2002 CHRYSLER VOYAGER 8w wiring
[x] Cancel search: 8w wiringPage 1385 of 2399

CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head cover is made of cast aluminum
and is also the intake manifold on this engine (Fig.
22).
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Before removing the cylinder head cover/
intake manifold the engine must put at 90É after
TDC. Failure to do so could result in valve and/or
piston damage during reassembly. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
REMOVAL).
(4) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Rotate engine until 90É after TDC is reached.
Install both camshaft locking pins and the crankshaft
locking pin. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(6) Remove air cleaner housing assembly.
(7) Remove power steering belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).(8) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(9) Remove generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOVAL).
(10) Support engine and remove right engine
mount (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/
RIGHT MOUNT - REMOVAL).
(11) Remove outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(12) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove inner timing belt cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(14) Disconnect camshaft position sensor, boost
pressure/intake air temperature sensor, EGR sole-
noid, and fuel pressure sensor electrical connectors
(Fig. 23).
Fig. 22 CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE
MANIFOLD
Fig. 23 ENGINE COMPONENT LOCATIONS
1 - FUEL INJECTOR RETURN LINE
2 - FUEL INJECTOR SUPPLY LINE
3 - OIL SEPARATOR
4 - FUEL INJECTOR
5 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
6 - BOOST PRESSURE/INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
7 - EGR SOLENOID
8 - FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
9 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOL
10 - FUEL RAIL
11 - WIRING HARNESS RETAINING CLIPS
9a - 24 ENGINERG
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1387 of 2399

NOTE: Be sure to lubricate cylinder head cover/in-
take manifold retaining bolts with engine oil before
assembly. If new bolts are being installed, DO NOT
lubricate before assembly.
(6) Install two cylinder head cover/intake manifold
retaining bolts and tighten finger tight.
(7) Remove alignment studs and install remaining
retaining bolts (Fig. 24). Tighten retaining bolts fin-
ger tight.
(8) Torque cylinder head cover/intake manifold
retaining bolts following procedure below.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
TIGHTENING PROCEDURE
(1) Coat all bolts being reused with clean engine
oil.
(2) Install the M8x35 bolts into holes 1,2,3,4,5, and
12. Install the M8x85 bolts into holes
6,7,8,9,10,11,13,14,15, and 16. Tighten all bolthand
tight.
(3) Alternate between bolts #11 and #16 to seat
cylinder head cover/intake manifold on cylinder head
(Fig. 27). Torque bolts to 7 N´m.
(4) Torque all cylinder head cover/intake manifold
retaining bolts to 25 N´m in numerical order starting
with #1 and ending with #16 (Fig. 27).(9) Connect EGR tube at intake manifold inlet
tube. Torque clamp to 10.8 N´m.
(10) Install turbo inlet tube retaining bolt at
intake manifold. Torque bolt to 27.5 N´m.
(11) Connect oil separator outlet hose at separator.
(12) Install oil dipstick tube retaining bolt at
intake manifold inlet. Torque bolt to 10 N´m.
(13) Install power steering pump reservoir in
bracket.
(14) Install fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - INSTALLATION).
(15) Install fuel injectors and fuel injector supply
lines (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJEC-
TION/FUEL INJECTOR - INSTALLATION).
(16) Connect vacuum lines at EGR solenoid.
(17) Clip wiring harness retainers on studs on fuel
rail (Fig. 23).
(18) Connect camshaft position sensor, boost pres-
sure/intake air temperature sensor, EGR solenoid,
and fuel pressure sensor electrical connectors (Fig.
23).
(19) Install inner timing belt cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(20) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION) .
(21) Install outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
Fig. 26 CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE
MANIFOLD ALIGNMENT STUDS VM.1066
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD ALIGNMENT
STUDS VM.1066
2 - CYLINDER HEAD
Fig. 27 CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE
MANIFOLD TIGHTENING SEQUENCE
9a - 26 ENGINERG
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1459 of 2399

FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump module is installed in the top of the
fuel tank (Fig. 10) .
The fuel pump module contains the following:
²Electric fuel pump
²Fuel pump reservoir
²Inlet strainer
²Fuel pressure regulator
²Fuel gauge sending unit
²Fuel supply line connection
The inlet strainer, fuel pressure regulator
and fuel level sensor are the only serviceable
items. If the fuel pump or electrical wiring har-
ness requires service, replace the fuel pump
module.
