2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Timing
[x] Cancel search: TimingPage 1543 of 2199
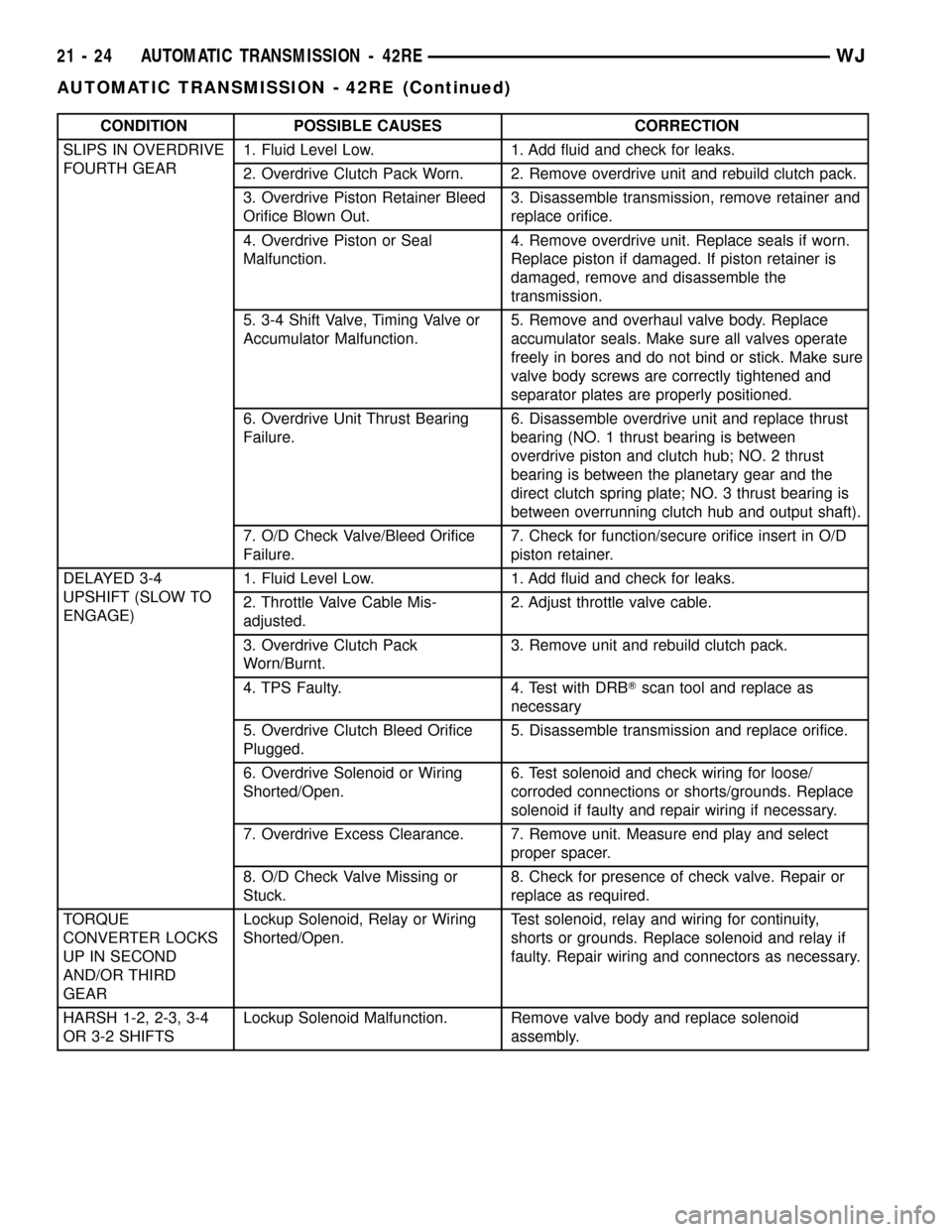
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SLIPS IN OVERDRIVE
FOURTH GEAR1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Overdrive Clutch Pack Worn. 2. Remove overdrive unit and rebuild clutch pack.
