2001 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 288 of 2321
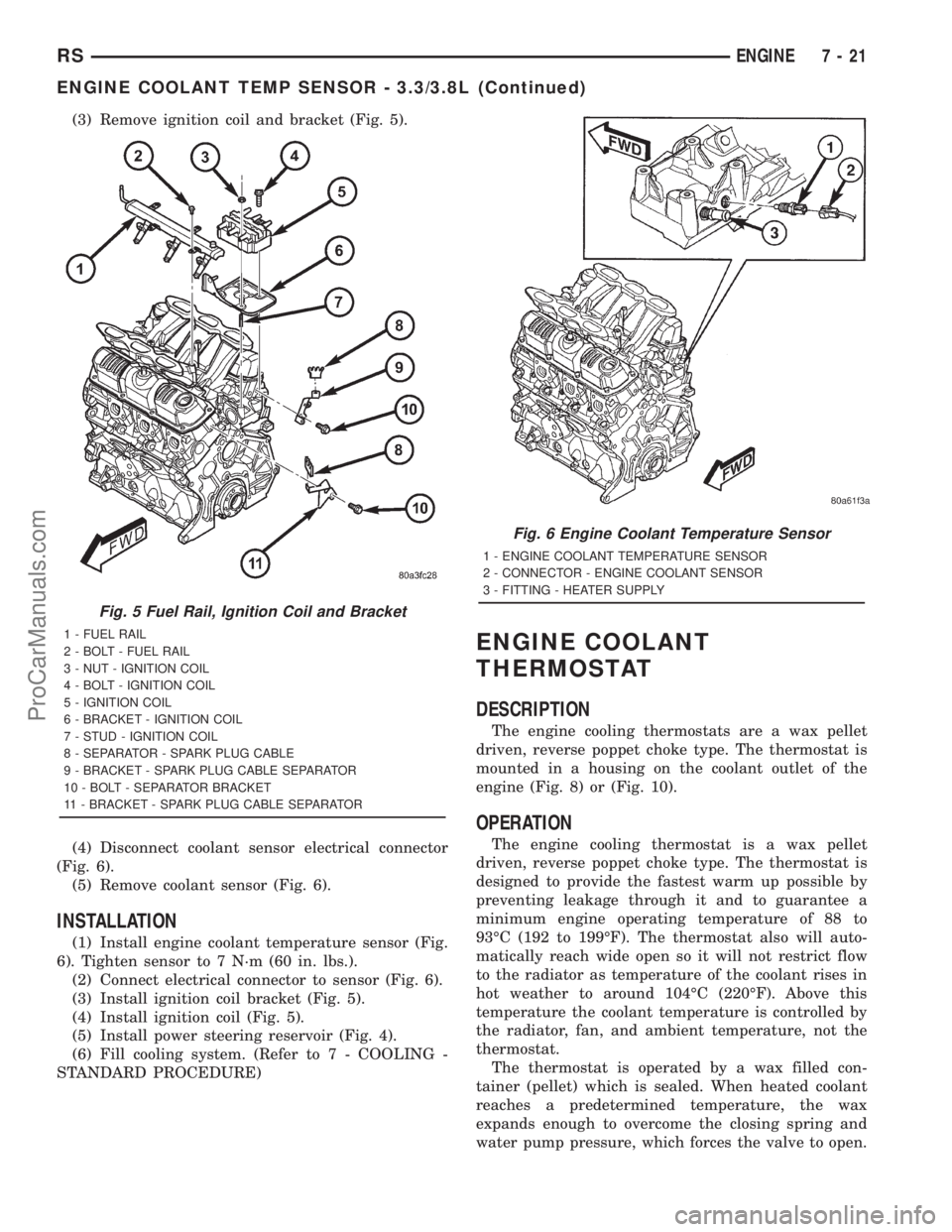
(3) Remove ignition coil and bracket (Fig. 5).
(4) Disconnect coolant sensor electrical connector
(Fig. 6).
(5) Remove coolant sensor (Fig. 6).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install engine coolant temperature sensor (Fig.
6). Tighten sensor to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.).
(2) Connect electrical connector to sensor (Fig. 6).
(3) Install ignition coil bracket (Fig. 5).
(4) Install ignition coil (Fig. 5).
