2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE page 1
[x] Cancel search: page 1Page 1786 of 2199

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 112) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 113).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 114) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston with friction material was added to the tur-
bine assembly to provide this mechanical lock-up.
In order to reduce heat build-up in the transmission
and buffer the powertrain against torsional vibrations,
the TCM can duty cycle the L/R-CC Solenoid to achieve
a smooth application of the torque converter clutch.
This function, referred to as Electronically Modulated
Converter Clutch (EMCC) can occur at various times
depending on the following variables:
²Shift lever position
²Current gear range
²Transmission fluid temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Input speed
²Throttle angle
²Engine speed
Fig. 112 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 113 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 114 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 267
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1797 of 2199

Inspect all the valve and plug bores in the valve
body. Use a penlight to view the bore interiors.
Replace the valve body if any bores are distorted or
scored. Inspect all of the valve body springs. The
springs must be free of distortion, warpage or broken
coils.
Trial fit each valve and plug in its bore to check
freedom of operation. When clean and dry, the valves
and plugs should drop freely into the bores.
Valve body bores do not change dimensionally with
use. If the valve body functioned correctly when new,
it will continue to operate properly after cleaning and
inspection. It should not be necessary to replace a
valve body assembly unless it is damaged in han-
dling.
Inspect all the accumulator bores in the valve body.
Use a penlight to view the bore interiors. Replace the
valve body if any bores are distorted or scored.Inspect all of the accumulator springs. The springs
must be free of distortion, warpage or broken coils.
Inspect all the fluid seals on the valve body (Fig.
133). Replace any seals that are cracked, distorted, or
damaged in any way. These seals pass fluid pressure
directly to the clutches. Any pressure leak at these
points, may cause transmission performance prob-
lems.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate valves, springs, and the housing
valve bores with clean transmission fluid.
(2) Install solenoid switch valve, manual valve,
and the low/reverse switch valve into the valve body.
(3) Install the retainers to hold each valve into the
valve body.
(4) Install the valve body check balls into their
proper locations.
(5) Position the transfer plate onto the valve body.
(6) Install the screws to hold the transfer plate to
the valve body. Tighten the screws to 5.6 N´m (50 in.
lbs.).
(7) Install the accumulator pistons and springs
into the valve body in the location from which they
were removed. Note that all accumulators except the
overdrive have two springs. The overdrive accumula-
