2002 FORD F350 ECO mode
[x] Cancel search: ECO modePage 122 of 264

Vehicles with a higher center of gravity such as utility and
four-wheel drive vehicles handle differently than vehicles with a
lower center of gravity. Utility and four-wheel drive vehicles arenot
designed for cornering at speeds as high as passenger cars any more
than low-slung sports cars are designed to perform satisfactorily under
off-road conditions. Avoid sharp turns, excessive speed and abrupt
maneuvers in these vehicles. Failure to drive cautiously could result in
an increased risk of loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover, personal
injury and death.
•If the vehicle goes from one type of surface to another (i.e., from
concrete to gravel) there will be a change in the way the vehicle
responds to a maneuver (steering, acceleration or braking). Again,
avoid these abrupt inputs.
Parking
On some 4WD vehicles, when the transfer case is in the N (Neutral)
position, the engine and transmission are disconnected from the rest of
the driveline. Therefore, the vehicle is free to roll even if the automatic
transmission is in P (Park) or the manual transmission is in gear. Do not
leave the vehicle unattended with the transfer case in the N (Neutral)
position. Always set the parking brake fully and turn off the ignition
when leaving the vehicle.
4WD Systems
4WD (when you select a 4WD mode), uses all four wheels to power the
vehicle. This increases traction, enabling you to drive over terrain and
road conditions that a conventional two-wheel drive vehicle can not.
Power is supplied to all four wheels
through a transfer case. On 4WD
vehicles, the transfer case allows
you to select 4WD when necessary.
Information on transfer case
operation and shifting procedures
can be found in theDriving
chapter. Information on transfer
case maintenance can be found in theMaintenance and specifications
chapter. You should become thoroughly familiar with this information
before you operate your vehicle.
Normal characteristics
On some 4WD models, the initial shift from two-wheel drive to 4x4 while
the vehicle is moving can cause some momentary clunk and ratcheting
Driving
122
ProCarManuals.com
Page 154 of 264

Improper removal/installation of the driveshaft can cause
transmission fluid loss, damage to the driveshaft and internal
transmission components.
RWD vehicles with 4x4 electronic shift transfer case or All Wheel
Drive (AWD) vehicles with automatic transmissions:
Regarding recreational towing or having your vehicle towed, 4x4 vehicles
with electronic shift on the fly and AWD vehicles cannot be towed with
any wheels on the ground (with the exception of moving it as a disabled
vehicle off the road out of traffic).
SNOWPLOWING
Note:Do not use your vehicle to snowplow until it has been driven at
least 800 km (500 miles). Follow the severe duty schedule in your
scheduled maintenance guide for engine oil and transmission fluid
change intervals.
Note:Ford does not install snowplows.
For low speed snow removal, Ford offers a Snowplow Package Option on
select 4x4 vehicles. To assist Ford dealers and equipment installers
further prepare the vehicle for snowplowing, Ford includes instructions
in theFord Truck Body Builders Layout BookandFord Truck Source
Book. These instructions are available through your Ford dealer; they
include the list of vehicle models recommended for snowplowing and
snowplow weight limits. Use of the Snowplow Package Option, or its
equivalent, along with these instructions will help avoid possible
powertrain and chassis damage from snowplowing.
The front and rear GAWR, GVWR, Total Accessory Reserve Capacity
(TARC) and tire inflation pressures are found on the Safety Compliance
Certification Label located on one of the vehicle’s door jambs. This label
is applied to all vehicles completed by Ford Motor Company. Incomplete
vehicles built by Ford Motor Company will have an Incomplete Vehicle
Label in place of the Safety Compliance Label. The TARC does not apply
to Incomplete Vehicles and will not be shown on the Incomplete Vehicle
Label. The weight of the vehicle with occupants must never exceed the
front and rear GAWR or the GVWR.
The TARC is the weight of the permanently attached equipment that can
be added to the vehicle without violating the vehicle’s Safety Compliance
Certification. This includes the snowplow mounting hardware but does
not include the removable portion of the snowplow assembly.
