2001 CHEVROLET MALIBU steering
[x] Cancel search: steeringPage 105 of 351

2-40
There is a delay in the transition between the daytime
and nighttime operation of the DRL and the ALC
systems so that driving under bridges or bright overhead
street lights does not affect the system. The DRL and
ALC systems will only be affected when the light sensor
sees a change in lighting lasting longer than this delay.
To idle your vehicle with the ALC system off, set the
park brake while the ignition is off. Then start the
vehicle. The ALC system will stay off until you release
the park brake.
As with any vehicle, you should turn on the regular
headlamp system when you need it.
Headlamps Dim to Park (If Equipped)
This feature works when the ignition is on and it is dark
outside. To turn the headlamps off when it is dark
outside, turn the headlamp control to the parking lamp
position. In this position, the parking lamps, sidemarker
lamps, taillamps, license plate lamps and instrument
panel lights will be on, but the headlamps will be off.
To turn on the headlamps along with the other lamps
when it is dark outside, turn the headlamp control to the
AUTO or headlamp position.
Delayed Headlamps
The delayed headlamps feature will continue to
illuminate the headlamps for 20 seconds after the key is
turned to OFF at night. Then the headlamps will
automatically turn off.
To override the 20 second delayed headlamp feature
while it is active turn the turn signal/multifunction lever
up one position and then back to AUTO.
Fog Lamps (If Equipped)
The button for the fog
lamps is on the instrument
panel, to the left of the
steering wheel, next to
the instrument panel
intensity control.
When using the fog lamps, the ignition must be on as
well as the parking lamps or the low
-beam headlamps.
Page 106 of 351
2-41
Push the button to turn the fog lamps on. An indicator
light on the button will glow when the fog lamps are on.
Push the button again to turn the fog lamps off.
The fog lamps will turn off whenever the high
-beam
headlamps are turned on. When the high beams are
turned off, the fog lamps will come on again.
Interior Lamps
Instrument Panel Intensity Control
You can brighten or dim the
instrument panel cluster
lights by turning the
thumbwheel, located on the
instrument panel to the left
of the steering wheel.
Illuminated Entry/Exit System
When you open any door, the lamps inside your vehicle
will go on. These lamps will fade out 10 seconds after
the last door is closed, or when the ignition is turned on
after all doors have been closed. These lamps will also
go on when you press the trunk release button, the
UNLOCK button or the horn symbol button on the
remote keyless entry transmitter.
The lamps inside your vehicle will stay on for about
10 seconds after your key is removed from the ignition
to provide an illuminated exit.
Mirror Reading Lamps (If Equipped)
Press the switch next to each lamp to turn on the lamp.
Press the switch again to turn the lamp off.
Three-Position Dome Lamp
The switch on this lamp has three positions. The ON
position will turn on the lamp. The DOOR position will
turn on the lamp whenever a door is opened. The OFF
position will shut off the lamp completely, even when a
door is opened.
Page 109 of 351

