Page 69 of 80
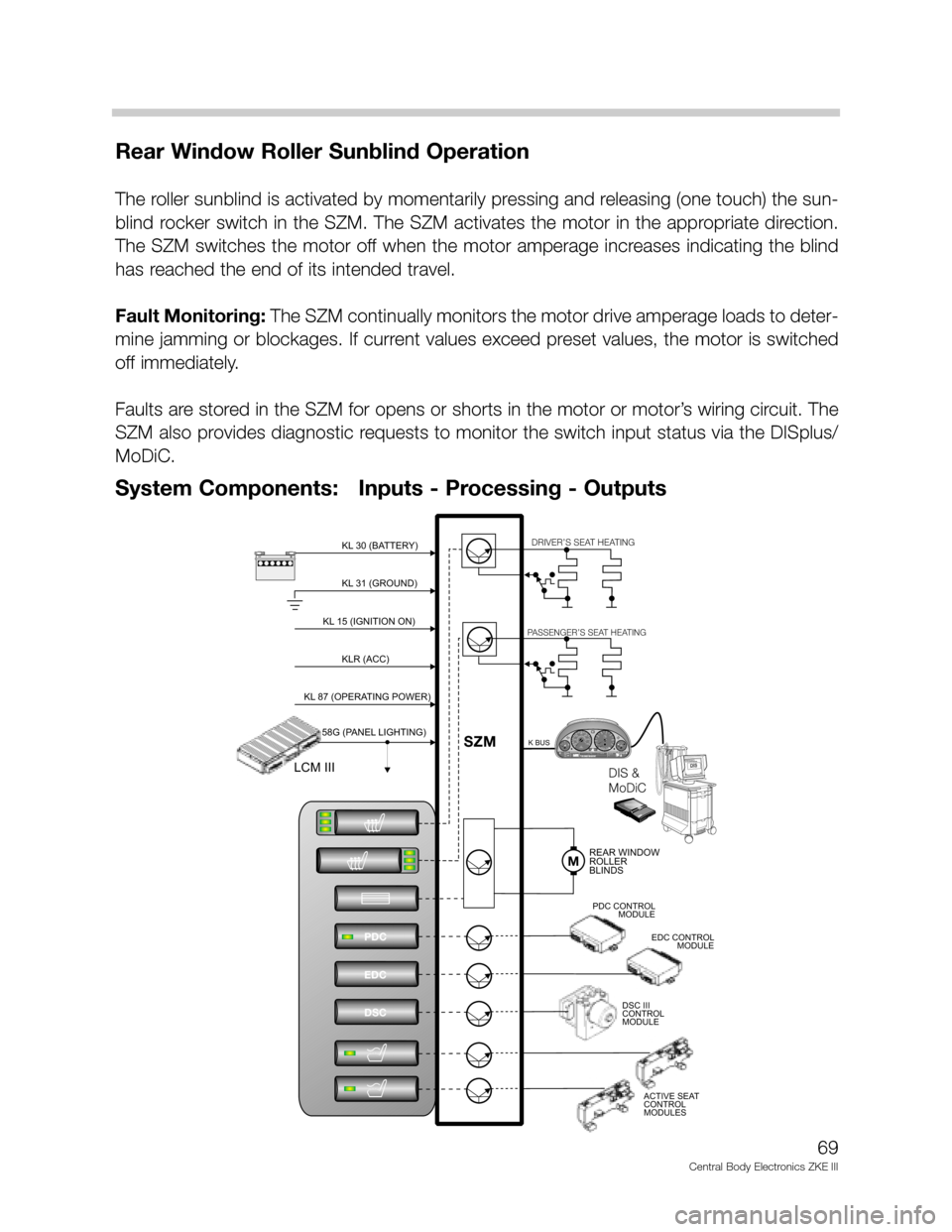
Rear Window Roller Sunblind Operation
The roller sunblind is activated by momentarily pressing and releasing (one touch) the sun-
blind rocker switch in the SZM. The SZM activates the motor in the appropriate direction.
The SZM switches the motor off when the motor amperage increases indicating the blind
has reached the end of its intended travel.
Fault Monitoring: The SZM continually monitors the motor drive amperage loads to deter-
mine jamming or blockages. If current values exceed preset values, the motor is switched
off immediately.
Faults are stored in the SZM for opens or shorts in the motor or motor’s wiring circuit. The
SZM also provides diagnostic requests to monitor the switch input status via the DISplus/
MoDiC.
