2001 FORD RANGER transmission
[x] Cancel search: transmissionPage 143 of 272

Water intrusion into the transmission may damage the
transmission.
Replace rear axle lubricant any time the axle has been submerged in
water. The rear axle does not normally require a lubricant change for the
life of the vehicle. Rear axle lubricant quantities are not to be checked or
changed unless a leak is suspected or repair is required.
Driving on hilly or sloping terrain
When driving on a hill, avoid driving crosswise or turning on steep
slopes. You could lose traction and slip sideways. Drive straight up,
straight down or avoid the hill completely. Know the conditions on the
other side of a hill before driving over the crest.
When climbing a steep hill, start in a lower gear rather than downshifting
to a lower gear from a higher gear once the ascent has started. This
reduces strain on the engine and the possibility of stalling.
When descending a steep hill, avoid sudden braking. Shift to a lower gear
when added engine braking is desired.
When speed control is on and you are driving uphill, your vehicle speed
may drop considerably, especially if you are carrying a heavy load.
If vehicle speed drops more than 16 km/h (10 mph), the speed control
will cancel automatically. Resume speed with accelerator pedal.
If speed control cancels after climbing the hill, reset speed by pressing
and holding the SET ACCEL button (to resume speeds over 50 km/h
[30 mph]).
Automatic transmissions may shift frequently while driving up steep
grades. Eliminate frequent shifting by shifting out of
(Overdrive) into
a lower gear.
Driving on snow and ice
A 4WD vehicle has advantages over 2WD vehicles in snow and ice but
can skid like any other vehicle.
Avoid sudden applications of power and quick changes of direction on
snow and ice. Apply the accelerator slowly and steadily when starting
from a full stop.
When braking, apply the brakes as you normally would. In order to allow
the anti-lock brake system (ABS) to operate properly, keep steady
pressure on the brake pedal.
Allow more stopping distance and drive slower than usual. Consider
using one of the lower gears.
Driving
143
Page 144 of 272

TRACTION-LOK AXLE (IF EQUIPPED)
This axle provides added traction on slippery surfaces, particularly when
one wheel is on a poor traction surface. Under normal conditions, the
Traction-Lok axle functions like a standard rear axle.
Extended use of other than the manufacturer's specified size tires on a
Traction-Lok rear axle could result in a permanent reduction in
effectiveness. This loss of effectiveness does not affect normal driving
and should not be noticeable to the driver.
To avoid injury, never run the engine with one wheel off the
ground, such as when changing a tire.
DRIVING THROUGH WATER
Do not drive quickly through standing water, especially if the depth is
unknown. Traction or brake capability may be limited and if the ignition
system gets wet, your engine may stall. Water may also enter your
engine's air intake and severely damage your engine.
If driving through deep or standing water is unavoidable, proceed very
slowly. Never drive through water that is higher than the bottom of the
hubs (for trucks) or the bottom of the wheel rims (for cars).
Once through the water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop
the vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by
moving your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake
pedal.
Driving through deep water where the transmission vent tube is
submerged may allow water into the transmission and cause
internal transmission damage.
VEHICLE LOADING
Before loading a vehicle, familiarize yourself with the following terms:
²Base Curb Weight:Weight of the vehicle including any standard
equipment, fluids, lubricants, etc. It does not include occupants or
aftermarket equipment.
²Payload:Combined maximum allowable weight of cargo, occupants
and optional equipment. The payload equals the gross vehicle weight
rating minus base curb weight.
Driving
144
Page 145 of 272

²GVW (Gross Vehicle Weight):Base curb weight plus payload
weight. The GVW is not a limit or a specification.
²GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating):Maximum permissable total
weight of the base vehicle, occupants, optional equipment and cargo.
The GVWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the Safety
Certification Label on the driver's door pillar.
²GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating):Carrying capacity for each axle
system. The GAWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the
Safety Certification Label on the driver's door pillar.
²GCW (Gross Combined Weight):The combined weight of the
towing vehicle (including occupants and cargo) and the loaded trailer.
²GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating):Maximum permissable
combined weight of towing vehicle (including occupants and cargo)
and the loaded trailer
²Maximum Trailer Weight Rating:Maximum weight of a trailer the
vehicle is permitted to tow. The maximum trailer weight rating is
determined by subtracting the vehicle curb weight for each
engine/transmission combination, any required option weight for trailer
towing and the weight of the driver from the GCWR for the towing
vehicle.
²Maximum Trailer Weight:Maximum weight of a trailer the loaded
vehicle (including occupants and cargo) is permitted to tow. It is
determined by subtracting the weight of the loaded trailer towing
vehicle from the GCWR for the towing vehicle.
²Trailer Weight Range:Specified weight range that the trailer must
fall within that ranges from zero to the maximum trailer weight rating.
Remember to figure in the tongue load of your loaded trailer when
figuring the total weight.
Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the
certification label.
Do not use replacement tires with lower load carrying capacities than the
originals because they may lower the vehicle's GVWR and GAWR
limitations. Replacement tires with a higher limit than the originals do
not increase the GVWR and GAWR limitations.
Driving
145
Page 147 of 272

