2001 BMW 525i Speed signal
[x] Cancel search: Speed signalPage 469 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Fuel Injection I
Connector X60004 (continued)
8 10
11
12
13
14
15
16
9
Output 0
Input
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
39
llnput lsignal l~oolant outlet temperature sensor
Output
Output
Ground
Input
Output
I I - I
40 /output Istart signal Istarter relay
Pedal position sensor (PWG), signal
Output Input
Output
input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
input
Input
Output
Input/-output
Input/-output
37
Connector X60003
Pedal position sensor
Fuel pump relay, activation
Oil pressure indicator Pedal position sensor (PWG), ground
Pedal position sensor (PWG), signal
Pedal position sensor (PWG), power supply
Not used
Not used Fuel
pump relay
Instrument cluster
Pedal position sensor
Pedal position sensor
Pedal position sensor
Engine speed signal output (TD)
Not used
Signal
back-up light
DM-TL (diagnostic module,
tank leakage)
Signal oil level sensor
Right rear wheel speed, signal
Clutch pedal position switch, signal
Brake light switch, signal
Not used
Voltage supply, terminal
15
Data link, MFL (multi-function steering wheel)
Brake light test signal
AJC compressor signal
DM-TL (diagnostic module, tank
leakage)
Not used
Diagnosis signal
TxD
Communication link (EWS)
Not used
Not used
CAN-BUS hiqh
38 1 Ground l~round I Coolant outlet temperature sensor
OED II plug
Integrated instrument cluster control module (IKE)
Light module
ABSIDSC control module
Clutch pedal position switch
Brake light switch
Fuse
F14
Airbag contact coil spring
Brake light switch
Heating and
A/C control module
OBD
II plug
Electronic immobilizer (EWS)
CAN-Bus link
CAN-Bus link
Input/-output CAN-Bus low
Page 501 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
170-5
Radiator and Cooling System
Fan switch calibration (M52, M62 engine)
coniprairoi OUt rlgnal
Auto. ciimilte ~ontioi inpuls via CAN bus
Electric fan activation:
Low speed
91°C (196°F)
High speed 104' C (21 9' F)
< In models manufactured after 911998 (M52 TU engine, M54
engine.
M62 TU engine), the electric cooling fan is controlled
by the engine control module (ECM) via the output final
stage.
The output final stage is mounted on the fan housing, next to
the fan motor. The fan is operated using a pulse width modu-
lated signal. Fan circuit wiring is protected by a 50-amp fuse.
Electric fan activation is based on the following inputs to the
ECM:
Radiator outlet temperature
Calculated catalytic converter temperature
Vehicle speed
* Battery voltage
Calculated
A/C pressure
When the vehicle is first started, the ECM activates the elec-
tric fan briefly at 20% of its maximum speed, then switches
off. This is for diagnostic monitoring. The voltage generated
by the fan when it slows down (acting as a generator) must
match the stored rpm values in the fan output stage toconfirm
that the fan is operating correctly.
NOTE-
If the ECM fault memory indicates a cooling fan fault, check
that the fan is not seized and that it spins freely.
When
A/C is switched ON, the electric fan is not immedi-
ately turned on.
After the engine is switched
OFF the fan may continue to
run at varying speeds for up to 10 minutes, based on cal-
culated catalyst temperature.
Transmission fluid heat exchanger
Automatic transmission fluid lines circulate transmission fluid
(ATF) to and from a heat exchanger at the radiator.
All 6-cylinder
models andV-8 models produced to 911998 are
equipped with a transmission cooler located in a cooling cas-
sette in front of the radiator.
Page 899 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Central Locking and Anti-Theft
DWA alarm
The DWA alarm system is
armedldisarmed when thevehicle
is locked / unlocked from either the door or trunk.
Convenience closing
I opening
The windows and sun roof can be closed or opened by hold-
ing the key in the
loclc I unlock position.
Crash sensor
The crash sensor is located in the left front
kick panel. It func-
tions by unlocking all doors in the event of an accident.
NOTE-
Continuous and repeated locliing / unlocking may cause
timedarrest of
the locliing system. When activated, the timed
arrest lasts for two minutes. The timed arrest does not affect
the crash sensor
unlocliing the doors in case of an accident.
Door locks
The driver's door lock location is the only point outside of the
vehicle where the ltey can mechanically control all of the cen-
tral locking system functions.
4 Door key positions for electrical / manual loclting and
unlocking are:
1. Manual unlock
2. Unlock, DWA disarmed, convenience open
(hold until activated)
3. Neutral position
4. Lock, DWA armed, convenience closing
(hold until activated)
5. Manual lock
The door lock actuators are sealed. self contained units with
no replaceable parts. The
actuators use Hall effect sensors in
place of pin contacts and microswitches to provide DOOR
OPEN
I DOOR CLOSED status signal. Each door lock button
only affects the actuator it controls. There is no effect on the
other doors.
