2002 CHRYSLER CARAVAN oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 1430 of 2399

OPERATION
Heat shields are needed to protect both the vehicle
and the environment from the high temperatures
developed near the catalytic converter.
Avoid application of rust prevention com-
pounds or undercoating materials to exhaust
system floor pan heat shields on cars so
equipped. Light over spray near the edges is
permitted. Application of coating will greatly
reduce the efficiency of the heat shields result-
ing in excessive floor pan temperatures and
objectionable fumes.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove fasteners attaching applicable heat
shield (Fig. 7), (Fig. 8), or (Fig. 9).
(3) Remove heat shield(s).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position heat shield(s) to underbody.
(2) Install heat shield fasteners and tighten to 2.6
N´m (23 in. lbs.) (Fig. 7), (Fig. 8), or (Fig. 9).
(3) Lower vehicle.
MUFFLER
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on a body contact type hoist.
NOTE: To provide removal clearance between muf-
fler/resonator pipe and rear axle parts, the rear sus-
pension must be relieved of all body weight.
(2) Apply a penetrating oil to clamp nuts of com-
ponent requiring removal.
CAUTION: When servicing the exhaust system, care
must be exercised not to dent or bend the bellows
of the flex-joint. Should this occur, the flex-joint will
eventually fail, requiring replacement of the cata-
lytic converter.
(3) Disconnect the right side axle half shaft from
the rear differential module (AWD equipped only).
Fig. 7 CATALYTIC CONVERTER HEAT SHIELD
1 - HEAT SHIELD - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
2 - SCREW (QTY. 4)
Fig. 8 MUFFLER HEAT SHIELD
1 - HEAT SHIELD - MUFFLER
2 - SCREW (QTY. 6)
Fig. 9 RESONATOR PIPE HEAT SHIELD
1 - SCREW (QTY. 3)
2 - HEAT SHIELD - RESONATOR PIPE
3 - MUFFLER
RSEXHAUST SYSTEM11-7
HEAT SHIELDS (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1436 of 2399
bearing housing, routes the engine oil back to the
crankcase.
The most common turbocharger failure is bearing
failure related to repeated hot shutdowns with inad-
equate ªcool-downº periods. A sudden engine shut
down after prolonged operation will result in the
transfer of heat from the turbine section of the tur-
bocharger to the bearing housing. This causes the oil
to overheat and break down, which causes bearing
and shaft damage the next time the vehicle is
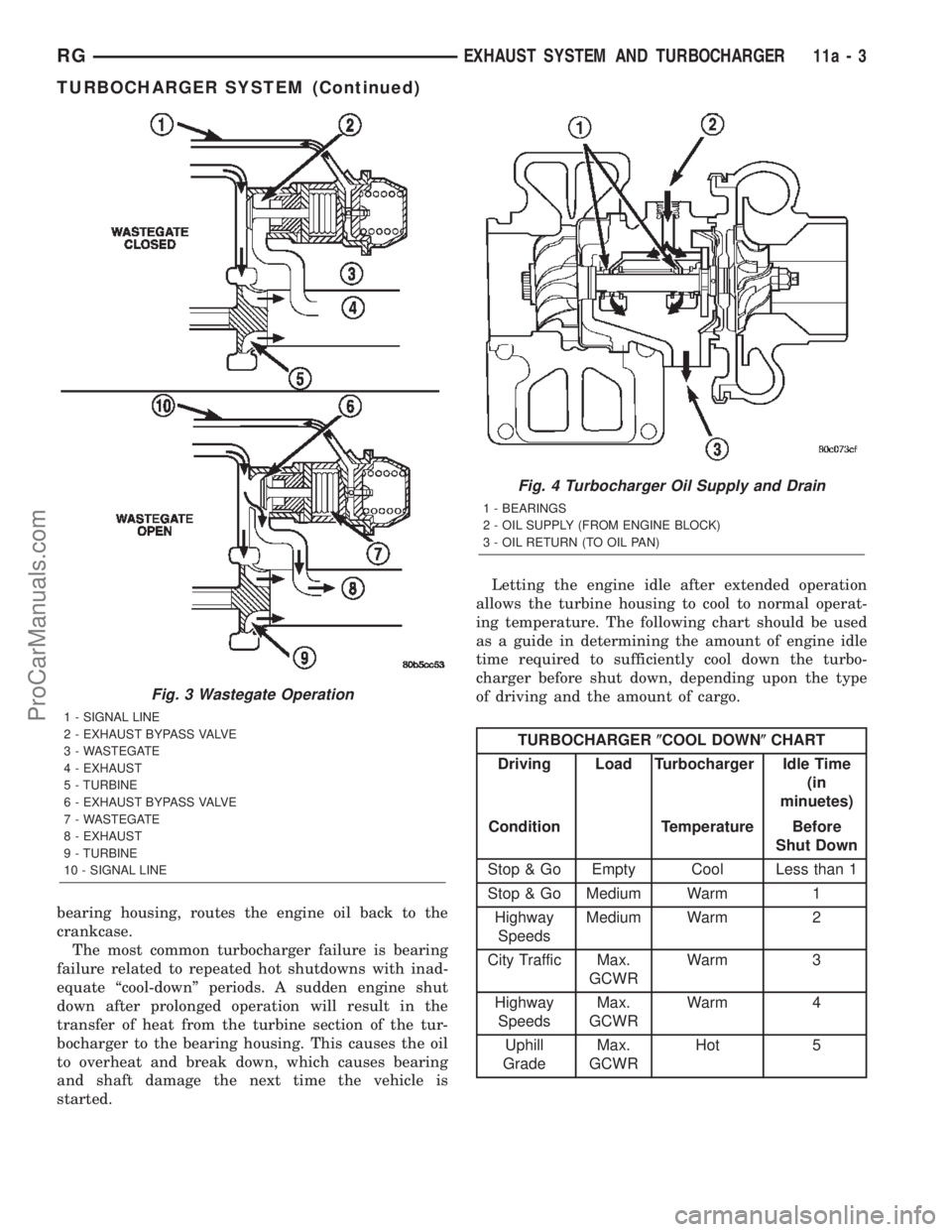
started.Letting the engine idle after extended operation
