2002 CHRYSLER CARAVAN tow bar
[x] Cancel search: tow barPage 68 of 2399

²Stabilizer bar-to-link bolts Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
INSTALLATION - FWD
(1) Lift the stabilizer bar onto the rear axle and
install the two retainer mounting bolts. DO NOT
TIGHTEN.
(2) Install the bolts attaching the stabilizer bar
links to the stabilizer bar. DO NOT TIGHTEN.
(3) Lower the vehicle so that the full weight of the
vehicle is on all four tires. With the vehicle at its
curb height, tighten the following bolts to the torques
listed:
²Stabilizer bar bushing retainer-to-axle bracket
bolts Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
²Stabilizer bar-to-link Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
TRACK BAR
DESCRIPTION
On front-wheel-drive applications of this vehicle
that are equipped with single leaf rear springs, a
track bar is used on the rear axle (Fig. 1).
The track bar connects the rear axle to the frame/
body of the vehicle. The track bar is isolated from the
body of the vehicle by an isolator bushing located in
each end of the track bar.
OPERATION
The track bar prevents excessive side-to-side move-
ment of the rear axle. The track bar is used to keep
the location of the axle in the correct position for
optimum handling and control of the vehicle.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the nut and bolt mounting the track
bar to the rear axle (Fig. 41).(2) Remove the nut and bolt attaching the track
bar to the track bar mount on the body of the vehicle.
Remove the track bar from the track bar mount.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the track bar first into the body mount
for the track bar (Fig. 42). Install the track bar bolt
with the head of the bolt facing toward the rear of
the vehicle (Fig. 43). Do not tighten.
(2) Install the track bar into its mounting bracket
on the rear axle (Fig. 41). Install the track bar bolt
with the head of the bolt facing toward the rear of
the vehicle. Do not tighten.
(3) Lower the vehicle to the ground until the full
weight of the vehicle is supported by the wheels.
Tighten both track bar attaching bolts to a torque of
95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 41 Track Bar Mounting To Axle (Typical)
1 - LOWER TRACK BAR BOLT INSTALLATION
Fig. 42 Track Bar Installation (Typical)
1 - TRACK BAR REPLACEMENT
Fig. 43 Track Bar Bolt Installation
1 - TRACK BAR BOLT
RSREAR SUSPENSION2-45
STABILIZER BAR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 455 of 2399

The electrically heated Rear Window Defogger (Fig.
1), Heated Power Side View Mirrors, and Heated
Windshield Wiper De-icer (Fig. 2)is available on
select models.
OPERATION
The Rear Window Defogger(Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/HEATED GLASS - DESCRIPTION) system con-
sists of two vertical bus bars linked by a series of
grid lines on the inside surface of the rear window.
The electrical circuit consists of the rear defogger
switch in the HVAC control assembly and a relay
with timer switch to turn OFF the system after ten
minutes. The main feed circuit is protected by fuse
13 (40 amp) in the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
which is connected directly to the front control mod-
ule (FCM) to form an integrated unit called an Inte-
grated Power Module (IPM). The rear defogger
switch and relay also activates the heated power side
view mirrors. The rear defogger switch also activates
the heated windshield wiper de-icer which is powered
by the RUN/ACC relay in the IPM and feed thru fuse
#11 (20 amp) in the PDC. The heated mirror circuit
is protected by a non-servicable Positive Temperature
Coefficient (PTC) located inside the PDC. The heated
windshield wiper de-icer circuit is protected by fuse
11 (20 amp) in the PDC.
The Heated Windshield Wiper Deicer is also acti-
vated when the DEFROST mode is selected on the
HVAC. In the DEFROST mode the rear defogger
timout is bypassed, the heated windshield wiper de-
icer will stay ON until the another mode is selected.
For circuit information and component location refer
to appropriate section for Wiring Diagrams.
CAUTION:
Since grid lines can be damaged or scraped off
with sharp instruments, care should be taken in
cleaning the glass or removing foreign materials,
decals or stickers. Normal glass cleaning solvents
or hot water used with rags or toweling is recom-
mended.
DEFOGGER RELAY
DESCRIPTION
There is no heated windshield wiper de-icer relay.
