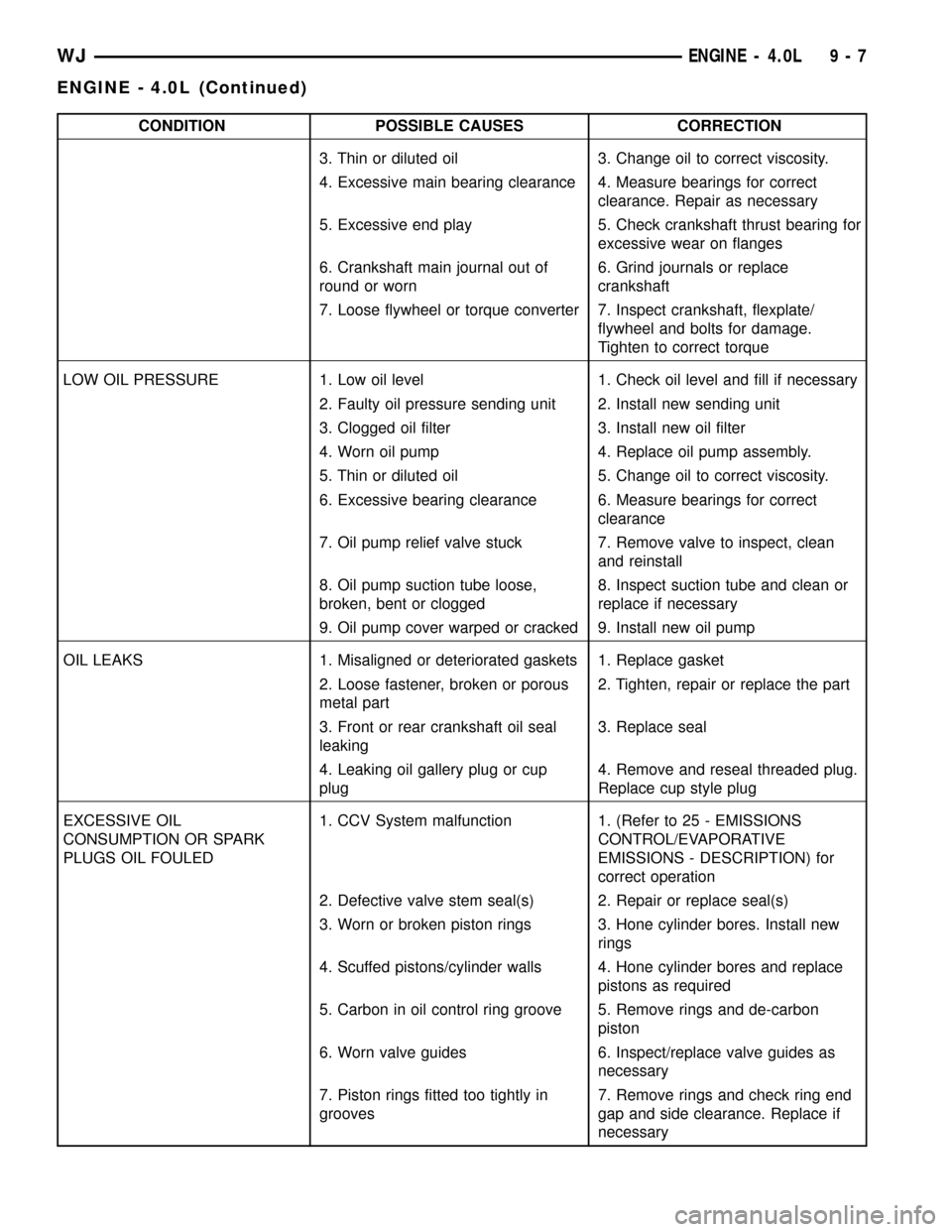
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
3. Thin or diluted oil 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Excessive main bearing clearance 4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary
5. Excessive end play 5. Check crankshaft thrust bearing for
excessive wear on flanges
6. Crankshaft main journal out of
round or worn6. Grind journals or replace
crankshaft
7. Loose flywheel or torque converter 7. Inspect crankshaft, flexplate/
flywheel and bolts for damage.