2-44 Convex Outside Mirror
Your passenger's side mirror is convex. A convex
mirror's surface is curved so you can see more from the
driver's seat.
CAUTION:
A convex mirror can make things (like other
vehicles) look farther away than they really are.
If you cut too sharply into the right lane, you
could hit a vehicle on your right. Check your
inside mirror or glance over your shoulder before
changing lanes.
Storage Compartments
Glove Box
To open, pull the handle to the left and pull the glove
box door down until it stops and is fully open.
Instrument Panel Cupholder
The instrument panel cupholder is located to the left of
the steering wheel. To use it, pull it out until the rubber
insert is revealed.
Center Console Storage Area
The center console has two separate storage areas. The
upper compartment, which is also the armrest, can be
used to store maps, gloves, etc. To open, pull up on the
driver's side of the lid.
The lower area can be used to store cassette tapes or
compact discs. To open the lower compartment, pull up
on the armrest.
Center Console Cupholder
The console provides space for holding a cup or soft
drink container. The cupholder is located at the rear of
the shift lever.
Rear Seat Cupholders
Pull down the door on the rear of the center console to
use the rear seat cupholders.
Page 173 of 351
4-
4-1
Section 4 Your Driving and the Road
Here you'll find information about driving on different kinds of roads and in varying weather conditions. We've also
included many other useful tips on driving.
4
-2 Defensive Driving
4
-3 Drunken Driving
4
-6 Control of a Vehicle
4
-6 Braking
4
-9 Steering
4
-11 Off-Road Recovery
4
-11 Passing
4
-13 Loss of Control
4
-14 Driving at Night
4
-15 Driving in Rain and on Wet Roads4
-18 City Driving
4
-19 Freeway Driving
4
-20 Before Leaving on a Long Trip
4
-21 Highway Hypnosis
4
-22 Hill and Mountain Roads
4
-24 Winter Driving
4
-27 Recreational Vehicle Towing
4
-30 Loading Your Vehicle
4
-32 Towing a Trailer
Page 178 of 351
4-6
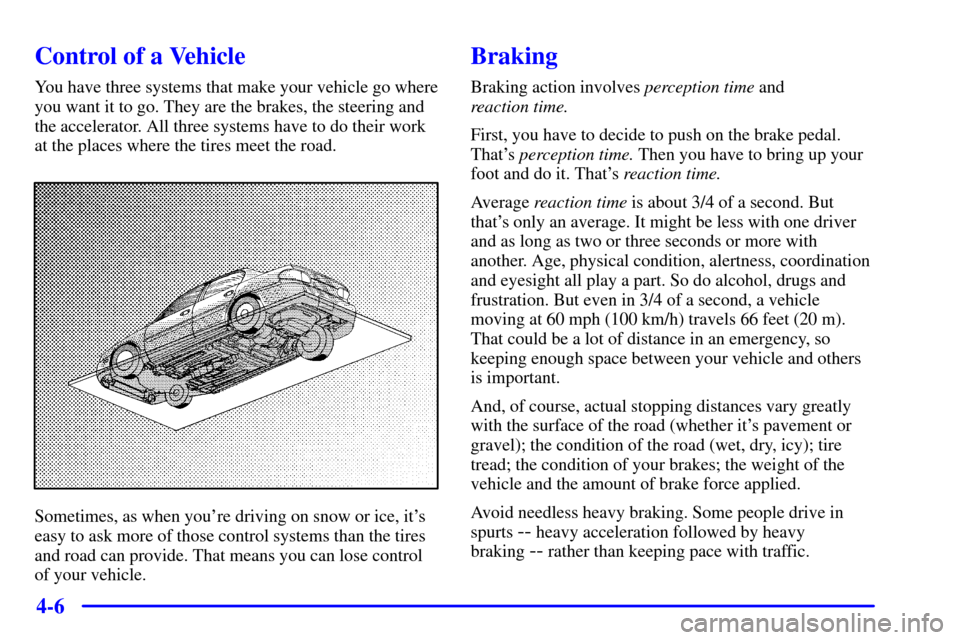
Control of a Vehicle
You have three systems that make your vehicle go where
you want it to go. They are the brakes, the steering and
the accelerator. All three systems have to do their work
at the places where the tires meet the road.
Sometimes, as when you're driving on snow or ice, it's
easy to ask more of those control systems than the tires
and road can provide. That means you can lose control
of your vehicle.
Braking
Braking action involves perception time and
reaction time.
First, you have to decide to push on the brake pedal.
That's perception time. Then you have to bring up your
foot and do it. That's reaction time.
Average reaction time is about 3/4 of a second. But
that's only an average. It might be less with one driver
and as long as two or three seconds or more with
another. Age, physical condition, alertness, coordination
and eyesight all play a part. So do alcohol, drugs and
frustration. But even in 3/4 of a second, a vehicle
moving at 60 mph (100 km/h) travels 66 feet (20 m).
That could be a lot of distance in an emergency, so
keeping enough space between your vehicle and others
is important.
And, of course, actual stopping distances vary greatly
with the surface of the road (whether it's pavement or
gravel); the condition of the road (wet, dry, icy); tire
tread; the condition of your brakes; the weight of the
vehicle and the amount of brake force applied.
Avoid needless heavy braking. Some people drive in
spurts
-- heavy acceleration followed by heavy
braking
-- rather than keeping pace with traffic.
Page 180 of 351