The electric fuel pump is located in and is part of
the fuel pump module. It is a positive displacement,
gerotor type, immersible pump with a permanent
magnet electric motor.
OPERATION
The pump draws fuel through a strainer and
pushes it through the motor to the outlet. The pump
contains one check valve. The check valve, in the
pump outlet, maintains pump pressure during engine
off conditions. The fuel pump relay provides voltage
to the fuel pump.
The fuel pump has a maximum deadheaded pres-
sure output of approximately 880 kPa (130 psi). The
regulator adjusts fuel system pressure to approxi-
mately 400 34 kPa (58 5 psi).
FUEL PUMP ELECTRICAL CONTROL
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay. For an electrical opera-tional description of the fuel pump refer to fuel Pump
RelayÐPCM Output.
ELECTRICAL PUMP REPLACEMENT
The electric fuel pump is not serviceable. If the
fuel pump or electrical wiring harness needs replace-
ment, the complete fuel pump module must be
replaced. Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release
procedure before servicing the fuel pump.
REMOVAL
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE.
(1) Remove fuel filler cap and perform Fuel Sys-
tem Pressure Release procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from auxiliary
jumper terminal.
(3) Drain fuel tank, refer to the Fuel Tank proce-
dure in the Fuel Delivery section.
(4) Remove fuel tank, refer to the Fuel Tank
removal section.
(5) Clean top of tank to remove loose dirt and
debris.
(6) Using a brass punch and hammer remove lock-
nut to release pump module (Fig. 11).
Fig. 10 Fuel Pump Module
1 - INLET STRAINER
2 - FUEL RESERVOIR
3 - FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - FUEL LEVEL SENSOR
Fig. 11 FUEL PUMP MODULE LOCKING RING
14 - 8 FUEL DELIVERYRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1460 of 2399

WARNING: THE FUEL RESERVOIR OF THE FUEL
PUMP MODULE DOES NOT EMPTY OUT WHEN THE
TANK IS DRAINED. THE FUEL IN THE RESERVOIR
MAY SPILL OUT WHEN THE MODULE IS REMOVED.
(7) Remove fuel pump module and O-ring from
tank (Fig. 12). Discard O-ring.
INSTALLATION
(1) Wipe seal area of tank clean and place a new
O-ring seal in position on pump.
(2) Position fuel pump module in tank.
(3) Tighten locknut using a brass punch and ham-
mer to install the locknut (Fig. 11).
(4) Install fuel tank, refer to the Fuel Tank instal-
lation section.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Connect negative cable battery.
(7) Fill fuel tank. Check for leaks.
(8) Install fuel filler cap.
FUEL RAIL
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before servicing or starting repairs.Refer to
Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure in this sec-
tion.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Disconnect the wiring connectors for fuel injec-
tors harness (Fig. 13).
(4) Remove wiring harness from brackets.(5) Disconnect the connectors from the fuel injec-
tors.
(6) Remove harness from vehicle.
(7) Remove fuel hose quick connect fitting from the
chassis tube.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.Place a
shop towel under the connections to absorb any fuel
spilled from the fitting.
WARNING: WRAP A SHOP TOWEL AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(8) Remove fuel rail attaching bolts.
(9) Remove fuel rail. Be careful not to damage the
injector O-rings upon removal from their ports.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before servicing or starting repairs.Refer to
Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure in this sec-
tion.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Remove upper intake manifold, refer to the
Engine/Manifolds/Upper Intake for more informa-
tion..
(4) Cover intake manifold with suitable cover
when servicing.
(5) Remove the fuel hose quick connect fitting from
the chassis tube.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps
and Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.
WARNING: WRAP A SHOP TOWEL AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(6) Remove the fuel rail attaching bolts (Fig. 14).
(7) Remove fuel rail. Be careful not to damage the
injector O-rings upon removal from their ports.
Fig. 12 Fuel Pump Module Removal
1 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
2 - O-RING
Fig. 13 FUEL RAIL AND INJECTORS 2.4L
1 - Fuel Injectors
2 - Fuel Rail
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-9
FUEL PUMP MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1461 of 2399

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Ensure injector holes are clean. Replace
O-rings if damaged.
(2) Lubricate injector O-rings with a drop of clean
engine oil to ease installation.
(3) Put the tip of each injector into their ports.
Push the assembly into place until the injectors are
seated in the ports.
(4) Install the fuel rail mounting bolts. Tighten
bolts to 22 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect the connectors to the fuel injectors.
