2001 SUZUKI GRAND VITARA ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 165 of 656

6-1-4 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
When disconnecting couplers, don’t pull wire harness but
make sure to hold coupler itself. With lock type coupler, be
sure to unlock before disconnection. Attempt to disconnect
coupler without unlocking may result in damage to coupler.
When connecting lock type coupler, insert it till clicking
sound is heard and connect it securely.
Precaution on Fuel System Service
Work must be done with no smoking, in a well-ventilated area and away from any open flames.
As fuel feed line (between fuel pump and fuel pressure regulator) is still under high fuel pressure even after
engine was stopped, loosening or disconnecting fuel feed line directly may cause dangerous spout of fuel to
occur where loosened or disconnected. Before loosening or disconnecting fuel feed line, make sure to
release fuel pressure according to “FUEL PRESSURE RELIEF PROCEDURE” in this section.
A small amount of fuel may be released after the fuel line is disconnected.
In order to reduce the chance of personal injury, cover the fitting to be disconnected with a shop cloth. Put
that cloth in an approved container when disconnection is completed.
Never run engine with fuel pump relay disconnected when engine and exhaust system are hot.
Fuel or fuel vapor hose connection varies with each type of
pipe. When reconnecting fuel or fuel vapor hose, be sure to
connect and clamp each hose correctly referring to left fig-
ure.
After connecting, make sure that the hose has no twist or
kink.
When installing fuel union bolt gasket, always use new gas-
ket and tighten union bolt to specified torque according to
“TIGHTENING TORQUE SPECIFICATION” in Section 6C.
When installing injector, fuel feed pipe or fuel pressure regu-
lator, lubricate its O-ring with gasoline.
When connecting fuel pipe flare nut, first tighten flare nut by
hand and then tighten it to specified torque.
[A] : With short pipe, fit hose as far as it reaches pipe joint as shown.
[B] : With following type pipe, fit hose as far as its peripheral projection as shown.
[C] : With bent pipe, fit hose as far as its bent part as shown or till pipe is about 20
to 30 mm (0.79 – 1.18 in.) into the hose.
[D] : With straight pipe, fit hose till pipe is about 20 to 30 mm (0.79 – 1.18 in.) into
the hose.
1. Hose
2. Pipe
3. Clamp
“a” : Clamp securely at a position 3 to 7 mm (0.12 – 0.27 in.) from hose end.
“b” : 20 to 30 mm (0.79 – 1.18 in.)
Page 167 of 656
6-1-6 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
Engine Diagnosis
General Description
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission control system which are under control of ECM (PCM).
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle are controlled by ECM (PCM). ECM (PCM) has an On-
Board Diagnostic system which detects a malfunction in this system and abnormality of those parts that influ-
ence the engine exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the
outline of “ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM” and each item in “PRECAUTION IN DIAGNOSING TROUBLE”
and execute diagnosis according to “ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
There is a close relationship between the engine mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system, exhaust
system, etc. and the engine and emission control system in their structure and operation. In case of an engine
trouble, even when the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed according to
“ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE” in this section.
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle without
Monitor Connector)
ECM (PCM) in this vehicle has following functions.
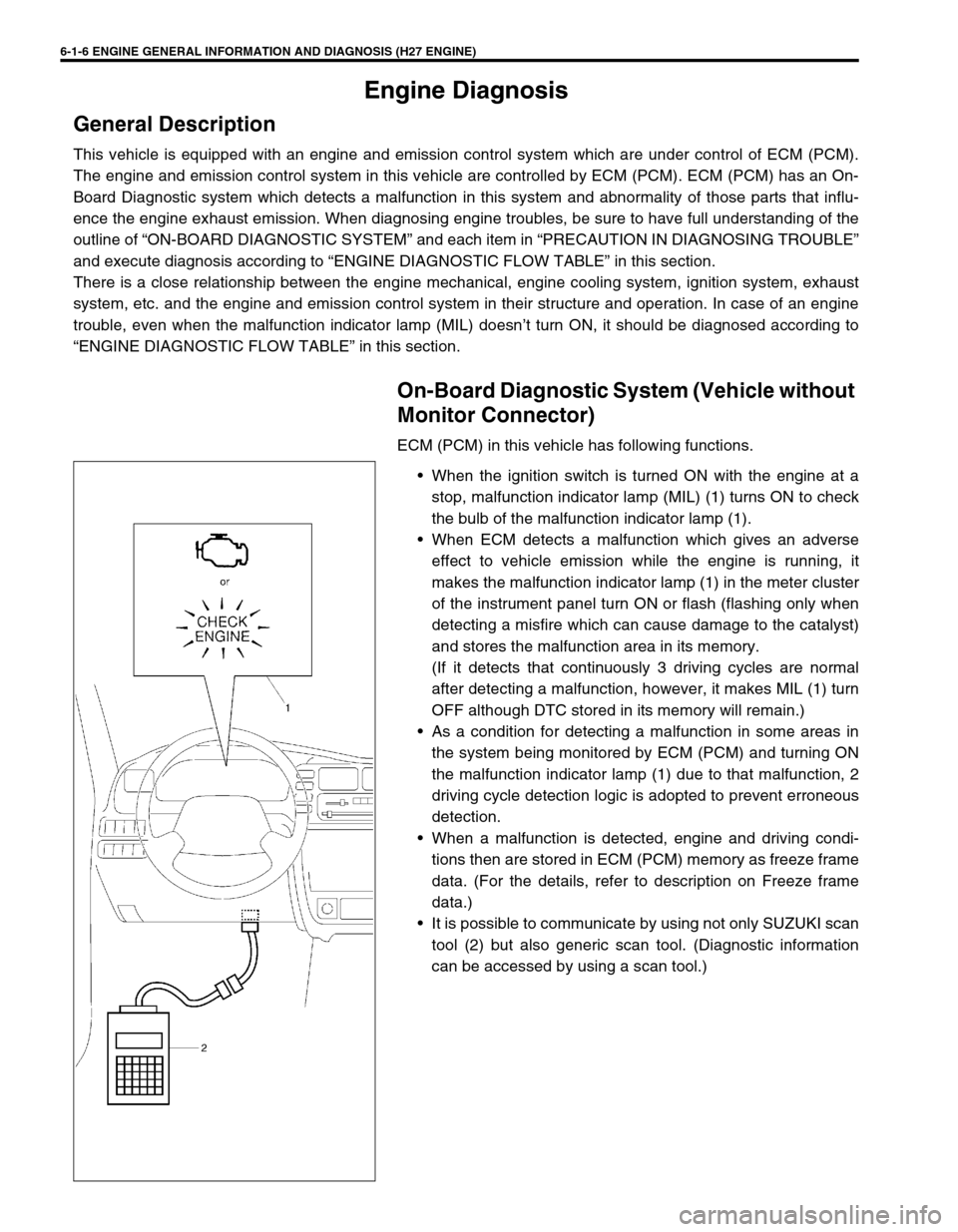
When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a
stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns ON to check
the bulb of the malfunction indicator lamp (1).
When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an adverse
effect to vehicle emission while the engine is running, it
makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in the meter cluster
of the instrument panel turn ON or flash (flashing only when
detecting a misfire which can cause damage to the catalyst)
and stores the malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that continuously 3 driving cycles are normal
after detecting a malfunction, however, it makes MIL (1) turn
OFF although DTC stored in its memory will remain.)
As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in
the system being monitored by ECM (PCM) and turning ON
the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to that malfunction, 2
driving cycle detection logic is adopted to prevent erroneous
detection.
When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving condi-
tions then are stored in ECM (PCM) memory as freeze frame
data. (For the details, refer to description on Freeze frame
data.)
It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan
tool (2) but also generic scan tool. (Diagnostic information
can be accessed by using a scan tool.)
Page 183 of 656