4-8
The anti-lock system can change the brake pressure
faster than any driver could. The computer is
programmed to make the most of available tire and road
conditions. This can help you steer around the obstacle
while braking hard.
As you brake, your computer keeps receiving updates on
wheel speed and controls braking pressure accordingly.Remember: Anti
-lock doesn't change the time you need
to get your foot up to the brake pedal or always decrease
stopping distance. If you get too close to the vehicle in
front of you, you won't have time to apply your brakes
if that vehicle suddenly slows or stops. Always leave
enough room up ahead to stop, even though you have
anti
-lock brakes.
Using Anti
-Lock
Don't pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal down
firmly and let anti
-lock work for you. You may feel a
slight brake pedal pulsation or notice some noise, but
this is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
With anti-lock, you can steer and brake at the same
time. In many emergencies, steering can help you more
than even the very best braking.
Page 181 of 351

4-9
Steering
Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine
stops or the system is not functioning, you can steer
but it will take much more effort.
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It's important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot of the ªdriver lost controlº accidents mentioned
on the news happen on curves. Here's why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each of us is subject to
the same laws of physics when driving on curves. The
traction of the tires against the road surface makes it
possible for the vehicle to change its path when you turn
the front wheels. If there's no traction, inertia will keep
the vehicle going in the same direction. If you've ever
tried to steer a vehicle on wet ice, you'll understand this.
The traction you can get in a curve depends on the
condition of your tires and the road surface, the angle at
which the curve is banked, and your speed. While you're
in a curve, speed is the one factor you can control.Suppose you're steering through a sharp curve.
Then you suddenly accelerate. Both control
systems
-- steering and acceleration -- have to do
their work where the tires meet the road. Adding the
sudden acceleration can demand too much of those
places. You can lose control.
What should you do if this ever happens? Ease up on
the accelerator pedal, steer the vehicle the way you want
it to go, and slow down.
Speed limit signs near curves warn that you should
adjust your speed. Of course, the posted speeds are
based on good weather and road conditions. Under
less favorable conditions you'll want to go slower.
If you need to reduce your speed as you approach a
curve, do it before you enter the curve, while your front
wheels are straight ahead.
Try to adjust your speed so you can ªdriveº through
the curve. Maintain a reasonable, steady speed. Wait
to accelerate until you are out of the curve, and then
accelerate gently into the straightaway.
Page 182 of 351

4-10 Steering in Emergencies
There are times when steering can be more effective
than braking. For example, you come over a hill and
find a truck stopped in your lane, or a car suddenly pulls
out from nowhere, or a child darts out from between
parked cars and stops right in front of you. You can
avoid these problems by braking
-- if you can stop in
time. But sometimes you can't; there isn't room.
That's the time for evasive action
-- steering around
the problem.
Your vehicle can perform very well in emergencies
like these. First apply your brakes. See ªBraking in
Emergenciesº earlier in this section. It is better to
remove as much speed as you can from a possible
collision. Then steer around the problem, to the left
or right depending on the space available.
An emergency like this requires close attention and a
quick decision. If you are holding the steering wheel at
the recommended 9 and 3 o'clock positions, you can
turn it a full 180 degrees very quickly without removing
either hand. But you have to act fast, steer quickly, and
just as quickly straighten the wheel once you have
avoided the object.
The fact that such emergency situations are always
possible is a good reason to practice defensive driving
at all times and wear safety belts properly.