(6) Install wiring harness to brackets.
(7) Connect the wiring connectors to fuel injectors
harness (Fig. 13).
(8) Connect negative battery cable.
(9) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to pressurize the
fuel system. Check for leaks.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Ensure injector holes are clean. Replace
O-rings if damaged.
(2) Lubricate injector O-rings with a drop of clean
engine oil to ease installation.
(3) Put the tip of each injector into their ports.
Push the assembly into place until the injectors are
seated in the ports.
(4) Install the fuel rail mounting bolts. Tighten
bolts to 22 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Remove covering on lower intake manifold and
clean surface.
(6) Install the Upper Intake Manifold, refer to
Engine/Manifolds/Upper Intake for more information.(7) Install fuel hose quick connector fitting to chas-
sis tubes.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.Push the
fitting onto the chassis tube until it clicks into place.
Pull on the fitting to ensure complete insertion.
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
(9) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to pressurize the
fuel system. Check for leaks.
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION
The fuel tank is constructed of a plastic material.
Its main functions are for fuel storage and for place-
ment of the fuel pump module. The tank is made
from High density Polyethylene (HDPE) material.If
equipped with ORVR (Onboard Refueling Vapor
Recovery) it has been added to the fuel tank to con-
trol refueling vapor emissions.
OPERATION
All models pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.
All models are equipped with either one or two
rollover valves mounted into the top of the fuel tank
(or pump module).
An evaporation control system is connected to the
rollover valve(s)/control valve(Refer to 25 - EMIS-
SIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS/
ORVR - OPERATION) to reduce emissions of fuel
vapors into the atmosphere, when the tank is vented
due to vapor expansion in the tank. When fuel evap-
orates from the fuel tank, vapors pass through vent
hoses or tubes to a charcoal canister where they are
temporarily held. When the engine is running, the
vapors are drawn into the intake manifold. In addi-
tion, fuel vapors produced during vehicle refueling
are allowed to pass through the vent hoses/tubes to
the charcoal canister(s) for temporary storage (prior
to being drawn into the intake manifold). All models
are equipped with a self-diagnosing system using a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP). Refer to the Emission
Control System for additional information.
INLET CHECK VALVE
All vehicles have an inlet check valve on the inside
of the fuel tank at the filler inlet
The valve prevents fuel from splashing back on
customer during vehicle refueling. The valve is a
non-serviceable item.
Fig. 14 FUEL INJECTORS 3.3/3.8L
14 - 10 FUEL DELIVERYRS
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1471 of 2399

Long Term
The second fuel correction program is the long
term adaptive memory. In order to maintain correct
emission throughout all operating ranges of the
engine, a cell structure based on engine rpm and load
(MAP) is used.
Ther number of cells varies upon the driving con-
ditions. Two cells are used only during idle, based
upon TPS and Park/Neutral switch inputs. There
may be two other cells used for deceleration, based
on TPS, engine rpm, and vehicle speed. The other
twelve cells represent a manifold pressure and an
rpm range. Six of the cells are high rpm and the
other six are low rpm. Each of these cells is a specific
MAP voltage range Typical Adaptive Memory Fuel
Cells .
As the engine enters one of these cells the PCM
looks at the amount of short term correction being
used. Because the goal is to keep short term at 0 (O2
Sensor switching at 0.5 volt), long term will updatein the same direction as short term correction was
moving to bring the short term back to 0. Once short
term is back at 0, this long term correction factor is
stored in memory.
The values stored in long term adaptive memory
are used for all operating conditions, including open
loop and cold starting. However, the updating of the
long term memory occurs after the engine has
exceeded approximately 170É-190É F, with fuel control
in closed loop and two minutes of engine run time.
This is done to prevent any transitional temperature
or start-up compensations from corrupting long term
fuel correction.
Long term adaptive memory can change the pulse-
width by as much as 25%, which means it can correct
for all of short term. It is possible to have a problem
that would drive long term to 25% and short term to
another 25% for a total change of 50% away from
base pulse-width calculation.
TYPICAL ADAPTIVE MEMORY FUEL CELLS
Open
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
Throttle Idle Decel
Vacuum 20 17 13 9 5 0
Above 1,984
rpm1 3 5 7 9 11 13 Drive 15
Below 1,984
rpm02 4 6 8 1012
Neutral14
MAP volt =0 1.4 2.0 2.6 3.3 3.9
Fuel Correction Diagnostics
There are two fuel correction diagnostic routines:
²Fuel System Rich
²Fuel System Lean
A DTC is set and the MIL is illuminated if the
PCM detects either of these conditions. This is deter-
mined based on total fuel correction, short term
times long term.
