2002 CHRYSLER TOWN AND COUNTRY catalytic converter
[x] Cancel search: catalytic converterPage 1482 of 2399

The downstream heated oxygen sensor threads into
the outlet pipe at the rear of the catalytic convertor
(Fig. 22).
OPERATION
A single sensor ground is used for all O2 sensors (2
senors on 4 cyl. vehicles and 4 sensors on 6 cyl. vehi-
cles).
As vehicles accumulate mileage, the catalytic con-
vertor deteriorates. The deterioration results in a
less efficient catalyst. To monitor catalytic convertor
deterioration, the fuel injection system uses two
heated oxygen sensors. One sensor upstream of the
catalytic convertor, one downstream of the convertor.
The PCM compares the reading from the sensors to
calculate the catalytic convertor oxygen storage
capacity and converter efficiency. Also, the PCM uses
the upstream heated oxygen sensor input when
adjusting injector pulse width.
When the catalytic converter efficiency drops below
emission standards, the PCM stores a diagnostic
trouble code and illuminates the malfunction indica-
tor lamp (MIL).
The O2 sensors produce voltages from 0 to 1 volt,
depending upon the oxygen content of the exhaust
gas. When a large amount of oxygen is present
(caused by a lean air/fuel mixture, can be caused by
misfire and exhaust leaks), the sensors produces a
low voltage. When there is a lesser amount of oxygen
present (caused by a rich air/fuel mixture, can be
caused by internal engine problems) it produces a
higher voltage. By monitoring the oxygen content
and converting it to electrical voltage, the sensors act
as a rich-lean switch.The oxygen sensors are equipped with a heating
element that keeps the sensors at proper operating
temperature during all operating modes. Maintaining
correct sensor temperature at all times allows the
system to enter into closed loop operation sooner.
Also, it allows the system to remain in closed loop
operation during periods of extended idle.
In Closed Loop operation the PCM monitors the O2
sensors input (along with other inputs) and adjusts
the injector pulse width accordingly. During Open
Loop operation the PCM ignores the O2 sensor input.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width based on pre-
programmed (fixed) values and inputs from other
sensors.
The Automatic Shutdown (ASD) relay supplies bat-
tery voltage to both the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The oxygen sensors are
equipped with a heating element. The heating ele-
ments reduce the time required for the sensors to
reach operating temperature. The PCM uses pulse
width modulation to control the ground side of the
heater to regulate the temperature on 4 cyl.
upstream O2 heater only. All other 4 cyl. and 6 cyl.
O2 heaters do not use pulse width modulation.
UPSTREAM OXYGEN SENSOR
The input from the upstream heated oxygen sensor
tells the PCM the oxygen content of the exhaust gas.
Based on this input, the PCM fine tunes the air-fuel
ratio by adjusting injector pulse width.
The sensor input switches from 0 to 1 volt, depend-
ing upon the oxygen content of the exhaust gas in
the exhaust manifold. When a large amount of oxy-
gen is present (caused by a lean air-fuel mixture), the
sensor produces voltage as low as 0.1 volt. When
there is a lesser amount of oxygen present (rich air-
fuel mixture) the sensor produces a voltage as high
as 1.0 volt. By monitoring the oxygen content and
converting it to electrical voltage, the sensor acts as
a rich-lean switch.
The heating element in the sensor provides heat to
the sensor ceramic element. Heating the sensor
allows the system to enter into closed loop operation
sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain in closed
loop operation during periods of extended idle.
In Closed Loop, the PCM adjusts injector pulse
width based on the upstream heated oxygen sensor
input along with other inputs. In Open Loop, the
PCM adjusts injector pulse width based on prepro-
grammed (fixed) values and inputs from other sen-
sors.
