2001 SUZUKI GRAND VITARA ig meter
[x] Cancel search: ig meterPage 142 of 656

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E2-17
Table-C ABS Warning Lamp Circuit Check – The Lamp Flashes Continuously
While Ignition Switch Is ON
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When diagnosis switch terminal is shorted or connected to the ground with ignition switch ON, diagnosis trouble
code (DTC) is indicated by flashing of ABS warning lamp only in the following cases.
Normal DTC (12) is indicated if no malfunction DTC is detected in the ABS.
A history malfunction DTC is indicated by flashing of the lamp if a current malfunction DTC is not detected at
that point although a history malfunction DTC is stored in memory.
INSPECTION
1. ABS warning lamp in combination meter 3. Diagnosis monitor coupler 3-2. Diagnosis ground terminal
2. ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly 3-1. Diagnosis switch terminal 4. ABS hydraulic unit/control module connector
Step Action Yes No
1 Is diagnosis switch terminal connected to
ground via service wire?Go to Step 3. Go to Step 2.
2 1) Ignition switch ON.
2) Measure voltage between diagnosis switch
terminal and ground.
Is it 10 – 14 V?Substitute a known-good
ABS hydraulic unit/con-
trol module assembly and
recheck.“PNK” wire circuit shorted
to ground.
3 1) Ignition switch ON.
2) Does flashing of ABS warning lamp indicate
DTC?Go to Step 7 of “ABS
DIAGNOSTIC FLOW
TABLE” in this section.Substitute a known-good
ABS hydraulic unit/con-
trol module assembly and
recheck.
Page 143 of 656

5E2-18 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
Table-D Code (DTC) Is Not Outputted Even with Diagnosis Switch Terminal
Connected to Ground
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When diagnosis switch terminal is connected to ground with ignition switch turned ON, the ABS control module
outputs diagnostic trouble code by flashing ABS warning lamp.
INSPECTION
1. ABS warning lamp in combination meter 3. Diagnosis monitor coupler 3-2. Diagnosis ground terminal
2. ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly 3-1. Diagnosis switch terminal 4. ABS hydraulic unit/control module connector
Step Action Yes No
1 Is it shorted diagnosis switch terminal and
ground terminal by service wire properly?Go to Step 2. Connect service wire
securely.
2 1) Disconnect service wire.
2) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit/control mod-
ule connector.
3) Measure resistance between diagnosis
switch terminal and connector terminal
“E136-12”.
Is it infinite (∞)?“PNK” circuit open. Go to Step 3.
3 1) Measure resistance between ground termi-
nal of monitor coupler and body ground.
Is continuity indicated?Go to Step 4.“BLK” circuit open or poor
connection.
4 1) Check for proper connection to ABS
hydraulic unit/control module at terminal
“E136-12”.
2) If OK, then check ABS warning lamp circuit
referring to TABLE A, B and C.
Is it in good condition?Substitute a known-good
ABS hydraulic with/control
module assembly and
recheck.Repair “ABS” warning
lamp circuit.
Page 144 of 656

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E2-19
Table-E EBD Warning Lamp (Brake Warning Lamp) Check – Lamp Comes
“ON” Steady
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
EBD warning lamp (brake warning lamp) is controlled by parking brake switch, brake fluid level switch and ABS
control module/hydraulic unit assembly through lamp driver module in combination meter. Refer to “TABLE – A”
for circuit diagram.
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1 1) Make sure that :
Parking brake is completely released.
Brake fluid level is upper than the minimum
level.
Are the check results OK?Go to Step 2. Release parking brake
completely and/or replen-
ish brake fluid.
2Does “ABS” warning lamp come on? Perform “TABLE – B” pre-
viously outlined.Go to Step 3.
3 1) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit/control mod-
ule connector.
2) Check for proper connection to ABS
hydraulic unit/control module connector at
terminals “E136-10”.
3) If OK, apply chocks to wheels and select
gear in neutral position (P range for A/T).
4) Keep brake pedal depressed and start
engine.
Release parking brake.
5) Connect terminal “E136-10” of discon-
nected connector to ground using service
wire.
Does EBD warning lamp (brake warning lamp)
turn off?Substitute a known-good
ABS hydraulic unit/con-
trol module assembly and
recheck.“BRN” circuit open.
If wire and connection are
OK, replace combination
meter.
Page 150 of 656

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 5E2-25
DTC C1057 (DTC 57) – Power Source Circuit
DESCRIPTION
The ABS control module monitors the power source voltage at terminal “E136-18”. When the power source volt-
age becomes extremely high or low, this DTC will be set. As soon as the voltage rises or lowers to the specified
level, the set DTC will be cleared.