6-1-22 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
For immobilizer control system (Refer to Section 8G for diagnosis)
P0753
(No.61)
(No.62)Shift solenoid A (#1) electricalMonitor signal OFF is detected when
shift solenoid A (#1) is ON or monitor
signal ON is detected when it is OFF.1 driving
cycleNot
applicable
P0756Shift solenoid B (#2) perfor-
mance or stuck offGear change control from PCM to A/T
does not agree with actual gear posi-
tion of A/T.2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable
P0758
(No.63)
(No.64)Shift solenoid B (#2) electricalMonitor signal OFF is detected when
shift solenoid B (#2) is ON or monitor
signal ON is detected when it is OFF.1 driving
cycleNot
applicable
P18754WD low switch circuit mal-
functionDifference between vehicle speed
detected by VSS and vehicle speed
detected by output speed sensor and
compensated by 4WD low switch is
larger than specification.2 driving
cyclesNot
applicable DTC NO. DETECTED ITEMDETECTING CONDITION
(DTC will set when detecting : )MIL
(vehicle
without
monitor
connector)MIL
(vehicle
with
monitor
connector)
DTC NO. DETECTED ITEMDETECTING CONDITION
(DTC will set when detecting : )MIL
(vehicle
without
monitor
connector)MIL
(vehicle
with
monitor
connector)
P1620
(No.84)ECU code not registered
Refer to Section 8G P1621
(No.83)NO ECU code transmitted
from Immobilizer Control Mod-
ule
P1622
(No.82)Fault ECM
P1623
(No.81)ECU code not matched
NOTE:
DTC NO. with (*) is detected only vehicle without monitor connector.
DTC No. with (**) is detected only vehicle with monitor connector.
For ( ) marked No. in DTC column, it is used for vehicle with monitor connector.
DTC No.12 appears when none of the other codes is identified.
Page 263 of 656

6-1-102 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
5) Connect 12 V-battery to EVAP canister purge valve (3) termi-
nals. In this state, blow hose “A” (1).
Air should come out of hose “B” (2).
If check result is not as described, replace EVAP canister
purge valve.
6) Connect vacuum hoses.
7) Connect EVAP canister purge valve coupler securely.WARNING:
Do not suck the air through valve. Fuel vapor inside valve
is harmful.
Page 331 of 656