An automatic locking feature activates door locks when a
road speed signal of 4 mph is detected via the K-Bus. The fac-
tory default coding for this feature is OFF, but can be coded
ON for individual users with the Key Memoryfunction. See
Car Memory
1 Key Memory later in this section.
Page 901 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Central Locking and Anti-Theft
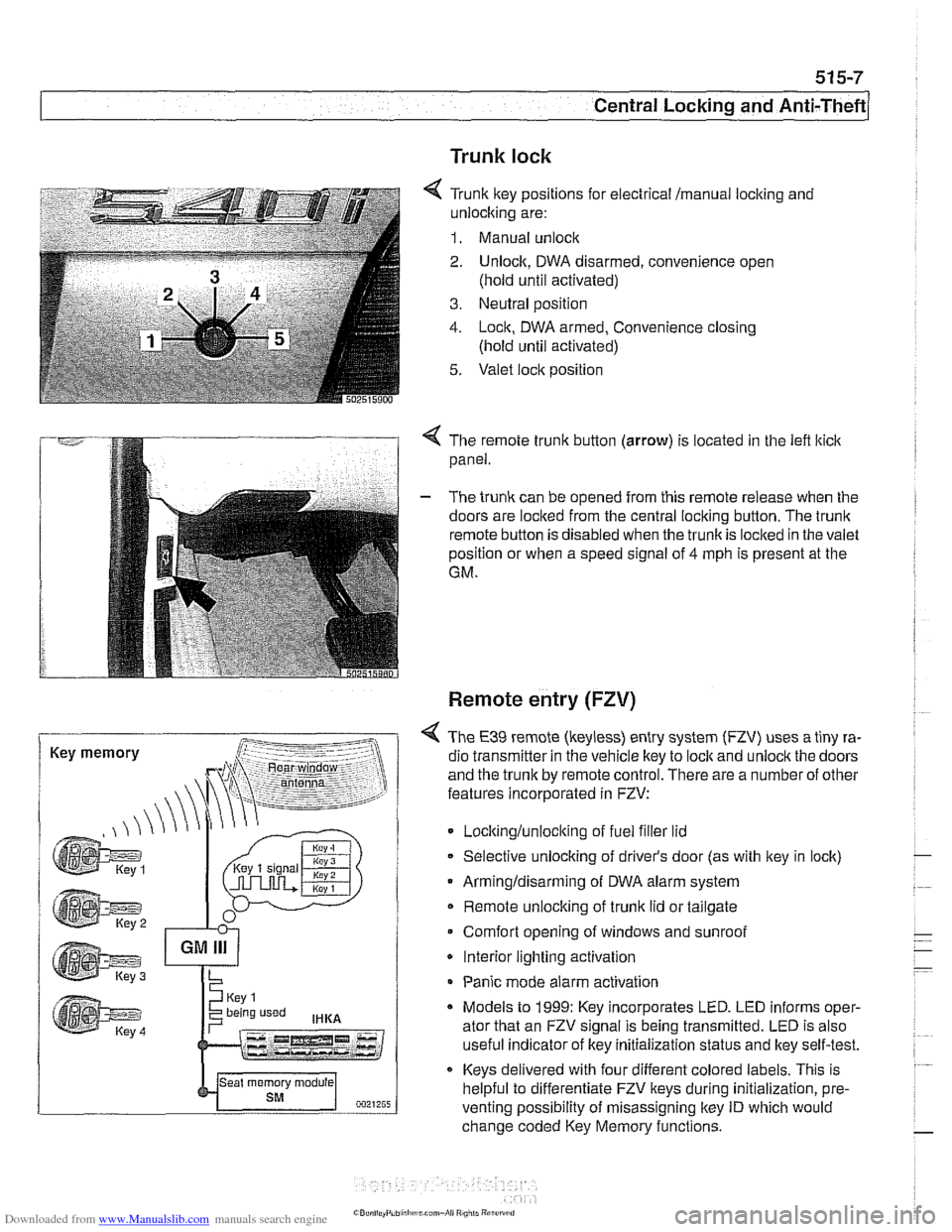
Trunk lock
6 Tr~nk ftey pos~rions for eecir'cal mama, locking and
-nlock~ng are:
1. Manual unock .. - - - ........ - ..- .- ................. s.=.=-- 2. Unlock. DWA oisarmed, conven:ence open
(nold
un1:l aclivaledj
3. Ne~tral posit'on
1. -ocn. DWA armeo, Convenience closng
(hold ~nti activated)
5. Valet .oc,t position
. -- .............-... .- . - -.....
