2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE power amp
[x] Cancel search: power ampPage 1423 of 2199
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE
Use following procedure if the fuel injector
rail is, or is not equipped with a fuel pressure
test port.
(1) Remove fuel fill cap.
(2) Remove fuel pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.
(3) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(4) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(5) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
CAUTION: Steps 1, 2, 3 and 4 must be performed to
relieve high pressure fuel from within fuel rail. Do
not attempt to use following steps to relieve this
pressure as excessive fuel will be forced into a cyl-
inder chamber.
(6) Unplug connector from any fuel injector.
(7) Attach one end of a jumper wire with alligator
clips (18 gauge or smaller) to either injector terminal.(8) Connect other end of jumper wire to positive
side of battery.
(9) Connect one end of a second jumper wire to
remaining injector terminal.
CAUTION: Powering an injector for more than a few
seconds will permanently damage the injector.
(10) Momentarily touch other end of jumper wire
to negative terminal of battery for no more than a
few seconds.
(11) Place a rag or towel below fuel line quick-con-
nect fitting at fuel rail.
(12) Disconnect quick-connect fitting at fuel rail.
Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(13) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(14) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRBtscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
339 kPa 34 kPa (49.2 psi 5 psi).
TORQUE - FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Accelerator Pedal Bracket Mounting Nuts
(without adjustable pedals)12 2 - 105 20
Fuel Filter/Fuel Press. Reg. Bolts 3 - 26
Fuel Hose Clamps 3 - 26
Fuel Injector Rail Mounting Bolts -4.0L Engine 11 - 100
Fuel Injector Rail Mounting Bolts -4.7L V-8
Engine11 - 100
Fuel Pump Module Locknut 74 55 -
Fuel Tank Filler Tube-to-Body Mounting Bolts 2 - 15
Fuel Tank-to-Body Mounting Bolts 88 65 -
Fuel Tank Support Bracket Bolts (large brackets) 88 65 -
Fuel Tank Support Bracket Bolts (small bracket) 5 - 45
Fuel Tank Support Bracket Nuts (large brackets) 61 45 -
Fuel Tank Heat Shield Nuts (shield-to-tank) 9 - 85
Fuel Tank Heat Shield Nuts (shield-to-body) 3 - 25
14 - 4 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1427 of 2199

(1) Remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Removal/
Installation.(2) Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
(3) Remove electrical wire connector at sending
unit terminals.
(4) Press upward on release tab (Fig. 7) to remove
sending unit from pump module.
INSTALLATION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) and
float assembly is located on the side of fuel pump
module (Fig. 6). The fuel pump module is located
within the fuel tank.
(1) Position sending unit to pump module and
snap into place.
(2) Connect electrical connector to terminals.
(3) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
(4) Install fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Removal/
Installation.
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION
Also refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP.
The lines/tubes/hoses used on fuel injected vehicles
are of a special construction. This is due to the
higher fuel pressures and the possibility of contami-
nated fuel in this system. If it is necessary to replace
these lines/tubes/hoses, only those marked EFM/EFI
may be used.
If equipped:The hose clamps used to secure rub-
ber hoses on fuel injected vehicles are of a special
rolled edge construction. This construction is used to
prevent the edge of the clamp from cutting into the
hose. Only these rolled edge type clamps may be
used in this system. All other types of clamps may
cut into the hoses and cause high-pressure fuel leaks.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located inside of the fuel
pump module. A 12 volt, permanent magnet, electric
motor powers the fuel pump. The electric fuel pump
is not a separate, serviceable component.
Fig. 6 Fuel Gauge Sending Unit Location
1 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
2 - FUEL GAUGE FLOAT
3 - ELECTRIC FUEL PUMP
4 - INLET FILTER
5 - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
6 - PIGTAIL HARNESS
Fig. 7 Fuel Gauge Sending Unit Release Tab
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
3 - RELEASE TAB
4 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
14 - 8 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1429 of 2199

(5) Connect (-) and (+) test cable leads into LCS
adapter receptacles. Use10 amp (10A +)receptacle
and common (-) receptacles.
(6) Gain access to MAIN MENU on DRB screen.
(7) Press DVOM button on DRB.
(8) Using left/right arrow keys, highlight CHAN-
NEL 1 function on DRB screen.
(9) Press ENTER three times.
