Page 27 of 319
This page brief ly summarizes
Honda’s recommendations on where
to place rear-facing and forward-
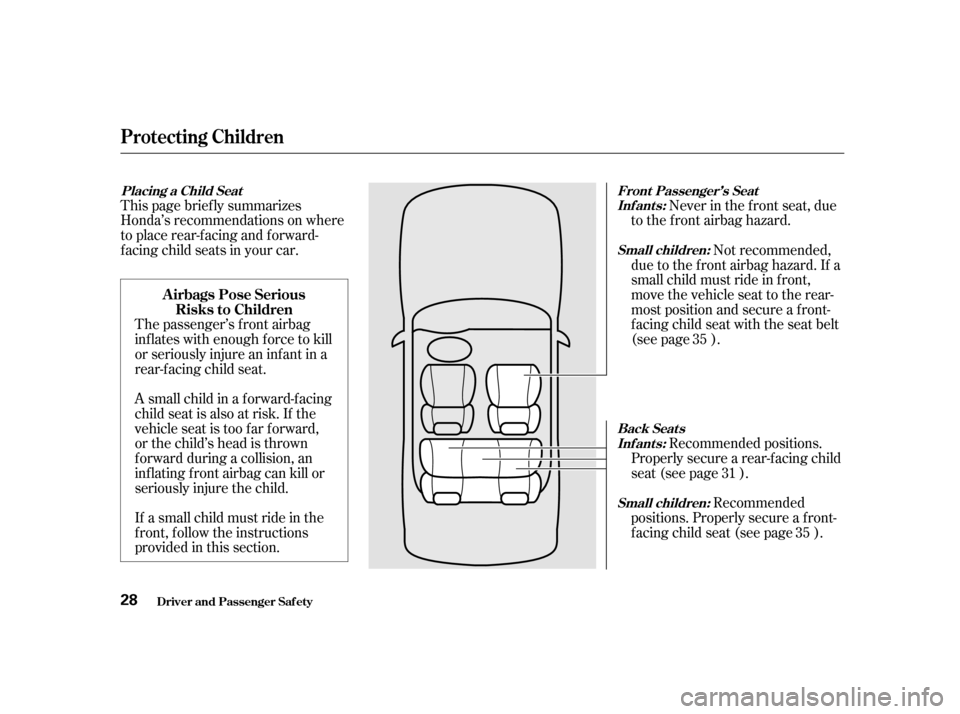
f acing child seats in your car.Never in the f ront seat, due
to the f ront airbag hazard.
The passenger’s f ront airbag
inf lates with enough f orce to kill
or seriously injure an inf ant in a
rear-facing child seat.
A small child in a f orward-f acing
child seat is also at risk. If the
vehicle seat is too f ar f orward,
or the child’s head is thrown
f orward during a collision, an
inf lating f ront airbag can kill or
seriously injure the child.
If a small child must ride in the
f ront, f ollow the instructions
provided in this section. Not recommended,
due to the f ront airbag hazard. If a
small child must ride in f ront,
move the vehicle seat to the rear-
most position and secure a f ront-
f acing child seat with the seat belt
(see page ).
Recommended positions.
Properlysecurearear-facingchild
seat (see page ).