The grid is powered directly from fuse #11 in the
PDC and is controlled directly from the HVAC con-
trol assembly.
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
GRID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - GRID LINE REPAIR
REAR
For Grid repair procedure for the rear window
defogger (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/HEATED
GLASS/WINDSHIELD GRID - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The rear window defogger switch is integrated into
the HVAC control panel assembly (Fig. 3)
OPERATION
A LED indicator will illuminate when the switch is
activated. The switch energizes the HVAC control
assembly when it requests the Front Control Module
(FCM) to activate the rear window defogger relay.
The relay controls the current to flow to the grids of
the rear window defogger, heated power side view
mirrors and the heated windshield wiper de-icer. The
defogger relay will be on for approximately 10 min-
utes or until the control switch or ignition is turned
off.
Fig. 3 HVAC CONTROL PANEL
1 - TRIM BEZEL
2 - ACT SENSOR
3 - A/C REQUEST SWITCH
4 - REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER/HEATED MIRRORS SWITCH
COMBO
5 - FRONT WINDOW DEFROSTER MODE SELECTOR
8G - 2 HEATED GLASSRS
HEATED GLASS (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1211 of 2399

Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum, with 552 kPa (80 psi) rec-
ommended.
Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage per cylinder.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 2).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (excluding spark plug
and camshaft bearing cap attaching threads) can be
repaired. Essentially, this repair consists of drilling
out worn or damaged threads, tapping the hole with
a special Heli-Coil Tap, (or equivalent) and installing
an insert into the tapped hole. This brings the hole
back to its original thread size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, the
following steps should be used.
CAUTION: DO NOT use starter motor to rotate the
engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
any fluid that may possibly be in the cylinder under
pressure.
(4) With all spark plugs removed, rotate engine
crankshaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., cool-
ant, fuel, oil or other).
(6) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., connecting
rods, pistons, valves, etc.)
(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from re-occurring.
Fig. 2 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
9 - 10 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1287 of 2399

STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, the
following steps should be used.
CAUTION: DO NOT use starter motor to rotate the
engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
any fluid that may possibly be in the cylinder under
pressure.
(4) With all spark plugs removed, rotate engine
crankshaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., cool-
ant, fuel, oil or other).
(6) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., connecting
rods, pistons, valves, etc.)
(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from re-occurring.
CAUTION: Squirt approximately one teaspoon of oil
into the cylinders, rotate engine to lubricate the cyl-
inder walls to prevent damage on restart.
(8) Install new spark plugs.
(9) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(10) Install a new oil filter.
(11) Fill engine with specified amount of approved
oil.
(12) Connect negative battery cable.
(13) Start engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (excluding spark plug
and camshaft bearing cap attaching threads) can be
repaired. Essentially, this repair consists of drilling
out worn or damaged threads, tapping the hole with
a special Heli-Coil Tap, (or equivalent) and installing
an insert into the tapped hole. This brings the hole
back to its original thread size.CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 5).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
Fig. 5 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
9 - 86 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1507 of 2399
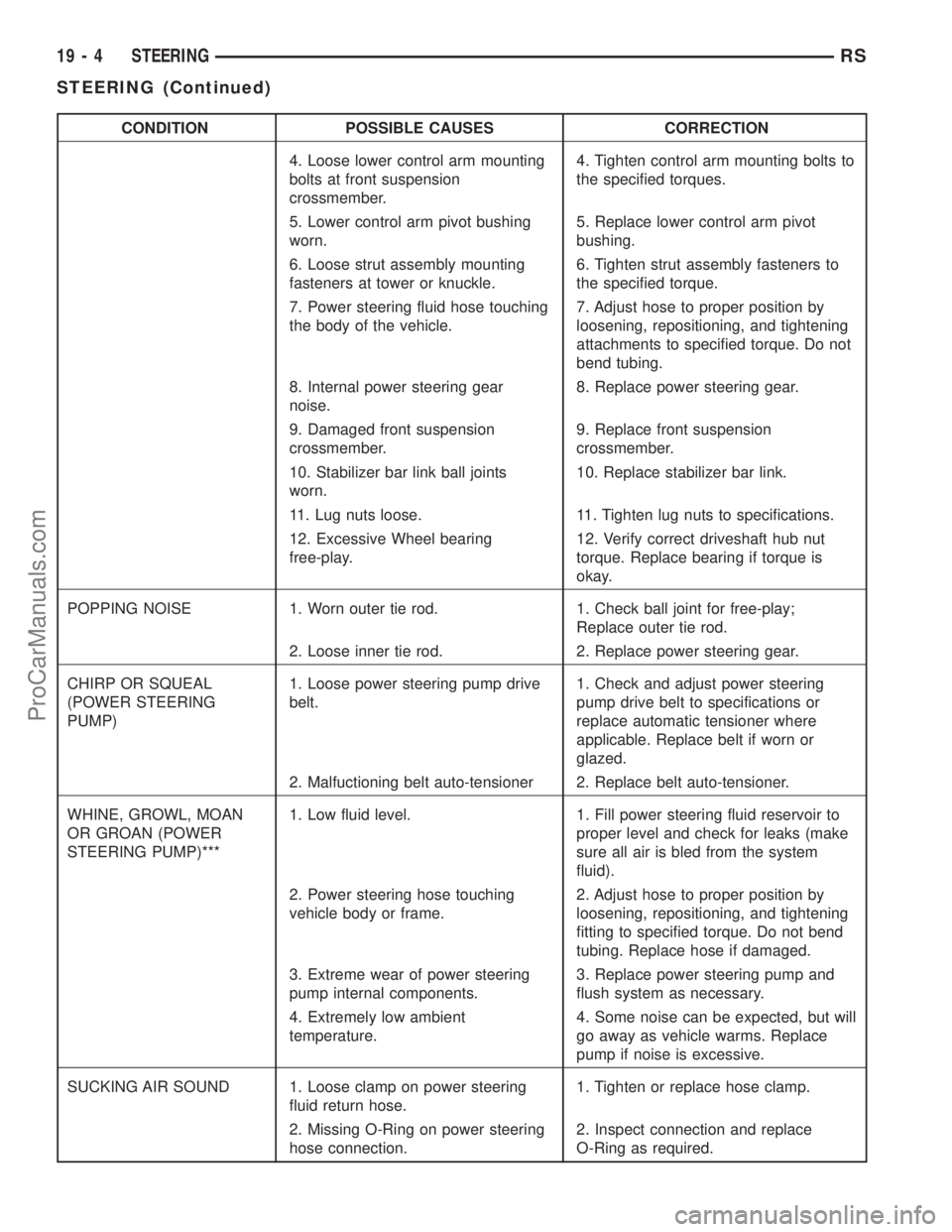
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
4. Loose lower control arm mounting
bolts at front suspension
crossmember.4. Tighten control arm mounting bolts to
the specified torques.
5. Lower control arm pivot bushing
worn.5. Replace lower control arm pivot
bushing.
6. Loose strut assembly mounting
fasteners at tower or knuckle.6. Tighten strut assembly fasteners to
the specified torque.
7. Power steering fluid hose touching
the body of the vehicle.7. Adjust hose to proper position by
loosening, repositioning, and tightening
attachments to specified torque. Do not
bend tubing.
8. Internal power steering gear
noise.8. Replace power steering gear.
9. Damaged front suspension
crossmember.9. Replace front suspension
crossmember.
10. Stabilizer bar link ball joints
worn.10. Replace stabilizer bar link.
11. Lug nuts loose. 11. Tighten lug nuts to specifications.
12. Excessive Wheel bearing
free-play.12. Verify correct driveshaft hub nut
torque. Replace bearing if torque is
okay.
POPPING NOISE 1. Worn outer tie rod. 1. Check ball joint for free-play;
Replace outer tie rod.
2. Loose inner tie rod. 2. Replace power steering gear.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL
(POWER STEERING
PUMP)1. Loose power steering pump drive
belt.1. Check and adjust power steering
pump drive belt to specifications or
replace automatic tensioner where
applicable. Replace belt if worn or
glazed.
2. Malfuctioning belt auto-tensioner 2. Replace belt auto-tensioner.
WHINE, GROWL, MOAN
OR GROAN (POWER
STEERING PUMP)***1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
proper level and check for leaks (make
sure all air is bled from the system
fluid).