3. Subtract your loaded vehicle weight from the maximum GCWR on the
following charts. This is the maximum trailer weight your vehicle can tow
and must fall below the maximum shown under maximum trailer weight
on the chart.
TRAILER TOWING
Your vehicle may tow a class I, II or III trailer provided the maximum
trailer weight is less than or equal to the maximum trailer weight listed
for your engine and rear axle ratio on the following charts.
Your vehicle's load capacity is designated by weight, not by volume, so
you cannot necessarily use all available space when loading a vehicle.
Towing a trailer places an additional load on your vehicle's engine,
transmission, axle, brakes, tires and suspension. Inspect these
components carefully after any towing operation.
4x2 w/manual transmission
Engine Rear
axle
ratioMaximum
GCWR - kg
(lbs.)Maximum
trailer
weight - kg
(lbs.)Maximum
frontal
area of
trailer -
m
2(ft2)
Regular Cab w/6' box
2.3L All 2 177 (4 800) 753 (1 660) Equal to
frontal area
of vehicle
3.0L
(non-torsion bar
suspension)All 2 722 (6 000) 1 207 (2 660) 4.64 (50)
3.0L (torsion
bar suspension)All 2 722 (6 000) 1 152 (2 540) 4.64 (50)
4.0L
(non-torsion bar
suspension)All 3 175 (7 000) 1 624 (3 580) 4.64 (50)
4.0L (torsion
bar suspension)All 3 175 (7 000) 1 569 (3 460) 4.64 (50)
Driving
147
Page 148 of 272
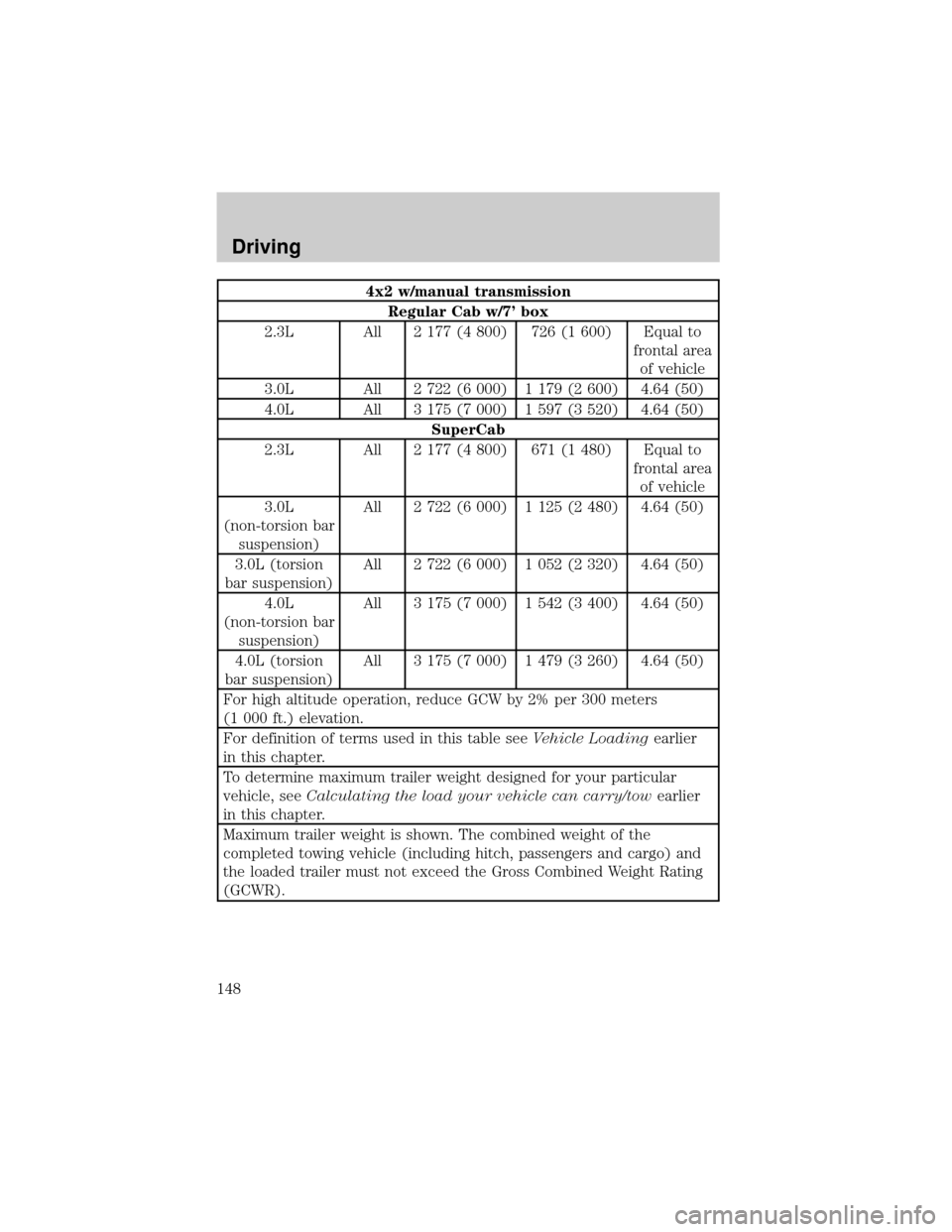
4x2 w/manual transmission
Regular Cab w/7' box
2.3L All 2 177 (4 800) 726 (1 600) Equal to
frontal area
of vehicle
3.0L All 2 722 (6 000) 1 179 (2 600) 4.64 (50)
4.0L All 3 175 (7 000) 1 597 (3 520) 4.64 (50)
SuperCab
2.3L All 2 177 (4 800) 671 (1 480) Equal to
frontal area
of vehicle
3.0L
(non-torsion bar
suspension)All 2 722 (6 000) 1 125 (2 480) 4.64 (50)
3.0L (torsion
bar suspension)All 2 722 (6 000) 1 052 (2 320) 4.64 (50)
4.0L
(non-torsion bar
suspension)All 3 175 (7 000) 1 542 (3 400) 4.64 (50)
4.0L (torsion
bar suspension)All 3 175 (7 000) 1 479 (3 260) 4.64 (50)
For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300 meters
(1 000 ft.) elevation.
For definition of terms used in this table seeVehicle Loadingearlier
in this chapter.
To determine maximum trailer weight designed for your particular
vehicle, seeCalculating the load your vehicle can carry/towearlier
in this chapter.
Maximum trailer weight is shown. The combined weight of the
completed towing vehicle (including hitch, passengers and cargo) and
the loaded trailer must not exceed the Gross Combined Weight Rating
(GCWR).
Driving
148
Page 149 of 272