DOWNSTREAM OXYGEN SENSOR
The downstream heated oxygen sensor input is
used to detect catalytic convertor deterioration. As
the convertor deteriorates, the input from the down-
Fig. 22 O2 SENSOR DOWNSTREAM 1/2 - 2.4/3.3/
3.8L
RSFUEL INJECTION14-31
O2 SENSOR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1483 of 2399

stream sensor begins to match the upstream sensor
input except for a slight time delay. By comparing
the downstream heated oxygen sensor input to the
input from the upstream sensor, the PCM calculates
catalytic convertor efficiency. Also used to establish
the upstream O2 goal voltage (switching point).
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - UPSTREAM 1/1 - 2.4L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Disconnect the electrical connector (Fig. 21).
(4) Use a socket such as the Snap-OntYA8875 or
equivalent to remove the sensor
(5) When the sensor is removed, the threads must
be cleaned with an 18 mm X 1.5 + 6E tap. If using
the original sensor, coat the threads with Loctite
771±64 anti-seize compound or equivalent.
REMOVAL - UPSTREAM 1/1 - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Remove battery, refer to the Battery section for
more information.
(2) Remove the battery tray, refer to the Battery
section for more information.
(3) Disconnect the speed control vacuum harness
from servo.
(4) Disconnect the electrical connector from servo.
(5) Remove the speed control servo and bracket
and reposition.
(6) Use a socket such as the Snap-OntYA8875 or
equivalent to remove the sensor (Fig. 23).(7) When the sensor is removed, the threads must
be cleaned with an 18 mm X 1.5 + 6E tap. If using
the original sensor, coat the threads with Loctite
771±64 anti-seize compound or equivalent.
REMOVAL - DOWNSTREAM 1/2 - 2.4/3.3/3.8L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Disconnect the electrical connector (Fig. 24).
(4) Use a socket such as the Snap-OntYA8875 or
equivalent to remove the sensor (Fig. 25).
(5) When the sensor is removed, the threads must
be cleaned with an 18 mm X 1.5 + 6E tap. If using
the original sensor, coat the threads with Loctite
771±64 anti-seize compound or equivalent.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - UPSTREAM 1/1 - 2.4L
The engines uses two heated oxygen sensors.
(1) After removing the sensor, the exhaust mani-
fold threads must be cleaned with an 18 mm X 1.5 +
6E tap. If reusing the original sensor, coat the sensor
threads with an anti-seize compound such as Loctite
771- 64 or equivalent. New sensors have compound
on the threads and do not require an additional coat-
ing.
(2) Install sensor and tighten to 27 N´m (20 ft.
lbs.) (Fig. 21).
(3) Connect the electrical connector for the O2 sen-
sor and install onto bracket.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
Fig. 23 O2 SENSOR 1/1
Fig. 24 Downstream Oxygen Sensor (1/2)
1 - OXYGEN SENSOR CONNECTOR
2 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
3 - DOWNSTREAM OXYGEN SENSOR
4 - ENGINE HARNESS CONNECTOR
14 - 32 FUEL INJECTIONRS
O2 SENSOR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1541 of 2399

(2) Fill the fluid reservoir to the proper level and
let the fluid settle for at least two (2) minutes.
(3) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds,
then turn the engine off.
(4) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above steps
until the fluid level remains constant after running
the engine.
(5) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(6) Start the engine.
(7) Slowly turn the steering wheel right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops.
(8) Add fluid if necessary.
(9) Lower the vehicle, then turn the steering wheel
slowly from lock-to-lock.
(10) Stop the engine. Check the fluid level and
refill as required.
(11) If the fluid is extremely foamy, allow the vehi-
cle to stabilize a few minutes, then repeat the above
procedure.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - PUMP (2.4L ENGINE)
(1) Remove the (-) negative battery cable from the
battery and isolate cable.
(2) Remove the cap from the power steering fluid
reservoir.
(3) Using a siphon pump, remove as much power
steering fluid as possible from the power steering
fluid reservoir.
(4) Raise the vehicle on jack stands or centered on
a frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in Lubrica-
tion and Maintenance.
(5) Disconnect the oxygen sensor wiring harness
from the vehicle wiring harness at the rear engine
mount bracket.