PROGRAMMABLE COMMUNICATIONS
INTERFACE (PCI) BUS
DESCRIPTION
The Programmable Communication Interface Mul-
tiplex system (PCI Bus) consist of a single wire. The
Body Control Module (BCM) acts as a splice to con-
nect each module and the Data Link Connector
(DLC) together. Each module is wired in parallel to
the data bus through its PCI chip set and uses its
ground as the bus reference. The wiring is a mini-
mum 20 gage wire.
OPERATION
Various modules exchange information through a
communications port called the PCI Bus. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) transmits the Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp (Check Engine) On/Off signal
and engine RPM on the PCI Bus. The PCM receives
the Air Conditioning select input, transaxle gear
position inputs over the PCI Bus. The PCM also
receives the air conditioning evaporator temperature
signal from the PCI Bus.
The following components access or send informa-
tion on the PCI Bus.
²Instrument Panel
²Body Control Module
²Air Bag System Diagnostic Module
²Full ATC Display Head (if equipped)
²ABS Module
²Transmission Control Module
²Powertrain Control Module
²Travel Module
²SKIM
14 - 20 FUEL INJECTIONRS
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1476 of 2399
OPERATION
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) supplies
the road speed and distance traveled inputs to the
PCM. From these inputs and the throttle position
sensor input, the PCM determines when a decelera-
tion condition occurs.
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION
The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold
or cylinder head with the nozzle ends directly above
the intake valve port (Fig. 9).
OPERATION
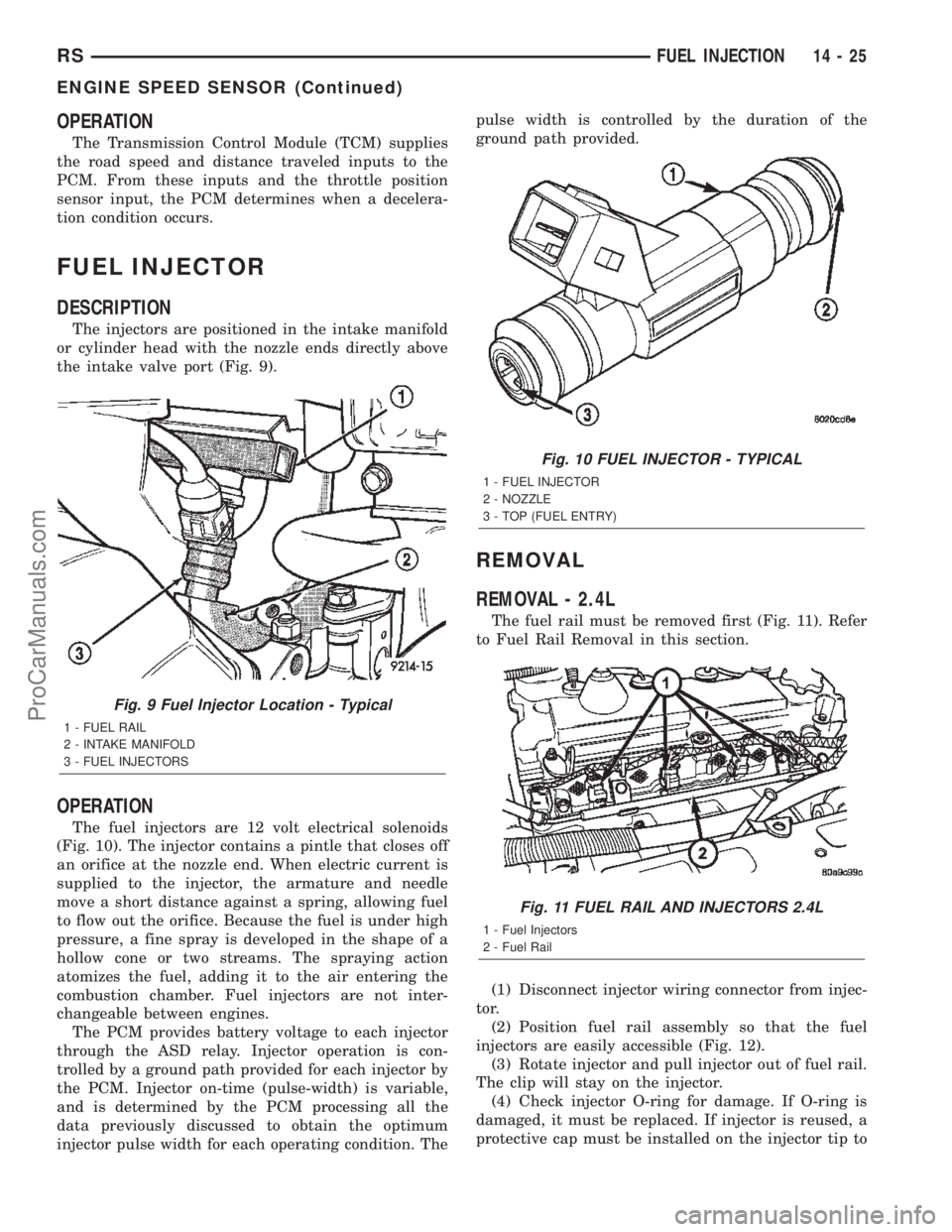
The fuel injectors are 12 volt electrical solenoids
(Fig. 10). The injector contains a pintle that closes off
an orifice at the nozzle end. When electric current is
supplied to the injector, the armature and needle
move a short distance against a spring, allowing fuel
to flow out the orifice. Because the fuel is under high
pressure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a
hollow cone or two streams. The spraying action
atomizes the fuel, adding it to the air entering the
combustion chamber. Fuel injectors are not inter-
changeable between engines.
The PCM provides battery voltage to each injector
through the ASD relay. Injector operation is con-
trolled by a ground path provided for each injector by
the PCM. Injector on-time (pulse-width) is variable,
and is determined by the PCM processing all the
data previously discussed to obtain the optimum
injector pulse width for each operating condition. Thepulse width is controlled by the duration of the
ground path provided.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L
The fuel rail must be removed first (Fig. 11). Refer
to Fuel Rail Removal in this section.
(1) Disconnect injector wiring connector from injec-