Tighten to correct torque
LOW OIL PRESSURE 1. Low oil level 1. Check oil level and fill if necessary
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit 2. Install new sending unit
3. Clogged oil filter 3. Install new oil filter
4. Worn oil pump 4. Replace oil pump assembly.
5. Thin or diluted oil 5. Change oil to correct viscosity.
6. Excessive bearing clearance 6. Measure bearings for correct
clearance
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck 7. Remove valve to inspect, clean
and reinstall
8. Oil pump suction tube loose,
broken, bent or clogged8. Inspect suction tube and clean or
replace if necessary
9. Oil pump cover warped or cracked 9. Install new oil pump
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated gaskets 1. Replace gasket
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part2. Tighten, repair or replace the part
3. Front or rear crankshaft oil seal
leaking3. Replace seal
4. Leaking oil gallery plug or cup
plug4. Remove and reseal threaded plug.
Replace cup style plug
EXCESSIVE OIL
CONSUMPTION OR SPARK
PLUGS OIL FOULED1. CCV System malfunction 1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS - DESCRIPTION) for
correct operation
2. Defective valve stem seal(s) 2. Repair or replace seal(s)
3. Worn or broken piston rings 3. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings
4. Scuffed pistons/cylinder walls 4. Hone cylinder bores and replace
pistons as required
5. Carbon in oil control ring groove 5. Remove rings and de-carbon
piston
6. Worn valve guides 6. Inspect/replace valve guides as
necessary
7. Piston rings fitted too tightly in
grooves7. Remove rings and check ring end
gap and side clearance. Replace if
necessary
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 7
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1398 of 2199
EXHAUST SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EXHAUST SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION - EXHAUST SYSTEM.........1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EXHAUST
SYSTEM.............................3
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE.............................3
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
4.0L ENGINE..........................4
REMOVAL.............................4
INSPECTION...........................5
INSTALLATION..........................5
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION - CATALYTIC CONVERTER.....6
REMOVAL.............................6
INSPECTION...........................7
INSTALLATION..........................7EXHAUST PIPE - 4.0L
REMOVAL.............................8
INSPECTION...........................8
INSTALLATION..........................8
EXHAUST PIPE - 4.7L
REMOVAL.............................10
INSPECTION..........................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
HEAT SHIELDS
DESCRIPTION.........................12
MUFFLER
DESCRIPTION.........................12
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
TAILPIPE
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
EXHAUST SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION - EXHAUST SYSTEM
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER WORK AROUND OR ATTEMPT
TO SERVICE ANY PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM
UNTIL IT IS COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE
TAKEN WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC
CONVERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CON-
VERTER RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT
PERIOD OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.
CAUTION: Avoid application of rust prevention com-
pounds or undercoating materials to exhaust sys-
tem floor pan heat shields. Light overspray near the
edges is permitted. Application of coating will result
in excessive floor pan temperatures and objection-
able fumes.
The exhaust system uses a single muffler with a
welded tailpipe.The 50 State Emissions vehicles use two mini cat-
alytic converters inline with the exhaust pipe below
the exhaust manifolds.
The exhaust manifolds are equipped with ball
flange outlets to assure a tight seal and strain free
connections.
The exhaust system must be properly aligned to
prevent stress, leakage and body contact. If the sys-
tem contacts any body panel, it may amplify objec-
tionable noises originating from the engine or body.
When inspecting an exhaust system, critically
inspect for cracked or loose joints, stripped screw or
bolt threads, corrosion damage and worn, cracked or
broken hangers. Replace all components that are
badly corroded or damaged. DO NOT attempt to
repair.
When replacement is required, use original equip-
ment parts (or their equivalent). This will assure
proper alignment and provide acceptable exhaust
noise levels.
The basic exhaust system consists of exhaust man-
ifold(s), exhaust pipe with oxygen sensors, catalytic
converter(s), heat shield(s), muffler and tailpipe (Fig.
1) and (Fig. 2).
WJEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 1
Page 1401 of 2199
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION - CATALYTIC CONVERTER 4.0L
ENGINE
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER WORK AROUND OR ATTEMPT
TO SERVICE ANY PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM
UNTIL IT IS COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE
TAKEN WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC
CONVERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CON-
VERTER RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT
PERIOD OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove spark plug wires from
plugs or by any other means short out cylinders.
Failure of the catalytic converter can occur due to a
temperature increase caused by unburned fuel
passing through the converter.The stainless steel catalytic converter body is
designed to last the life of the vehicle. Excessive heat
can result in bulging or other distortion, but exces-
sive heat will not be the fault of the converter. If
unburned fuel enters the converter, overheating may
occur. If a converter is heat-damaged, correct the
cause of the damage at the same time the converter
is replaced. Also, inspect all other components of the
exhaust system for heat damage.
Unleaded gasoline must be used to avoid con-
taminating the catalyst core.
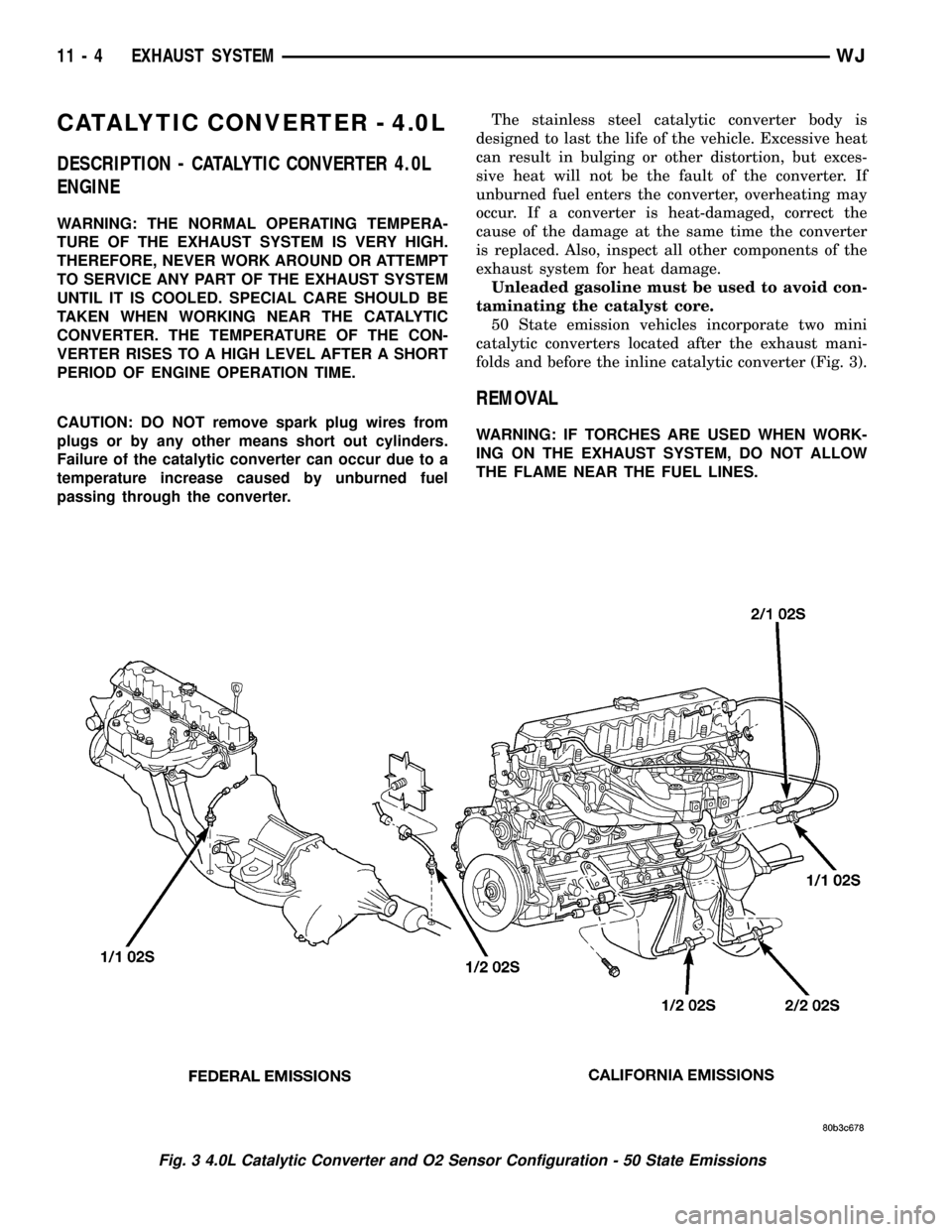
50 State emission vehicles incorporate two mini
catalytic converters located after the exhaust mani-
folds and before the inline catalytic converter (Fig. 3).