3. Overdrive Piston Retainer Bleed
Orifice Blown Out.3. Disassemble transmission, remove retainer and
replace orifice.
4. Overdrive Piston or Seal
Malfunction.4. Remove overdrive unit. Replace seals if worn.
Replace piston if damaged. If piston retainer is
damaged, remove and disassemble the
transmission.
5. 3-4 Shift Valve, Timing Valve or
Accumulator Malfunction.5. Remove and overhaul valve body. Replace
accumulator seals. Make sure all valves operate
freely in bores and do not bind or stick. Make sure
valve body screws are correctly tightened and
separator plates are properly positioned.
6. Overdrive Unit Thrust Bearing
Failure.6. Disassemble overdrive unit and replace thrust
bearing (NO. 1 thrust bearing is between
overdrive piston and clutch hub; NO. 2 thrust
bearing is between the planetary gear and the
direct clutch spring plate; NO. 3 thrust bearing is
between overrunning clutch hub and output shaft).
7. O/D Check Valve/Bleed Orifice
Failure.7. Check for function/secure orifice insert in O/D
piston retainer.
DELAYED 3-4
UPSHIFT (SLOW TO
ENGAGE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Throttle Valve Cable Mis-
adjusted.2. Adjust throttle valve cable.
3. Overdrive Clutch Pack
Worn/Burnt.3. Remove unit and rebuild clutch pack.
4. TPS Faulty. 4. Test with DRBTscan tool and replace as
necessary
5. Overdrive Clutch Bleed Orifice
Plugged.5. Disassemble transmission and replace orifice.
6. Overdrive Solenoid or Wiring
Shorted/Open.6. Test solenoid and check wiring for loose/
corroded connections or shorts/grounds. Replace
solenoid if faulty and repair wiring if necessary.
7. Overdrive Excess Clearance. 7. Remove unit. Measure end play and select
proper spacer.
8. O/D Check Valve Missing or
Stuck.8. Check for presence of check valve. Repair or
replace as required.
TORQUE
CONVERTER LOCKS
UP IN SECOND
AND/OR THIRD
GEARLockup Solenoid, Relay or Wiring
Shorted/Open.Test solenoid, relay and wiring for continuity,
shorts or grounds. Replace solenoid and relay if
faulty. Repair wiring and connectors as necessary.
HARSH 1-2, 2-3, 3-4
OR 3-2 SHIFTSLockup Solenoid Malfunction. Remove valve body and replace solenoid
assembly.
21 - 24 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1596 of 2199

FRONT SERVO
DESCRIPTION
The kickdown servo (Fig. 98) consists of a two-land
piston with an inner piston, a piston rod and guide,
and a return spring. The dual-land piston uses seal
rings on its outer diameters and an O-ring for the
inner piston.
OPERATION
The application of the piston is accomplished by
applying pressure between the two lands of the pis-
ton. The pressure acts against the larger lower land
to push the piston downward, allowing the piston rod
to extend though its guide against the apply lever.
Release of the servo at the 2-3 upshift is accom-
plished by a combination of spring and line pressure,
acting on the bottom of the larger land of the piston.
The small piston is used to cushion the application of
the band by bleeding oil through a small orifice in
the larger piston. The release timing of the kickdown
servo is very important to obtain a smooth but firm
shift. The release has to be very quick, just as the
front clutch application is taking place. Otherwise,
engine runaway or a shift hesitation will occur. To
accomplish this, the band retains its holding capacity
until the front clutch is applied, giving a small
amount of overlap between them.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove seal ring from rod guide (Fig. 99).(2) Remove small snap-ring from servo piston rod.
Then remove piston rod, spring and washer from pis-
ton.
(3) Remove and discard servo component o-ring
and seal rings.
CLEANING
Clean the servo piston components (Fig. 100) with
solvent and dry them with compressed air.
INSPECTION
Inspect the servo components (Fig. 101). Replace
the springs if collapsed, distorted or broken. Replace
the guide, rod and piston if cracked, bent, or worn.
Discard the servo snap-ring if distorted or warped.