69
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
KL 31 (GROUND)KL 31 (GROUND)
DIS
DIS
BMWDIS
B
M
WD
I
S
BMWDIS
BMW
DIS
D
ia
g
n
o
s
e
-
a
n
d
In
fo
r
m
a
ti
o
n
S
y
s
t
e
mDIS &
MoDiCDIS &
MoDiC
M
o
Di
C
0½
CHECK
ENGINE
CHECK
ENGINEOIL SERVICEOIL SERVICEINSPECTIONINSPECTIONP
1/min
x1000km/hELECTRONICMPH1
2020404060608080100180160140 1201002001202201402400234
5
6
7!!ABS20 DIGIT READOUT20 DIGIT READOUT
123456
prnd432
m
prnd432
m
122.4 +72.0 fo
+72.0 fomiles0
10
15 20 40
KL 30 (BATTERY)KL 30 (BATTERY)-+
KL 15 (IGNITION ON)KL 15 (IGNITION ON)
KLR (ACC)KLR (ACC)
KL 87 (OPERATING POWER)KL 87 (OPERATING POWER)
58G (PANEL LIGHTING)58G (PANEL LIGHTING)
LCM IIILCM III
PDC
EDC
DSC
MREAR WINDOW
ROLLER
BLINDSREAR WINDOW
ROLLER
BLINDS
DRIVER’S SEAT HEATINGDRIVER’S SEAT HEATING
PASSENGER’S SEAT HEATINGPASSENGER’S SEAT HEATING
K BUSK BUS
PDC CONTROL
MODULEPDC CONTROL
MODULE
EDC CONTROL
MODULEEDC CONTROL
MODULE
SZMSZM
DSC III
CONTROL
MODULEDSC III
CONTROL
MODULE
ACTIVE SEAT
CONTROL
MODULESACTIVE SEAT
CONTROL
MODULES
System Components: Inputs - Processing - Outputs
Page 70 of 80
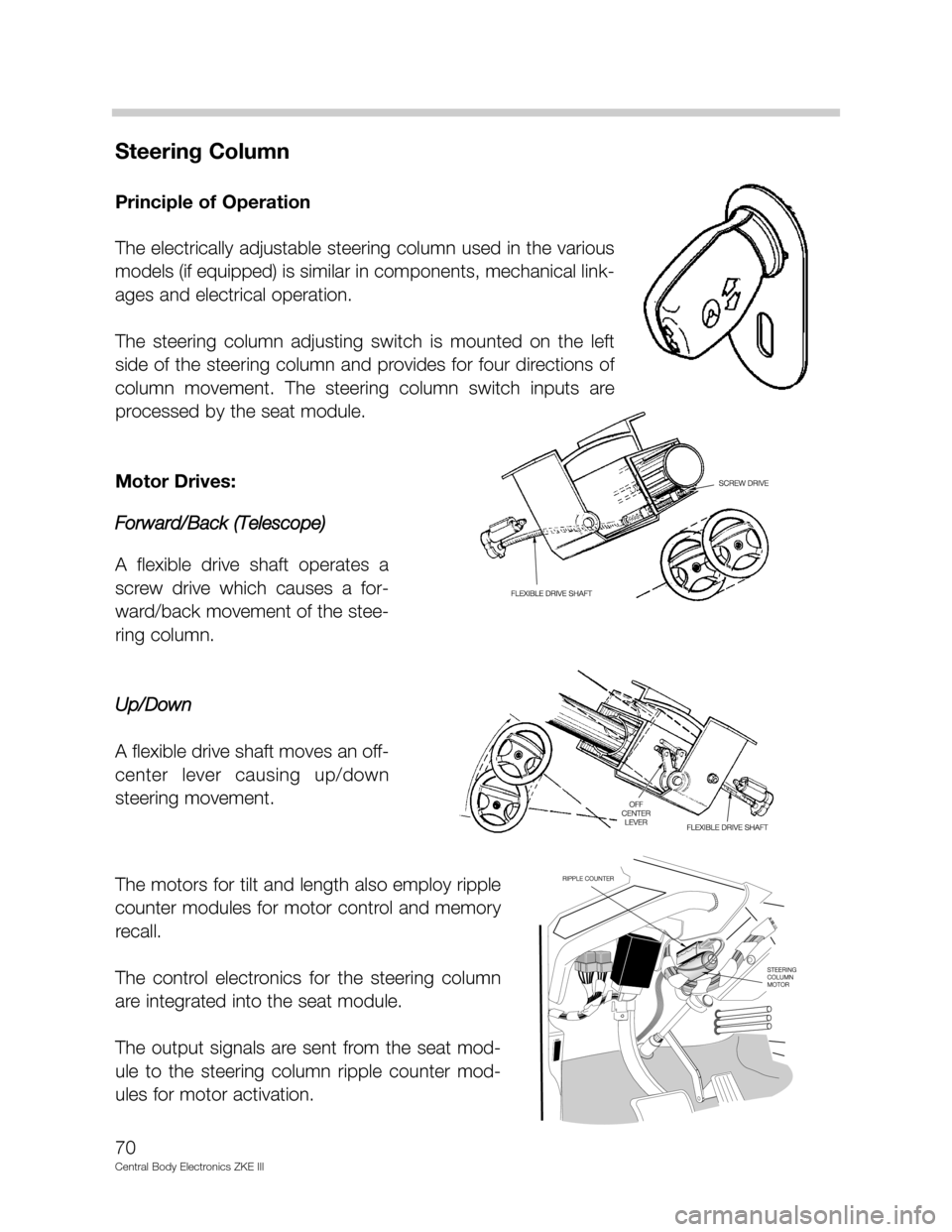
Steering Column
Principle of Operation
The electrically adjustable steering column used in the various
models (if equipped) is similar in components, mechanical link-
ages and electrical operation.