Driving
154
ProCarManuals.com
Page 176 of 264
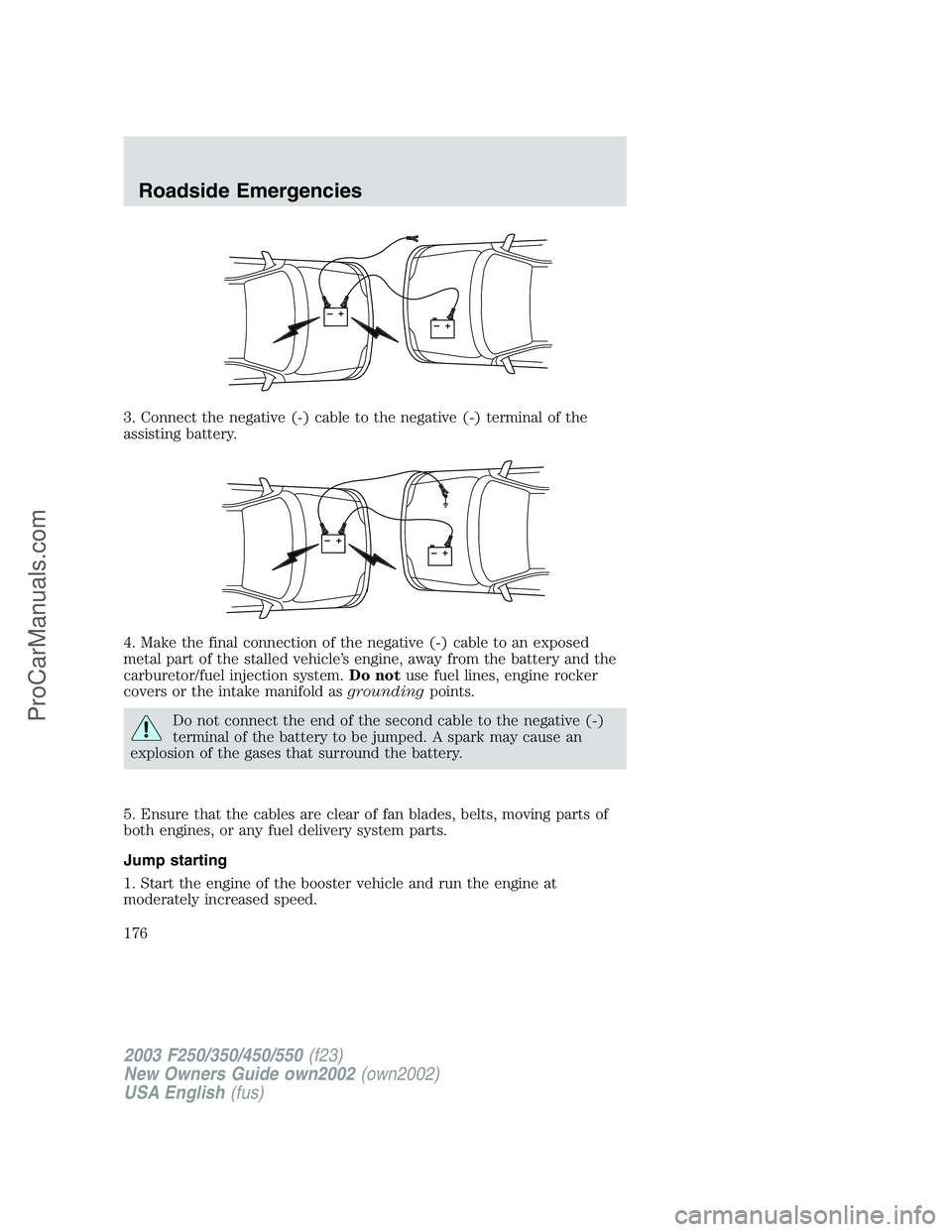
3. Connect the negative (-) cable to the negative (-) terminal of the
assisting battery.