Check the servo piston bore for wear. If the bore is
severely scored, or damaged, it will be necessary to
replace the case.
Replace any servo component if doubt exists about
condition. Do not reuse suspect parts.
ASSEMBLY
Clean and inspect front servo components.
(1) Lubricate new o-ring and seal rings with petro-
leum jelly and install them on piston, guide and rod.
(2) Install rod in piston. Install spring and washer
on rod. Compress spring and install snap-ring (Fig.
102).
Fig. 98 Front Servo
1 - VENT
2 -PISTON ROD
3 - PISTON
4 - SPRING
5 - RELEASE PRESSURE
6 - APPLY PRESSURE
Fig. 99 Front Servo
1 - PISTON RINGS
2 - O-RING
3 - SNAP-RING
4 - SEAL RING
5 - PISTON ROD GUIDE
6 - SNAP-RING
7 - SERVO SPRING
8 - PISTON ROD
9 - SERVO PISTON
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 77
Page 1654 of 2199

VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and transfer plate. The valve
body contains valves and check balls that control
fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch, bands,
and frictional clutches. The valve body contains the
following components (Fig. 255), (Fig. 256), (Fig.
257), and (Fig. 258):
²Regulator valve
²Regulator valve throttle pressure plug
²Line pressure plug and sleeve
²Kickdown valve
²Kickdown limit valve
²1-2 shift valve
²1-2 control valve
²2-3 shift valve²2-3 governor plug
²3-4 shift valve
²3-4 timing valve
²3-4 quick fill valve
²3-4 accumulator
²Throttle valve
²Throttle pressure plug
²Switch valve
²Manual valve
²Converter clutch lock-up valve
²Converter clutch lock-up timing Valve
²Shuttle valve
²Shuttle valve throttle plug
²Boost Valve
²10 check balls
By adjusting the spring pressure acting on the reg-
ulator valve, transmission line pressure can be
adjusted.
Fig. 255 Upper Housing Control Valve Locations
1 - UPPER HOUSING 8 - MANUAL VALVE
2 - REGULATOR VALVE 9 - 1-2 GOVERNOR PLUG
3 - SWITCH VALVE 10 - GOVERNOR PLUG COVER
4 - REGULATOR VALVE SPRING 11 - THROTTLE PLUG
5 - KICKDOWN VALVE 12 - 2-3 GOVERNOR PLUG
6 - KICKDOWN DETENT 13 - SHUTTLE VALVE PRIMARY SPRING
7 - THROTTLE VALVE AND SPRING
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 135