allows the turbine housing to cool to normal operat-
ing temperature. The following chart should be used
as a guide in determining the amount of engine idle
time required to sufficiently cool down the turbo-
charger before shut down, depending upon the type
of driving and the amount of cargo.
TURBOCHARGER(COOL DOWN(CHART
Driving Load Turbocharger Idle Time
(in
minuetes)
Condition Temperature Before
Shut Down
Stop & Go Empty Cool Less than 1
Stop & Go Medium Warm 1
Highway
SpeedsMedium Warm 2
City Traffic Max.
GCWRWarm 3
Highway
SpeedsMax.
GCWRWarm 4
Uphill
GradeMax.
GCWRHot 5
Fig. 3 Wastegate Operation
1 - SIGNAL LINE
2 - EXHAUST BYPASS VALVE
3 - WASTEGATE
4 - EXHAUST
5 - TURBINE
6 - EXHAUST BYPASS VALVE
7 - WASTEGATE
8 - EXHAUST
9 - TURBINE
10 - SIGNAL LINE
Fig. 4 Turbocharger Oil Supply and Drain
1 - BEARINGS
2 - OIL SUPPLY (FROM ENGINE BLOCK)
3 - OIL RETURN (TO OIL PAN)
RGEXHAUST SYSTEM AND TURBOCHARGER11a-3
TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1448 of 2399

SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Front Cradle Crossmember to Fram Rail Attaching Bolts (4) 163 120 Ð
Reinforcement Plate to Crossmember Attaching Bolt Size M14 (9) 153 113 Ð
Reinforcement Plate to Crossmember Attaching Bolt Size M12 (1) 106 78 Ð
Reinforcement Plate to Crossmember Attaching Bolt Size M10 (4) 61 45 Ð
Rear Engine Mount to Crossmember Attaching Through Bolt 68 50 Ð
Radiator Support Crossmember Attaching Bolts 51 38 Ð
FRONT CRADLE
CROSSMEMBER
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - FRONT CRADLE
CROSSMEMBER
This vehicle uses a one piece cast aluminum cradle
for the front cradle crossmember. The cradle cross-
member is used as the attaching points for the lower
control arms, stabilizer bar and steering gear. The
cradle also has the power steering hoses and the
chassis brake tubes attached to it.
WARNING: If a threaded hole in the suspension cra-
dle needs to be repaired, only use the type of
thread insert and installation procedure specified
for this application.
The threaded holes in the front cradle crossmem-
ber that are used for attachment of the lower control
arm rear bushing retainer, power steering hose and
chassis brake tubes can be repaired. The repair is
done by the installation of a Heli-Coiltthread insert
which has been specifically developed for this appli-
cation. Refer to the Mopar Parts Catalog for the spec-
ified Heli-Coiltthread insert to be used for this
application. The procedure for installing the Heli-
Coiltthread insert is detailed in the Service Proce-
dures section in this group of the service manual.
