2001 FORD POSTAL EXPLORER four wheel drive
[x] Cancel search: four wheel drivePage 3 of 88

WARNINGS
Warnings provide information which may reduce the risk of personal
injury and prevent possible damage to others, your vehicle and its
equipment.
BREAKING-IN YOUR VEHICLE
There are no particular breaking-in rules for your vehicle. During the
first 1 600 km (1 000 miles) of driving, vary speeds frequently. This is
necessary to give the moving parts a chance to break in.
INFORMATION ABOUT THIS GUIDE
The information found in this guide was in effect at the time of printing.
Ford may change the contents without notice and without incurring
obligation.
SPECIAL NOTICES
Notice to owners of pickup trucks and utility type vehicles
Utility vehicles have a significantly higher rollover rate than
other types of vehicles.
Before you drive your vehicle, please read this Owner's Guide carefully.
Your vehicle is not a passenger car. As with other vehicles of this type,
failure to operate this vehicle correctly may result in loss of control or an
accident.
Be sure to readDriving off roadin theDrivingchapter as well as the
ªFour Wheelingº supplement included with 4WD and utility type vehicles.
Introduction
3
Page 23 of 88
BRAKES
Your service brakes are self-adjusting. Refer to the scheduled
maintenance guide for scheduled maintenance.
Occasional brake noise is normal and often does not indicate a
performance concern with the vehicle's brake system. In normal
operation, automotive brake systems may emit occasional or intermittent
squeal or groan noises when the brakes are applied. Such noises are
usually heard during the first few brake applications in the morning;
however, they may be heard at any time while braking and can be
aggravated by environmental conditions such as cold, heat, moisture,
road dust, salt or mud. If a ªmetal-to-metal,º ªcontinuous grindingº or
ªcontinuous squealº sound is present while braking, the brake linings
may be worn-out and should be inspected by a qualified service
technician.
Four-wheel anti-lock brake system (ABS)
This vehicle is equipped with an anti-lock braking system (ABS). A noise
from the hydraulic pump motor and pulsation in the pedal may be
observed during ABS braking events. Pedal pulsation coupled with noise
while braking under panic conditions or on loose gravel, bumps, wet or
snowy roads is normal and indicates proper functioning of the vehicle's
anti-lock brake system. The ABS performs a self-check after you start
the engine and begin to drive away. A brief mechanical noise may be
heard during this test. This is normal. If a malfunction is found, the ABS
warning light will come on. If the vehicle has continuous vibration or
shudder in the steering wheel while braking, the vehicle should be
inspected by a qualified service technician.
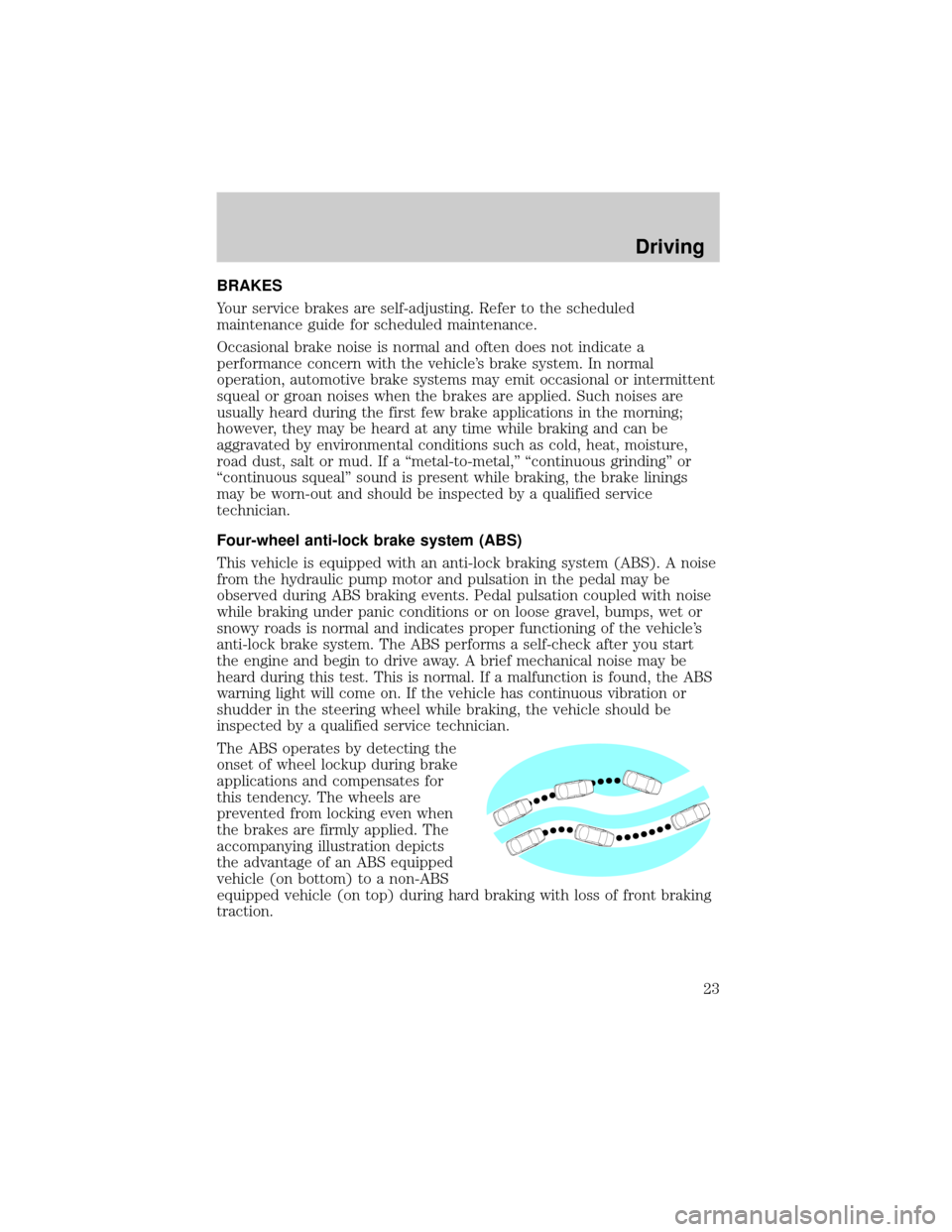
The ABS operates by detecting the
onset of wheel lockup during brake
applications and compensates for
this tendency. The wheels are
prevented from locking even when
the brakes are firmly applied. The
accompanying illustration depicts
the advantage of an ABS equipped
vehicle (on bottom) to a non-ABS
equipped vehicle (on top) during hard braking with loss of front braking
traction.
Driving
23
Page 30 of 88