tor.
(2) Position fuel rail assembly so that the fuel
injectors are easily accessible (Fig. 12).
(3) Rotate injector and pull injector out of fuel rail.
The clip will stay on the injector.
(4) Check injector O-ring for damage. If O-ring is
damaged, it must be replaced. If injector is reused, a
protective cap must be installed on the injector tip to
Fig. 9 Fuel Injector Location - Typical
1 - FUEL RAIL
2 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 - FUEL INJECTORS
Fig. 10 FUEL INJECTOR - TYPICAL
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - NOZZLE
3 - TOP (FUEL ENTRY)
Fig. 11 FUEL RAIL AND INJECTORS 2.4L
1 - Fuel Injectors
2 - Fuel Rail
RSFUEL INJECTION14-25
ENGINE SPEED SENSOR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1477 of 2399

prevent damage. Replace the injector clip if it is dam-
aged.
(5) Repeat for remaining injectors.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the Intake Manifold, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL)
(3) Disconnect injector wiring connector from injec-
tor.
(4) Position fuel rail assembly so that the fuel
injectors are easily accessible (Fig. 12).
(5) Rotate injector and pull injector out of fuel rail.
The clip will stay on the injector.
(6) Check injector O-ring for damage. If O-ring is
damaged, it must be replaced. If injector is reused, a
protective cap must be installed on the injector tip to
prevent damage. Replace the injector clip if it is dam-
aged.
(7) Repeat for remaining injectors.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The fuel rail must be removed first. Refer to Fuel
Injector Rail Removal in this section.(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.
(2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into the
top slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip.
(3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during installa-
tion (Fig. 13).
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Connect fuel injector wiring.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.
(2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into the
top slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip (Fig. 12).
(3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during installa-
tion (Fig. 12).
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Install fuel rail, refer to Fuel Rail in the Fuel
Delivery section.
(6) Connect fuel injector wiring.
(7) Install the Intake Manifold, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
(8) Connect the negative battery cable.
Fig. 12 FUEL INJECTOR AND RAIL TYPICAL
1 - FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
2 - FUEL INJECTOR
3 - FUEL RAIL RECEIVER
Fig. 13 SERVICING FUEL INJECTOR TYPICAL
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - LOCKING SLOT
3 - FUEL RAIL RECEIVER CUP
14 - 26 FUEL INJECTIONRS
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com