Page 1657 of 2199

Fig. 258 Lower Housing Shift Valves and Springs
1 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING 11 - TIMING VALVE COVER
2 - 3-4 SHIFT VALVE AND SPRING 12 - PLUG
3 - PLUG 13 - 3-4 TIMING VALVE AND SPRING
4 - SPRING RETAINER 14 - LOWER HOUSING
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH VALVE AND SPRING 15 - ACCUMULATOR END PLATE
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH TIMING VALVE AND SPRING 16 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR PISTON AND SPRING
7 - OVERDRIVE SEPARATOR PLATE 17 - E-CLIP
8 - CASE CONNECTOR 18 - 3-4 QUICK FILL SPRING AND VALVE
9 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID 19 - SOLENOID GASKET
10 - OVERDRIVE SOLENOID 20 - HARNESS
21 - 138 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1658 of 2199
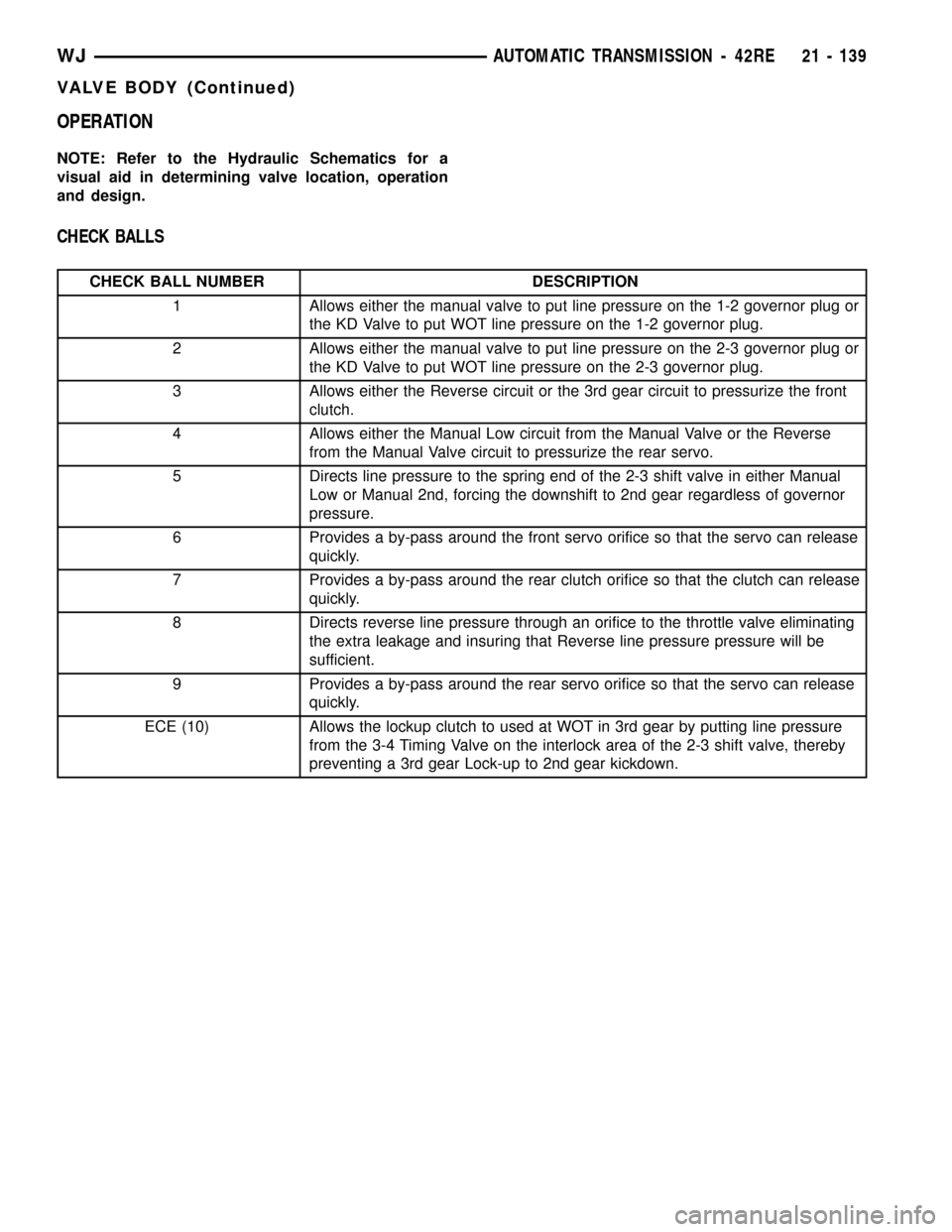
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
CHECK BALLS
CHECK BALL NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 Allows either the manual valve to put line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug or
the KD Valve to put WOT line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug.
2 Allows either the manual valve to put line pressure on the 2-3 governor plug or
the KD Valve to put WOT line pressure on the 2-3 governor plug.
3 Allows either the Reverse circuit or the 3rd gear circuit to pressurize the front
clutch.
4 Allows either the Manual Low circuit from the Manual Valve or the Reverse
from the Manual Valve circuit to pressurize the rear servo.
5 Directs line pressure to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve in either Manual
Low or Manual 2nd, forcing the downshift to 2nd gear regardless of governor
pressure.
6 Provides a by-pass around the front servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
7 Provides a by-pass around the rear clutch orifice so that the clutch can release
quickly.
8 Directs reverse line pressure through an orifice to the throttle valve eliminating
the extra leakage and insuring that Reverse line pressure pressure will be
sufficient.