DESCRIPTION - FRONT CRADLE
CROSSMEMBER THREAD REPAIR
WARNING: When performing this procedure use
only the thread inserts which are specified in the
Mopar Parts Catalog for this repair procedure.
These thread inserts have been specifically devel-
oped for this application and use of other types of
thread inserts can result in an inferior long term
repair.The threaded holes in the front cradle crossmem-
ber, if damaged, can repaired by installing a Heli-
Coiltthread insert.
The threaded holes that are repairable using the
thread insert, are the lower control arm rear bushing
retainer mounting bolt holes, routing bracket attach-
ing locations for the power steering hoses, and brake
hose attachment holes.
This repair procedure now allows the threaded
holes in the cradle crossmember to be repaired, elim-
inating the need to replace the cradle crossmember if
damage occurs to one of the threaded holes.
The thread inserts for this application are specified
by part number in the Mopar Parts Catalog.Do not
use a substitute thread insert.
The specific tools and equipment required to install
the thread insert are listed below. Refer to the
instructions included with the thread insert for the
detailed procedure used for the installation of the
thread insert.
NOTE: The thread inserts for this application are for
the repair of M8x1.25 and M10x1.5 threads. Be sure
the correct tools are used for the required thread
insert size.
TOOL REQUIREMENT FOR M8x1.25 Thread
²8.3mm (5/16 in.) Drill Bit
²120É Countersink
²Heli-CoiltTap #4863-8
²Heli-CoiltGage #4624-8
²Heli-CoiltHand Inserting Tool 7751-8
²Needle Nose Pliers ± For Removal Of Thread
Insert Driving Tang
TOOL REQUIREMENT FOR M10x1.5 Thread
²10.5mm (25/64 in.) Drill Bit
²120É Countersink
²Heli-CoiltTap #4863-10
²Heli-CoiltGage #4624-10
²Heli-CoiltHand Inserting Tool 7751-10
²Needle Nose Pliers ± For Removal Of Thread
Insert Driving Tang
RSFRAME & BUMPERS13-9
FRAME (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1458 of 2399

leaks are not present. The component should be
replaced immediately if there is any evidence of deg-
radation that could result in failure.
Never attempt to repair a plastic fuel line/tube.
Replace as necessary.
Avoid contact of any fuel tubes/hoses with other
vehicle components that could cause abrasions or
scuffing. Be sure that the plastic fuel lines/tubes are
properly routed to prevent pinching and to avoid heat
sources.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
OPERATION
The fuel system uses a nonadjustable pressure reg-
ulator that maintains fuel system pressure at
approximately 400 34 kPa (58 5 psi). The fuel
pressure regulator contains a diaphragm, calibrated
spring and a fuel return valve. The spring pushes
down on the diaphragm and closes off the fuel return
port. System fuel pressure reflects the amount of fuel
pressure required to open the return port.
The pressure regulator is a mechanical device that
is NOT controlled by the PCM or engine vacuum.
REMOVAL
The fuel pressure regulator is part of the fuel
pump module (Fig. 9). Remove the fuel pump module
from the fuel tank to access the fuel pressure regula-
tor. Refer to the Fuel Pump Module removal in this
section.
(1) Spread tangs on pressure regulator retainer.
(2) Pry fuel pressure regulator out of housing.
(3) Ensure both upper and lower O-rings were
removed with regulator.
INSTALLATION
The fuel pressure regulator is part of the fuel
pump module. Remove the fuel pump module from
the fuel tank to access the fuel pressure regulator.
Refer to the Fuel Pump Module removal in this sec-
tion.
(1) Lightly lubricate the O-rings with clean engine
oil and place them into opening in pump module (Fig.
9).
(2) Push regulator into opening in pump module.
(3) Fold tangs on regulator retainer over tabs on
housing.
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located in and is part of
the fuel pump module. It is a positive displacement,
gerotor type, immersible pump with a permanent
magnet electric motor. The fuel pump module is sus-
pended in fuel in the fuel tank.
OPERATION
The pump draws fuel through a strainer and
pushes it through the motor to the outlet. The pump
contains a check valve. The valve, in the pump out-
let, maintains pump pressure during engine off con-
ditions, for a short while. It is normal for fuel
pressure to drop to zero after cooldown. The fuel
pump relay provides voltage to the fuel pump. The
fuel pump has a maximum deadheaded pressure out-
put of approximately 880 kPa (130 psi). The regula-
tor adjusts fuel system pressure to approximately
400 kpa 34 kpa (58 psi 5 psi).