4. Make the final connection of the negative (-) cable to an exposed
metal part of the stalled vehicle’s engine, away from the battery and the
carburetor/fuel injection system.Do notuse fuel lines, engine rocker
covers or the intake manifold asgroundingpoints.
Do not connect the end of the second cable to the negative (-)
terminal of the battery to be jumped. A spark may cause an
explosion of the gases that surround the battery.
5. Ensure that the cables are clear of fan blades, belts, moving parts of
both engines, or any fuel delivery system parts.
Jump starting
1. Start the engine of the booster vehicle and run the engine at
moderately increased speed.
+–+–
+–+–
2003 F250/350/450/550(f23)
New Owners Guide own2002(own2002)
USA English(fus)
Roadside Emergencies
176
ProCarManuals.com
Page 185 of 264

Board membership
The Board consists of:
•Three consumer representatives
•A Ford or Lincoln Mercury dealership representative
Consumer candidates for Board membership are recruited and trained by
an independent consulting firm. The dealership Board member is chosen
from Ford and Lincoln Mercury dealership management, recognized for
their business leadership qualities.
What the Board needs
To have your case reviewed you must complete the application in the
DSB brochure and mail it to the address provided on the application
form. Some states will require you to use certified mail, with return
receipt requested.
Your application is reviewed and, if it is determined to be eligible, you
will receive an acknowledgment indicating:
•The file number assigned to your application.
•The toll-free phone number of the DSB’s independent administrator.
Your dealership and a Ford Motor Company representative will then be
asked to submit statements.
To properly review your case, the Board needs the following information:
•Legible copies of all documents and maintenance or repair orders
relevant to the case.
•The year, make, model, and Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) listed
on your vehicle ownership license.
•The date of repair(s) and mileage at the time of occurrence(s).
•The current mileage.
•The name of the dealer(s) who sold or serviced the vehicle.
•A brief description of your unresolved concern.
•A brief summary of the action taken by the dealer(s) and Ford Motor
Company.
•The names (if known) of all the people you contacted at the
dealership(s).
•A description of the action you expect to resolve your concern.
You will receive a letter of explanation if your application does not
qualify for Board review.
Oral presentations
If you would like to make an oral presentation, indicate YES to question
6 on the application. While it is your right to make an oral presentation
Customer Assistance
185
ProCarManuals.com
Page 216 of 264

•Have the vehicle loading and distribution the same every time.
Your results will be most accurate if your filling method is consistent.
Calculating fuel economy
1. Fill the fuel tank completely and record the initial odometer reading
(in kilometers or miles).
2. Each time you fill the tank, record the amount of fuel added (in liters
or gallons).
3. After at least three to five tank fill-ups, fill the fuel tank and record
the current odometer reading.
4. Subtract your initial odometer reading from the current odometer
reading.
5. Follow one of the simple calculations in order to determine fuel
economy:
Multiply liters used by 100, then divide by total kilometers
traveled.
Divide total miles traveled by total gallons used.
Keep a record for at least one month and record the type of driving (city
or highway). This will provide an accurate estimate of the vehicle’s fuel
economy under current driving conditions. Additionally, keeping records
during summer and winter will show how temperature impacts fuel
economy. In general, lower temperatures give lower fuel economy.
Driving style — good driving and fuel economy habits
Give consideration to the lists that follow and you may be able to change
a number of variables and improve your fuel economy.
Habits
•Smooth, moderate operation can yield up to 10% savings in fuel.
•Steady speeds without stopping will usually give the best fuel
economy.
•Idling for long periods of time (greater than one minute) may waste
fuel.
•Anticipate stopping; slowing down may eliminate the need to stop.
•Sudden or hard accelerations may reduce fuel economy.
•Slow down gradually.
•Driving at reasonable speeds (traveling at 88 km/h [55 mph] uses 15%
less fuel than traveling at 105 km/h [65 mph]).
Maintenance and Specifications
216
ProCarManuals.com