9 Provides a by-pass around the rear servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
ECE (10) Allows the lockup clutch to used at WOT in 3rd gear by putting line pressure
from the 3-4 Timing Valve on the interlock area of the 2-3 shift valve, thereby
preventing a 3rd gear Lock-up to 2nd gear kickdown.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 139
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1665 of 2199
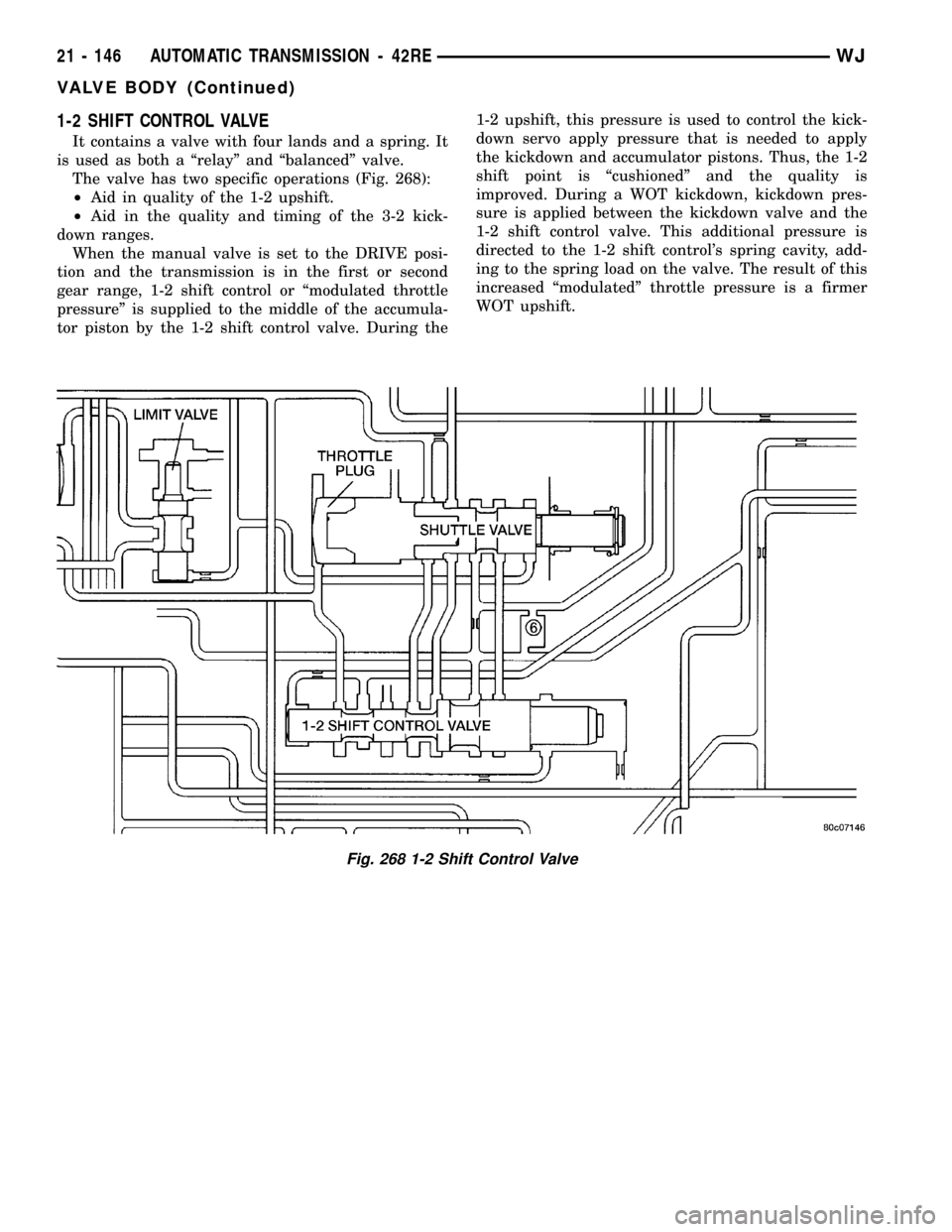
1-2 SHIFT CONTROL VALVE
It contains a valve with four lands and a spring. It
is used as both a ªrelayº and ªbalancedº valve.