Forced Downshifts
To gain acceleration in(Overdrive) or Drive (O/D OFF) when
passing another vehicle, push the accelerator to the floor. The
transmission will downshift to the appropriate gear: fourth, third, second
or first gear.
FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE (4WD) OPERATION (IF EQUIPPED)
When Four-wheel drive (4WD) is engaged, power is supplied to all four
wheels through a transfer case. 4WD power can be selected when
additional driving power is desired.
If equipped with the Electronic Shift 4WD System, and the 4x4
Low button is pressed while the vehicle is moving, the system will
not engage and no damage will occur to the 4WD system.
4x4 High and 4x4 Low operation is not recommended on dry
pavement. Doing so could result in difficult disengagement of the
transfer case, increased tire wear and decreased fuel economy.
Positions of the 4WD system
The 4WD system functions in two modes:
²The 4x4 High mode provides
four-wheel drive with full power
to both axles. It is only intended
for severe winter or off-road
conditions, such as deep snow
and ice (where no dry or wet
pavement remains uncovered),
and shallow sand.
²The 4x4 Low mode supplies
four-wheel drive with full power
to both axles and includes a
lower gear ratio for low-speed. It
is only intended for off-road
applications that require extra
power including deep sand, steep
grades and pulling a boat and
trailer out of the water.
HIGH4x4
LOW 4x2
HIGH4x4
LOW 4x2
Driving
30
Page 31 of 88

The vehicle should not be operated in 4x4 High and 4x4 Low on
dry or merely wet pavement. Doing so will produce excessive
noise, increase tire wear and may damage driveline components.
These modes are intended for use only on consistently slippery or
loose surfaces.
If your vehicle is equipped with 4WD, a spare tire of a different
size than the road tires should never be used. Such a tire could
result in damage to driveline components and make the vehicle
difficult to control.
Utility and four-wheel drive vehicles arenotdesigned for
cornering at speeds as high as passenger cars any more than
low-slung sports cars are designed to perform satisfactorily under
off-road conditions. Avoid sharp turns or abrupt maneuvers in these
vehicles.
Driving with 4WD
Your vehicle is specially equipped for driving on sand, snow, mud and
rough terrain and has operating characteristics that are somewhat
different from conventional vehicles, both on and off the road.
Maintain steering wheel control at all times, especially in rough terrain.
Since sudden changes in terrain can result in abrupt steering wheel
motion, make sure you grip the steering wheel from the outside. Do not
grip the spokes.
If your vehicle gets stuck
If the vehicle is stuck in mud or snow it may be rocked out by shifting
from forward and reverse gears, stopping between shifts, in a steady
pattern. Press lightly on the accelerator in each gear.
Do not rock the vehicle if the engine is not at normal operating
temperature or damage to the transmission may occur.
Do not rock the vehicle for more than a few minutes or damage
to the transmission and tires may occur or the engine may
overheat.
Do not spin the wheels at over 56 km/h (35 mph). The tires may
fail and injure a passenger or bystander.
Driving
31
Page 32 of 88