tor piston has only one spring.
Fig. 132 Valve Body Components
1 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
2 - MANUAL VALVE
3 - LOW REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR
5 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
6 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
7 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
8 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
9 - CHECK BALLS (7)
Fig. 133 Valve Body Seals
1 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
2 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
3 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
5 - LOW/REVERSE PASSAGE SEAL
6 - 2ND CLUTCH PASSAGE SEAL
7 - 4TH CLUTCH PASSAGE SEAL
8 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR (1 SPRING)
21 - 278 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1799 of 2199
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION........................280
OPERATION..........................281
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV242.......................281
REMOVAL............................282
DISASSEMBLY........................282
CLEANING...........................292
INSPECTION.........................293
ASSEMBLY...........................295
INSTALLATION........................307
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN/
REFILL............................310FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................310
INSTALLATION........................310
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................311
OPERATION..........................311
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
REAR RETAINER BUSHING AND SEAL -
NV242HD
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL............................313
INSTALLATION........................313
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
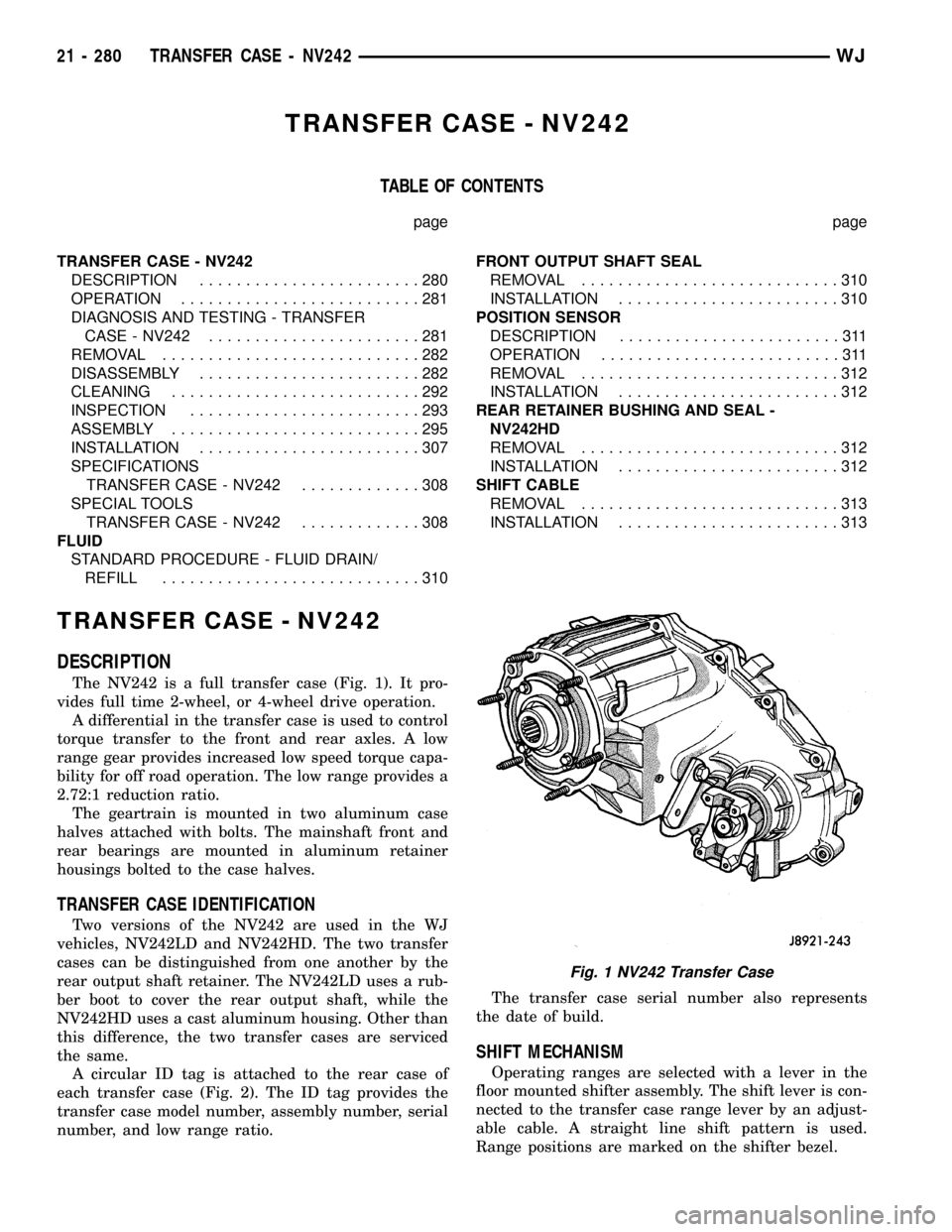
DESCRIPTION
The NV242 is a full transfer case (Fig. 1). It pro-
vides full time 2-wheel, or 4-wheel drive operation.
A differential in the transfer case is used to control
torque transfer to the front and rear axles. A low
range gear provides increased low speed torque capa-
bility for off road operation. The low range provides a
2.72:1 reduction ratio.
The geartrain is mounted in two aluminum case
halves attached with bolts. The mainshaft front and
rear bearings are mounted in aluminum retainer
housings bolted to the case halves.
TRANSFER CASE IDENTIFICATION
Two versions of the NV242 are used in the WJ
vehicles, NV242LD and NV242HD. The two transfer
cases can be distinguished from one another by the
rear output shaft retainer. The NV242LD uses a rub-
ber boot to cover the rear output shaft, while the
NV242HD uses a cast aluminum housing. Other than
this difference, the two transfer cases are serviced
the same.
A circular ID tag is attached to the rear case of
each transfer case (Fig. 2). The ID tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a lever in the
floor mounted shifter assembly. The shift lever is con-
nected to the transfer case range lever by an adjust-
able cable. A straight line shift pattern is used.