INSPECTION
1. Ignition switch 3. ABS hydraulic unit/control module assembly
2. Main fuse 4. ABS hydraulic unit/control module connector
Step Action Yes No
1 1) Connect a voltmeter between battery posi-
tive (+) terminal and body ground.
2) Start the engine and measure the maximum
voltage when racing the engine.
Is it over 18V?Check charging system
referring to “CHARGING
SYSTEM” section.Go to Step 2.
2 1) Disconnect ABS hydraulic unit/control mod-
ule connector.
2) Keep the engine idling, measure the voltage
between terminal “E136-18” of ABS control
module and body ground.
Is it always under 9V?Check charging system
referring to “CHARGING
SYSTEM” section.
Imperfect short between
wire “GRN/ORN” and
ground.Poor connection of termi-
nal “E136-18” or “E136-
24” of the ABS control
module.
If the above are in good
condition, substitute a
known-good ABS hydrau-
lic unit/control module and
recheck.
Page 164 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-3
General Information
Statement of Cleanliness and Care
An automobile engine is a combination of many machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with tolerances
that are measured in the thousands of an millimeter (ten thousands of inch). Accordingly, when any internal
engine parts are serviced, care and cleanliness are important. Throughout this section, it should be understood
that proper cleaning and protection of machined surfaces and friction areas is part of the repair procedure. This
is considered standard shop practice even if not specifically stated.
A liberal coating of engine oil should be applied to friction areas during assembly to protect and lubricate the
surface on initial operation.
Whenever valve train components, pistons, piston rings, connecting rods, rod bearings and crankshaft jour-
nal bearings are removed for service, they should be retained in order. At the time of installation, they should
be installed in the same locations and with the same mating surfaces as when removed.
Battery cables should be disconnected before any major work is performed on the engine. Failure to discon-
nect cables may result in damage to wire harness or other electrical parts.
Throughout this manual, the 6 cylinders of the engine are
identified by numbers; No.1, No.2, No.3, No.4, No.5 and No.6
as counted from crankshaft pulley side to flywheel side.
Figure at the left shows engine with intake manifold removed
and viewed from the top.
LH (No.1) bank consists of No.1, No.3 and No.5 cylinders.
RH (No.2) bank consists of No.2, No.4 and No.6 cylinders.
General Information on Engine Service
When raising or supporting engine for any reason, do not use a jack under oil pan. Due to small clearance
between oil pan and oil pump strainer, jacking against oil pan may cause it to be bent against strainer result-
ing in damaged oil pick-up unit.
It should be kept in mind, while working on engine, that 12-volt electrical system is capable of violent and
damaging short circuits.
When performing any work where electrical terminals could possibly be grounded, ground cable of the bat-
tery should be disconnected at battery.
Any time the air cleaner, air cleaner outlet hose, throttle body, surge tank pipe, intake collector or intake man-
ifold is removed, the intake opening should be covered. This will protect against accidental entrance of for-
eign material which could follow intake passage into cylinder and cause extensive damage when engine is
started.
1. No.1 cylinder 6. No.6 cylinder
2. No.2 cylinder 7. LH (No.1) bank
3. No.3 cylinder 8. RH (No.2) bank
4. No.4 cylinder 9. Crank shaft pulley side
5. No.5 cylinder
CAUTION:
The following information on engine service should be noted carefully, as it is important in preventing
damage, and in contributing to reliable engine performance.
Page 167 of 656
6-1-6 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
Engine Diagnosis
General Description
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission control system which are under control of ECM (PCM).
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle are controlled by ECM (PCM). ECM (PCM) has an On-
Board Diagnostic system which detects a malfunction in this system and abnormality of those parts that influ-
ence the engine exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the
outline of “ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM” and each item in “PRECAUTION IN DIAGNOSING TROUBLE”
and execute diagnosis according to “ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
There is a close relationship between the engine mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system, exhaust
system, etc. and the engine and emission control system in their structure and operation. In case of an engine
trouble, even when the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed according to
“ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle without
Monitor Connector)
ECM (PCM) in this vehicle has following functions.