Recommended
positions. Properly secure a f ront-
f acing child seat (see page ). 35
35
31
Placing a Child Seat
Front Passenger’s Seat
Inf ant s:
Back Seat s
Small children:
Inf ant s:Small children:
Airbags Pose SeriousRisks to Children
Protecting Children
Driver and Passenger Saf ety
28
Page 29 of 319
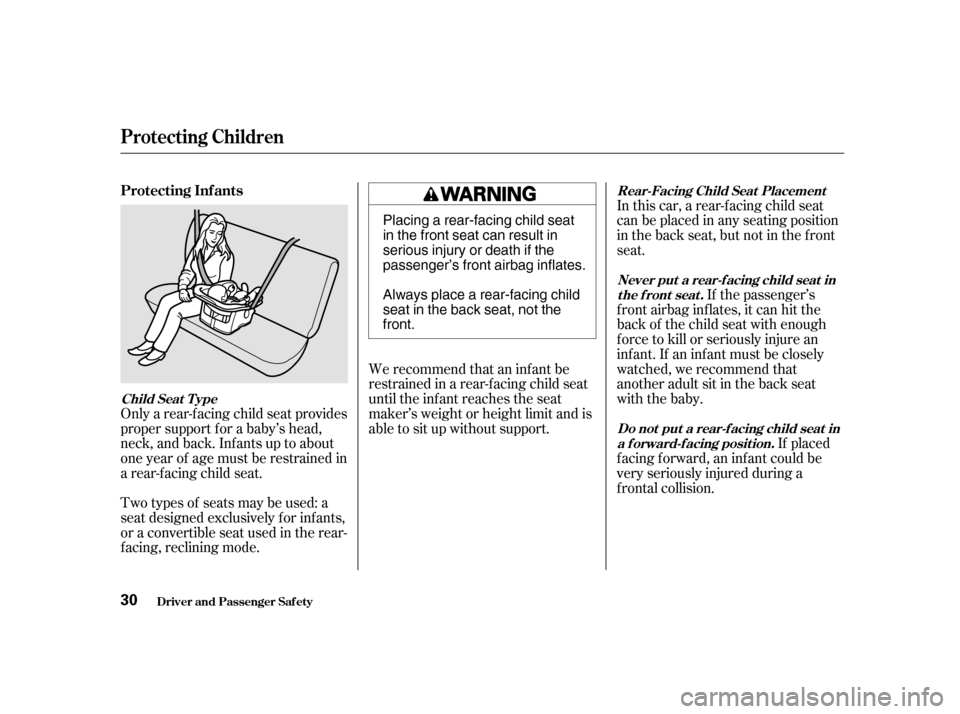
Only a rear-f acing child seat provides
proper support f or a baby’s head,
neck, and back. Inf ants up to about
one year of age must be restrained in
a rear-f acing child seat.In this car, a rear-f acing child seat
canbeplacedinanyseatingposition
in the back seat, but not in the f ront
seat.
Two types of seats may be used: a
seat designed exclusively f or inf ants,
or a convertible seat used in the rear-
f acing, reclining mode. We recommend that an inf ant be
restrained in a rear-f acing child seat
until the inf ant reaches the seat
maker’s weight or height limit and is
able to sit up without support.
If the passenger’s
f ront airbag inf lates, it can hit the
back of the child seat with enough
forcetokillorseriouslyinjurean
inf ant. If an inf ant must be closely
watched, we recommend that
another adult sit in the back seat
with the baby.
If placed
f acing f orward, an inf ant could be
very seriously injured during a
f rontal collision.
Protecting Inf ants
Child Seat T ype
Rear-Facing Child Seat Placement
Never put a rear-f acing child seat inthe front seat.
Do not put a rear-f acing child seat ina f orward-f acing position.
Protecting Children
Driver and Passenger Saf ety
30 Placing a rear-facing child seat
in the front seat can result in
serious injury or death if the
passenger’s front airbag inflates.
Always place a rear-facing child
seat in the back seat, not thefront.
Page 33 of 319
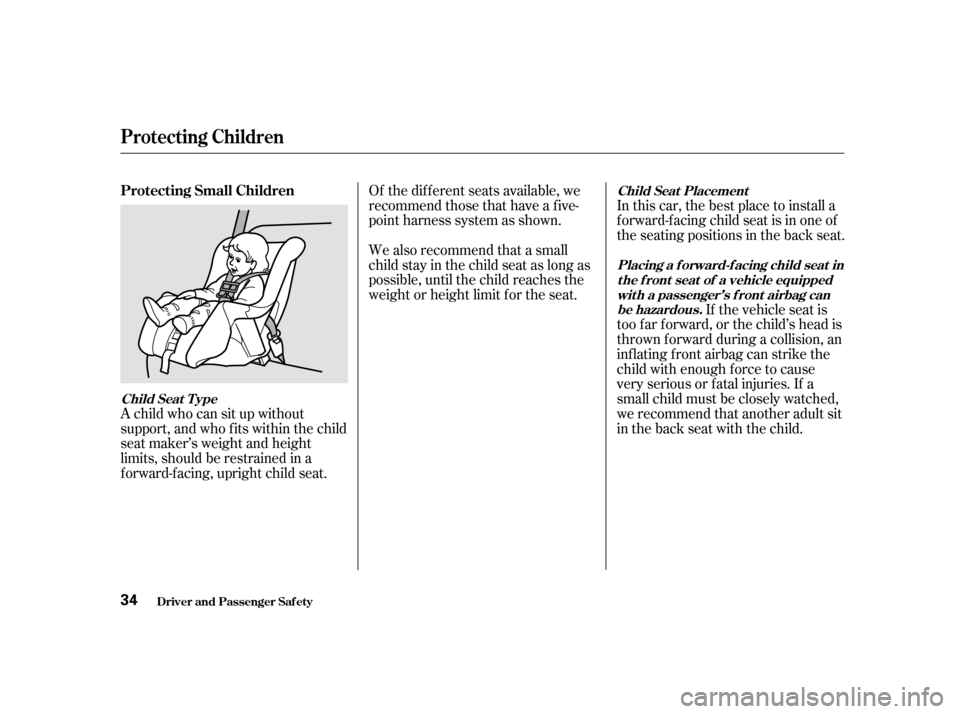
A child who can sit up without
support, and who f its within the child
seat maker’s weight and height
limits, should be restrained in a
f orward-f acing, upright child seat.In this car, the best place to install a
f orward-f acing child seat is in one of
the seating positions in the back seat.