REMOVAL
WARNING: IF TORCHES ARE USED WHEN WORK-
ING ON THE EXHAUST SYSTEM, DO NOT ALLOW
THE FLAME NEAR THE FUEL LINES.
Fig. 3 4.0L Catalytic Converter and O2 Sensor Configuration - 50 State Emissions
11 - 4 EXHAUST SYSTEMWJ
Page 1403 of 2199
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER WORK AROUND OR ATTEMPT
TO SERVICE ANY PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM
UNTIL IT IS COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE
TAKEN WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC
CONVERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CON-
VERTER RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT
PERIOD OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove spark plug wires from
plugs or by any other means short out cylinders.
Failure of the catalytic converter can occur due to a
temperature increase caused by unburned fuel
passing through the converter.The stainless steel catalytic converter body is
designed to last the life of the vehicle. Excessive heat
can result in bulging or other distortion, but exces-
sive heat will not be the fault of the converter. If
unburned fuel enters the converter, overheating may
occur. If a converter is heat-damaged, correct the
cause of the damage at the same time the converter
is replaced. Also, inspect all other components of the
exhaust system for heat damage.
Unleaded gasoline must be used to avoid con-
taminating the catalyst core.
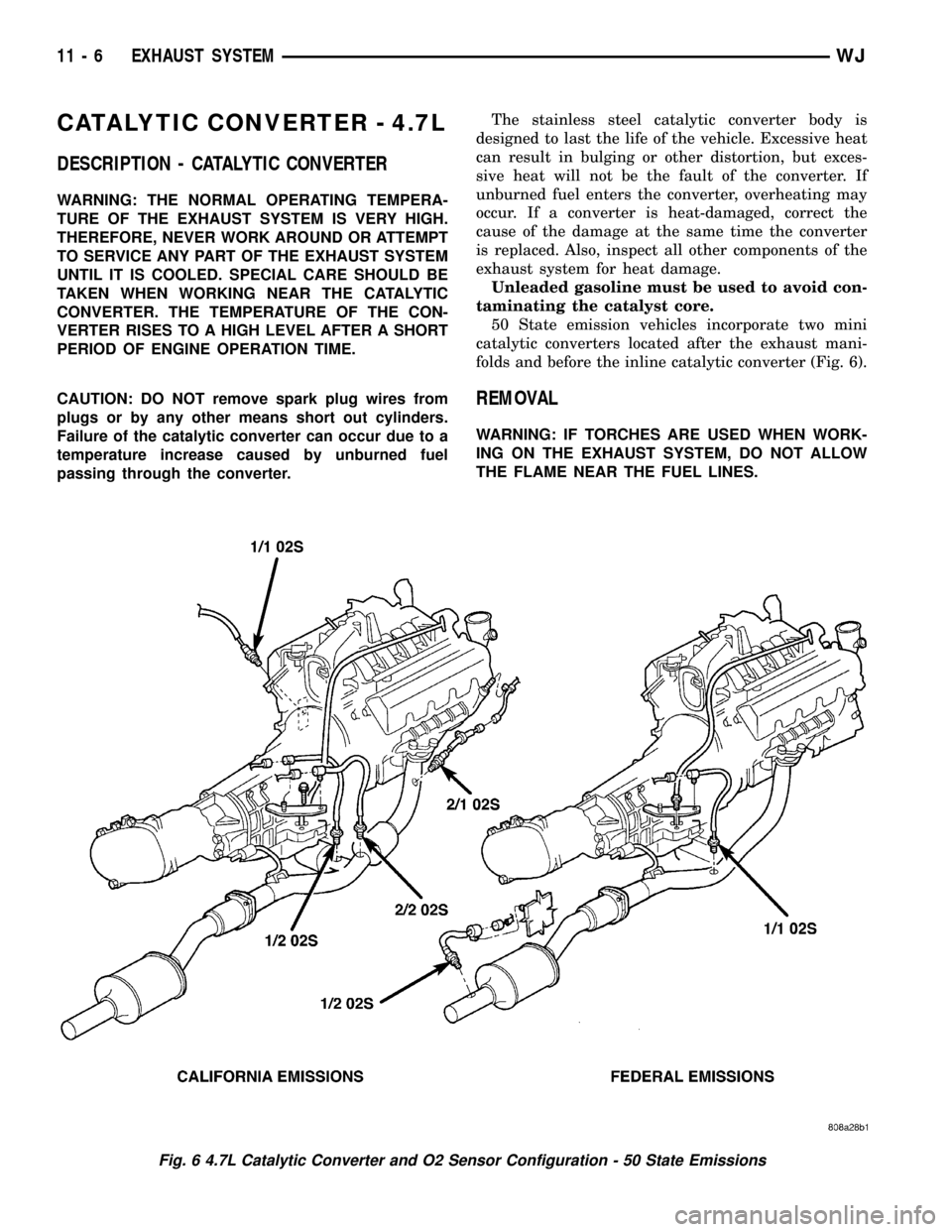
50 State emission vehicles incorporate two mini