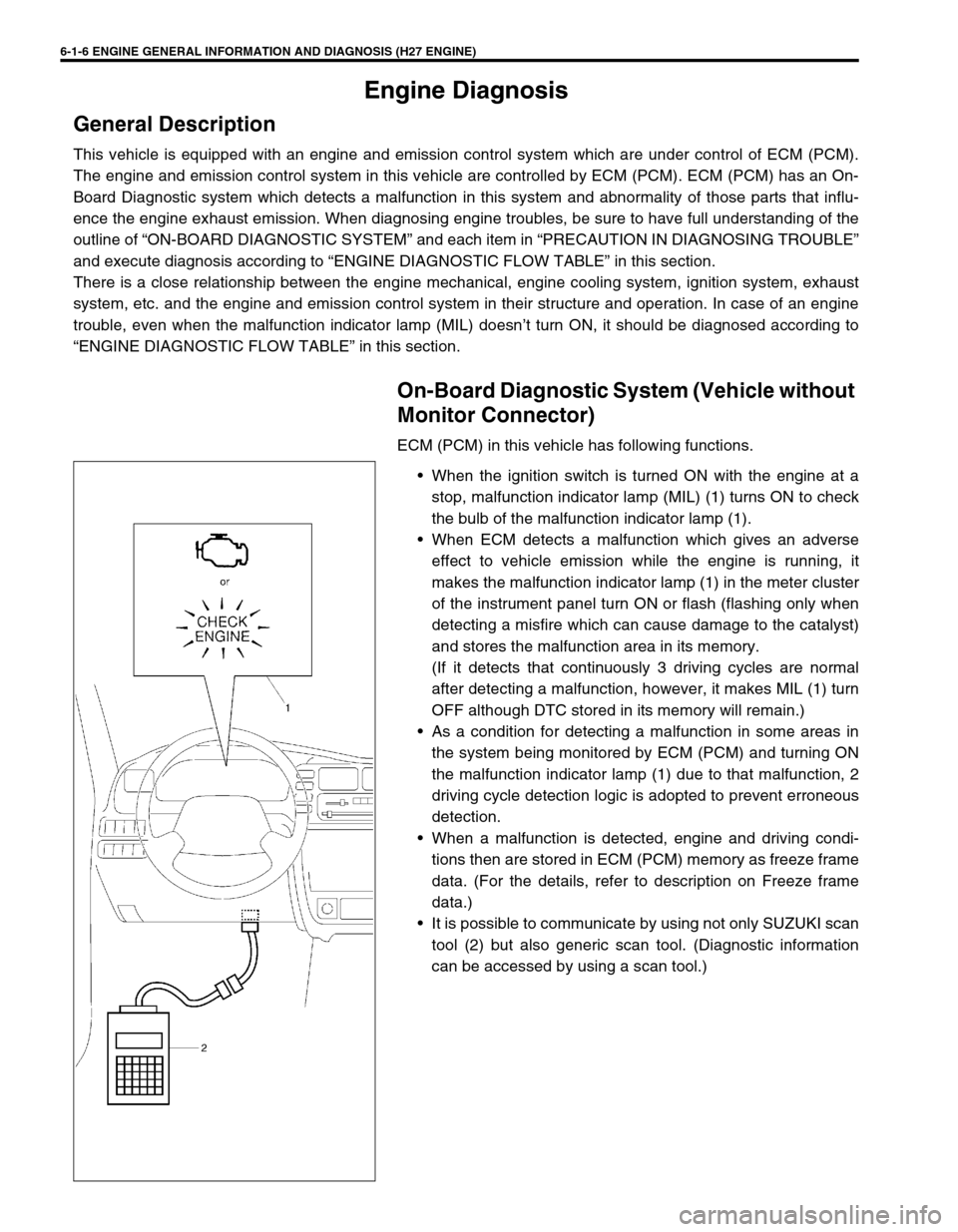
When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a
stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns ON to check
the bulb of the malfunction indicator lamp (1).
When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an adverse
effect to vehicle emission while the engine is running, it
makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in the meter cluster
of the instrument panel turn ON or flash (flashing only when
detecting a misfire which can cause damage to the catalyst)
and stores the malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that continuously 3 driving cycles are normal
after detecting a malfunction, however, it makes MIL (1) turn
OFF although DTC stored in its memory will remain.)
As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in
the system being monitored by ECM (PCM) and turning ON
the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to that malfunction, 2
driving cycle detection logic is adopted to prevent erroneous
detection.
When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving condi-
tions then are stored in ECM (PCM) memory as freeze frame
data. (For the details, refer to description on Freeze frame
data.)
It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan
tool (2) but also generic scan tool. (Diagnostic information
can be accessed by using a scan tool.)
Page 174 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-13
STEP 2. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC)/FREEZE FRAME DATA CHECK
First, check DTC, referring to “DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHECK” in this section. If DTC is indicated,
record DTC and freeze frame data.
After that clear DTC referring to “DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CLEARANCE” in this section. DTC indicates
malfunction that occurred in the system but does not indicate whether it exists now or it occurred in the past and
the normal condition has been restored now. To check which case applies, check the symptom in question
according to Step 5 and recheck DTC according to Step 6, 7.
Attempt to diagnose a trouble based on DTC in this step only or failure to clear the DTC (including pending DTC)
in this step will lead to incorrect diagnosis, trouble diagnosis of a normal circuit or difficulty in troubleshooting.