(5) Install power steering reservoir (Fig. 4).
(6) Fill cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT
DESCRIPTION
The engine cooling thermostats are a wax pellet
driven, reverse poppet choke type. The thermostat is
mounted in a housing on the coolant outlet of the
engine (Fig. 8) or (Fig. 10).
OPERATION
The engine cooling thermostat is a wax pellet
driven, reverse poppet choke type. The thermostat is
designed to provide the fastest warm up possible by
preventing leakage through it and to guarantee a
minimum engine operating temperature of 88 to
93ÉC (192 to 199ÉF). The thermostat also will auto-
matically reach wide open so it will not restrict flow
to the radiator as temperature of the coolant rises in
hot weather to around 104ÉC (220ÉF). Above this
temperature the coolant temperature is controlled by
the radiator, fan, and ambient temperature, not the
thermostat.
The thermostat is operated by a wax filled con-
tainer (pellet) which is sealed. When heated coolant
reaches a predetermined temperature, the wax
expands enough to overcome the closing spring and
water pump pressure, which forces the valve to open.
Fig. 5 Fuel Rail, Ignition Coil and Bracket
1 - FUEL RAIL
2 - BOLT - FUEL RAIL
3 - NUT - IGNITION COIL
4 - BOLT - IGNITION COIL
5 - IGNITION COIL
6 - BRACKET - IGNITION COIL
7 - STUD - IGNITION COIL
8 - SEPARATOR - SPARK PLUG CABLE
9 - BRACKET - SPARK PLUG CABLE SEPARATOR
10 - BOLT - SEPARATOR BRACKET
11 - BRACKET - SPARK PLUG CABLE SEPARATOR
Fig. 6 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
1 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 - CONNECTOR - ENGINE COOLANT SENSOR
3 - FITTING - HEATER SUPPLY
RSENGINE7-21
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR - 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 289 of 2321

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT
The thermostat is operated by a wax filled cham-
ber (pellet) which is sealed. When heated coolant
reaches a predetermined temperature the wax pellet
expands enough to overcome the closing spring and
water pump pressure, which forces the valve to open.
Coolant leakage into the pellet will cause a thermo-
stat to fail open. Do not attempt to free up a thermo-
stat with a screwdriver.
Thermostat diagnostics is included in powertrain
control module's (PCM) programing for on-board
diagnosis. The malfunction indicator light (MIL) will
illuminate and a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) will
be set when an ªopen too soonº condition occurs. Do
not change a thermostat for lack of heater perfor-
mance or temperature gauge position, unless a DTC
is present. For other probable causes, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) .
Thermostat failing shut is the normal long term
mode of failure, and normally, only on high mileage
vehicles. The temperature gauge will indicate this
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING) .
ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT - 2.4L
REMOVAL
(1) Drain cooling system below the thermostat
level. (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(2) Remove radiator upper hose from the coolant
outlet housing (Fig. 7).
(3) Remove coolant outlet housing bolts and hous-
ing (Fig. 8).
(4) Remove thermostat. Discard gasket and clean
both gasket sealing surfaces.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place a new gasket (dipped in clean water) on
the coolant outlet connector surface. Position thermo-
stat with air bleed at the 12 o'clock position in ther-
mostat housing (Fig. 8).
(2) Position the coolant outlet connector and gas-
ket over the thermostat, making sure thermostat is
seated in the thermostat housing.
(3) Position outlet connector to thermostat housing
and install bolts (Fig. 8). Tighten bolts to 28 N´m
(250 in. lbs.).
(4) Install the radiator upper hose to coolant outlet
housing (Fig. 7).
