2001 BMW 528i oil temperature
[x] Cancel search: oil temperaturePage 423 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Fuel lniection I
4 Remove complete air filter housing:
Disconnect electrical harness connector on mass air flow
sensor
(A).
Disconnect vacuum line at intake boot (B).
Loosen Intake air duct clamp (C).
Remove filter housing mounting screws
Disconnect air duct and
lift complete air filter housing and
MAF sensor out of engine compartment, pulling it forward
away from throttle housing.
- Pull throttle cable upwards out of rubber retainer and unhoolc
ball end of cable from throttle actuator.
4 Remove nuts and bolts (arrows) retaining wiring harness to
throttle housing.
- Working at throttle housing, turn harness plug counterclock-
wise and remove plug.
4 Working at side of intake manifold, disconnect electrical har-
ness connectors:
Idle control valve (A)
lntalce manifold resonance valve (B)
- Disconnect electrical harness connectors at oil pressure
sender and oil temperature sender at base of oil filter hous-
ing.
CO,l,> ti,, "F"bl,rl,irrm.,-AI ",",>ti
Page 426 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
130-36
[~uel Injection
4 Remove nuts and bolts (arrows) retaining wiring harness to
throttle housing.
- Working at throttle housing, turn harness plug countercloclc
wise and remove.
4 Working at side of intake manifold, disconnect electrical bar-
ness connectors:
Idle control valve (A)
Intake manifold resonance valve (B)
- Disconnect electrical harness connectors at oil pressure
sender and oil temperature sender at base of oil filter hous-
ing.
4 Remove dipstick guide tube:
Disconnect wiring harness brackets from tube
(A)
Unclip fuel lines from tube (B).
Remove lower guide tube mounting bolt (C).
Pull out dipstick guide tube.
Page 433 of 1002
![BMW 528i 2001 E39 Workshop Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
130-43
Fuel Injection ]
I I I
12 llnput IFeedback signal, engine start /Starter
Table c. Siemens MS 42.0 and MS 43.0 ECM pin assignments BMW 528i 2001 E39 Workshop Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
130-43
Fuel Injection ]
I I I
12 llnput IFeedback signal, engine start /Starter
Table c. Siemens MS 42.0 and MS 43.0 ECM pin assignments](/manual-img/1/2822/w960_2822-432.png)
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
130-43
Fuel Injection ]
I I I
12 llnput IFeedback signal, engine start /Starter
Table c. Siemens MS 42.0 and MS 43.0 ECM pin assignments (continued)
I I - I
13 Input /I Alternator (generator) Notes
Throttle
valve
Crankshaft position sensor
Throttle valve (MS
42.0)
Throttle valve
Pin
6
7
8
9
10
11
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
I 1- I
23 l~round I~round, intaite air temperature sensor /Intake air temperature sensor
Signal
Output
Input
Input
Input
I I I
Component/function
Not used