Range positions are marked on the shifter bezel.
Fig. 1 NV242 Transfer Case
21 - 280 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
Page 1834 of 2199
TRANSFER CASE - NV247
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV247
DESCRIPTION........................315
OPERATION..........................316
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV247.......................316
REMOVAL............................317
DISASSEMBLY........................317
CLEANING...........................324
INSPECTION.........................324
ASSEMBLY...........................326
INSTALLATION........................335
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV247.............336
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV247.............337FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN/
REFILL............................338
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................338
INSTALLATION........................338
REAR RETAINER BUSHING AND SEAL
REMOVAL............................339
INSTALLATION........................339
SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL............................340
INSTALLATION........................340
TRANSFER CASE - NV247
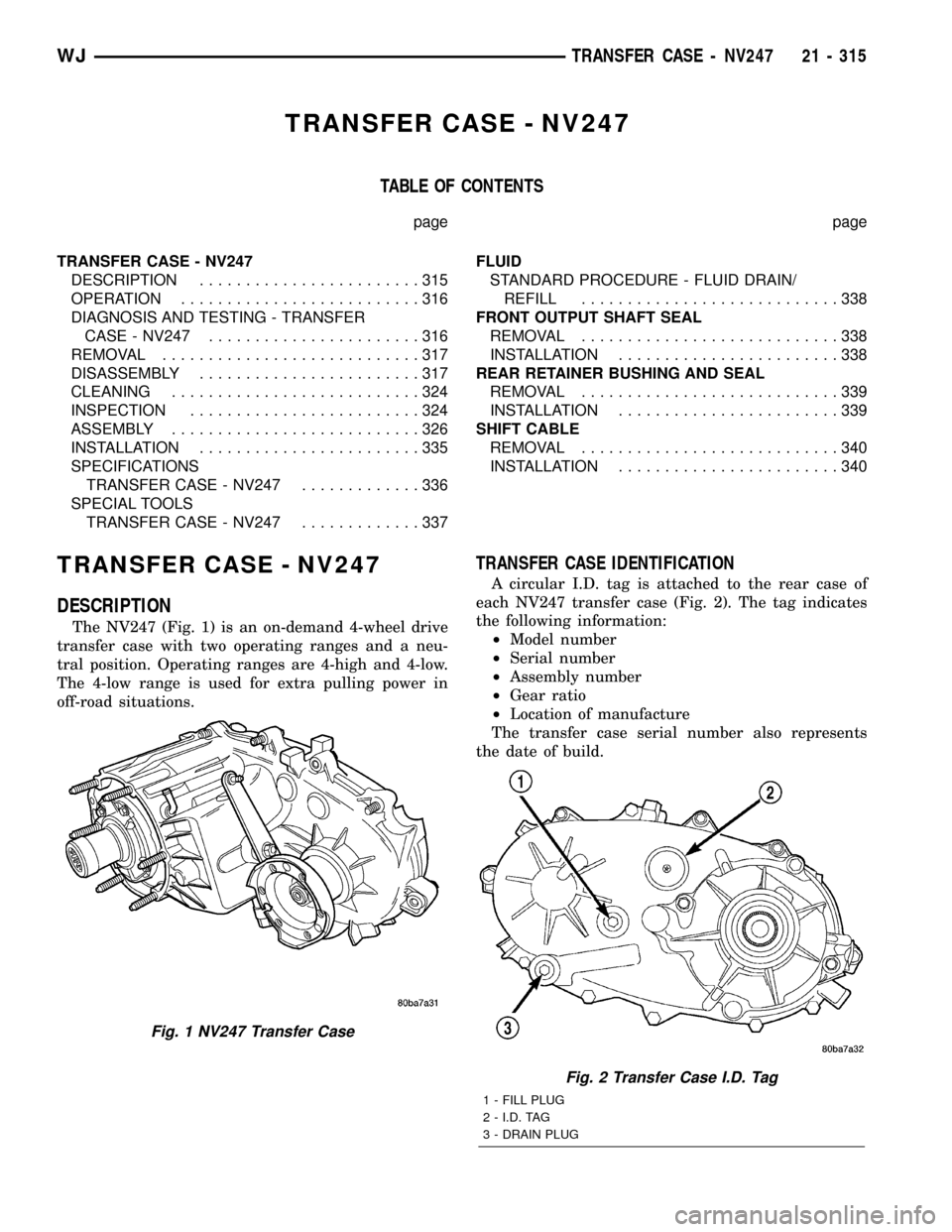
DESCRIPTION
The NV247 (Fig. 1) is an on-demand 4-wheel drive
transfer case with two operating ranges and a neu-
tral position. Operating ranges are 4-high and 4-low.