The steering column adjusting switch is mounted on the left
side of the steering column and provides for four directions of
column movement. The steering column switch inputs are
processed by the seat module.
Motor Drives:
Forward/Back (Telescope)
A flexible drive shaft operates a
screw drive which causes a for-
ward/back movement of the stee-
ring column.
Up/Down
A flexible drive shaft moves an off-
center lever causing up/down
steering movement.
The motors for tilt and length also employ ripple
counter modules for motor control and memory
recall.
The control electronics for the steering column
are integrated into the seat module.
The output signals are sent from the seat mod-
ule to the steering column ripple counter mod-
ules for motor activation.
70
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Page 74 of 80

Principle of Operation
Control logic (example E38) includes:
• Servotronic control electronics active with KL R being switched "ON" - ensure no delay
in operation if engine is started and vehicle is immediately driven.
• Plausibility check for speed signal - the control electronics monitor both the Speed sig-
nal "A" from the IKE and the vehicle speed signal on the K-Bus.
• The ability to detect both acceleration and deceleration from the two speed signals - the
speed signal from the IKE is updated every two seconds.
• The servotronic assist is reduced gradually when the vehicle is under acceleration.
• The servotronic assist is adopted to the lower direct reading during decel or braking.
Electric/electronic failures with the servotronic system will result in the following:
• Power/electronic failure of the control module or solenoid - steering assist the same as
high speed driving (increased effort).
• Vehicle speed signal missing - control module retains the assist mode in effect when the
speed signal was lost.
• Speed signal implausible - steering assist the same as high speed driving (increased
effort).
The GM also provides the diagnostic “gateway” to the Servotronic status and Component
Activation via the DISplus/MoDiC.
74
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Page 76 of 80

Sleep Mode
To lower the constant battery draw when the vehicle is parked, the complete ZKE system
will go into the “Sleep Mode” 16 minutes after the ignition has been switched off and no
further ZKE function is active.
For example, the approximate E39 (528i) Battery draw is:
• Ignition switch off = approx 750 mA.
• One minute after = approx. 560 mA.
• After 16 minutes (sleep mode) = approx. 18 mA.
All modules in the ZKE system will go into the sleep mode. The P-Bus remains active, how-
ever no data transfer takes place until a wake-up request is received. The general module,
door modules or keyless remote module can wake the system up and put the ZKE back
on line. The K-Bus is active (high) in the sleep mode.
Sleep Mode Criteria:
KL R, KL 15 OFF and no further function activated for 16 minutes.
Wake Up Criteria:
KL R or 15 “ON” or a change in one of the signals listed below.
76
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
SIGNAL ACTIVITY ORIGINATING
MODULE
K-BUS High General Module
Door jamb switches (possibility of 4) Low “
Trunk lid lock cylinder microswitch High “
Trunk lid pushbutton microswitch Low “
Interior Trunk lid pushbutton microswitch Low “
Central locking button Low “
Hood microswitch Low “
Trunk Lid microswitch Low “
Interior light switch Low “
FIS sensor Low “
Tilt Alarm sensor Low “
FBZV operational signal High FBZV Module
Driver’s door lock microswitch - (lock) High PM-FT/SB
“ “ “ “ - (unlock) High “
Passenger door lock microswitch - (lock) High PM-BT
“ “ “ “ - (unlock) High “