Throttle valve supply potentiometer
2
Signal, crankshaft position sensor
Signal,
pedal position sensor 2 (MS 42.0)
Signal, throttle position sensor 1
Not used
Ground
Ground
Input
Ground
Ground
Input
Ground Cranltshaft position sensor
21
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
I 1- I
33 1 input ISignal, cylinder 1 fuel injector /cylinder 1 fuel injector
Ground, throttle position sensor (MS
42.0)
Ground, exhaust camshaftsensor I
Signal, pedal position sensor 1 (MS 42.0)
Ground, mass air flow sensor
Ground, intake camshaft sensor
1
Signal, throttle potentiometer 1
Ground, throttle position sensor
22 loutput I~ignal, intake air temperature Ilntake air temperature sensor
I I - I
Throttle
valve (MS 42.0)
Camshaft position sensor I
Throttle valve (MS
42.0)
Hot film mass air flow sensor
Camshaft position sensor i
Throttle valve
Throttle valve
Ground
Output
Ground Input
Output
Ground
Output
Out~ut
Ground, crankshaft position sensor
Knoclt sensor
31
34
35
36
37
38
39
Signal, coolant temperature sensor
Ground, coolant temperature sensor
Signal,
oil pressure
Signal, engine
oil temperature sensor
Ground, engine oil temperature sensor
Signal, knock sensor
Signal, knock sensor
32 loutput ISignal, ltnock sensor l~nock sensor
40
41
Coolant temperature sensor
Coolant temperature sensor
Oil pressure switch
Oil temperature sensor
Oil temperature sensor
Knoclt sensor
I
Input
input
Input
Input
Input
Inout
Signal, knock sensor
Input
Input Signal, cylinder
2 fuel injector
Signal, cylinder
3 fuel injector
Signal, cylinder
4 fuel injector
Signal, cylinder
5 fuel injector
Signal, cylinder
6 fuel injector
Sianai, oil level sensor Cylinder
2 fuel
injector
Cylinder
3 fuel injector
Cylinder
4 fuel injector
Cylinder
5 fuel injector
Cylinder
6 fuel injector
Oil level sensor
-
Signal. VANOS inlet valve
Signal. VANOS outlet valve VANOS
inlet valve
VANOS outlet valve
Page 454 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
-
Fuel Injection
Table e. Bosch 5.2.1 ECM pin assignments
Pin
I~iqnal 1 Description 1 Note
I I I
46 llnput ICrankshaft position sensor Icrankshaft positionlrpm sensor
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45 Ground Input
Output
Output
Output
Output
Ground
47
48
49
50
51
Not used
I Not used
52
Shield, knock sensor
Oil level
- thermal
Injection signal
injection signal
Idle speed control - opening winding
Idle speed control - closing winding
Not used
Ground
Ground
-- Ground Input
Ground
Ground Not used Knock sensor
Oil level sensor
Cylinder
4 fuel injector
valve
Cylinder
1 fuel injector valve
Idle speed control valve
Idle speed control valve
Shield, crankshaft sensor
5
6
7
12 Not used
Ground
Intake air temperature sensor
Connector
X60004
8
9 10
11
14 1 1 Not used I
Shield, knock sensor
Shield, sensor
I
Shield, sensor 3
Shield, itnock sensor
Input
- Knoclc sensor