If the vehicle seat is
too far forward, or the child’s head is
thrown f orward during a collision, an
inflating front airbag can strike the
child with enough f orce to cause
very serious or f atal injuries. If a
small child must be closely watched,
we recommend that another adult sit
in the back seat with the child.
We also recommend that a small
child stay in the child seat as long as
possible, until the child reaches the
weight or height limit f or the seat.
Of the different seats available, we
recommend those that have a f ive-
point harness system as shown.
Protecting Small Children
Child Seat T ype Child Seat Placement
Placing a f orward-f acing child seat int he f ront seat of a vehicle equippedwit h a passenger’s f ront airbag canbe hazardous.
Protecting Children
Driver and Passenger Saf ety
34
Page 34 of 319

With the child seat in the desired
seating position, route the belt
through the child seat according
to the seat maker’s instructions,
then insert the latch plate into the
buckle.
The lap/shoulder belts in the back
and f ront passenger seating positions
have a locking mechanism that must
be activated to secure a child seat.
The f ollowing pages provide
instructions on how to secure a
f orward-f acing child seat with this
type of seat belt.
If you have a child seat designed to
attach to the vehicle’s lower
anchorages, f ollow the instructions
on page .
If it is necessary to put a f orward-
f acing child seat in the f ront, move
the vehicle seat as far to the rear as
possible, be sure the child seat is
f irmly secured to the car, and the
child is properly strapped in the seat. 1.
42
CONT INUED
Child Seat Inst allat ion
Protecting Children
Driver and Passenger Saf ety 35
Improperly placing a forward-
facing child seat in the front
seat can result in serious injury
or death if the front airbagsinflate.
Ifyoumustplaceaforward-
facing child seat in front, move
the vehicle seat as far back as
possible and properly restrain
the child.
Page 36 of 319

When a child reaches the
recommended weight or height limit
for a forward-facing child seat, the
child should sit in the back seat and
wear a lap/shoulder belt.
If a child is too short f or the shoulder
part of the belt to properly f it, we
recommend that the child use a
booster seat until the child is tall
enough to use the seat belt without a
booster.
The f ollowing pages give
instructions on how to check proper
seat belt f it, what kind of booster
seat to use if one is needed, and
important precautions f or a child
who must sit in the f ront seat.
To deactivate the locking
mechanism in order to remove a
child seat, unlatch the buckle,
unroute the seat belt, and let the belt
fully retract.
Protecting L arger Children
Protecting Children
Driver and Passenger Saf ety
37
Allowing a larger child to sit
improperly in the front seat can
result in injury or death if the
passenger’s front airbag inflates.
If a larger child must sit in front,
make sure the child moves the
seat as far back as possible
and wears the seat belt properly.
Page 38 of 319

The back seat is the saf est place f or
a child of any age or size.
The National Highway Traffic Safety
Administration and Transport
Canada recommend that all children
ages 12 and under be properly
restrained in a back seat.
In addition, the passenger’s f ront
airbag poses serious risks to children.
If the seat is too f ar f orward, or the
child’s head is thrown f orward
during a collision, or the child is
unrestrained or out of position, an
inf lating f ront airbag can kill or
seriously injure the child.
Thesideairbagalsoposesrisks.If
any part of a larger child’s body is in
the path of a deploying airbag, the
child could receive possibly serious
injuries.
A child may continue using a booster
seat until the tops of the ears are
even with the top of the seat-back. A
child of this height should be tall
enough to use the lap/shoulder belt
without a booster.
If a child needs a booster seat, we
recommend choosing a style that
allows the child to use the lap/
shoulder belt directly, without a
shield, as shown.
Whichever style you select, f ollow
the booster seat maker’s instructions.