2. Power steering hose touching
vehicle body or frame.2. Adjust hose to proper position by
loosening, repositioning, and tightening
fitting to specified torque. Do not bend
tubing. Replace hose if damaged.
3. Extreme wear of power steering
pump internal components.3. Replace power steering pump and
flush system as necessary.
4. Extremely low ambient
temperature.4. Some noise can be expected, but will
go away as vehicle warms. Replace
pump if noise is excessive.
SUCKING AIR SOUND 1. Loose clamp on power steering
fluid return hose.1. Tighten or replace hose clamp.
2. Missing O-Ring on power steering
hose connection.2. Inspect connection and replace
O-Ring as required.
19 - 4 STEERINGRS
STEERING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2003 of 2399

(5) Disengage clip holding door latch linkage to
door latch (Fig. 12).
(6) Remove latch linkage from latch.
(7) Disengage clip holding door lock linkage to
door latch.
(8) Remove lock linkage from latch.
(9) Remove nuts attaching outside door handle to
door outer panel.
(10) Remove outside door handle from vehicle.
(11) Disengage clip holding lock cylinder into out-
side handle.
(12) Pull lock cylinder from door handle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Engage clip into outside handle to hold lock
cylinder (Fig. 12).
(2) With link arm toward rear of vehicle, push lock
cylinder into door handle until clip snaps into place.
(3) Insert lock linkage into door latch.
(4) Engage clip to hold door lock linkage to latch.
(5) Insert latch linkage into door latch.
(6) Engage clip to hold door latch linkage to latch.
(7) Install push in fasteners attaching VTSS
switch harness to inner door reinforcement bar, if
equipped.
(8) Connect VTSS switch connector into door har-
ness, if equipped.
(9) Verify door latch operation.(10) Install watershield and door trim panel.
TRIM PANEL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the plug and remove screw attaching
door pull cup to inner door panel.
(2) Remove switch bezel and disconnect power win-
dow/memory switch.
(3) Remove screws attaching trim panel to door
from below map pocket.
(4) If equipped, remove window crank. (Refer to 23
- BODY/DOOR - FRONT/WINDOW CRANK -
REMOVAL)
(5) Remove screw holding door trim to door panel
from behind inside latch release handle.
(6) Disengage clips attaching door trim to door
frame around perimeter of panel.
(7) Lift trim panel upward to disengage flange
from inner belt molding at top of door.
(8) Tilt top of trim panel away from door to gain
access to latch linkage.
(9) Disengage clip attaching linkage rod to inside
latch release handle (Fig. 13).
(10) Separate linkage rod from latch handle.
(11) Disconnect the power door switch, courtesy
lamp electrical connectors.
Fig. 12 OUTSIDE DOOR HANDLE
1 - CLIP
2 - LOCK CYLINDER
3 - KEY CYLINDER TO LATCH LINK
4 - OUTSIDE HANDLE TO LATCH LINK
5 - LOCK KNOB LINK6 - FRONT DOOR
7 - KEY POSITION SWITCH
8 - OUTSIDE HANDLE
23 - 20 DOOR - FRONTRS
LOCK CYLINDER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2040 of 2399

INSTALLATION
NOTE: The crossbar assemblies are designed to be
installed in only one way. Check top and bottom
surfaces of the crossbar for the word FRONT and
directional arrows. The directional arrows must
point toward the front of the vehicle.
(1) Place crossbar in position on vehicle.
(2) Work from side to side sliding the crossbar
assembly back a little at a time to ensure it remains
perpendicular to the side rails.
(3) Position first crossbar assembly crossbar at the
second most rearward locator holes. Press the top of
the stanchion lever to lock it into position.
(4) Position the second crossbar assembly in the
second hole from the front. Lock into place.
(5) Place luggage rack riser into position.
(6) Install two fasteners into riser. Tighten fasten-
ers to 4 mm (35 in. lbs.) torque.
REAR QUARTER PANEL/
FENDER AIR EXHAUSTER
DESCRIPTION
Air exhausters, designed to conform to the body
structure, allow air entering at the front of the vehi-
cle to flow out the back. By reducing air pressure
within the vehicle, the exhausters also reduce blower
noise at any given air flow level compared to operat-
ing without them and help reduce door closing effort.