Knock sensor
Knock sensor
Knock sensor
Instrument cluster
Output
2 llnput l~erminal 30 voltage supply /Megrated instrument cluster control module (IKE)
Alt. charge indicator signal, terminal 61 1
Not used
Start signal terminal
50
Not used
15
16
17
18
Output
Ignition switch
Not used
Not used
Activation of relay for fuel pump
Not used
19
Fuel pump relay
Output Not used
I I I 20 loutput ICARB signal /Data link connector
Not
used
Not used
Engine speed signal output (TD)
Not used
Light module
21
Cruise control module (Tempomat)
22 llnput I Right rear wheel speed signal /ABS/ASC or ABSIDSC control module
Oulput
Washer
fluid level,
brake fluid level
Page 469 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Fuel Injection I
Connector X60004 (continued)
8 10
11
12
13
14
15
16
9
Output 0
Input
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
39
llnput lsignal l~oolant outlet temperature sensor
Output
Output
Ground
Input
Output
I I - I
40 /output Istart signal Istarter relay
Pedal position sensor (PWG), signal
Output Input
Output
input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
input
Input
Output
Input/-output
Input/-output
37
Connector X60003
Pedal position sensor
Fuel pump relay, activation
Oil pressure indicator Pedal position sensor (PWG), ground
Pedal position sensor (PWG), signal
Pedal position sensor (PWG), power supply
Not used
Not used Fuel
pump relay
Instrument cluster
Pedal position sensor
Pedal position sensor
Pedal position sensor
Engine speed signal output (TD)
Not used
Signal
back-up light
DM-TL (diagnostic module,
tank leakage)
Signal oil level sensor
Right rear wheel speed, signal
Clutch pedal position switch, signal
Brake light switch, signal
Not used
Voltage supply, terminal
15
Data link, MFL (multi-function steering wheel)
Brake light test signal
AJC compressor signal
DM-TL (diagnostic module, tank
leakage)
Not used
Diagnosis signal
TxD
Communication link (EWS)
Not used
Not used
CAN-BUS hiqh
38 1 Ground l~round I Coolant outlet temperature sensor
OED II plug
Integrated instrument cluster control module (IKE)
Light module
ABSIDSC control module
Clutch pedal position switch
Brake light switch
Fuse
F14
Airbag contact coil spring
Brake light switch
Heating and
A/C control module
OBD
II plug
Electronic immobilizer (EWS)
CAN-Bus link
CAN-Bus link
Input/-output CAN-Bus low
Page 502 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
.. - -
I Radiator and Cooling System
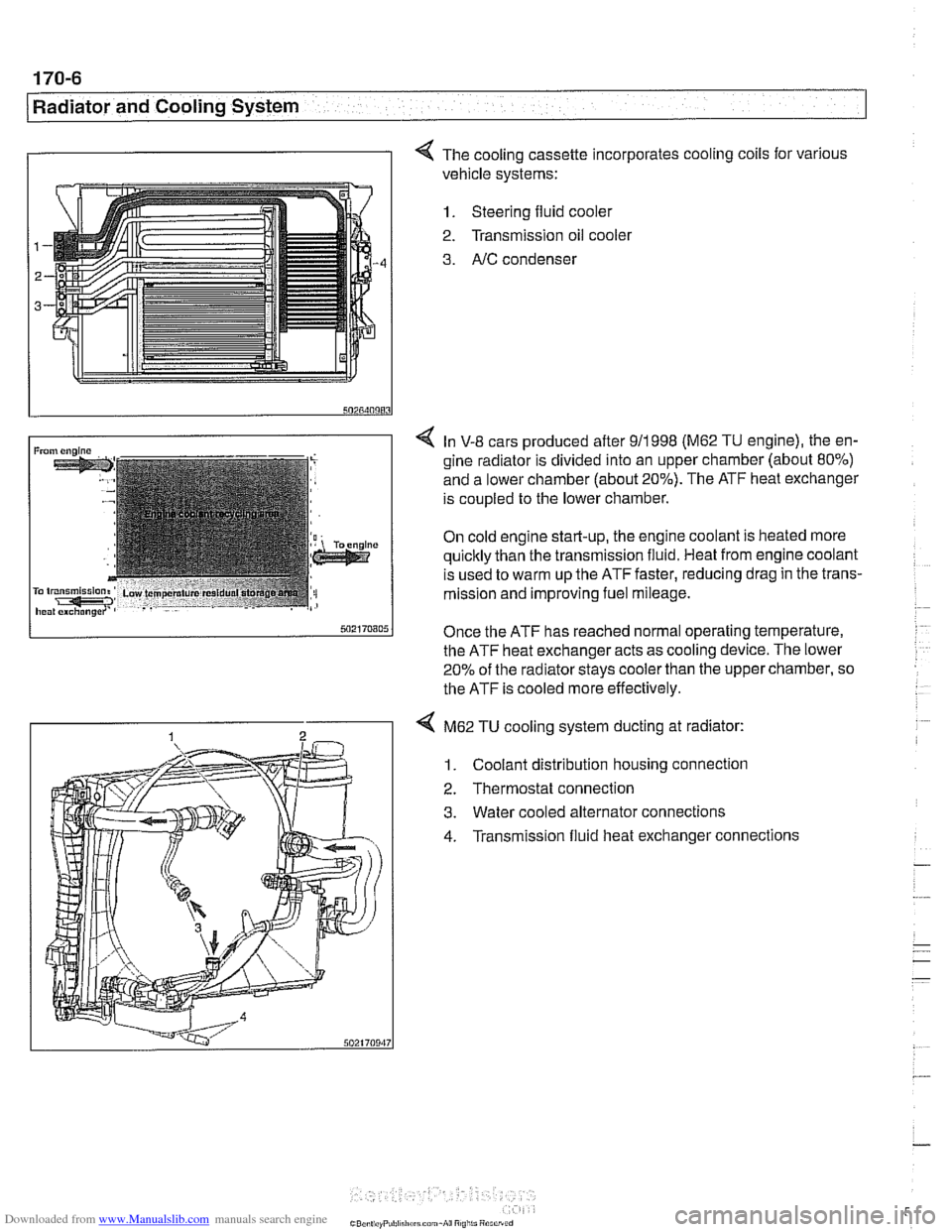
I I 4 The cooling cassette incorporates cooling coils for various
vehicle systems:
1. Steering fluid cooler
2. Transmission oil
coolel
3. AIC condenser
4 In V-8 cars produced after 911998 (M62 TU engine), the en-
gine radiator is divided into an upper chamber (about 80%)
and a lower chamber (about 20%). The ATF heat exchanger
is coupled to the lower chamber.