6C-4 ENGINE FUEL
INSTALLATION
1) Install fuel pump assembly, fuel cut valve and vapor control
valve to fuel tank. Refer to “FUEL PUMP” in this section.
2) Connect fuel hoses to fuel tank, fuel cut valve, and vapor
control valve, check valve and fuel pump assembly.
After connecting, clamp hoses securely.
3) Install inlet valve to fuel tank. If deformed or damaged in any
other way, replace with a new one.
4) Install fuel tank by using fuel tank belts and then install pro-
tector to vehicle.
Tightening torque
Fuel tank bolt (a) : 50 N·m (5.0 kg-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
Fuel tank protector bolt (a) : 50 N·m (5.0 kg-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
5) Connect fuel filler hose to fuel filler neck with match the
match marks. And then clamp the securely.
6) Connect fuel filler hose to fuel tank and breather hose to fuel
filler neck. Clamp them securely.
Tightening torque
Breather hose clamp (b) : 2.0 N·m (0.2 kg-m, 2.0 lb-ft)
Fuel filler hose clamp (c) : 4.0 N·m (0.4 kg-m, 3.0 lb-ft)
7) Install fuel filler hose protector.
8) Connect fuel vapor hose (1) and return hose (2) to fuel pipe
and clamp them securely.
9) Connect fuel filter inlet hose to fuel filter.
10) Connect coupler to fuel pump assembly.
11) Connect negative (–) cable to battery.
12) Upon completion of installation, check fuel system for leak-
age.
1. Fuel tank 9. Fuel tank protector
2. Fuel pump (with fuel level gauge) 10. Belt
3. Fuel filter 11. Filler neck
4. Fuel filler cap 12. Breather pipe
5. Breather hose 13. Filler hose
6. Fuel feed line (to delivery pipe) 14. Tank inlet valve
7. Fuel return line (from delivery pipe) 15. Fuel cut valve
8. Fuel vapor line (to EVAP canister)
1. Fuel filter
2. Fuel filter outlet hose
3. Fuel filter inlet hose
Page 332 of 656

ENGINE FUEL 6C-5
Fuel Lines
Due to the fact that fuel feed line is under high pressure, this sys-
tem requires special consideration for service.
The feed pipe uses screw couplings and hose clamps.
INSPECTION
Visually inspect fuel lines for evidence of fuel leakage, hose
cracking and deterioration, or damage. Make sure all clamps are
secure. Replace parts as needed.
Page 348 of 656

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (SEQUENTIAL MULTIPORT FUEL INJECTION FOR H27 ENGINE) 6E2-15
Idle Speed/Idle Air Control (IAC) Duty Inspec-
tion
Before idle speed/IAC duty check, make sure of the following.
•Lead wires and hoses of engine/emission control systems
are connected securely.
•Accelerator cable is adjusted.
•Ignition timing is within specification.
•All accessories (wipers, heater, lights, A/C, etc.) are out of
service.
•Air cleaner has been properly installed and is in good condi-
tion.
•ECM (PCM) does not detect any malfunction DTC.
After above items are all confirmed, check idle speed and IAC
duty as follows.
[Using SUZUKI scan tool]
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A) : SUZUKI scan tool
2) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
3) Check IAC duty and idle speed by using “Data List” mode of
SUZUKI scan tool.
Engine idle speed:
A/C OFF: 700 ± 50 r/min.
A/C ON: 750 ± 50 r/min.
IAC duty at specified idle speed:
5 – 40 % (at A/C OFF)
4) If duty and/or idle speed is out of specifications, check idle
air control system referring to “DIAG. FLOW TABLE B-4” in
Section 6-1.
5) Check that specified engine idle speed is obtained with A/C
ON if vehicle is equipped with A/C. If not, check A/C ON sig-
nal circuit and idle air control system. NOTE:
Before starting engine, place transmission gear shift
lever in “Neutral” (shift selector lever to “P” range for A/T
vehicle), and set parking brake and block drive wheels.
Page 355 of 656

6E2-22 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (SEQUENTIAL MULTIPORT FUEL INJECTION FOR H27 ENGINE)
3) Remove air cleaner outlet hose and remove IAC valve from
throttle body.
4) Connect connector to IAC valve.
5) Check that plunger (1) of IAC valve moves once and then
stops as soon as ignition switch (2) is turned OFF after
cranking engine for 2 sec.
If plunger (1) of IAC valve does not operate at all, check wire
harnesses for open and short. If wire harnesses are in good
condition, replace IAC valve and recheck.
INSTALLATION
1) Install new O-ring to throttle body.
2) Install IAC valve to throttle body.
3) Tighten IAC valve screws to specified torque.
Tightening torque
IAC valve screw (a) : 3.5N·m (0.35 kg-m, 2.5 lb-ft)
4) Connect IAC valve connector securely.
5) Connect negative (–) cable to battery.
Fast idle air valve
1) Disconnect IAC valve coupler with ignition switch OFF.
2) Check that with cold engine started, as cooling water tem-
perature rises, engine idle speed reduces gradually.
If check result is as described above, fast idle air valve is in
good condition.
If not, fast idle air valve, air passage or coolant passage is
faulty. NOTE:
This check should be performed by two people, one per-
son operates ignition switch while the other checks
plunger operation.