They are located in the lower rear comers of the
body.
REMOVAL
SHORT WHEELBASE
(1) Remove the rear fascia from the body. (Refer to
13 - FRAMES & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/REAR FAS-
CIA - REMOVAL).
(2) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide flat
bladed tool, carefully pry the air exhauster away
from the opening in the lower aperture panel until
the snap features release (Fig. 19).
(3) Remove the air exhauster from the hole in the
lower aperture panel.
LONG WHEELBASE
NOTE: Models with the optional rear heater and air
conditioner do not have an air exhauster on the
right side of the vehicle, but have a plastic plug
installed in the right lower aperture panel. This plug
is removed using the same procedure used toremove the air exhauster from the short wheelbase
model. Refer to SHORT WHEELBASE .
(1) Remove the quarter trim panel from the inside
of the left or right quarter inner panel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/RIGHT QUARTER TRIM PANEL
- REMOVAL) or (Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/
LEFT QUARTER TRIM PANEL - REMOVAL).
(2) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide flat
bladed tool, carefully pry the air exhauster away
from the opening in the lower aperture panel until
the snap features release (Fig. 20).
(1) Remove the air exhauster from the hole in the
lower aperture panel.
Fig. 19 AIR EXHAUSTER - SWB
1 - LOWER APERTURE PANEL
2 - AIR EXHAUSTER
Fig. 20 AIR EXHAUSTER - LWB
1 - AIR EXHAUSTER
2 - PLUG
3 - LOWER APERTURE PANEL
RSEXTERIOR23-57
LUGGAGE RACK CROSSBAR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2322 of 2399

CAUTION:
When removing the heater hose from the heater
core or supply and return tube nipples, DO NOT
apply excessive pressure. Excessive pressure may
damage or deform the nipples and/or the heater
core causing an engine coolant leak.(3) After the clamp has been moved, grasp the end
of the hose firmly and carefully twist the hose back
and forth while pulling it away from the barbed end
of the nipple. Repeat this procedure at the opposite
end of the hose being removed. If this procedure is
not successful in removing the hose from the nipple,
carefully make a parallel cut through the hose where
it is engaged on the nipple and peel the hose off of
the nipple. This method of removal will require
heater hose replacement.
INSTALLATION
There are several heater core plumbing configura-
tions used on this model, depending upon the engine
size and other optional equipment. One plumbing
configuration is used for all 2.4L engines, while the
3.3L and 3.8L engines have unique heater return
plumbing on the engine for models with or without
an optional engine oil cooler. There are also unique
plumbing configurations at the heater core for mod-
els with or without the optional rear heater and air
conditioner. All models use a combination of formed
steel tubing and rubber hoses. In most cases, the
rubber hose is secured to the steel tubing with a
spring tension clamp.
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING FRONT - WARNING - HEATER PLUMB-
ING).
(1) Using spring tension clamp pliers, compress
and slide the clamps that secure each end of the
heater hose toward the center of the hose being
installed. Release the clamp when it is near the cen-
ter of the hose.
(2) Grasp one end of the heater hose being
installed firmly and carefully twist the hose back and
forth while pushing it over from the barbed end of
the nipple. Repeat this procedure at the opposite end
of the hose being installed.
(3) Using spring tension clamp pliers, compress
and slide the clamps that secure each end of the
heater hose over the tube or nipple. Release the
clamp when it is over the tube or nipple.
(4) Refill the engine cooling system. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM REFILL).
Fig. 24 Heater Return - 3.3/3.8L Engine w/o Oil
Cooler
1 - WATER PUMP RETURN NIPPLE
2 - HEATER RETURN TUBE & HOSE
3 - SCREW
4 - SCREW
Fig. 25 Heater Return - 3.3/3.8L Engine w/Oil Cooler
1 - ENGINE INLET NIPPLE
2 - HEATER RETURN TUBE & HOSE
3 - SCREW
4 - SCREW
5 - OIL COOLER
6 - HEATER RETURN HOSE
RSPLUMBING - FRONT24-79
HEATER HOSE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com