The 4-low range is used for extra pulling power in
off-road situations.
TRANSFER CASE IDENTIFICATION
A circular I.D. tag is attached to the rear case of
each NV247 transfer case (Fig. 2). The tag indicates
the following information:
²Model number
²Serial number
²Assembly number
²Gear ratio
²Location of manufacture
The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
Fig. 1 NV247 Transfer Case
Fig. 2 Transfer Case I.D. Tag
1 - FILL PLUG
2 - I.D. TAG
3 - DRAIN PLUG
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV247 21 - 315
Page 1860 of 2199

TIRES/WHEELS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE AND
WHEEL RUNOUT......................1
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE AND
WHEEL BALANCE......................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MATCH
MOUNTING...........................4
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE ROTATION . 5
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL
INSTALLATION........................5
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRES..................6
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL±PLY TIRES.......6
DESCRIPTION - TIRE INFLATION
PRESSURES..........................6
DESCRIPTION - TIRE PRESSURE FOR
HIGH SPEED..........................7
DESCRIPTION - REPLACEMENT TIRES.....7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRESSURE
GAUGES.............................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS..........................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR
PATTERNS...........................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE
OR VIBRATION........................8STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIRING
LEAKS...............................8
CLEANING.............................9
SPECIFICATIONS
TIRES...............................9
SPECIFICATIONS -.....................9
SPARE TIRE
DESCRIPTION - SPARE / TEMPORARY TIRE . . 10
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION.........................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WHEEL
INSPECTION.........................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL
REPLACEMENT.......................10
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................11
STUDS
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING
DESCRIPTION.........................12
OPERATION...........................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE PRESSURE
MONITORING SYSTEM.................12
SENSOR
REMOVAL - TIRE PRESSURE SENSOR/
TRANSMITTER.......................12
INSTALLATION - TIRE PRESSURE SENSOR/
TRANSMITTER.......................13
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE AND WHEEL
RUNOUT
Radial runout is the difference between the high
and low points on the tire or wheel (Fig. 1).
Lateral runout is thewobbleof the tire or wheel.
Radial runout of more than 1.5 mm (.060 inch)
measured at the center line of the tread may cause
the vehicle to shake.
Lateral runout of more than 2.0 mm (.080 inch)
measured near the shoulder of the tire may cause the
vehicle to shake.
Sometimes radial runout can be reduced. Relocate
the wheel and tire assembly on the mounting studs
(See Method 1). If this does not reduce runout to an
acceptable level, the tire can be rotated on the wheel.
(See Method 2).
METHOD 1 (RELOCATE WHEEL ON HUB)
(1) Drive vehicle a short distance to eliminate tire
flat spotting from a parked position.
(2) Check wheel bearings and adjust if adjustable
or replace if necessary.
(3) Check the wheel mounting surface.
(4) Relocate wheel on the mounting, two studs
over from the original position.
(5) Tighten wheel nuts until all are properly
torqued, to eliminate brake distortion.
(6) Check radial runout. If still excessive, mark
tire sidewall, wheel, and stud at point of maximum
runout and proceed to Method 2.
METHOD 2 (RELOCATE TIRE ON WHEEL)
NOTE: Rotating the tire on wheel is particularly
effective when there is runout in both tire and
wheel.