STEP 3. and 4. VISUAL INSPECTION
Be sure to perform visual check of the following items that support proper function of the engine.
STEP 5. TROUBLE SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION
Based on information obtained in Step 1 “CUSTOMER COMPLAINT ANALYSIS” and Step 2 “DTC/FREEZE
FRAME DATA CHECK”, confirm trouble symptoms. Also, reconfirm DTC according to “DTC CONFIRMATION
PROCEDURE” described in each “DTC FLOW TABLE”.NOTE:
For A/T vehicle, if only DTC P0705, P0715, P0720, P0741, P0743, P0751, P0753, P0756, P0758, or P1875
is indicated in this step, proceed to “DIAGNOSIS” in SECTION 7B1.
INSPECTION ITEM REFERRING SECTION
• Engine oil - - - - - level, leakage
• Engine coolant - - - - - level, leakage
• Fuel - - - - - level, leakage
• A/T fluid - - - - - level, leakage
• Air cleaner element - - - - - dirt, clogging
• Battery - - - - - fluid level, corrosion of terminal
• Water pump belt and/or cooling fan belt - - - - - tension, damage
• Accelerator cable - - - - - play, installation
• A/T throttle cable - - - - - play, installation
• Vacuum hoses of air intake system
- - - - - disconnection, looseness, deterioration, bend
• Connectors of electric wire harness - - - - - disconnection, friction
• Fuses - - - - - burning
• Parts - - - - - installation, bolt - - - - - looseness
• Parts - - - - - deformation
• Other parts that can be checked visually
• Also check following items at engine start, if possible
– Malfunction indicator lamp - - - - - operation
– Charge warning lamp - - - - - operation
– Engine oil pressure warning lamp - - - - - operation
– Engine coolant temp. meter - - - - - operation
– Fuel lever meter - - - - - operation
– Abnormal air being inhaled from air intake system
– Exhaust system - - - - - leakage of exhaust gas, noise
– Other parts that can be checked visuallySECTION 0B
SECTION 0B
SECTION 0B
SECTION 0B
SECTION 0B
SECTION 0B
SECTION 6C
SECTION 6E2
SECTION 6E2
SECTION 6A2
SECTION 8
SECTION 6-1
SECTION 6H
SECTION 8/6A2
SECTION 8
SECTION 8
Page 188 of 656

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE) 6-1-27
Scan tool data definitions
COOLANT TEMP (Engine Coolant Temp., °C/°F)
It is detected by engine coolant temp. sensor.
INTAKE AIR TEMP (°C/°F)
It is detected by intake air temp. sensor.
DESIRE IDLE (Desired Idle Speed RPM)
The desired idle speed is an ECM (PCM) internal parameter which indicates the ECM (PCM) requested idle. If
the engine is not running, the number is not valid.
CLOSED THROT POS (Closed Throttle Position ON/OFF)
This parameter will read ON when the throttle valve is fully closed. Or OFF when the throttle is not fully closed.
IAC FLOW DUTY (%)
This parameter indicates IAC valve opening rate which controls bypass air flow.
ENGINE SPEED (RPM)
It is computed by reference pulses from the Camshaft Position Sensor.
SHORT FT B1 (Short Term Fuel Trim Bank 1, %) / SHORT FT B2 (Short Term Fuel Trim Bank 2, %)
Short term fuel trim value represents short term corrections to the air/fuel mixture computation. A value of 0 indi-
cates no correction, a value greater than 0 means an enrichment correction, and a value less than 0 implies an
enleanment correction.
LONG FT B1 (Long Term Fuel Trim Bank 1, %) / LONG FT B2 (Long Term Fuel Trim Bank 2, %)
Long term fuel trim value represents long term corrections to the air/fuel mixture computation. A value of 0 indi-
cates no correction, a value greater than 0 means an enrichment correction, and a value less than 0 implies an
enleanment correction.
IGNITION ADVANCE (Ignition Timing Advance For No.1 Cylinder, °)
Ignition timing of No.1 cylinder is commanded by ECM (PCM). The actual ignition timing should be checked by
using the timing light.
BATTERY VOLTAGE (V)
This parameter indicates battery positive voltage inputted from main relay to ECM (PCM).
MAF (Mass Air Flow Rate, g/s, lb/min)
It represents total mass of air entering intake manifold which is measured by mass air flow sensor.
INJ PULSE WIDTH B1 (Fuel Injection Pulse Width Bank 1, msec) / INJ PULSE WIDTH B2 (Fuel Injec-
tion Pulse Width Bank 2, msec)
This parameter indicates time of the injector drive (valve opening) pulse which is output from ECM (PCM).
THROTTLE POS (Absolute Throttle Position, %)
When throttle position sensor is fully closed position, throttle opening is indicated as 0 % and 100 % for full open
position.