Page 19 of 48
19
M54engMS43/ST039/3/17/00
DM-TL (DIAGNOSIS MODULE - TANK LEAKAGE)
FUNCTION
The DC Motor LDP ensures accurate fuel system leak detection for leaks as small as
0.5mm (.020”). The pump contains an integral DC motor which is activated directly by the
engine control module. The ECM monitors the pump motor operating current as the mea-
surement for detecting leaks.
The pump also contains an ECM controlled change over valve that is energized closed dur-
ing a Leak Diagnosis test. The change over valve is open during all other periods of oper-
ation allowing the fuel system to “breath” through the inlet filter (similar to the full down
stroke of the current vacuum operated LDP).
Page 38 of 48
38
M54engMS43/ST036/6/2000
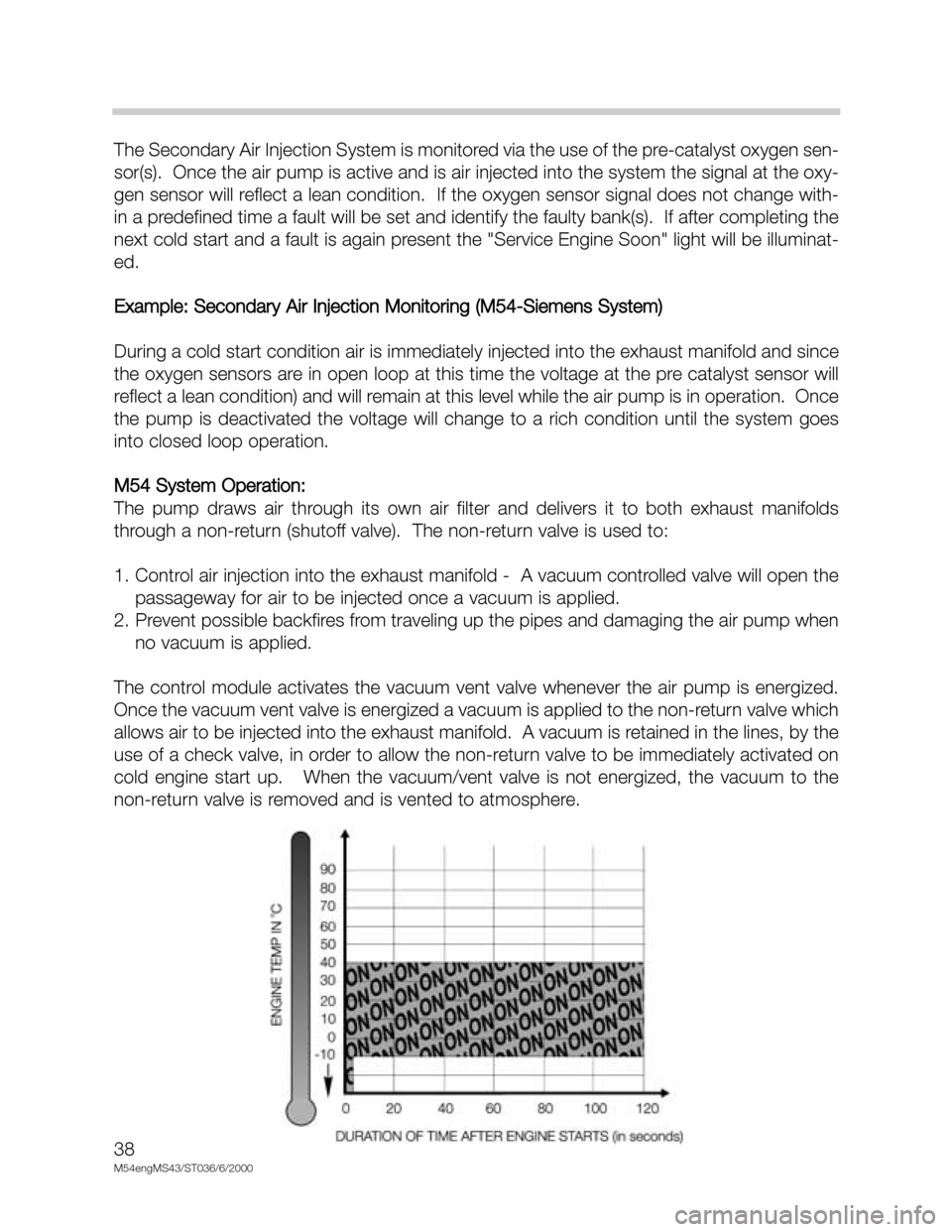
The Secondary Air Injection System is monitored via the use of the pre-catalyst oxygen sen-
sor(s). Once the air pump is active and is air injected into the system the signal at the oxy-
gen sensor will reflect a lean condition. If the oxygen sensor signal does not change with-
in a predefined time a fault will be set and identify the faulty bank(s). If after completing the
next cold start and a fault is again present the "Service Engine Soon" light will be illuminat-
ed.