catalytic converters located after the exhaust mani-
folds and before the inline catalytic converter (Fig. 6).
REMOVAL
WARNING: IF TORCHES ARE USED WHEN WORK-
ING ON THE EXHAUST SYSTEM, DO NOT ALLOW
THE FLAME NEAR THE FUEL LINES.
Fig. 6 4.7L Catalytic Converter and O2 Sensor Configuration - 50 State Emissions
11 - 6 EXHAUST SYSTEMWJ
Page 1407 of 2199
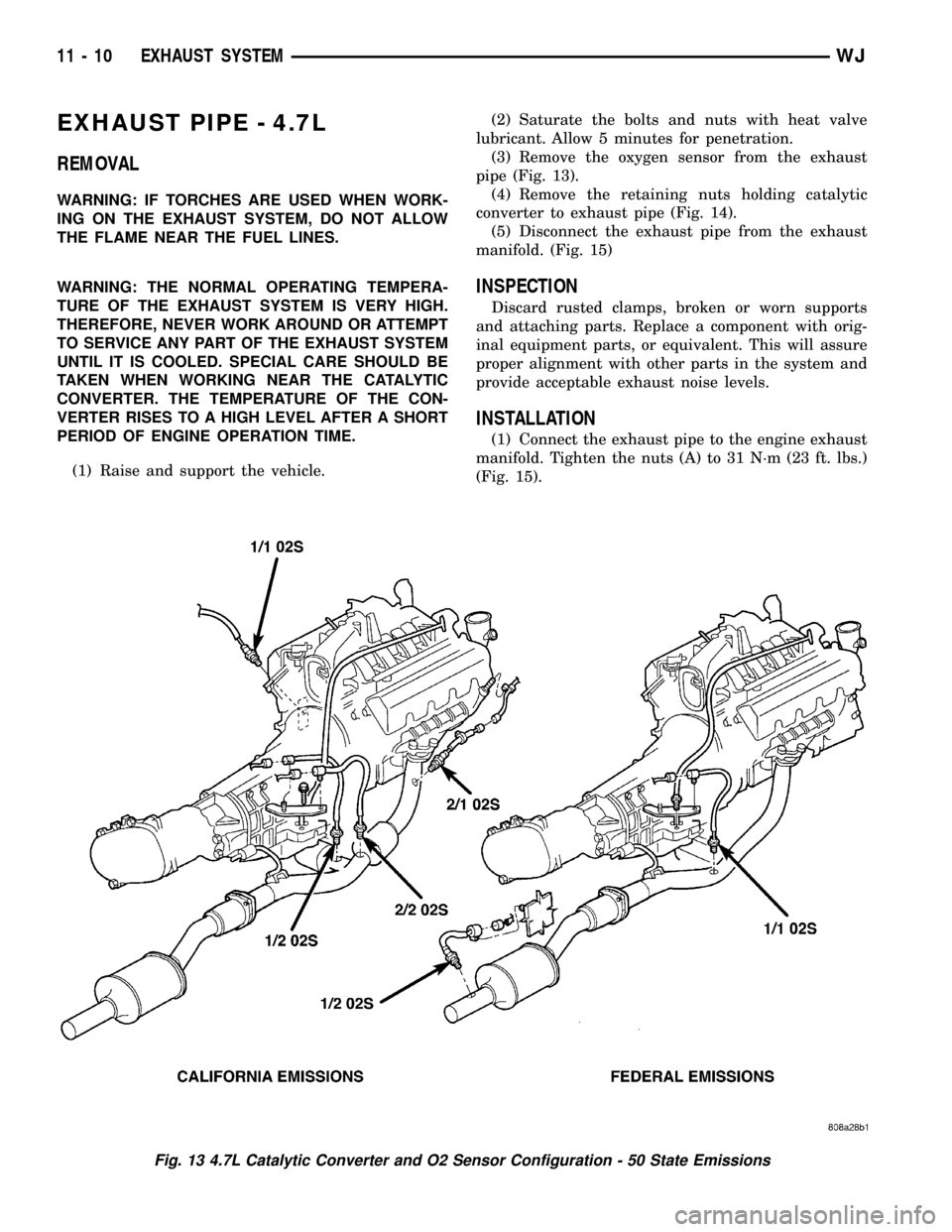
EXHAUST PIPE - 4.7L
REMOVAL
WARNING: IF TORCHES ARE USED WHEN WORK-
ING ON THE EXHAUST SYSTEM, DO NOT ALLOW
THE FLAME NEAR THE FUEL LINES.
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER WORK AROUND OR ATTEMPT
TO SERVICE ANY PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM
UNTIL IT IS COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE
TAKEN WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC
CONVERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CON-
VERTER RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT
PERIOD OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.(2) Saturate the bolts and nuts with heat valve
lubricant. Allow 5 minutes for penetration.
(3) Remove the oxygen sensor from the exhaust
pipe (Fig. 13).
(4) Remove the retaining nuts holding catalytic
converter to exhaust pipe (Fig. 14).
(5) Disconnect the exhaust pipe from the exhaust
manifold. (Fig. 15)
INSPECTION
Discard rusted clamps, broken or worn supports
and attaching parts. Replace a component with orig-
inal equipment parts, or equivalent. This will assure