NOTE: The exhaust system needs to be removed
from the engine to allow for an area to remove the
power steering pump from the vehicle.
(6) Remove the four bolts and flag nuts securing
the catalytic converter from the exhaust manifold
(Fig. 3).(7) Disconnect all the exhaust system isolators/
hangers from the brackets on the exhaust system (2
at the mufflers and 1 at the resonator) (Fig. 4).
(8) Remove the exhaust system by moving it as far
rearward, then lowering the front below the cross-
member and out of the vehicle.
(9) Remove the power steering fluid supply hose
from the fitting on the power steering pump. Drain
off excess power steering fluid from hose.
(10) Move the heat sleeve on the power steering
return hose to expose the hose connection at the
pump (Fig. 5). Remove the hose from the power
steering Pump. Allow the remaining power steering
fluid to drain from the power steering pump and res-
ervoir through the removed return hose.
(11) Remove the power steering fluid pressure line
from the power steering pump (Fig. 6). Drain excess
power steering fluid from tube.
(12) Remove the fasteners, then the accessory
drive splash shield.
Fig. 3 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
1 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
2 - BOLT
3 - GASKET
4 - FLAG NUT
19 - 38 PUMPRS
PUMP (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1542 of 2399
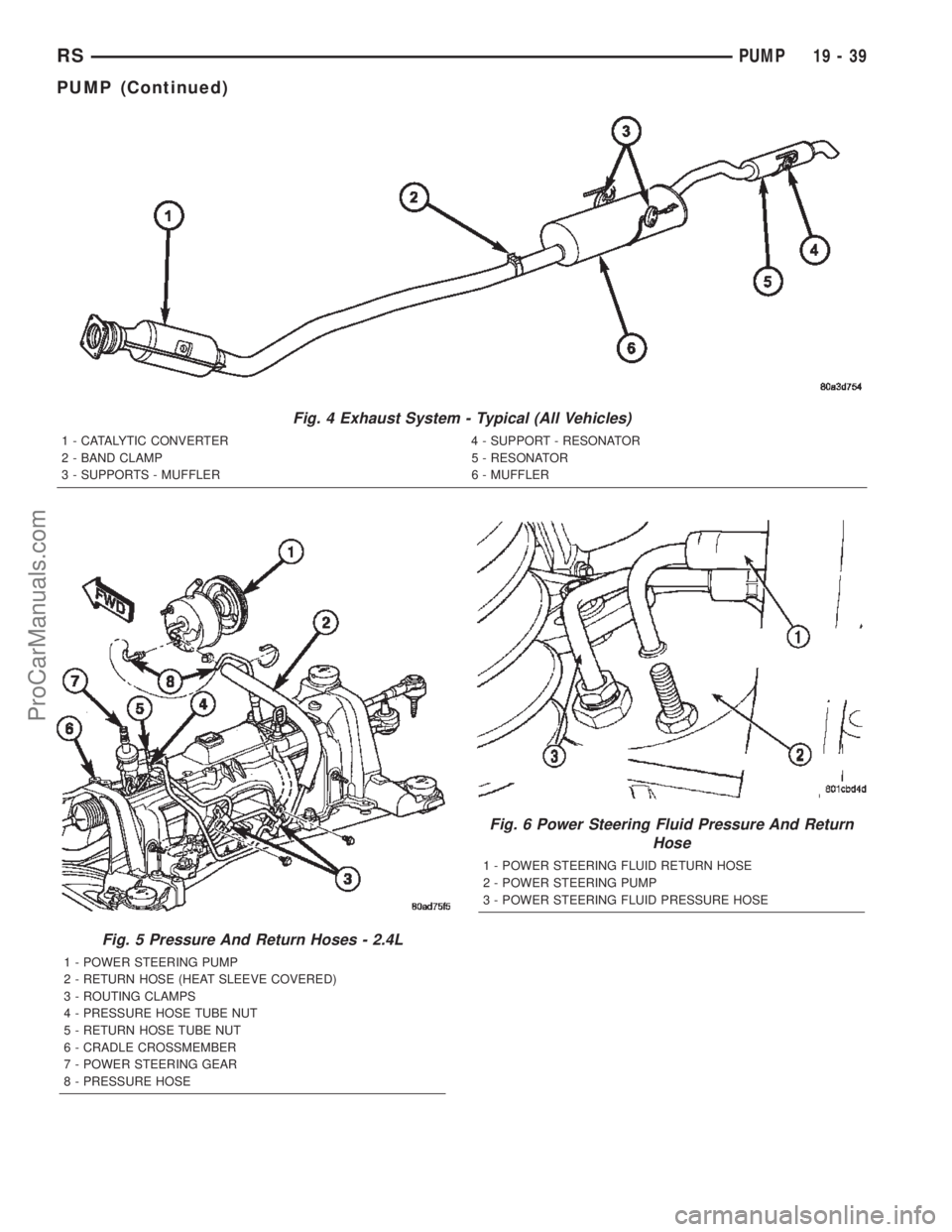
Fig. 4 Exhaust System - Typical (All Vehicles)
1 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER 4 - SUPPORT - RESONATOR
2 - BAND CLAMP 5 - RESONATOR
3 - SUPPORTS - MUFFLER 6 - MUFFLER
Fig. 5 Pressure And Return Hoses - 2.4L
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP
2 - RETURN HOSE (HEAT SLEEVE COVERED)
3 - ROUTING CLAMPS
4 - PRESSURE HOSE TUBE NUT
5 - RETURN HOSE TUBE NUT
6 - CRADLE CROSSMEMBER
7 - POWER STEERING GEAR
8 - PRESSURE HOSE
Fig. 6 Power Steering Fluid Pressure And Return
Hose
1 - POWER STEERING FLUID RETURN HOSE
2 - POWER STEERING PUMP
3 - POWER STEERING FLUID PRESSURE HOSE
RSPUMP19-39
PUMP (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2363 of 2399

The PCM sends a 5 volt bias to the oxygen sensor
every 1.6 seconds. The PCM keeps it biased for 35
ms each time. As the sensor cools down, the resis-
tance increases and the PCM reads the increase in
voltage. Once voltage has increased to a predeter-
mined amount, higher than when the test started,
the oxygen sensor is cool enough to test heater oper-