NOTE: Checkvalve maintains volume of fuel in the
rail and lines, not pressure.
Fig. 9 Fuel Pressure Regulator O-rings
1 - UPPER O-RING
2 - LOWER 0-RING
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-7
FUEL LINES (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1466 of 2399

(6) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(7) Insert quick-connect fitting to component being
serviced and into plastic retainer. When a connection
is made, a click will be heard.
(8) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(9) Connect negative cable to battery or auxiliary
jumper terminal.
(10) Use the DRB IIItscan tool ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
PLASTIC RETAINER RING TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting can be identified by the use of a
full-round plastic retainer ring (Fig. 25) usually black
in color.CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers, retainers) of this type of quick-connect fitting
are not serviced separately. Do not attempt to repair
damaged fittings or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is nec-
essary, replace the complete fuel tube assembly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this section.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To release fuel system component from quick-
connect fitting, firmly push fitting towards compo-
nent being serviced while firmly pushing plastic
retainer ring into fitting (Fig. 25). With plastic ring
depressed, pull fitting from component.The plastic
retainer ring must be pressed squarely into fit-
ting body. If this retainer is cocked during
removal, it may be difficult to disconnect fit-
ting. Use an open-end wrench on shoulder of
plastic retainer ring to aid in disconnection.
(5) After disconnection, plastic retainer ring will
remain with quick-connect fitting connector body.
(6) Inspect fitting connector body, plastic retainer
ring and fuel system component for damage. Replace
as necessary.
(7) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(8) Insert quick-connect fitting into component
being serviced until a click is felt.
(9) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(10) Connect negative battery cable to battery or
auxiliary jumper terminal.
(11) Use the DRB IIItscan tool ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
Fig. 25 Plastic Retainer Ring Type Fitting
1 - FUEL TUBE
2 - QUICK CONNECT FITTING
3 - PUSH
4 - PLASTIC RETAINER
5 - PUSH
6 - PUSH
7 - PUSH
8 - PUSH
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-15
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1502 of 2399

INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The boost pressure sensor/intake air temperature
sensor is located in the top of the intake manifold
(Fig. 6). The intake air temperature sensor is used to
measure the intake air temperature. The intake air
temperture sensor is a dual purpose sensor. It is also
used as a boost pressure sensor.
OPERATION
The intake air temperature sensor is a negative
temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor (resistance
varies inversly with temperature). This means at
cold air temperature its resistance is high, sothe volt-
age signal will be high. As intake air temperature
increases, sensor resistance decreases and the signal
voltage will be low. This allows the sensor to provide
an analog voltage signal (0.2-4.8 volts) to the ECM.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove engine cover retaining bolts and cover-
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE COVER - REMOVAL).(3) Disconnect intake air temperature electrical
connector.
(4) Remove intake air temperature sensor retain-
ing screws and sensor (Fig. 6).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install intake air temperature sensor and
retaining bolts (Fig. 6). Torque to 5.4 N´m.
(2) Connect intake air temperature sensor.
(3) Install engine cover and retaining bolts (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE COVER - INSTALLATION).
CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft position sensor is mounted in the
right rear of the engine block below the turbocharger
(Fig. 7). This sensor is used to detect engine speed.
OPERATION
The crankshaft position sensor is a magnetic
pickup type sensor that generates an ac signal. The
sensor contains a permanent magent and a coil of
wire. The sensor generates an ac signal each time a
notch in the reluctor wheel on the crankshaft passes
across the permanent magnet. The ECM calculates
engine speed based on the frequency of the ac signal.
The ECM supplies the sensor ground.
Fig. 6 BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR/INTAKE AIR
TEMPERATURE SENSOR LOCATION
1 - FUEL RAIL
2 - FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE/BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR
4 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
Fig. 7 CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR ELECTRICAL
CONNECTOR
RGFUEL INJECTION14a-15
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1529 of 2399

GEAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GEAR
DESCRIPTION.........................26
OPERATION...........................26
WARNING
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS.............26
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - LHD GEAR.................26
REMOVAL - RHD GEAR................29INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - LHD GEAR.............32
INSTALLATION - RHD GEAR.............33
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING GEAR..............34
OUTER TIE ROD
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
GEAR
DESCRIPTION
This vehicle is equipped with a rack and pinion
power steering gear (Fig. 1). It is mounted to the
underside of the front suspension cradle/crossmem-
ber.
