Page 77 of 656

3C1-2 AIR BAG STEERING WHEEL AND COLUMN
General Description
This double tube type steering column has the following three important features in addition to the steering func-
tion:
The column is energy absorbing, designed to compress in a front-end collision.
The ignition switch and lock are mounted conveniently on this column.
With the column mounted lock, the ignition and steering operations can be locked to inhibit theft of the vehi-
cle.
To insure the energy absorbing action, it is important that only the specified screws, bolts, and nuts be used as
designated and that they are tightened to the specified torque. When the column assembly is removed from the
vehicle, special care must be taken in handling it. Use of a steering wheel puller other than the one recom-
mended in this manual or a sharp blow on the end of the steering shaft, leaning on the assembly, or dropping
the assembly could shear the plastic shear pins which maintain column length and position.
The driver air bag (inflator) module is one of the supplemental restraint (air bag) system components and is
mounted to the center of the steering wheel. During certain frontal crashes, the air bag system supplements the
restraint of the driver’s and passenger’s seat belts by deploying the air bags. The air bag (inflator) module
should be handled with care to prevent accidental deployment. When servicing, be sure to observe all WARN-
INGS in this section. Refer to “SERVICE PRECAUTIONS” in Section 10B.
1. Driver air bag (inflator) module 5. Steering column upper cover 9. Steering column hole cover 13. Steering column lower seal
2. Steering wheel 6. Steering column lower cover 10. Steering shaft joint 14. Cap (if equipped)
3. Steering wheel nut 7. Steering column assembly 11. Steering lower shaft assembly 15. Steering upper shaft assembly
4. Contact coil and combination
switch assembly8. Steering lock assembly 12. Adjustable steering column
release lever
Page 79 of 656

3C1-4 AIR BAG STEERING WHEEL AND COLUMN
Steering Column
REMOVAL
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Disable air bag system. Refer to “DISABLING AIR BAG SYSTEM” under “SERVICE PRECAUTIONS” in
Section 10B.
3) Remove steering wheel and contact coil and combination switch assembly, if necessary. Refer to “STEER-
ING WHEEL” and “CONTACT COIL AND COMBINATION SWITCH ASSEMBLY” in this section.
Perform the following procedure if not removing steering wheel and/or combination switch.
a) Turn steering wheel so that vehicle’s front tires are at straight-ahead position.
b) Turn ignition switch to “LOCK” position and remove key.
4) Remove steering column hole cover (1).
5) Disconnect all connectors for the following parts.
Contact coil and combination switch
Ignition switch CAUTION:
Once the steering column is removed from the vehicle, the column is extremely susceptible to dam-
age.
Dropping the column assembly on its end could collapse the steering shaft or loosen the plastic
shear pins which maintain column length leaning on the column assembly could cause it to bend or
deform.
Any of the above damage could impair the column’s collapsible design.
When loosening steering column mounting bolts and nuts, make sure that steering column assembly
and steering upper shaft assembly have been separated. Loosening them with steering column
assembly and steering upper shaft assembly assembled could cause damage to upper joint and
mounting bracket in steering upper shaft assembly.
NOTE:
When servicing steering column or any column-mounted component, remove steering wheel. But
when removing steering column simply to gain access to instrument panel components, leave steer-
ing wheel installed on steering column.
WARNING:
Never rest a steering column assembly on the steering wheel with air bag (inflator) module face down
and column vertical. Otherwise personal injury may result.
CAUTION:
Never turn steering wheel while steering column with steering wheel is removed. Turning steering
wheel more than about two and a half turns will break contact coil.
Page 86 of 656

AIR BAG STEERING WHEEL AND COLUMN 3C1-11
Checking Steering Column and Steering
Upper Shaft for Accident Damage
Check that 2 capsules are attached to steering column
bracket securely. Check clearance between capsules and
steering column bracket. Clearance should be 0 mm (0 in.)
on both sides. If found loose or clearance, replace steering
column assembly.
Take measurement “a” as shown in the figure. If it is shorter
than specified length, replace column assembly with new
one.
Steering column assembly length “a” :
490.3 ± 1.0 mm (19.30 ± 0.04 in.)
Check steering shaft for smooth rotation.
If found defective, replace as column assembly.
Check steering shaft and column for bend, cracks or defor-
mation.
If found defective, replace as column assembly.
Check steering upper shaft lower seal (1) for breakage or
deformation.
If found defective, replace.
Check steering shaft joints and shaft for any damages such
as crack, breakage, malfunction or excessive play.
If anything is found faulty, replace steering upper shaft
assembly, steering lower shaft assembly or steering column
assembly. NOTE:
Vehicles involved in accidents resulting in body damage,
where steering column has been impacted or air bag
deployed, may have a damaged or misaligned steering
column.