ation.
When the oxygen sensor is cool enough, the PCM
energizes the ASD relay. Voltage to the O2 sensor
begins to increase the temperature. As the sensor
temperature increases, the internal resistance
decreases. The PCM continues biasing the 5 volt sig-
nal to the sensor. Each time the signal is biased, the
PCM reads a voltage decrease. When the PCM
detects a voltage decrease of a predetermined value
for several biased pulses, the test passes.
The heater elements are tested each time the
engine is turned OFF if all the enabling conditions
are met. If the monitor fails, the PCM stores a
maturing fault and a Freeze Frame is entered. If two
consecutive tests fail, a DTC is stored. Because the
ignition is OFF, the MIL is illuminated at the begin-
ning of the next key cycle.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must be met for the PCM to run the oxygen sensor
heater test:
²Engine run time of at least 3 minutes
²Engine run time at a predetermind speed and
throttle opening.
²Key OFF power down
²Battery voltage of at least 10 volts
²Sufficient Oxygen Sensor cool down
Pending ConditionsÐThere are not conditions or
situations that prompt conflict or suspension of test-
ing. The oxygen sensor heater test is not run pending
resolution of MIL illumination due to oxygen sensor
failure.
SuspendÐThere are no conditions which exist for
suspending the Heater Monitor.
CATALYST MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide.
Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. A meltdown of the ceramic core can
cause a reduction of the exhaust passage. This can
increase vehicle emissions and deteriorate engine
performance, driveability and fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2S strategy is based on the fact that as a cat-
alyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity and its
efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring the oxy-gen storage capacity of a catalyst, its efficiency can
be indirectly calculated. The upstream O2S is used to
detect the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas
before the gas enters the catalytic converter. The
PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the output of
the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxygen content
(lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a low content
of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL (check
engine lamp) will be illuminated.