On cold engine start-up, the engine coolant is heated more
quicltly than the transmission fluid. Heat from engine coolant
is used to warm up the ATF faster, reducing drag in the trans-
mission and improving fuel mileage.
Once the ATF has reached normal operating temperature,
the ATF heat exchanger acts as cooling device. The lower
20% of the radiator
stays cooler than the upper chamber, so
the ATF is cooled more effectively.
4 M62 TU cooling system ducting at radiator:
1. Coolant distribution housing connection
2. Thermostat connection
3. Water cooled alternator connections
4. Transmission fluid heat exchanger connections
Page 503 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Warnings and cautions
Obse~e the following warnings and cautions when worlting
on the cooling system.
WARNING -
. At normal operating temperature the cooling system is
pressurized. Allow the system to cool as long as possible
before opening (a minimum of one hour), then release the
cap slowly to allow safe release ofpressure.
a Releasing the coolant system pressure lowers the cool-
ant boilingpoint and the coolant may boil suddenly. Use
1 heavy and wear eye and face protection to
guard against scalding.
Use extreme care when draining and disposing of en-
gine coolant. Coolant is poisonous and lethal to hu-
mans andpets. Pets are attracted to coolant because
of its sweet smell and taste. Seek medical attention im-
mediately if coolant is ingested.
CAUTIOG
Avoid adding cold water to the coolant while the engine is
hot or overheated. If it is necessary to add coolant to a
hol
system, do so only with the engine running and coolanl
pump turning.
To avoid excess silicate gel precipitation in the cooling
system and loss of cooling capacity, use BMW coolant
or equivalent low silicate antifreeze.
a If oil enters the cooling system, the radiator, expansion
tank and heating circuit must be flushed with cleaning
agent. BMW recommends removal of the radiator and
expansion
tank to flush.
When
worlcing on the cooling system, cover the alter-
nator to protect it against coolant drips.
Prior to disconnecting the battery, read the battery dis-
connection cautions given in
001 General Warnings
and Cautions.
Begin the diagnosis of cooling system problems with a thor-
ough visual inspection.
If no visual faults are found, it is rec-
ommend that the engine control module (ECM) fault memory
be checked for stored diagnostic trouble codes
(DTCs) using
BMW scan tool
DlSplus or equivalent.
Page 504 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
170-8
I Radiator and Cooling System
Common cooling system faults can be grouped into one of 4
categories:
Cooling system
lealts
Poor coolant circulation
Radiator cooling fan faults
Electrical/electronic faults
Cooling system inspection
- Check that coolant pump drive belt tensioner is functioning
properly and that belt tension is correct. Belt tensioner sys-
tems for the different models are shown in
020 Maintenance.
- Check condition of coolant pump drive belt.
- Checlc coolant hoses for cracks or softness. Checlc clamps
for looseness. Check coolant level and check for evidence of
coolant
lealts from engine.
- Check that radiator fins are not blocked with dirt or debris.
Clean radiator using low-pressure water or compressed air.
Blow outward, from engine side out.
- To check coolant pump:
Remove mechanical cooling fan. See Mechanical
(vis.
cous clutch) cooling fan, removing and installing.
Remove drive belt from coolant pump pulley. See
020
Maintenance.
Firmly grasp opposite sides of pulley and check for play in
all directions.
Spin pulley and check that shaft runs smoothly without
play.
NOTE-
The coolant provides lubrication for the pump shaft, so an oc-
casional drop of coolant
lealing from the pump is acceptable.
If coolant drips steadily from the vent hole, replace the pump.
- At normal engine operating temperature, cooling system is
pressurized. This raises boiling point of coolant.
Leaks may
prevent system from becoming pressurized. If visual evi-
dence is inconclusive, pressure test cooling system as de-
scribed later to help pinpoint hard-to-find leaks.
- If cooling system is full of coolant and holds pressure:
- Use an appropriate scan tool to interrogate engine control
module (ECM) for radiator fan or DME control circuit faults.
Checlc for loose or worn drive belt.
0 Test for failed thermostat or coolant pump impeller. Some
pumps may be fitted with plastic impellers.