(10) Using up/down arrow keys, highlight RANGE
on DRB screen (screen will default to 2 amp scale).
(11) Press ENTER to change 2 amp scale to 10
amp scale.This step must be done to prevent
damage to DRB scan tool or LCS adapter
(blown fuse).
(12) Remove cover from Power Distribution Center
(PDC).
(13) Remove fuel pump relay from PDC. Refer to
label on PDC cover for relay location.
WARNING: BEFORE PROCEEDING TO NEXT STEP,
NOTE THE FUEL PUMP WILL BE ACTIVATED AND
SYSTEM PRESSURE WILL BE PRESENT. THIS WILL
OCCUR AFTER CONNECTING TEST LEADS FROM
LCS ADAPTER INTO FUEL PUMP RELAY CAVITIES.
THE FUEL PUMP WILL OPERATE EVEN WITH IGNI-
TION KEY IN OFF POSITION. BEFORE ATTACHING
TEST LEADS, BE SURE ALL FUEL LINES AND
FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS ARE CONNECTED.
CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the vehi-
cle electrical system and LCS adapter, the test
leads must be connected into relay cavities exactly
as shown in following steps.
Depending upon vehicle model, year or engine con-
figuration, three different types of relays may be
used: Type-1, type-2 and type±3.
(14) If equipped withtype±1 relay(Fig. 9), attach
test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay cavities
number 30 and 87. For location of these cavities,
refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay (Fig. 9).
(15) If equipped withtype±2 relay(Fig. 10),
attach test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay
cavities number 30 and 87. For location of these cav-
ities, refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay
(Fig. 10).
(16) If equipped withtype±3 relay(Fig. 11),
attach test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay
cavities number 3 and 5. For location of these cavi-
ties, refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay
(Fig. 11).
(17) When LCS adapter test leads are attached
into relay cavities, fuel pumpwill be activated.
Determine fuel pump amperage on DRB screen.
Amperage should be below 10.0 amps. If amperage is
below 10.0 amps, and specifications for the FuelPump Pressure, Fuel Pump Capacity and Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down tests were met, the fuel pump mod-
ule is OK.
(18) If amperage is more than 10.0 amps, replace
fuel pump module assembly. The electric fuel pump
is not serviced separately.
Fig. 9 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 1
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 10 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 2
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
14 - 10 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
FUEL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1430 of 2199

(19) Disconnect test leads from relay cavities
immediately after testing.
FUEL PUMP PRESSURE TEST
Use this test in conjunction with other fuel system
tests. Refer to the Fuel Pump Capacity Test, Fuel
Pressure Leak Down Test and Fuel Pump Amperage
Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
The fuel system is equipped with a combination
fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pressure
regulator is not controlled by engine vacuum.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF. BEFORE DISCONNECTING FUEL LINE AT
FUEL RAIL, THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
RELEASE PROCEDURE.
(1) Remove pressure test port cap at fuel rail test
port (Fig. 12) or (Fig. 13) . Connect 0±414 kPa (0-60
psi) fuel pressure gauge (from gauge set 5069) to test
port pressure fitting on fuel rail (Fig. 14) .The DRB
III Scan Tool along with the PEP module, the
500 psi pressure transducer, and the transduc-
er-to-test port adapter may also be used in
place of the fuel pressure gauge.
(2) Start and warm engine and note pressure
gauge reading. The DRB scan tool may also be used
to power fuel pump. Fuel pressure should be 339 kPa
34 kPa (49.2 psi 5 psi) at idle.
(3) If engine runs, but pressure is below 44.2 psi,
determine if fuel pump or filter/regulator is defective.
Proceed to next step:
(a) Check for a kinked fuel supply line some-
where between fuel rail and fuel pump module.
Fig. 11 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 3
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
1 COIL BATTERY
2 COIL GROUND
3 COMMON FEED
4 NORMALLY CLOSED
5 NORMALLY OPEN
Fig. 12 Test Port Cap LocationÐ4.0L Engine
1 - INJ. #1
2 - INJ. #2
3 - INJ. #3
4 - INJ. #4
5 - INJ. #5
6 - INJ. #6
7 - FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
8 - FUEL DAMPER
9 - PRESSURE TEST PORT CAP
10 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
11 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
WJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 11
FUEL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1464 of 2199

The PCM uses the IAC motor to control idle speed
(along with timing) and to reach a desired MAP dur-
ing decel (keep engine from stalling).