proper alignment with other parts in the system and
provide acceptable exhaust noise levels.
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect the exhaust pipe to the engine exhaust
manifold. Tighten the nuts (A) to 31 N´m (23 ft. lbs.)
(Fig. 15).
Fig. 13 4.7L Catalytic Converter and O2 Sensor Configuration - 50 State Emissions
11 - 10 EXHAUST SYSTEMWJ
Page 1436 of 2199

(12) Remove first three ignition coils on each bank
(cylinders #1, 3, 5, 2, 4 and 6). Refer to Ignition Coil
Removal/Installation.
(13) Remove 4 fuel rail mounting bolts (Fig. 22).
(14) Gently rock and pullleftside of fuel rail until
fuel injectors just start to clear machined holes in
cylinder head. Gently rock and pullrightside of rail
until injectors just start to clear cylinder head holes.
Repeat this procedure (left/right) until all injectors
have cleared cylinder head holes.
(15) Remove fuel rail (with injectors attached)
from engine.
(16) If fuel injectors are to be removed, refer to
Fuel Injector Removal/Installation.
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The fuel damper is not serviced separately.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF.
THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED BEFORE
SERVICING FUEL RAIL.
(1) Remove fuel tank filler tube cap.
(2) Perform Fuel System Pressure Release Proce-
dure.
(3) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.(4) Remove air tube at top of throttle body. Note:
Some engine/vehicles may require removal of air
cleaner ducts at throttle body.