Monitor OperationÐTo monitor catalyst effi-
ciency, the PCM expands the rich and lean switch
points of the heated oxygen sensor. With extended
switch points, the air/fuel mixture runs richer and
leaner to overburden the catalytic converter. Once
the test is started, the air/fuel mixture runs rich and
lean and the O2 switches are counted. A switch is
counted when an oxygen sensor signal goes from
below the lean threshold to above the rich threshold.
The number of Rear O2 sensor switches is divided by
the number of Front O2 sensor switches to determine
the switching ratio.
The test runs for 20 seconds. As catalyst efficiency
deteriorated over the life of the vehicle, the switch
rate at the downstream sensor approaches that of the
upstream sensor. If at any point during the test
period the switch ratio reaches a predetermined
value, a counter is incremented by one. The monitor
25 - 4 EMISSIONS CONTROLRS
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2366 of 2399

Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperatures of 300É to 350ÉC (572 É to 662ÉF),
the sensor generates a voltage that is inversely pro-
portional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
The information obtained by the sensor is used to
calculate the fuel injector pulse width. This main-
tains a 14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture
ratio, the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons
(HC), carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide
(NOx) from the exhaust.
The voltage readings taken from the O2S are very
temperature sensitive. The readings are not accurate
below 300ÉC. Heating of the O2S is done to allow the
engine controller to shift to closed loop control as
soon as possible. The heating element used to heat
the O2S must be tested to ensure that it is heating
the sensor properly.
The O2S circuit is monitored for a drop in voltage.
The sensor output is used to test the heater by iso-
lating the effect of the heater element on the O2S
output voltage from the other effects.
EGR MONITOR (if equipped)
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) performs
an on-board diagnostic check of the EGR system.
The EGR monitor is used to test whether the EGR
system is operating within specifications. The diag-
nostic check activates only during selected engine/
driving conditions. When the conditions are met, the
EGR is turned off (solenoid energized) and the O2S
compensation control is monitored. Turning off the
EGR shifts the air fuel (A/F) ratio in the lean direc-
tion. The O2S data should indicate an increase in the
O2 concentration in the combustion chamber when
the exhaust gases are no longer recirculated. While
this test does not directly measure the operation of
the EGR system, it can be inferred from the shift in
the O2S data whether the EGR system is operating
correctly. Because the O2S is being used, the O2S
test must pass its test before the EGR test. Also
looks at EGR linear potentiometer for feedback.
MISFIRE MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.FUEL SYSTEM MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide. The catalyst works best
when the air fuel (A/F) ratio is at or near the opti-
mum of 14.7 to 1.
The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio. This is done by making short term cor-
rections in the fuel injector pulse width based on the
O2S output. The programmed memory acts as a self
calibration tool that the engine controller uses to
compensate for variations in engine specifications,
sensor tolerances and engine fatigue over the life
span of the engine. By monitoring the actual air-fuel
ratio with the O2S (short term) and multiplying that
with the program long-term (adaptive) memory and
comparing that to the limit, it can be determined
whether it will pass an emissions test. If a malfunc-
tion occurs such that the PCM cannot maintain the
optimum A/F ratio, then the MIL will be illuminated.
CATALYST MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide.
Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. A meltdown of the ceramic core can
cause a reduction of the exhaust passage. This can
increase vehicle emissions and deteriorate engine
performance, driveability and fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2S's strategy is based on the fact that as a cat-
alyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity and its
efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring the oxy-
gen storage capacity of a catalyst, its efficiency can
be indirectly calculated. The upstream O2S is used to
detect the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas
before the gas enters the catalytic converter. The
PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the output of
the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxygen content
(lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a low content
of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
RSEMISSIONS CONTROL25-7
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com