1. Capsule
2. Steering column bracket
1
2
“a”
Page 87 of 656
3C1-12 AIR BAG STEERING WHEEL AND COLUMN
Take measurement “b” as shown in the figure. If it is shorter
than specified length, replace steering upper shaft assembly
with new one.
Steering upper shaft assembly length “b” :
419.0 ± 1.0 mm (16.50 ± 0.04 in.)
Tightening Torque Specification
“b”
Fastening partTightening torque
Nm kg-m lb-ft
Driver air bag (inflator) module bolt 9 0.9 6.5
Steering shaft nut 33 3.3 23.5
Steering column mounting bolt and nut 25 2.5 18.0
Steering shaft joint bolt 25 2.5 18.0
Steering lower shaft assembly lower joint bolt 25 2.5 18.0
Shift (key) interlock cable screw 2.2 0.22 1.6
Steering upper shaft mounting bolt 23 2.3 17.0
Steering upper shaft upper joint nut 23 2.3 17.0
Page 93 of 656
3E-4 REAR SUSPENSION
5) Apply grease “A” to axle shaft inner oil seal lip as shown in
the figure.
“A” : Grease 99000-25010
6) Apply water tight sealant “B” to mating surfaces of brake
back plate and rear axle hub (2).
“B” : Water tight sealant 99000-31110
7) Install rear axle shaft to rear axle housing and tighten bear-
ing retainer nuts to specified torque.
Rear axle shaft length “L”
Left side : 700.5 mm (27.6 in.)
Right side : 769.5 mm (30.3 in.)
Tightening torque
Bearing retainer nut (a) : 50 N·m (5.0 kg-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
8) Tighten wheel speed sensor bolt to specified torque (if
equipped with ABS).
Tightening torque
Wheel speed sensor bolt (b) : 21 N·m (2.1 kg-m, 15.5 lb-ft)
9) Refill rear axle housing with new specified gear oil.
Refer to “MAINTENANCE SERVICE” in Section 7F.
10) Install brake drum. Refer to “BRAKE DRUM” in Section 5C.
1. Axle housing
NOTE:
When installing rear axle shaft, be careful not to cause
damage to oil seal lip in axle housing.
(b)
Page 102 of 656
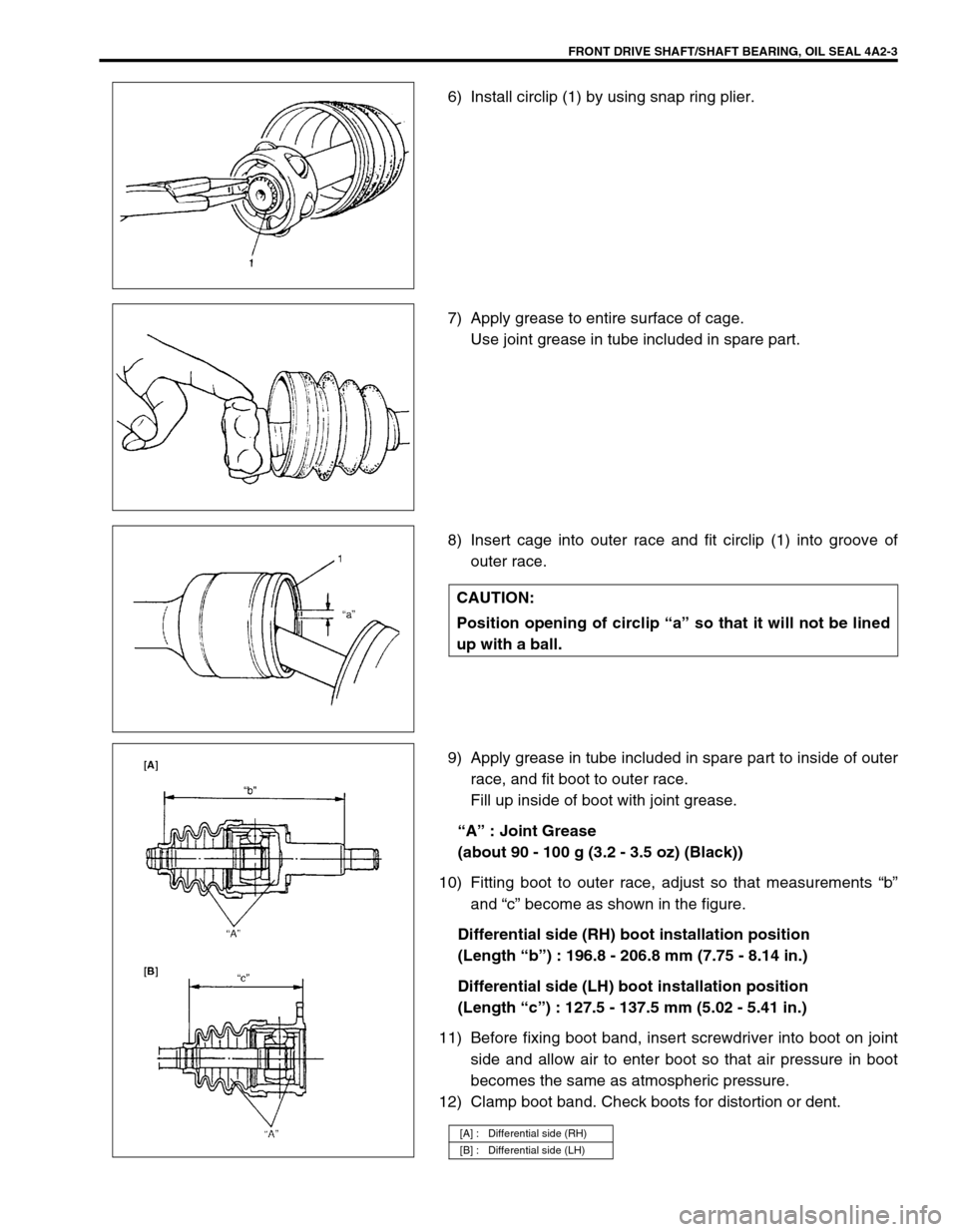
FRONT DRIVE SHAFT/SHAFT BEARING, OIL SEAL 4A2-3
6) Install circlip (1) by using snap ring plier.
7) Apply grease to entire surface of cage.
Use joint grease in tube included in spare part.
8) Insert cage into outer race and fit circlip (1) into groove of
outer race.
9) Apply grease in tube included in spare part to inside of outer
race, and fit boot to outer race.
Fill up inside of boot with joint grease.
“A” : Joint Grease
(about 90 - 100 g (3.2 - 3.5 oz) (Black))