The steering column is attached to the gear
through the use of an intermediate shaft and cou-
plers. The outer ends of the power steering gear's
outer tie rods connect to the steering knuckles.
NOTE: The power steering gear should NOT be ser-
viced or adjusted unless DaimlerChrysler Corpora-
tion authorizes. If a malfunction or oil leak occurs,
the complete steering gear should be replaced.
Only the outer tie rods may be replaced separately
from the rest of the gear.
OPERATION
Turning of the steering wheel is converted into lin-
ear (side-to-side) travel through the meshing of the
helical pinion teeth with the rack teeth in the steer-
ing gear. This travel pushes and pulls the tie rods to
change the direction of the vehicle's front wheels.
Power assist steering provided by the power steer-
ing pump is controlled by an open center, rotary type
control valve which directs oil from the pump to
either side of the integral rack piston upon demand.
Road feel is controlled by the diameter of a torsion
bar which initially steers the vehicle. As required
steering effort increases, as in a turn, the torsion bar
twists, causing relative rotary motion between the
rotary valve body and the valve spool. This move-
ment directs oil behind the integral rack piston
which, in turn, builds hydraulic pressure and assists
in the turning effort.Manual steering control of the vehicle can be main-
tained if power steering assist is lost. However,
under this condition, steering effort is significantly
increased.
WARNING
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: POWER STEERING FLUID, ENGINE
PARTS AND EXHAUST SYSTEM MAY BE
EXTREMELY HOT IF ENGINE HAS BEEN RUNNING.
DO NOT START ENGINE WITH ANY LOOSE OR DIS-
CONNECTED HOSES. DO NOT ALLOW HOSES TO
TOUCH HOT EXHAUST MANIFOLD OR CATALYST.
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT PERSONAL
INJURY FROM MOVING PARTS.
CAUTION: When the system is open, cap all open
ends of the hoses, power steering pump fittings or
power steering gear ports to prevent entry of for-
eign material into the components.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - LHD GEAR
(1) Remove cap from power steering fluid reser-
voir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much fluid as
possible from the power steering fluid reservoir.Use
care not to damage the filter mesh below the
fluid surface.
19 - 26 GEARRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1561 of 2399

FLUID LEAK DIAGNOSIS
When diagnosing fluid leaks on the Power Transfer
Unit two weep holes are provided to diagnose certain
seal leaks. These holes are located on the bottom side
of the assembly (Fig. 5).
If fluid leak is detected from either weep hole, seal
replacement is necessary.Do not attempt to repair
the leak by sealing weep holes,they must be kept
clear of sealants for proper seal operation.
If fluid is leaking from weep hole A (Fig. 5) the
type of fluid leaking will determine which seal needs
to be replaced. If the fluid leaking is red in color(transmission fluid) this indicates that the Transmis-
sion differential carrier seal should be replaced. If
the fluid leaking is light brown (gear lube) this indi-
cates that the Power Transfer Unit input seal should
be replaced. For replacement of these seals refer to
Power Transfer Unit Service Procedures.
If fluid is leaking from weep hole B (Fig. 5) the
type of fluid leaking will determine which seal is
leaking. If the fluid leaking is red in color (transmis-
sion fluid) this indicates that the input shaft end seal
should be replaced. If the fluid leaking is light brown
(gear lube) this indicates that the half shaft inner
seal and P.T.U. input shaft cover seal should be
replaced. For replacement of these seals refer to
Power Transfer Unit Service Procedures.
Before condemning any seal or gasket be sure that
the rear rocker arm cover on the engine is not the
cause of the oil leak. Oil leaking from the rocker arm
cover is easily mistaken for a leaking Power Transfer
Unit.
Fig. 3 Seal Location
1 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OUTPUT SHAFT
3 - REAR COVER
4 - P.T.U. CASE
5 - INPUT SHAFT SEAL
Fig. 4 Seal Location
1 - P.T.U. INPUT SHAFT COVER SEAL
2 - HALF SHAFT INNER SEAL
3 - INSIDE VIEW OF P.T.U. END COVER
Fig. 5 Weep Hole Locations
1 - ENGINE OIL PAN
2 - WEEP HOLE ªAº
3 - TRANSAXLE CASE
4 - P.T.U.
5 - WEEP HOLE ªBº
21 - 4 POWER TRANSFER UNITRS
POWER TRANSFER UNIT (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com