The valve has two specific operations (Fig. 268):
²Aid in quality of the 1-2 upshift.
²Aid in the quality and timing of the 3-2 kick-
down ranges.
When the manual valve is set to the DRIVE posi-
tion and the transmission is in the first or second
gear range, 1-2 shift control or ªmodulated throttle
pressureº is supplied to the middle of the accumula-
tor piston by the 1-2 shift control valve. During the1-2 upshift, this pressure is used to control the kick-
down servo apply pressure that is needed to apply
the kickdown and accumulator pistons. Thus, the 1-2
shift point is ªcushionedº and the quality is
improved. During a WOT kickdown, kickdown pres-
sure is applied between the kickdown valve and the
1-2 shift control valve. This additional pressure is
directed to the 1-2 shift control's spring cavity, add-
ing to the spring load on the valve. The result of this
increased ªmodulatedº throttle pressure is a firmer
WOT upshift.
Fig. 268 1-2 Shift Control Valve
21 - 146 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1668 of 2199
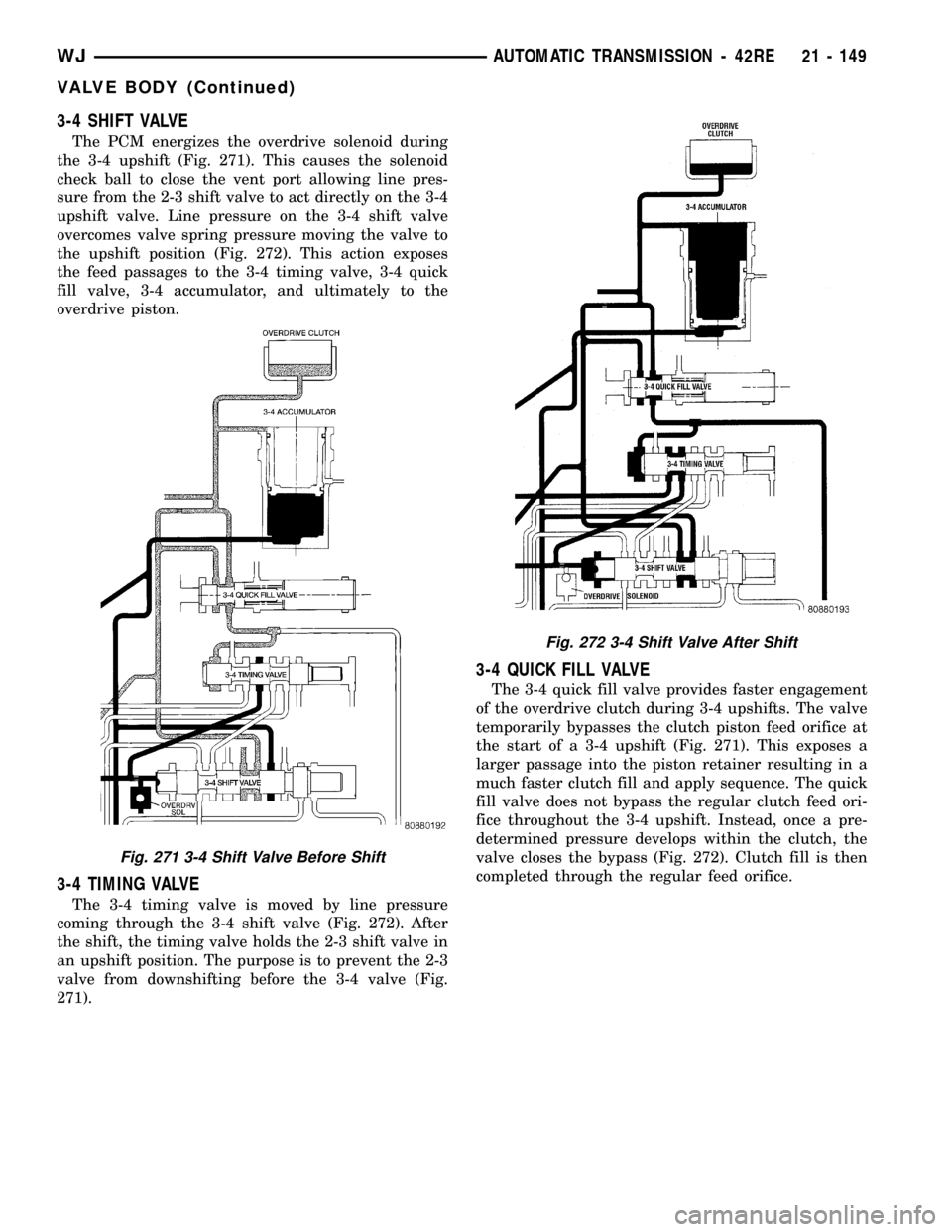
3-4 SHIFT VALVE
The PCM energizes the overdrive solenoid during
the 3-4 upshift (Fig. 271). This causes the solenoid
check ball to close the vent port allowing line pres-
sure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly on the 3-4
upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4 shift valve
overcomes valve spring pressure moving the valve to
the upshift position (Fig. 272). This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston.
3-4 TIMING VALVE
The 3-4 timing valve is moved by line pressure
coming through the 3-4 shift valve (Fig. 272). After