(5) Refill the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 7 RADIATOR HOSES TO ENGINE - 2.4L
1 - UPPER HOSE
2 - LOWER HOSE
Fig. 8 Thermostat and Outlet Connector - 2.4L
Engine
1 - THERMOSTAT
2 - GASKET
3 - COOLANT OUTLET CONNECTOR
4 - BOLT
7 - 22 ENGINERS
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 295 of 2321
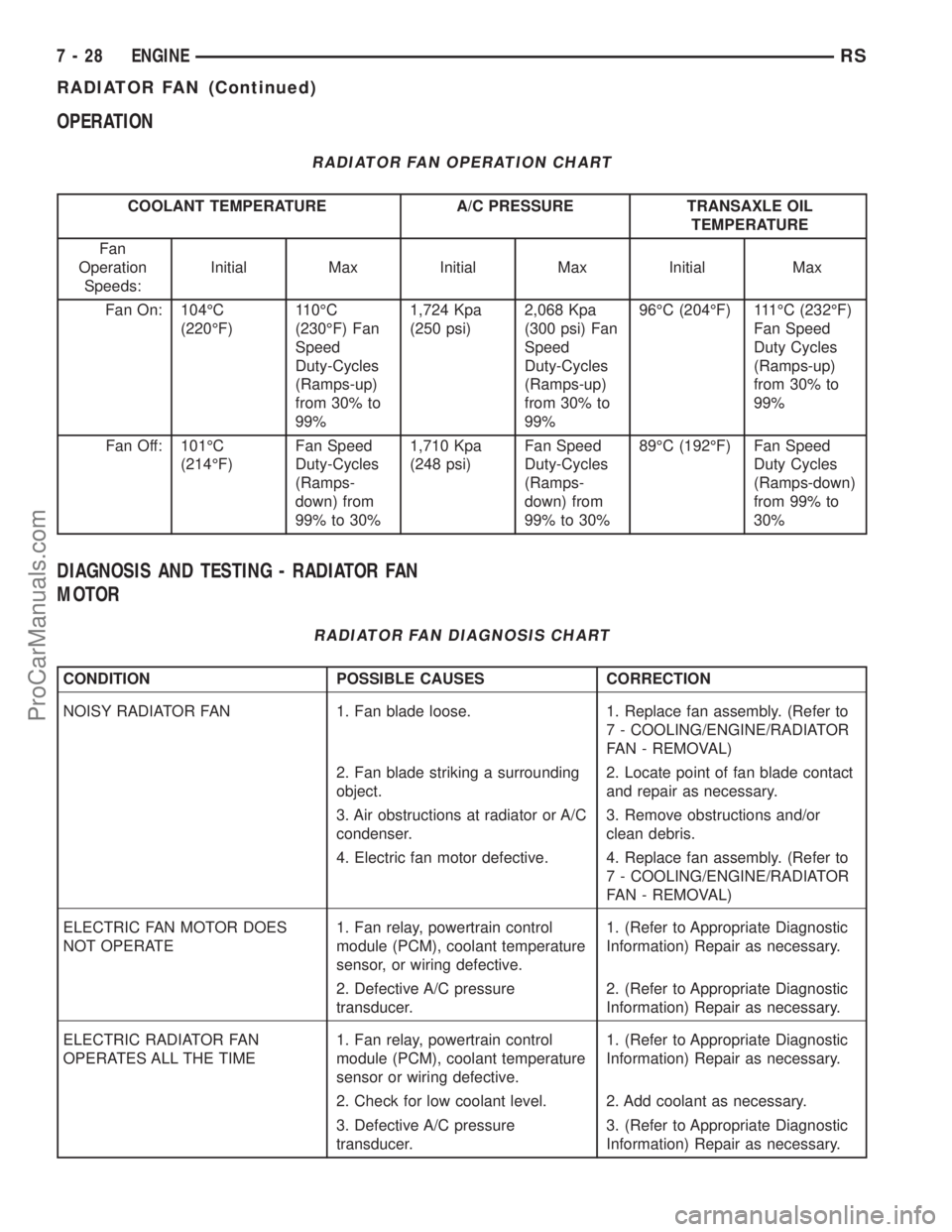
OPERATION
RADIATOR FAN OPERATION CHART
COOLANT TEMPERATURE A/C PRESSURE TRANSAXLE OIL
TEMPERATURE
Fan
Operation
Speeds:Initial Max Initial Max Initial Max
Fan On: 104ÉC
(220ÉF)110ÉC
(230ÉF) Fan
Speed
Duty-Cycles
(Ramps-up)
from 30% to
99%1,724 Kpa
(250 psi)2,068 Kpa
(300 psi) Fan
Speed
Duty-Cycles
(Ramps-up)
from 30% to
99%96ÉC (204ÉF) 111ÉC (232ÉF)
Fan Speed
Duty Cycles
(Ramps-up)
from 30% to
99%
Fan Off: 101ÉC
(214ÉF)Fan Speed
Duty-Cycles
(Ramps-
down) from
99% to 30%1,710 Kpa
(248 psi)Fan Speed
Duty-Cycles
(Ramps-
down) from
99% to 30%89ÉC (192ÉF) Fan Speed
Duty Cycles
(Ramps-down)
from 99% to
30%
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RADIATOR FAN
MOTOR
RADIATOR FAN DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY RADIATOR FAN 1. Fan blade loose. 1. Replace fan assembly. (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
FAN - REMOVAL)
2. Fan blade striking a surrounding
object.2. Locate point of fan blade contact
and repair as necessary.