(5) Disconnect electrical connectors at all 6 fuel
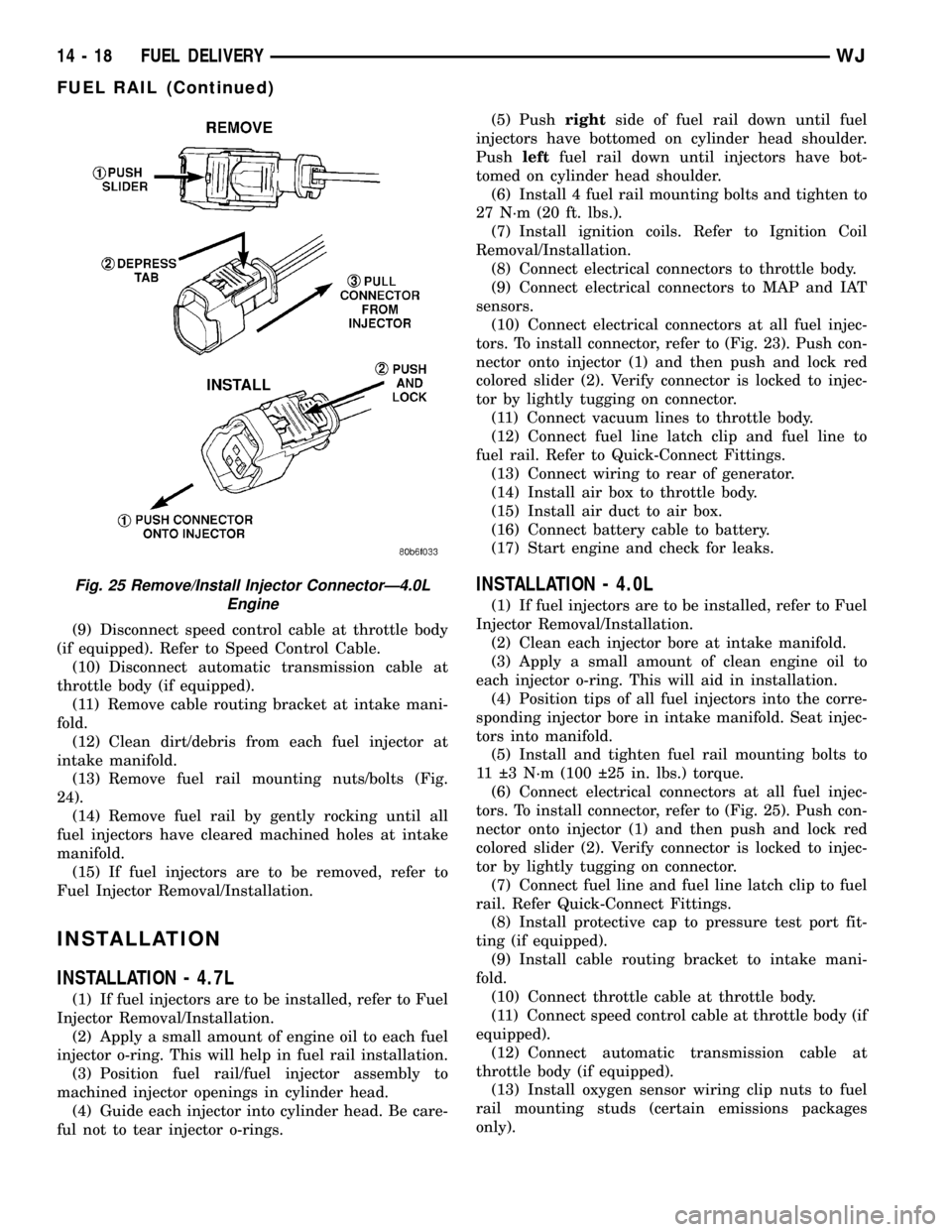
injectors. To remove connector refer to (Fig. 25). Push
red colored slider away from injector (1). While push-
ing slider, depress tab (2) and remove connector (3)
from injector. The factory fuel injection wiring har-
ness is numerically tagged (INJ 1, INJ 2, etc.) for
injector position identification. If harness is not
tagged, note wiring location before removal.