The IAC motor has 4 wires with 4 circuits. Two of
the wires are for 12 volts and ground to supply elec-
trical current to the motor windings to operate the
stepper motor in one direction. The other 2 wires are
also for 12 volts and ground to supply electrical cur-
rent to operate the stepper motor in the opposite
direction.
To make the IAC go in the opposite direction, the
PCM just reverses polarity on both windings. If only
1 wire is open, the IAC can only be moved 1 step
(increment) in either direction. To keep the IAC
motor in position when no movement is needed, the
PCM will energize both windings at the same time.
This locks the IAC motor in place.
In the IAC motor system, the PCM will count
every step that the motor is moved. This allows the
PCM to determine the motor pintle position. If the
memory is cleared, the PCM no longer knows the
position of the pintle. So at the first key ON, the
PCM drives the IAC motor closed, regardless of
where it was before. This zeros the counter. From
this point the PCM will back out the IAC motor and
keep track of its position again.
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following:
²Off-idle dashpot (throttle blade will close quickly
but idle speed will not stop quickly)
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
²Power steering load control
The PCM can control polarity of the circuit to con-
trol direction of the stepper motor.
IAC Stepper Motor Program:The PCM is also
equipped with a memory program that records the
number of steps the IAC stepper motor most recently
advanced to during a certain set of parameters. For
example: The PCM was attempting to maintain a
1000 rpm target during a cold start-up cycle. The last
recorded number of steps for that may have been
125. That value would be recorded in the memory
cell so that the next time the PCM recognizes the
identical conditions, the PCM recalls that 125 steps
were required to maintain the target. This program
allows for greater customer satisfaction due to
greater control of engine idle.
Another function of the memory program, which
occurs when the power steering switch (if equipped),
or the A/C request circuit, requires that the IAC step-
per motor control engine rpm, is the recording of the
last targeted steps into the memory cell. The PCMcan anticipate A/C compressor loads. This is accom-
plished by delaying compressor operation for approx-
imately 0.5 seconds until the PCM moves the IAC
stepper motor to the recorded steps that were loaded
into the memory cell. Using this program helps elim-
inate idle-quality changes as loads change. Finally,
the PCM incorporates a9No-Load9engine speed lim-
iter of approximately 1800 - 2000 rpm, when it rec-
ognizes that the TPS is indicating an idle signal and