3. Air obstructions at radiator or A/C
condenser.3. Remove obstructions and/or
clean debris.
4. Electric fan motor defective. 4. Replace fan assembly. (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
FAN - REMOVAL)
ELECTRIC FAN MOTOR DOES
NOT OPERATE1. Fan relay, powertrain control
module (PCM), coolant temperature
sensor, or wiring defective.1. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
2. Defective A/C pressure
transducer.2. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
ELECTRIC RADIATOR FAN
OPERATES ALL THE TIME1. Fan relay, powertrain control
module (PCM), coolant temperature
sensor or wiring defective.1. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
2. Check for low coolant level. 2. Add coolant as necessary.
3. Defective A/C pressure
transducer.3. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
7 - 28 ENGINERS
RADIATOR FAN (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 296 of 2321

REMOVAL
There are no repairs to be made to the fan or
shroud assembly. If the fan is warped, cracked, or
otherwise damaged, it must be replaced as an assem-
bly (Fig. 21).
(1) Remove the radiator upper crossmember. (Refer
to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPENING REIN-
FORCEMENT - REMOVAL)
(2) Disconnect the radiator fan electrical connec-
tors.
(3) Remove radiator fan(s) retaining screw (Fig.
21).
(4) Remove the radiator fan(s) by lifting upward to
release from mounts.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the radiator fan(s) into mounts and
attaching clips on the radiator.
(2) Install radiator fan(s) attaching screws (Fig.
21). Tighten to 5 N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the radiator fan(s) electrical connec-
tors.
(4) Install the radiator upper support crossmem-
ber. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPEN-
ING REINFORCEMENT - INSTALLATION)
(5) Install the upper radiator mounts to the cross-
member bolts, if removed. Tighten to 8 N´m (70 in.
lbs.).
(6) Install the radiator upper hose to the support
clip (2.4L engine).
RADIATOR FAN RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The radiator fan relay is a solid state type and is
located on the front bumper reinforcment (Fig. 22).
Refer to WIRING DIAGRAMS for a circuit sche-
matic.
OPERATION
The solid state radiator fan relay is controlled by
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) by way of a
Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) signal. The relay con-
trol circuit supplies a 12 volt signal to the PCM. The
PCM then pulses the ground circuit to achieve fan on
time. The relay provides a voltage to the fan motors
which is proportional to the pulse width it receives
from the PCM. The duty cycle ranges from 30% for
low speed operation, then ramps-up to 100% for high
speed operation. This fan control system provides
infinitely variable fan speeds, allowing for improved
fan noise, A/C performance, better engine cooling,
and additional vehicle power.
To control operation of the relay, the PCM looks at
inputs from:
²Engine coolant temperature
²A/C pressure transducer
²Ambient temperature from the body controller
²Vehicle speed
²Transmission oil temperature
The PCM uses these inputs to determine when the
fan should operate and at what speed. For further
information on fan operation, (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - OPERATION).
REMOVAL
(1) Open hood.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Remove the radiator crossmember to front fas-
cia closure panel.
(4) Disconnect the relay electrical connector (Fig.
22).
(5) Remove the rivet attaching the relay to the
front bumper beam (Fig. 22).
(6) Remove the relay.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The relay mounting location is designed
to dissipate heat. Ensure the relay is securely
attached to prevent relay ªthermalº shutdown and
relay damage, resulting in possible engine over-
heating.