(6) Remove oxygen sensor wiring clip nuts at fuel
rail mounting studs (certain emissions packages
only).
(7) Disconnect fuel supply line latch clip and fuel
line at fuel rail. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(8) Disconnect throttle cable at throttle body. Refer
to Throttle Cable Removal/Installation.
Fig. 23 Remove/Install Injector ConnectorÐ4.7L V-8
Engine
Fig. 24 Fuel Rail MountingÐ4.0L Engine
1 - INJ. #1
2 - INJ. #2
3 - INJ. #3
4 - INJ. #4
5 - INJ. #5
6 - INJ. #6
7 - FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
8 - FUEL DAMPER
9 - PRESSURE TEST PORT CAP
10 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
11 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
WJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 17
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1437 of 2199
(9) Disconnect speed control cable at throttle body
(if equipped). Refer to Speed Control Cable.
(10) Disconnect automatic transmission cable at
throttle body (if equipped).
(11) Remove cable routing bracket at intake mani-
fold.
(12) Clean dirt/debris from each fuel injector at
intake manifold.
(13) Remove fuel rail mounting nuts/bolts (Fig.
24).
(14) Remove fuel rail by gently rocking until all
fuel injectors have cleared machined holes at intake
manifold.
(15) If fuel injectors are to be removed, refer to
Fuel Injector Removal/Installation.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.7L
(1) If fuel injectors are to be installed, refer to Fuel
Injector Removal/Installation.
(2) Apply a small amount of engine oil to each fuel
injector o-ring. This will help in fuel rail installation.
(3) Position fuel rail/fuel injector assembly to
machined injector openings in cylinder head.
(4) Guide each injector into cylinder head. Be care-
ful not to tear injector o-rings.(5) Pushrightside of fuel rail down until fuel
injectors have bottomed on cylinder head shoulder.
Pushleftfuel rail down until injectors have bot-
tomed on cylinder head shoulder.
(6) Install 4 fuel rail mounting bolts and tighten to
27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install ignition coils. Refer to Ignition Coil
Removal/Installation.
(8) Connect electrical connectors to throttle body.
(9) Connect electrical connectors to MAP and IAT
sensors.
(10) Connect electrical connectors at all fuel injec-
tors. To install connector, refer to (Fig. 23). Push con-
nector onto injector (1) and then push and lock red
colored slider (2). Verify connector is locked to injec-
tor by lightly tugging on connector.
(11) Connect vacuum lines to throttle body.
(12) Connect fuel line latch clip and fuel line to
fuel rail. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(13) Connect wiring to rear of generator.
(14) Install air box to throttle body.
(15) Install air duct to air box.
(16) Connect battery cable to battery.
(17) Start engine and check for leaks.
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
(1) If fuel injectors are to be installed, refer to Fuel
Injector Removal/Installation.
(2) Clean each injector bore at intake manifold.
(3) Apply a small amount of clean engine oil to
each injector o-ring. This will aid in installation.
(4) Position tips of all fuel injectors into the corre-
sponding injector bore in intake manifold. Seat injec-
tors into manifold.
(5) Install and tighten fuel rail mounting bolts to
11 3 N´m (100 25 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect electrical connectors at all fuel injec-
tors. To install connector, refer to (Fig. 25). Push con-
nector onto injector (1) and then push and lock red
colored slider (2). Verify connector is locked to injec-
tor by lightly tugging on connector.
(7) Connect fuel line and fuel line latch clip to fuel
rail. Refer Quick-Connect Fittings.
(8) Install protective cap to pressure test port fit-
ting (if equipped).
(9) Install cable routing bracket to intake mani-
fold.
(10) Connect throttle cable at throttle body.
(11) Connect speed control cable at throttle body (if
equipped).
(12) Connect automatic transmission cable at
throttle body (if equipped).
(13) Install oxygen sensor wiring clip nuts to fuel
rail mounting studs (certain emissions packages
only).
Fig. 25 Remove/Install Injector ConnectorÐ4.0L
Engine
14 - 18 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
FUEL RAIL (Continued)