IAC motor cannot maintain engine idle.
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the IAC motor through the PCM.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The IAC motor is located on the throttle body.
(1) Remove air duct and air resonator box at throt-
tle body.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor
(Fig. 40).
(3) Remove two mounting bolts (screws) (Fig. 26).
(4) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
REMOVAL - 4.7L
(1) Remove air duct and air resonator box at throt-
tle body.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor
(Fig. 36).
(3) Remove two mounting bolts (screws) (Fig. 42).
(4) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
Fig. 26 Mounting Bolts (Screws)ÐIAC
1 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
2 - MOUNTING SCREWS
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 45
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1479 of 2199
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
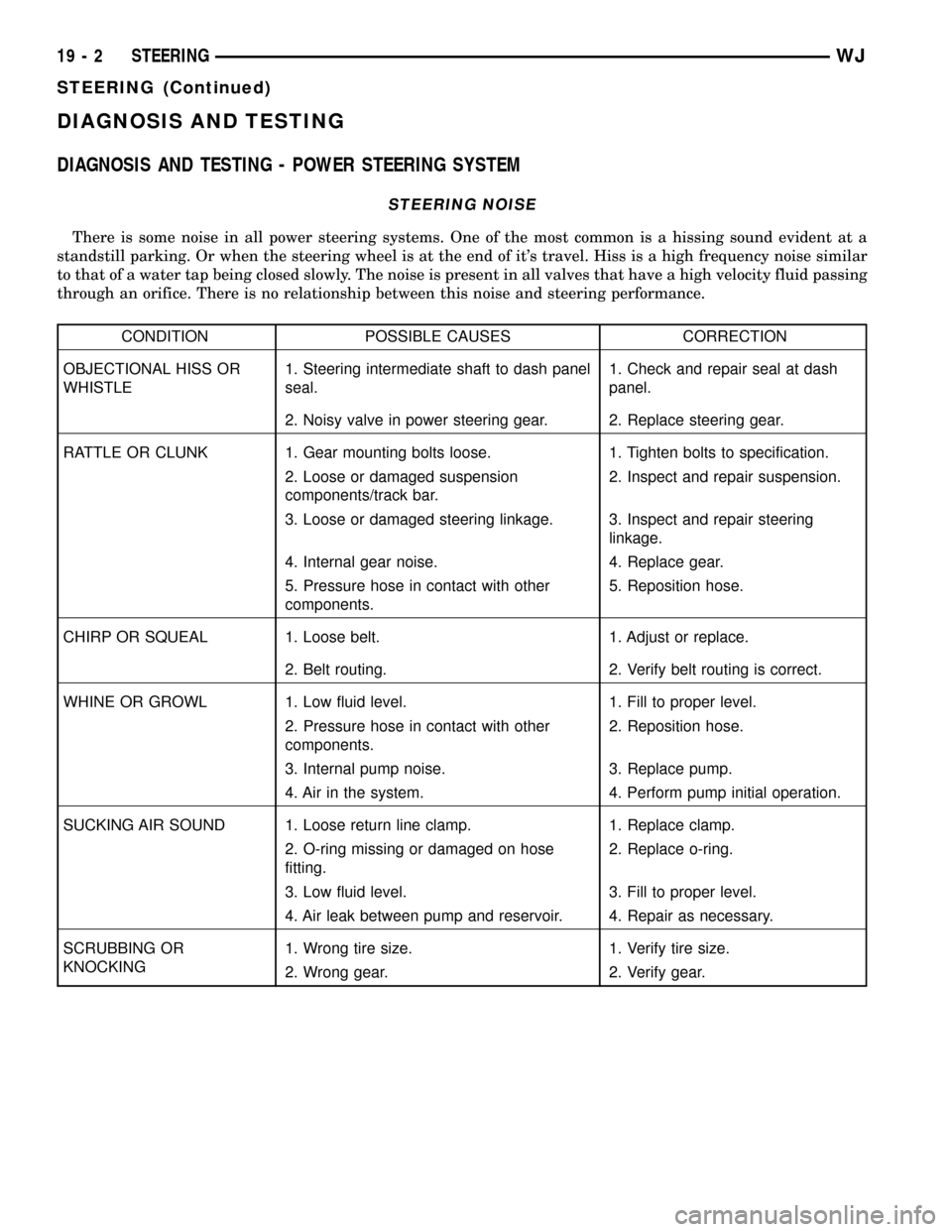
STEERING NOISE
There is some noise in all power steering systems. One of the most common is a hissing sound evident at a
standstill parking. Or when the steering wheel is at the end of it's travel. Hiss is a high frequency noise similar
to that of a water tap being closed slowly. The noise is present in all valves that have a high velocity fluid passing
through an orifice. There is no relationship between this noise and steering performance.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OBJECTIONAL HISS OR
WHISTLE1. Steering intermediate shaft to dash panel
seal.1. Check and repair seal at dash
panel.
2. Noisy valve in power steering gear. 2. Replace steering gear.
RATTLE OR CLUNK 1. Gear mounting bolts loose. 1. Tighten bolts to specification.
2. Loose or damaged suspension
components/track bar.2. Inspect and repair suspension.
3. Loose or damaged steering linkage. 3. Inspect and repair steering
linkage.
4. Internal gear noise. 4. Replace gear.
5. Pressure hose in contact with other
components.5. Reposition hose.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL 1. Loose belt. 1. Adjust or replace.
2. Belt routing. 2. Verify belt routing is correct.
WHINE OR GROWL 1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill to proper level.
2. Pressure hose in contact with other
components.2. Reposition hose.
3. Internal pump noise. 3. Replace pump.
4. Air in the system. 4. Perform pump initial operation.
SUCKING AIR SOUND 1. Loose return line clamp. 1. Replace clamp.
2. O-ring missing or damaged on hose
fitting.2. Replace o-ring.
3. Low fluid level. 3. Fill to proper level.
4. Air leak between pump and reservoir. 4. Repair as necessary.
SCRUBBING OR
KNOCKING1. Wrong tire size. 1. Verify tire size.