Fig. 21 Radiator Fans
1 - SCREWS - RADIATOR FAN ATTACHING
2 - RADIATOR FAN - RIGHT
3 - MOUNT - RIGHT RADIATOR FAN
4 - CLIPS - RADIATOR FAN LOWER
5 - MOUNT - LEFT RADIATOR FAN
6 - RADIATOR FAN - LEFT
RSENGINE7-29
RADIATOR FAN (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 308 of 2321

COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
DESCRIPTION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................1
COOLING SYSTEM......................1
COOLING SYSTEM LEAK TEST.............6
COOLING SYSTEM FLOW CHECK..........7COOLING SYSTEM AERATION.............7
CLEANING...............................7
INSPECTION.............................7
SPECIFICATIONS.........................8
ACCESSORY DRIVE.......................9
ENGINE................................14
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system regulates engine operating tem-
perature. It allows the engine to reach normal oper-
ating temperature as quickly as possible, maintains
normal operating temperature and prevents over-
heating.
The cooling system also provides a means of heat-
ing the passenger compartment. The cooling system
is pressurized and uses a centrifugal water pump to
circulate coolant throughout the system. A separate
and remotely mounted, pressurized coolant tank
using a pressure/vent cap is used.
COOLING SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The cooling system consists of:
²Charge Air Cooler
²Electric Cooling Fans
²A aluminum-core radiator with plastic side
tanks
²A separate pressurized coolant tank
²A pressure/vent cap on the coolant tank
²Fan shroud
²Thermostat
²Coolant
²Low coolant warning lamp
²Coolant temperature gauge
²Water pump
²Hoses and hose clamps
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
Establish what driving conditions caused the com-
plaint. Abnormal loads on the cooling system such as
the following may be the cause:
(1) PROLONGED IDLE, VERY HIGH AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE, SLIGHT TAIL WIND AT IDLE,
SLOW TRAFFIC, TRAFFIC JAMS, HIGH SPEED
OR STEEP GRADES.
Driving techniques that avoid overheating are:
²Idle with A/C off when temperature gauge is at
end of normal range.
²Increasing engine speed for more air flow is rec-
ommended.
(2) TRAILER TOWING:
Consult Trailer Towing section of owners manual.
Do not exceed limits.
(3) RECENT SERVICE OR ACCIDENT REPAIR:
Determine if any recent service has been per-
formed on vehicle that may effect cooling system.
This may be:
²Engine adjustments (incorrect timing)
²Slipping engine accessory drive belt
²Brakes (possibly dragging)
²Changed parts (incorrect water pump)
²Reconditioned radiator or cooling system refill-
ing (possibly under filled or air trapped in system).