Key memory
< The remote trunk button (arrow) is located in the lefl lticlc
panel.
- The trunk can be opened from this remote release when the
doors are locked from the central locking button. The
trunk
remote button is disabled when the trunkis loclted in the valet
position or when a speed signal of
4 mph is present at the
GM.
Remote entry (FZV)
< The €39 remote (keyless) entry system (FZV) uses a tiny ra-
dio transmitter in the vehicle key to
lock and unlock the doors
and the trunk by remote control. There are a number of other
features incorporated in FZV:
Locltinglunloclting of fuel filler lid
Selective unlocking of driver's door (as with key in lock)
Armingldisarming of DWA alarm system
Remote unlocking of
trunk lid or tailgate
Comfort opening of windows and sunroof
* Interior lighting activation
Panic mode alarm activation
* Models to 1999: Key incorporates LED. LED informs oper-
ator that an FZV signal is being transmitted. LED is also
useful indicator of key initialization status and lkey self-test.
Keys delivered with four different colored labels. This is
helpful to differentiate FZV keys during initialization,
pre.
venting possibility of misassigning key ID which would
change coded Key Memory functions.
Page 965 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
On-Board Diagnostics
Catalyst monitoring. Thisstrategy monitors the outputofthe
precatalyst and post-catalyst oxygen sensors, comparing the
oxygen content going into the catalytic converter to the
oxygen leaving the converter.
The diagnostic executive
lknows that most of the oxygen
should be used up during the oxidation phase. If it detects
higherthan programmed values, afault is set and the MIL
illuminates.
Misfire detection. This strategy monitors crankshaft speed
fluctuations and determines if an enoine misfire occurs bv
monitoring variations in speed between each crankshaft
sensortrigger point. This strategy is so finely tuned that it can
determine the severity of the misfire.
The system determines
if a misfire is occurring, as well as
other pertinent misfire
information such as:
Specific
cylinder(s)
Severity of the misfire event
Emissions relevant or catalyst damaging
Misfire detection is an on-going monitoring process that is
only disabled under certain limited conditions.
Secondary air injection monitoring. Secondary air
injection is used to reduce HC and CO emissions during
engine warm up. Immediately following a cold engine start
(-1 0" to 40°C), fresh air (and therefore oxygen) is pumped
directly into the exhaust
manifold. By injecting additional
oxygen into the exhaust manifold, catalyst warm-up time is
reduced.
Secondary air system components are:
Electric air injection pump
* Electric pump relay
* Non-return valve
Vacuum
I vent valve
- Stainless steel air injection pipes
Vacuum reservoir
The secondary air system is monitored via the use
of the pre-
catalyst oxygen sensors. Once the air pump is active and air
is injected into the system, the signal at the oxygen sensor
reflects a lean condition. If the oxygen sensor signal does not
change, a fault is set and the faulty
bank(s) identified. If after
completing the next cold startafault is again present, the MIL
illuminates.
Page 966 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-6
On-Board Diagnostics
Fuel system monitoring. This monitor looks at the fuel
delivery needed (long
/short term fuel trim) for proper engine
operation based on programmed data. If too much or not
enough fuel is delivered over a predetermined time, a DTC is
set and the MIL illuminates.
Fuel trim refers to adiustments to base fuel schedule.
Lono- ., term fuel trim refers to gradual adjustments to the fuel
calibration adjustment as compared to short term fuel trim.
Long term fuel trim adjustments compensate for gradual
changes that occur over time.
Fuel system monitoring monitors the calculated injection time
(ti) in relation to enginespeed, load and precatalyticconverter
oxygen
sensor(s) signals.
Using this data, the system optimizes fuel delivery for all
engine operating conditions.
Evaporative system monitoring. This monitor checks the
the fuel storage system and related fuel lines for leaks. It can
detect very small leaks anywhere in the system.
A leak detection unit (LDP or DMTL) is used to pressurize the
evaporative control system on a continuous basis (as the
drive cycle allows) and to
check system integrity.
Drive cycle
The OED II drive cycle is an important concept in
understanding OBD
II requirements. The purpose of the drive
cycle is to run ail of the emission-related on-board diagnostics
over a broad range of driving conditions.
A drive cycle is considered complete when all of the
diagnostic monitors have run their tests without interruption.
~ora drive cycle to be initiated, the vehicle must be started
cold and brought up to
1 60°F and at least 40°F above its
original starting temperature.
Readiness codes
Inspection/maintenance (I/M) readiness codes are mandated
as part of OBD
II. The readiness code is stored aftercomplete
diagnostic monitoring of specified components and systems
is carried out. The readiness code function was designed to
prevent manipulating an
I/M emission test procedure by
clearing faults codes or disconnecting the ECM or battery.