WJTIRES/WHEELS 22 - 1
Page 1874 of 2199

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS........................1
WIND NOISE..........................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BODY
LUBRICATION.........................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRILLING AND
WELDING............................3
SPECIFICATIONS
BODY LUBRICANTS....................3
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE.............4
SPECIAL TOOLS
BODY...............................4DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE........5
DOOR - FRONT.........................11
DOORS - REAR.........................19
EXTERIOR.............................25
HOOD.................................33
INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM.............36
INTERIOR..............................69
PAINT.................................81
SEATS................................83
STATIONARY GLASS.....................93
SUNROOF.............................96
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS..................105
BODY STRUCTURE.....................112
BODY
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.
²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-
cle. For hoisting recommendations refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance, General Information
section.
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
WJBODY 23 - 1
Page 1878 of 2199

DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EXTERIOR HANDLE
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................5
FLIP-UP GLASS
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................6
FLIP-UP GLASS LATCH
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
FLIP-UP GLASS LATCH STRIKER
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................7
FLIP-UP GLASS SWITCH
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................7
HINGE
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................7
LATCH
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................8LATCH STRIKER
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................8
LIFTGATE
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION..........................9
ADJUSTMENTS
LIFTGATE ADJUSTMENT................9
TRIM PANEL
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - LIFTGATE TRIM PANEL........9
REMOVAL - LOWER LIFTGATE OPENING
TRIM PANEL.........................10
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - LIFTGATE TRIM PANEL . . . 10
INSTALLATION - LOWER LIFTGATE
OPENING TRIM PANEL.................10
LIFTGATE INSULATOR
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
EXTERIOR HANDLE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the liftgate trim panel refer to (Refer
to 23 - BODY/DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAIL-
GATE/TRIM PANEL - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the latch, outside handle linkage, and
power lock connector.
(3) Remove the fasteners attaching the outside
handle to the liftgate.
(4) Remove the outside handle from the liftgate.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the outside handle on the liftgate.
(2) Install the fasteners attaching outside handle
to liftgate.
(3) Connect outside handle link and power lock
connector.
(4) Install liftgate trim panel, refer to (Refer to 23
- BODY/DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE/
TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION).
FLIP-UP GLASS
REMOVAL
CAUTION: DO NOT DISCONNECT THE PROP ROD
CYLINDERS WITH THE LIFTGATE FLIP UP GLASS
CLOSED. THE PROP ROD PISTONS ARE OPER-
ATED BY HIGH PRESSURE GAS. THIS PRESSURE
COULD CAUSE DAMAGE AND/OR PERSONAL
INJURY IF THEY ARE REMOVED WHILE THE PIS-
TONS ARE COMPRESSED.
(1) Using a trim stick or other suitable device, sep-
arate the flip up glass hinge cover from the hinge on
the liftgate (Fig. 1).
(2) Open liftgate flip up glass. Support the glass
for ease of repair.
(3) Using a small flat blade or equivalent tool, gen-
tly pry open the locking caps on the end of the prop
rods.
(4) Remove prop rod cylinders from ball studs.
(5) Lower the flip up glass.
(6) Remove hinge fasteners from liftgate.
(7) Separate flip up glass from liftgate.
WJDECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE 23 - 5
Page 1884 of 2199
DOOR - FRONT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHECK STRAP
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
DOOR
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
ADJUSTMENTS
DOOR ADJUSTMENT..................12
DOOR GLASS
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
EXTERIOR HANDLE
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
GLASS RUN CHANNEL
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................14
HINGE
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................15
INSIDE HANDLE ACTUATOR
REMOVAL.............................15INSTALLATION.........................15
LATCH
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
ADJUSTMENTS
DOOR LATCH........................16
LATCH STRIKER
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
LOCK CYLINDER
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................17
TRIM PANEL
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
WATERDAM
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
WINDOW REGULATOR
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................18
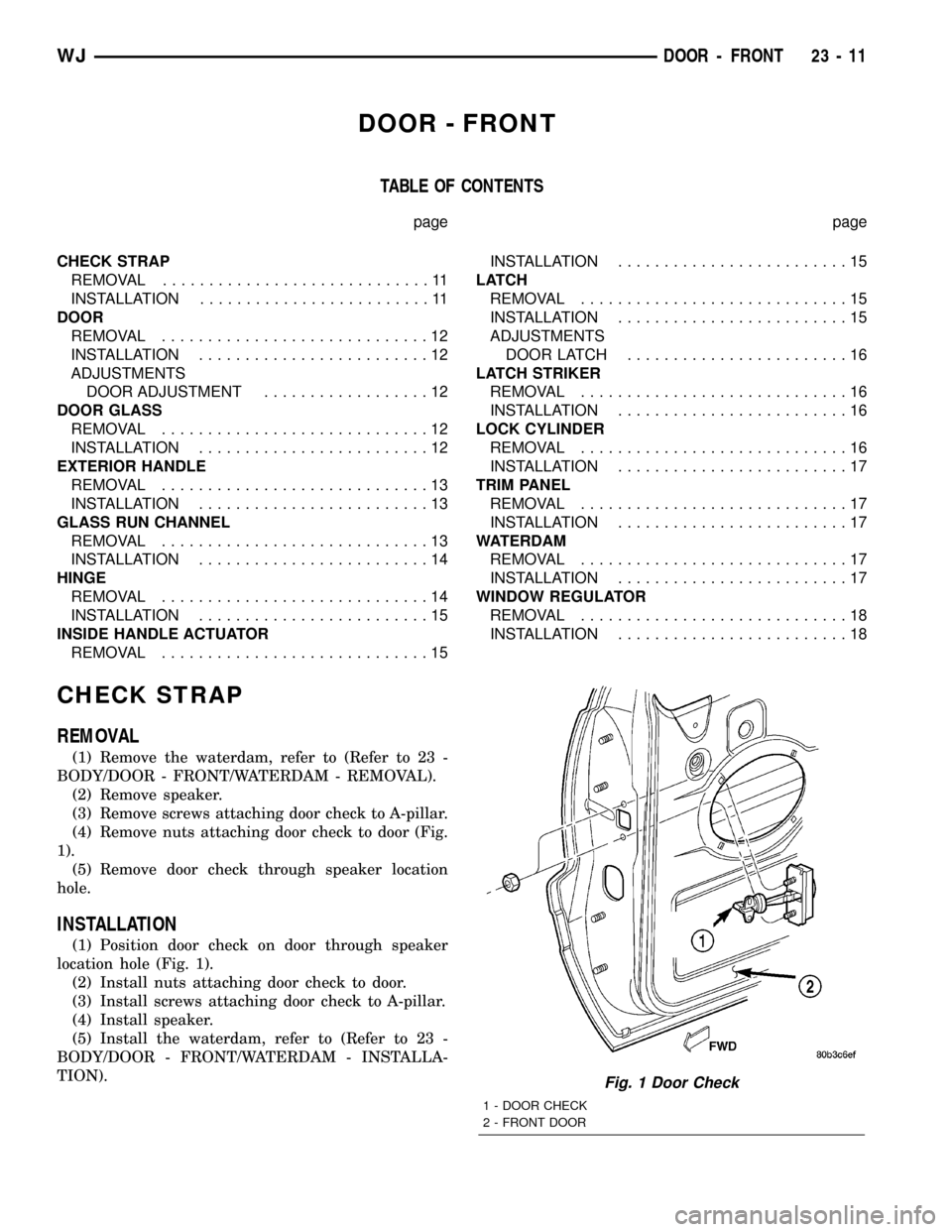
CHECK STRAP
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the waterdam, refer to (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DOOR - FRONT/WATERDAM - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove speaker.
(3) Remove screws attaching door check to A-pillar.
(4) Remove nuts attaching door check to door (Fig.
1).
(5) Remove door check through speaker location
hole.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position door check on door through speaker
location hole (Fig. 1).
(2) Install nuts attaching door check to door.
(3) Install screws attaching door check to A-pillar.
(4) Install speaker.
(5) Install the waterdam, refer to (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DOOR - FRONT/WATERDAM - INSTALLA-
TION).
Fig. 1 Door Check
1 - DOOR CHECK
2 - FRONT DOOR
WJDOOR - FRONT 23 - 11