CONT INUED
When Can a Larger Child Sit in Front
Using a Boost er Seat
Protecting Children
Driver and Passenger Saf ety 39
Page 44 of 319
If the shoulder part of the belt is
pulled all the way out, the locking
mechanism will activate. The belt
will retract, but it will not allow the
passenger to move f reely.
To deactivate the locking
mechanism, unlatch the buckle and
let the seat belt f ully retract. To
ref asten the belt, pull it out only as
f ar as needed.
See page f or instructions on how
to wear the lap/shoulder belt
properly.The tensioners are designed to
activate primarily in f rontal collisions.
The tensioners are independent of
the airbag system, so they can be
activated during a collision that
might not cause the airbags to
deploy. In this case, the airbags
would not be needed but the
additional seat belt tension can be
helpf ul.
The tensioners will be activated in a
collision severe enough to cause the
f ront airbags to inf late.
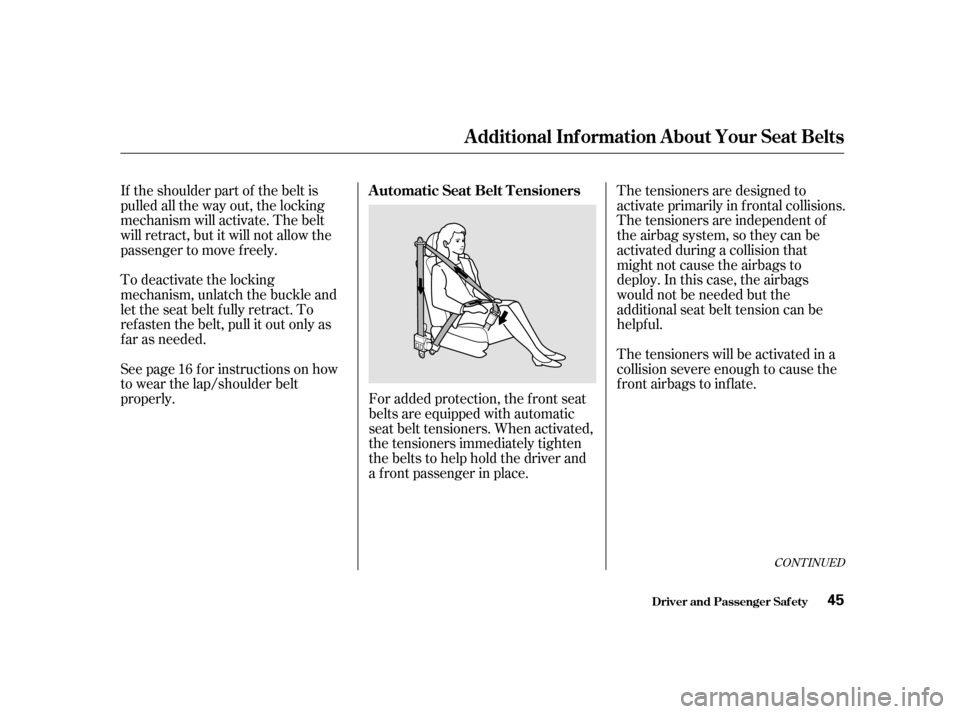
For added protection, the f ront seat
belts are equipped with automatic
seat belt tensioners. When activated,
the tensioners immediately tighten
the belts to help hold the driver and
a f ront passenger in place.
16
CONT INUED
A utomatic Seat Belt T ensioners
Additional Inf ormation About Your Seat Belts
Driver and Passenger Saf ety
45
Page 47 of 319

Your Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS) includes:Two f ront airbags. The driver’s
airbag is stored in the center of
the steering wheel; the f ront
passenger’sairbagisstoredinthe
dashboard. Both are marked ‘‘SRS
AIRBAG.’’
If you ever have a moderate to
severe f rontal collision, the sensors
will detect the vehicle’s rapid
deceleration. If the rate of
deceleration is high enough, the
control unit will instantly inf late the
f ront airbags.
A sophisticated electronic system
that continually monitors and
records inf ormation about the
sensors, the control unit, the
airbag activators, and driver and
passenger seat belt use when the
ignition is ON (II).
Sensors that can detect a
moderate to severe frontal
collision.
Automatic seat belt tensioners
(see page ).
An indicator light on the
instrument panel that alerts you to
a possible problem with the
system (see page ).
Emergency backup power in case
your car’s electrical system is
disconnected in a crash.
45
51
SRS Components
How Your Front A irbags Work
Additional Inf ormation About Your Airbags
Driver and Passenger Saf ety
48