NOTE: If investigation reveals none of the previous
items as a cause for an engine overheating com-
plaint, refer to following Cooling System Diagnosis
charts.
These charts are to be used as a quick-reference
only.
RGCOOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL7a-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 309 of 2321
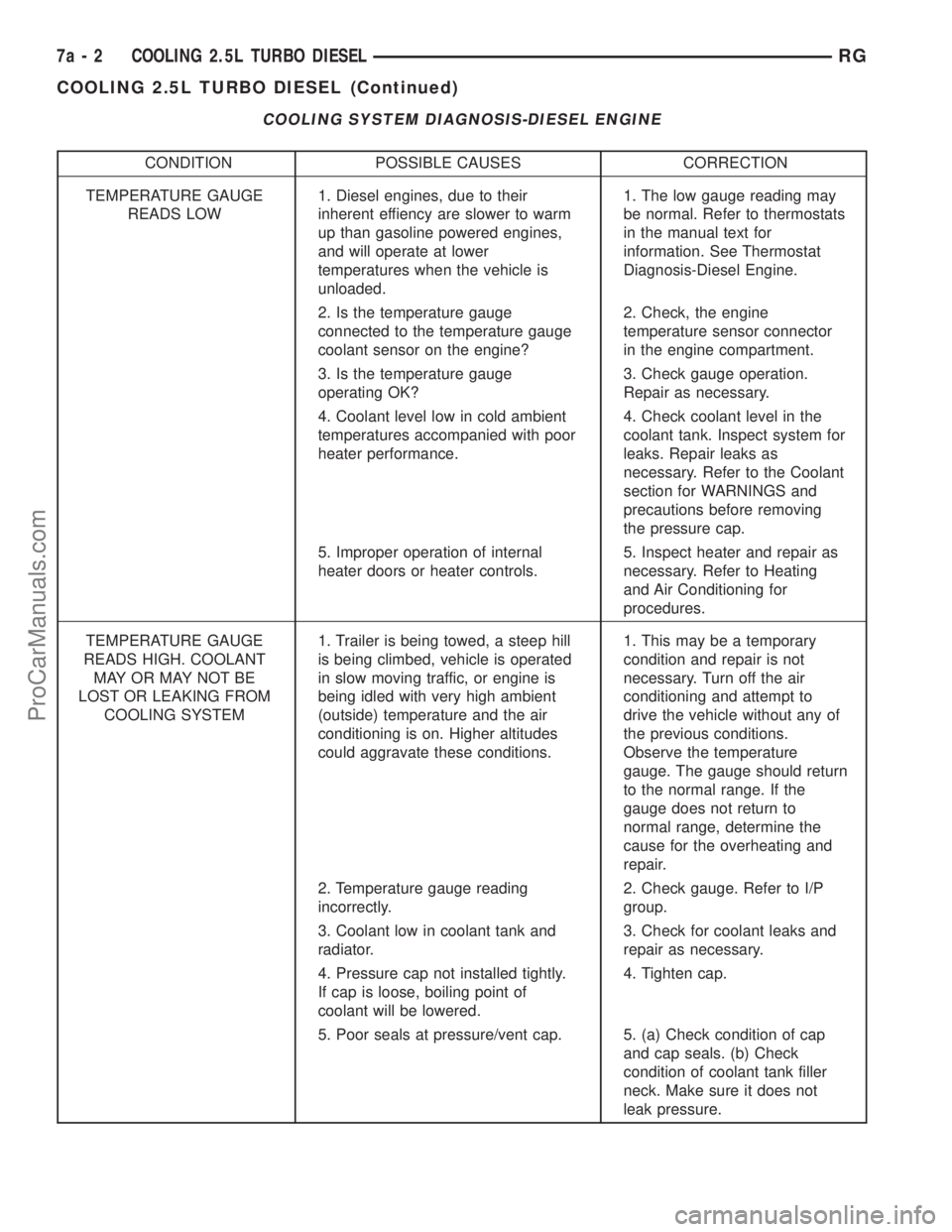
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS-DIESEL ENGINE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READS LOW1. Diesel engines, due to their
inherent effiency are slower to warm
up than gasoline powered engines,
and will operate at lower
temperatures when the vehicle is
unloaded.1. The low gauge reading may
be normal. Refer to thermostats
in the manual text for
information. See Thermostat
Diagnosis-Diesel Engine.
2. Is the temperature gauge
connected to the temperature gauge
coolant sensor on the engine?2. Check, the engine
temperature sensor connector
in the engine compartment.
3. Is the temperature gauge
operating OK?3. Check gauge operation.
Repair as necessary.
4. Coolant level low in cold ambient
temperatures accompanied with poor
heater performance.4. Check coolant level in the
coolant tank. Inspect system for
leaks. Repair leaks as
necessary. Refer to the Coolant
section for WARNINGS and
precautions before removing
the pressure cap.
5. Improper operation of internal
heater doors or heater controls.5. Inspect heater and repair as
necessary. Refer to Heating
and Air Conditioning for
procedures.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READS HIGH. COOLANT
MAY OR MAY NOT BE
LOST OR LEAKING FROM
COOLING SYSTEM1. Trailer is being towed, a steep hill
is being climbed, vehicle is operated
in slow moving traffic, or engine is
being idled with very high ambient
(outside) temperature and the air
conditioning is on. Higher altitudes
could aggravate these conditions.1. This may be a temporary
condition and repair is not
necessary. Turn off the air
conditioning and attempt to
drive the vehicle without any of
the previous conditions.
Observe the temperature
gauge. The gauge should return
to the normal range. If the
gauge does not return to
normal range, determine the
cause for the overheating and
repair.
2. Temperature gauge reading
incorrectly.2. Check gauge. Refer to I/P
group.
3. Coolant low in coolant tank and
radiator.3. Check for coolant leaks and
repair as necessary.
4. Pressure cap not installed tightly.
If cap is loose, boiling point of
coolant will be lowered.4. Tighten cap.
5. Poor seals at pressure/vent cap. 5. (a) Check condition of cap
and cap seals. (b) Check
condition of coolant tank filler
neck. Make sure it does not
leak pressure.