2. Wrong gear. 2. Verify gear.
19 - 2 STEERINGWJ
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1514 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Position and install the power steering cooler
to the vehicle.
(2) Install the three mounting bracket bolts (Fig.
6).
(3) Reconnect the upper hose at cooler (Fig. 6).
(4) Reconnect the lower hose at cooler (Fig. 6).
(5) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(6) Refill the power steering fluid and bleed the
system,(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(7) Start engine and check for leaks.
(8) Install the grille opening reinforcement panel
(9) Install the front fascia grille,(Refer to 13 -
FRAMES & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT FASCIA
- INSTALLATION).
HOSES - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - PRESSURE LINE
The hose consists of two metal ends and rubber
center section that contains a tuning cable. The
pump end uses a quick connect fitting. Lubircation
must be used on the quick connect nut and o-ring
when installing.
DESCRIPTION - RETURN LINE
Power steering return line is a hose which is
clamped at the pump and the gear.
OPERATION
OPERATION - PRESSURE LINE
Power steering pressure line, is used to transfer
high pressure power steering fluid, from the power
steering pump to the power steering gear on the
4.0L. The 4.7L power steering pressure line, is used
to transfer high pressure power steering fluid, from
the power steering pump to the engine cooling fan
and the steering gear.
OPERATION - RETURN LINE
Power steering return line, is used to transfer low
pressure power steering fluid, from the power steer-
ing gear to the power steering pump.
REMOVAL
(1) Drain the power steering fluid from the reser-
voir.
(2) Remove the air box,(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING -
REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the power steering pressure hose
from the power steering pump and then the power
steering gear (Fig. 7).
(4) Disconnect the power steering return hose from
the power steering cooler and the reservoir.
(5) Remove the hoses from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the hoses to the vehicle.
(2) Reconnect the power steering return hose to
the power steering cooler and the reservoir.
(3) Reconnect the power steering pressure hose to
the power steering pump and then the power steer-
ing gear.
(4) Install the air box,(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Refill the power steering fluid and bleed the
system,(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 7 POWER STEERING HOSES
1 - RETURN HOSE
2 - HIGH PRESSURE HOSE
3 - STEERING GEAR
WJPUMP 19 - 37
FLUID COOLER (Continued)
Page 1515 of 2199

HOSES - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 1/2º PRESSURE HOSE
The hose consists of two metal ends and a rubber
center with quick connect nuts at both ends. The
hose connects the power steering pump to the
hydraulic fan motor and is clipped to the fan shroud
(Fig. 8). Lubrication must be used on the quick con-
nect nuts and o-rings when installing.
DESCRIPTION - 1/2º RETURN HOSE
The fan motor return line is a molded rubber hose
that is clamped at the hydraulic motor and the power
steering reservoir (Fig. 9).
DESCRIPTION - 3/8º PRESSURE HOSE
The hose consists of two metal ends and two rub-
ber sections one of which contains a tuning cable
(Fig. 10). The hose is clipped in two places to the fan
shroud. Lubrication must be used on the o-rings
when installing.
DESCRIPTION - 3/8º GEAR OUTLET HOSE
The gear outlet line consists of a metal section that
connects to the gear and a rubber section that clamps
to the steering cooler inlet tube (Fig. 11).
DESCRIPTION - 3/8º RETURN HOSE
The return hose is a formed rubber hose that con-
nects the steering cooler outlet tube to the power
steering reservoir (Fig. 12). It is clamped at both
ends.
OPERATION
OPERATION - 1/2º PRESSURE HOSE
The 1/2º pressure hose is used to transfer high
pressure power steering fluid from the power steer-
ing pump to the engine cooling fan motor (Fig. 8).
OPERATION - 1/2º RETURN HOSE
The power steering return line returns low pres-
sure excess flow from the hydraulic fan motor back to
the power steering pump (Fig. 9).
Fig. 8 1/2(PRESSURE HOSE
1 - 1/29PRESSURE HOSE
2 - POWER STEERING PUMP
3 - STEERING GEAR
Fig. 9 1/2(RETURN HOSE
1 - 1/29RETURN HOSE
2 - HOSE CLAMP
Fig. 10 3/8(PRESSURE HOSE
1 - 3/89PRESSURE HOSE
2 - STEERING GEAR
19 - 38 PUMPWJ