the shift, the timing valve holds the 2-3 shift valve in
an upshift position. The purpose is to prevent the 2-3
valve from downshifting before the 3-4 valve (Fig.
271).
3-4 QUICK FILL VALVE
The 3-4 quick fill valve provides faster engagement
of the overdrive clutch during 3-4 upshifts. The valve
temporarily bypasses the clutch piston feed orifice at
the start of a 3-4 upshift (Fig. 271). This exposes a
larger passage into the piston retainer resulting in a
much faster clutch fill and apply sequence. The quick
fill valve does not bypass the regular clutch feed ori-
fice throughout the 3-4 upshift. Instead, once a pre-
determined pressure develops within the clutch, the
valve closes the bypass (Fig. 272). Clutch fill is then
completed through the regular feed orifice.
Fig. 271 3-4 Shift Valve Before Shift
Fig. 272 3-4 Shift Valve After Shift
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 149
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1672 of 2199
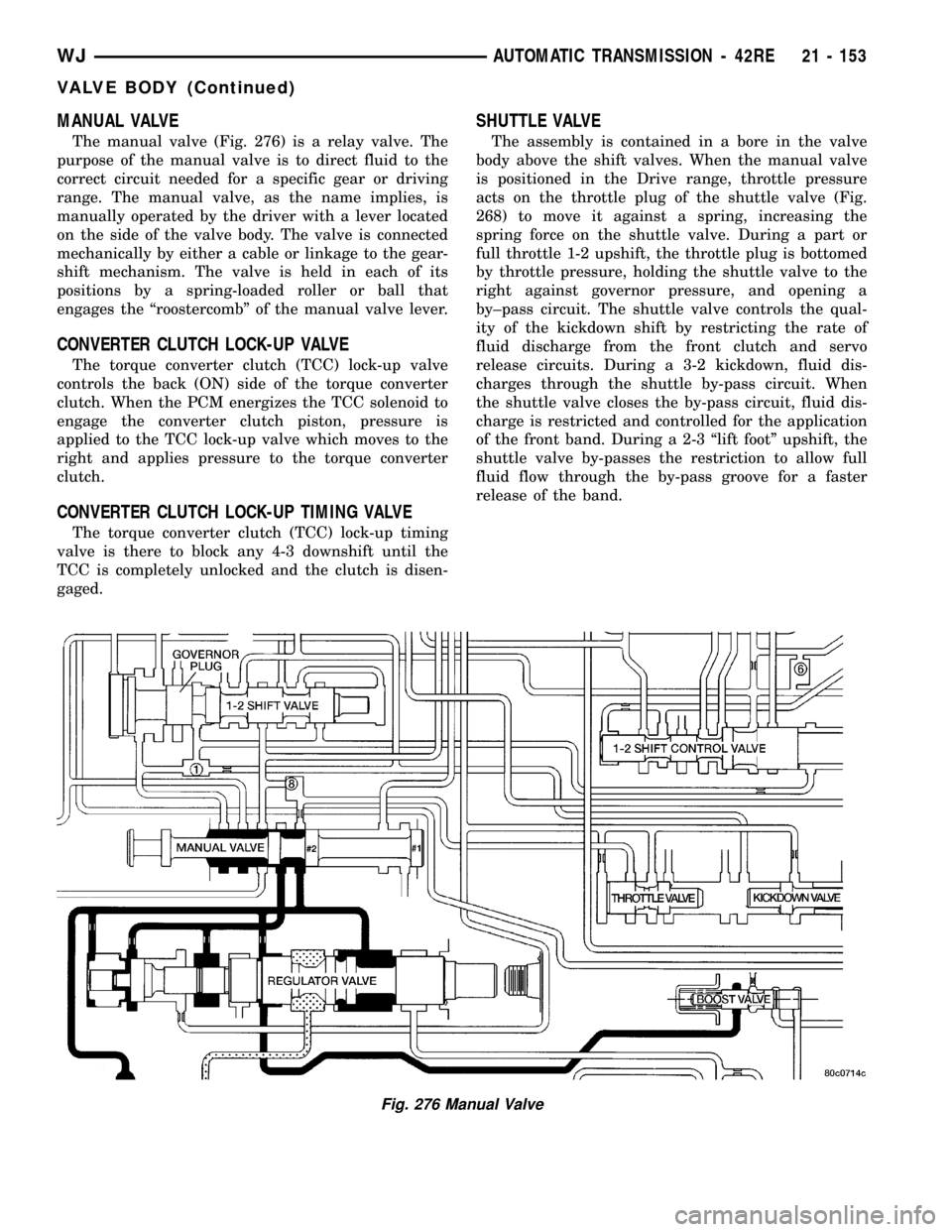
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve (Fig. 276) is a relay valve. The
purpose of the manual valve is to direct fluid to the
correct circuit needed for a specific gear or driving
range. The manual valve, as the name implies, is
manually operated by the driver with a lever located
on the side of the valve body. The valve is connected
mechanically by either a cable or linkage to the gear-
shift mechanism. The valve is held in each of its
positions by a spring-loaded roller or ball that
engages the ªroostercombº of the manual valve lever.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up valve