Page 969 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
On-Board Diagnostics
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(DTCs)
Below is a listing of E39 powertrain (automatic transmission
and engine)
SAE P-codes, the corresponding BMW fault
codes, and the fault code definitions.
BMW fault codes expand on the SAE sanctioned DTCs and
are accessible primarily through the BMW diagnostic scan
tool or a BMW-specific scan tool.
l~utomatic transmission diagnostic trouble codes
P-code
IBMW-FC I DTC Definition
Ip0560 196 ISystem Voltage I
IPO~OO I129 l~eriai Communication Link I
1~0715 116 I InpuVTurbine Speed Sensor 'A' Circuit I
PO600
PO601
PO603
PO606
PO705
PO705
PO709
144
80
81
82
8
60
60
PO71 5
PO71 6
PO717
PO720
PO720
PO720
I I
PO721 159 loutput Speed Sensor Circuit RangeIPerformance I
Serial Communication Link
Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum Error
Internal Control Module Keep Alive Memory (KAM) Error
ECMIPCM Processor
Transmission Range Sensor 'A' Circuit Maliunction (PRNDL Input)
Transmission Range Sensor
'A' Circuit Malfunction (PRNDL input)
Transmission Range Sensor
'A' Circuit Intermittent
I I'
1~0722 132 IOutput Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal I
33
33
33
32
42
59
PO720
I I
PO727 1150 I Engine Speed Input Circuit No Signal
InpuVTurbine Speed Sensor 'A' Circuit
inpuVTurbine Speed Sensor 'A' Circuit RangeiPerformance
InpuVTurbine Speed Sensor 'A' Circuit No Signal
Output Speed Sensor Circuit
Output Speed Sensor Circuit
Out~ut Speed Sensor Circuit
PO720 1106 /output Speed Sensor Circuit
62
Output Speed Sensor Circuit
PO730
PO730
PO731
PO731
PO731 I I
100
102
50
51
100
PO731
incorrect Gear Ratio
Incorrect Gear Ratio
Gear 1 incorrect Ratio
Gear 1 incorrect Ratio
Gear 1 Incorrect Ratio
PO732 152 /Gear 2 Incorrect Ratio
131
Gear
1 Incorrect Ratio
Page 975 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-15
On-Board ~iagnosticsl
Engine diagnostic trouble codes: M52 engine (continued)
P-code
PO340
PO412
PO420
PO430
PO440
PO441
PO442
PO443
PO500
PO505
PO600
PO601
PO601
I PO601
~1132
~1133
BMW-FC
65
62
233
234
250 144
-
145
68
214
i I
DTC Definition
Camshalt Position Sensor 'A' Circuit (Bank 1 or Single Sensor)
Secondary Air Injection System Switching Valve A Circuit
Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
(Bank 1)
Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
Evaporative Emission System
Eva~orative Emission Svstem Incorrect Purge Flow .
Evaporative Emission System Leak Detected (small leak)
Evaporative Emission System Purge Control Valve Circuit
Vehicle Speed Sensor 'A'
204
21 7
100
170
171
188
189
PI161
PI180
PI181
PI184
PI185
PI178
02 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 2) I
idle Air Control System
Serial Communication
Link
Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum Error
Internal Control Module Memory
Check Sum Error
Internal Control Module Memory
Check Sum Error
02 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor
1)
02 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit RangeIPerlormance Problem PI140
I
I I
P1188 1227 I Fuel Control (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
PI145 150 /Solenoid Valve Running Losses Control Circuit Electrical
149
122
223
224
220 221
231
I I
P1189 1228 I Fuel Control (Banlc 2 Sensor 1)
Fuel Trim Adaptation Additive High (Bank 2) (M52: Engine Oil Temperature Sensor Circuit)
02 Sensor Signal Circuit Slow Switching from Rich to Lean
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
02 Sensor Signal Circuit Slow Switching from Rich to Lean
(Bank 2 Sensor 2)
H02S Sensor Voltage Excursion Electrical (Banlc 1 Sensor 1)
HO2S Sensor Voltage Excursion Electrical (Banlc 2 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Sianai Circuit Slow Switchina from Rich to Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Signal Circuit Slow Switching from Rich to Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) PI179
I I
PI190 1235 I Pre Catalyst Fuel Trim System (Banlc 1)
PI186 1190 102 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Banlc 1 Sensor 2)
232
I I
PI191 1236 I Pre
Catalyst Fuel Trim System (Banlc 2)
PI192
. . -- - i Pi193 1226 I Post Catalvst Fuel Trim Svstem (Bank 2)
225
PI397
I I
Post Catalyst Fuel Trim System (Bank 1)
PI421 1246 /Secondarv Air System (Bank 2)
18
Secondary Air System (Bank
1) PI423
Camshaft Position Sensor '0' Circuit (Bank 1)
I 245