7a - 2 COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESELRG
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 310 of 2321

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
6. Freeze point of antifreeze not
correct. Mixture may be too rich.6. Check antifreeze. Adjust
antifreeze-to-water ratio as
required.
7. Coolant not flowing through
system.7. Check for coolant flow in
coolant tank with engine warm
and thermostat open. Coolant
should be observed flowing
through the tank. If flow is not
observed, determine reason for
lack of flow and repair as
necessary.
8. Radiator or A/C condensor fins
are dirty or clogged.8. Clean debris from radiator or
A/C condensor
9. Radiator core is corroded or
plugged.9. Have radiator re-cored or
replaced.
10. Aftermarket A/C installed without
proper A/C condensor.10. Install proper A/C
condensor.
11. Dragging Brakes. 11. Check and correct as
necessary.
12. Non-factory bug screen is being
used reducing airflow.12. Only a factory screen
should be used.
13. Thermostat partially or
completely shut. This is more
prevalent on high mileage vehicles.13. Check thermostat and
replace if necessary.
14. Cylinder head gasket leaking. 14. Check cylinder head gasket
for leaks.
15. Heater core leaking. 15. Check heater cor for leaks.
Repair as necessary.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READING IS
INCONSISTENT
(FLUCTUATES, CYCLES
OR IS ERRATIC)1. During cold weather operation,
with the heater blower in the high
position, the gauge reading may
drop slightly. Fluctuation is also
influenced by loads, outside
temperature and extended idle time
with diesel engines.1. A normal condition. No
correction is necessary.
2. Temperature gauge or engine
mounted gauge sensor defective or
shorted. Also, corroded or loose
wiring in this circuit.2. Check operation of gauge
and repair as necessary.
3. Gauge reading rises when vehicle
is brought to a stop after heavy use
(engine still running).3. A normal condition. No
correction needed. Gauge
should return to normal range
after vehicle is driven.
4. Gauge reading high after starting
a warm-iup (hot) engine.4. A normal condition. No
correction needed. Gauge
should return to normal after a
few minutes of engine
operation.
RGCOOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL7a-3
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 311 of 2321

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
5. Coolant level low in the coolant
tank (air will build up in the cooling
system causing the thermostat to
open late).5. Check and correct coolant
leaks.
6. Cylinder head gasket leaking
allowing exhaust gases to enter the
cooling system causing the
thermostat to open late.6. (a) Check for cylinder head
gasket leaks with a
commercially available leak
tester. (b) Check for coolant in
engine oil. Inspect for white
steam emitting from exhaust
system. Repair as necessary.
7. Water pump impeller loose on
shaft.7. Check water pump and
replace as necessary.
8. Loose accessory drive belt (water
pump slipping).8. Check and correct as
necessary.
9. Air leak on the suction side of the
water pump allowing air to build up
in the cooling system causing the
thermostat to open late.9. Locate leak and repair as
necessary.
PRESSURE CAP IS
BLOWING OFF STEAM
AND/OR COOLANT.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READING MAY BE ABOVE
NORMAL BUT NOT HIGH.
COOLANT LEVEL MAY BE
HIGH IN COOLANT TANK1. Pressure relief valve in pressure/
vent cap is defective.1. Check condition of
pressure/vent cap and cap
seals.
2. Head gasket leak or cracked
cylinder head.2. Repair as necessary.
COOLANT LOSS TO THE
GROUND WITHOUT
PRESSURE CAP
BLOWOFF. GAUGE IS
READING HIGH OR HOT1. Coolant leaks in radiator, cooling
system hoses, water pump, or
engine.1. Pressure test cooling system
and repair as necessary.
HOSE OR HOSES
COLLAPSE WHEN
ENGINE IS COOLING1. Vacuum created in cooling system
on engine cool-down is not being
relieved through pressure/vent cap.1. Cap relief valve stuck.
Replace if necessary.
NOISY FAN 1. Cooling fan blades loose. 1. Replace cooling fan
assembly.
2. Cooling fan blades striking a
surrounding object.2. Locate point of fan blade
contact and repair as
necessary.
3. Air obstructions at radiator or A/C
condensor.3. Remove obstructions or
clean debris from radiator or
A/C condensor.
7a - 4 COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESELRG
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com