controls the back (ON) side of the torque converter
clutch. When the PCM energizes the TCC solenoid to
engage the converter clutch piston, pressure is
applied to the TCC lock-up valve which moves to the
right and applies pressure to the torque converter
clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP TIMING VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up timing
valve is there to block any 4-3 downshift until the
TCC is completely unlocked and the clutch is disen-
gaged.
SHUTTLE VALVE
The assembly is contained in a bore in the valve
body above the shift valves. When the manual valve
is positioned in the Drive range, throttle pressure
acts on the throttle plug of the shuttle valve (Fig.
268) to move it against a spring, increasing the
spring force on the shuttle valve. During a part or
full throttle 1-2 upshift, the throttle plug is bottomed
by throttle pressure, holding the shuttle valve to the
right against governor pressure, and opening a
by±pass circuit. The shuttle valve controls the qual-
ity of the kickdown shift by restricting the rate of
fluid discharge from the front clutch and servo
release circuits. During a 3-2 kickdown, fluid dis-
charges through the shuttle by-pass circuit. When
the shuttle valve closes the by-pass circuit, fluid dis-
charge is restricted and controlled for the application
of the front band. During a 2-3 ªlift footº upshift, the
shuttle valve by-passes the restriction to allow full
fluid flow through the by-pass groove for a faster
release of the band.
Fig. 276 Manual Valve
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 153
VALVE BODY (Continued)