Example: Secondary Air Injection Monitoring (M54-Siemens System)
During a cold start condition air is immediately injected into the exhaust manifold and since
the oxygen sensors are in open loop at this time the voltage at the pre catalyst sensor will
reflect a lean condition) and will remain at this level while the air pump is in operation. Once
the pump is deactivated the voltage will change to a rich condition until the system goes
into closed loop operation.
M54 System Operation:
The pump draws air through its own air filter and delivers it to both exhaust manifolds
through a non-return (shutoff valve). The non-return valve is used to:
1. Control air injection into the exhaust manifold - A vacuum controlled valve will open the
passageway for air to be injected once a vacuum is applied.
2. Prevent possible backfires from traveling up the pipes and damaging the air pump when
no vacuum is applied.
The control module activates the vacuum vent valve whenever the air pump is energized.
Once the vacuum vent valve is energized a vacuum is applied to the non-return valve which
allows air to be injected into the exhaust manifold. A vacuum is retained in the lines, by the
use of a check valve, in order to allow the non-return valve to be immediately activated on
cold engine start up. When the vacuum/vent valve is not energized, the vacuum to the
non-return valve is removed and is vented to atmosphere.
Page 41 of 48

41
M54engMS43/ST036/6/20000
RESONANCE/TURBULENCE INTAKE SYSTEM
On the M54, the intake manifold is split into 2 groups of 3 (runners) which increases low
end torque. The intake manifold also has separate (internal) turbulence bores which chan-
nels air from the idle speed actuator directly to one intake valve of each cylinder (matching
bore of 5.5mm in the cylinder head).
Routing the intake air to only one intake valve causes the intake to swirl in the cylinder.
Together with the high flow rate of the intake air due to the small intake cross sections, this
results in a reduction in fluctuations and more stable combustion.
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
MDK
HFMHFM
MAGNETIC
VALVE
VACUUM
UNIT
MS42.0MS42.0
RAM TUBE
MAIN MAINIFOLD
RESONANCE TUBE
IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE
(ZWD)
RESONANCE MANIFOLD
CRANKCASE VENTILATIONTURBULENCE MANIFOLD
TURBULENCE BORE 0:5.5mm
MS 43.0
EDK
Page 42 of 48

42
M54engMS43/ST036/6/2000
RESONANCE SYSTEM
The resonance system provides increased engine torque at low RPM, as well as addition-
al power at high RPM. Both of these features are obtained by using a resonance flap (in
the intake manifold) controlled by the ECM.
During the low to mid range rpm, the resonance flap is closed. This produces a long/sin-
gle intake tube for velocity, which increases engine torque.
During mid range to high rpm, the resonance flap is open. This allows the intake air to pull
through both resonance tubes, providing the air volume necessary for additional power at
the upper RPM range.
When the flap is closed , this creates another “dynamic” effect. For example, as the intake
air is flowing into cylinder #1, the intake valves will close. This creates a “roadblock” for the
in rushing air. The air flow will stop and expand back (resonance wave back pulse) with the
in rushing air to cylinder #5. The resonance “wave”, along with the intake velocity,
enhances cylinder filling.
The ECM controls a solenoid valve for resonance flap activation. At speeds below 3750
RPM, the solenoid valve is energized and vacuum supplied from an accumulator closes
the resonance flap. This channels the intake air through one resonance tube, but increas-
es the intake velocity.
When the engine speed is greater than 4100 RPM (which varies slightly - temperature influ-
enced), the solenoid is de-energized. The resonance flap is sprung open, allowing flow
through both resonance tubes, increasing volume.