Sand
When driving over sand, try to keep all four wheels on the most solid
area of the trail. Do not reduce the tire pressures but shift to a lower
gear and drive steadily through the terrain. Apply the accelerator slowly
and avoid spinning the wheels.
Mud and water
If you must drive through high water, drive slowly. Traction or brake
capability may be limited.
When driving through water, determine the depth; avoid water higher
than the bottom of the hubs (if possible) and proceed slowly. If the
ignition system gets wet, the vehicle may stall.
Once through water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop the
vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by moving
your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal.
After driving through mud, clean off residue stuck to rotating driveshafts
and tires. Excess mud stuck on tires and rotating driveshafts causes an
imbalance that could damage drive components.
If the transmission, transfer case or front axle are submerged in water,
their fluids should be checked and changed, if necessary.
Water intrusion into the transmission may damage the
transmission.
If the rear axle is submerged in water, the rear axle lubricant should be
checked and changed, if necessary. The rear axle is filled with a
synthetic lubricant and does not normally require a lubricant change for
the life of the vehicle. Rear axle lubricant quantities should not need to
be checked unless a leak is suspected.
Driving on hilly or sloping terrain
When climbing a steep hill, start in a lower gear rather than downshifting
to a lower gear from a higher gear once the ascent has started. This
reduces the strain on the engine.
When descending a steep hill, avoid sudden braking. Shift to a lower gear
when added engine braking is desired.
Automatic transmissions may shift frequently while driving up steep
grades. Eliminate frequent shifting by shifting out of
(Overdrive) into
D (Drive).
Driving
32
Page 37 of 88

Fuse/Relay
LocationFuse Amp
RatingPassenger Compartment
Fuse Panel Description
13 15A EEC System, Stop Lamps, Four Wheel
Anti-Lock Brake System (4WABS),
4 x 4 Module
14 10A Four Wheel Anti-Lock Brake System
(4WABS) Module
15 7.5A Alternator Warning Lamp
16 30A Windshield Wiper Motor, Wiper Module
17 25A Cigar Lighter
18 Ð Not Used
19 25A EEC System, Ignition Coil
20 Ð Not Used
21 15A Flasher (Hazard)
22 Ð Not Used
23 Ð Not Used
24 7.5A Starter Relay
25 7.5A Speedometer
26 10A Interior Lamps
27 15A Backup Lamps, Overdrive Cancel
28 Ð Not Used
29 Ð Not Used
30 Ð Not Used
31 Ð Not Used
32 Ð Not Used
33 5A Headlamps (Highbeams)
34 Ð Not Used
35 7.5A RH Park Lamps
36 7.5A LH Park Lamps
Power distribution box
The power distribution box is located in the engine compartment. The
power distribution box contains high-current fuses that protect your
vehicle's main electrical systems from overloads.
Roadside emergencies
37
Page 85 of 88

checking and adding ................54
dipstick ......................................54
filter, specifications ............55, 80
recommendations .....................55
refill capacities ..........................80
specifications ......................81±82
Exhaust fumes ............................21
F
Fluid capacities ...........................80
Four-Wheel Drive vehicles .........30
control trac ...............................17
description ................................30
driving off road .........................31
electronic shift ..........................17
Fuel ..............................................71
cap .............................................77
capacity .....................................80
choosing the right fuel .............74
detergent in fuel .......................76
filling your vehicle
with fuel ..............................71, 77
filter, specifications ............78, 80
fuel pump shut-off switch .......34
gauge .........................................12
octane rating .......................75, 82
quality ........................................75
running out of fuel ...................76
safety information relating
to automotive fuels ..................71
Fuses ......................................34±35
G
Gas cap (see Fuel cap) ..............77
Gauges ...........................................9
battery voltage gauge ...............11
engine coolant
temperature gauge ...................10engine oil pressure gauge ........11
fuel gauge ..................................12
odometer ...................................10
speedometer ...............................9
trip odometer ............................11
H
Headlamps ...................................13
flash to pass ..............................14
high beam .............................8, 13
turning on and off ....................13
I
Ignition ...................................14, 82
Inspection/
maintenance (I/M) testing .........79
Instrument panel
cluster ..........................................6
lighting up
panel and interior .....................13
J
Jack ..............................................40
positioning .................................40
storage .......................................40
Jump-starting your vehicle ........43
K
Keys
positions of the ignition ...........14
L
Lamps
cargo lamps ...............................13
headlamps .................................13
Index
85