10) Fitting boot to outer race, adjust so that measurements “b”
and “c” become as shown in the figure.
Differential side (RH) boot installation position
(Length “b”) : 196.8 - 206.8 mm (7.75 - 8.14 in.)
Differential side (LH) boot installation position
(Length “c”) : 127.5 - 137.5 mm (5.02 - 5.41 in.)
11) Before fixing boot band, insert screwdriver into boot on joint
side and allow air to enter boot so that air pressure in boot
becomes the same as atmospheric pressure.
12) Clamp boot band. Check boots for distortion or dent.
CAUTION:
Position opening of circlip “a” so that it will not be lined
up with a ball.
[A] : Differential side (RH)
[B] : Differential side (LH)
Page 115 of 656
5A-8 BRAKES PIPE/HOSE/MASTER CYLINDER
Brake Booster
CLEARANCE BETWEEN BOOSTER PISTON ROD AND
MASTER CYLINDER PISTON CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT
The length of booster piston rod (1) is adjusted to provide speci-
fied clearance “0” between piston rod (1) end and master cylinder
piston (2).
1) Before measuring clearance, push piston rod several times
so as to make sure reaction disc is in place.
2) Keep inside of booster at atmospheric pressure for measure-
ment.
3) Check depth of piston rod, i.e. distance between piston rod
and mating surface of booster-to-master cylinder.
Depth “c” of piston rod for check :
15.8 – 16.6 mm (0.623 – 0.653 in.)
1. Brake master cylinder assembly 4. Push rod clevis 7. Clip
2. Brake booster assembly 5. Nut 8. Plate
3. Gasket 6. Clevis pin 9. Seal
19
2 3
8546 7
Page 247 of 656
6-1-86 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (H27 ENGINE)
DTC P0340 (DTC No.42) Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
WIRING DIAGRAM
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
CMP sensor detects REF signal and POS signal.
• REF signal : 4 pulses/1 revolution of camshaft. There are 2 different kinds of wavelength. Based on REF sig-
nal, ECM (PCM) judges which cylinder is at TDC.
• POS signal : 6 pulse/1 revolution of camshaft. Each of POS signals has equivalent wavelength. Based on
POS signal, ECM (PCM) judges the wavelength of REF signals, engine speed and piston position.
REFERENCE
Connect oscilloscope between terminals C51-1-13 (POS) or C51-1-12 (REF) and C51-3-26 (ground) of ECM
(PCM) connector connected to ECM (PCM) and check CMP sensor signal.
1. CMP sensor
2. To main relay
3. ECM (PCM)