Page 45 of 48
45
M54engMS43/ST036/6/20000
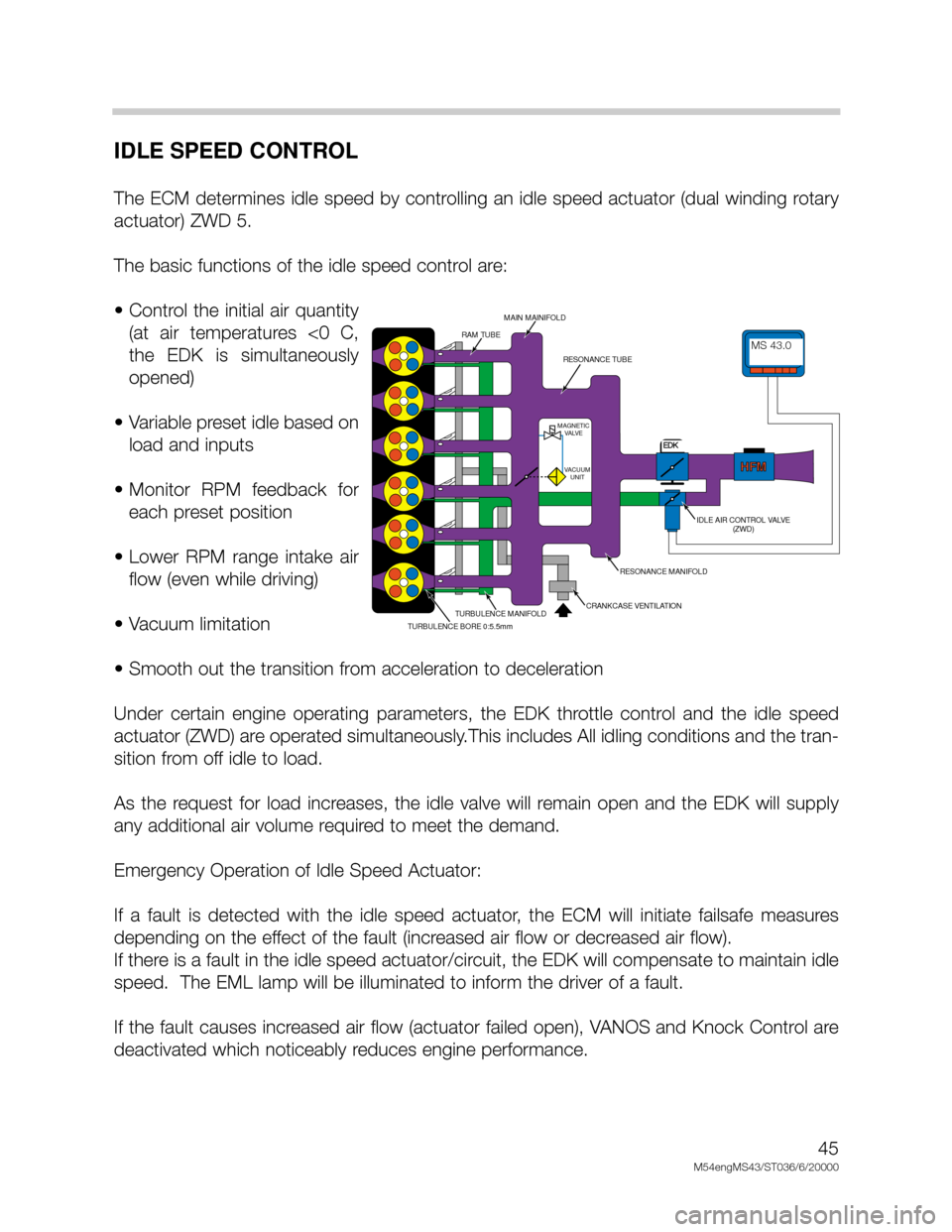
IDLE SPEED CONTROL
The ECM determines idle speed by controlling an idle speed actuator (dual winding rotary
actuator) ZWD 5.
The basic functions of the idle speed control are:
• Control the initial air quantity
(at air temperatures <0 C,
the EDK is simultaneously
opened)
• Variable preset idle based on
load and inputs
• Monitor RPM feedback for
each preset position
• Lower RPM range intake air
flow (even while driving)
• Vacuum limitation
• Smooth out the transition from acceleration to deceleration
Under certain engine operating parameters, the EDK throttle control and the idle speed
actuator (ZWD) are operated simultaneously.This includes All idling conditions and the tran-
sition from off idle to load.
As the request for load increases, the idle valve will remain open and the EDK will supply
any additional air volume required to meet the demand.
Emergency Operation of Idle Speed Actuator:
If a fault is detected with the idle speed actuator, the ECM will initiate failsafe measures
depending on the effect of the fault (increased air flow or decreased air flow).
If there is a fault in the idle speed actuator/circuit, the EDK will compensate to maintain idle
speed. The EML lamp will be illuminated to inform the driver of a fault.
If the fault causes increased air flow (actuator failed open), VANOS and Knock Control are
deactivated which noticeably reduces engine performance.
MDK
HFMHFM
MAGNETIC
VALVE
VACUUM
UNIT
MS42.0MS42.0
RAM TUBE
MAIN MAINIFOLD
RESONANCE TUBE
IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE
(ZWD)
RESONANCE MANIFOLD
CRANKCASE VENTILATIONTURBULENCE MANIFOLD
TURBULENCE BORE 0:5.5mm
MS 43.0
EDK