4x4 w/manual transmission
Engine Rear
axle
ratioMaximum
GCWR - kg
(lbs.)Maximum
trailer weight
- kg (lbs)Maximum
frontal area
of trailer -
m
2(ft2)
Regular Cab w/6' box
3.0L All 2 722 (6 000) 1 180 (2 380) 4.64 (50)
4.0L All 3 175 (7 000) 1 506 (3 320) 4.64 (50)
Regular Cab w/7' box
3.0L All 2 722 (6 000) 1 061 (2 340) 4.64 (50)
4.0L All 3 175 (7 000) 1 479 (3 260) 4.64 (50)
SuperCab
3.0L All 2 722 (6 000) 1 007 (2 220) 4.64 (50)
4.0L All 3 175 (7 000) 1 424 (3 140) 4.64 (50)
4.0L (FX4
package)All 3 175 (7 000) 1 234 (2 720) 4.64 (50)
For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300 meters (1 000
ft.) of elevation.
For definition of terms used in this table, seeVehicle loadingearlier
in this chapter.
To determine maximum trailer weight designed for your vehicle, see
Calculating the load your vehicle can carry/towearlier in this
chapter.
Maximum trailer weight is shown. The combined weight of the
completed towing vehicle (including hitch, passengers and cargo) and
the loaded trailer must not exceed the Gross Combined Weight Rating
(GCWR).
Driving
149
Page 150 of 272

4x2 w/automatic transmission
Engine Rear
axle
ratioMaximum
GCWR - kg
(lbs.)Maximum
trailer
weight - kg
(lbs.)Maximum
frontal area
of trailer -
m
2(ft2)
Regular Cab w/6' box
2.3L All 2 495 (5 500) 1 025 (2 260) Equal to
frontal area of
vehicle
3.0L
(non-torsion
bar suspensionAll 3 402 (7 500) 1 869 (4 120) 4.64 (50)
3.0L (tosion
bar suspension)All 3 402 (7 500) 1 814 (4 000) 4.64 (50)
4.0L
(non-torsion
bar suspension)All 4 309 (9 500) 2 740 (6 040) 4.64 (50)
4.0L (torsion
bar suspension)All 4 309 (9 500) 2 685 (5 920) 4.64 (50)
Regular Cab w/7' box
2.3L All 2 495 (5 500) 1 007 (2 220) Equal to
frontal area of
vehicle
3.0L All 3 402 (7 500) 1 842 (4 060) 4.64 (50)
4.0L All 4 309 (9 500) 2 712 (5 980) 4.64 (50)
Driving
150
Page 151 of 272

4x2 w/automatic transmission
SuperCab
3.0L
(non-torsion
bar suspension)All 3 402 (7 500) 1 787 (3 940) 4.64 (50)
3.0L (torsion
bar suspension)All 3 402 (7 500) 1 715 (3 780) 4.64 (50)
4.0L
(non-torsion
bar suspension)All 4 309 (9 500) 2 667 (5 880) 4.64 (50)
4.0L (torsion
bar suspension)All 4 309 (9 500) 2 595 (5 720) 4.64 (50)
For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300 meters
(1 000 ft.) elevation.
For definition of terms used in this table seeVehicle Loadingearlier
in this chapter.
To determine maximum trailer weight designed for your particular
vehicle, seeCalculating the load your vehicle can carry/towearlier
in this chapter.
Maximum trailer weight is shown. The combined weight of the
completed towing vehicle (including hitch, passengers and cargo) and
the loaded trailer must not exceed the Gross Combined Weight Rating
(GCWR).
Driving
151