2000 SUZUKI SWIFT tire pressure
[x] Cancel search: tire pressurePage 169 of 698
3B1-28 ELECTRICAL POWER STEERING (P/S) SYSTEM
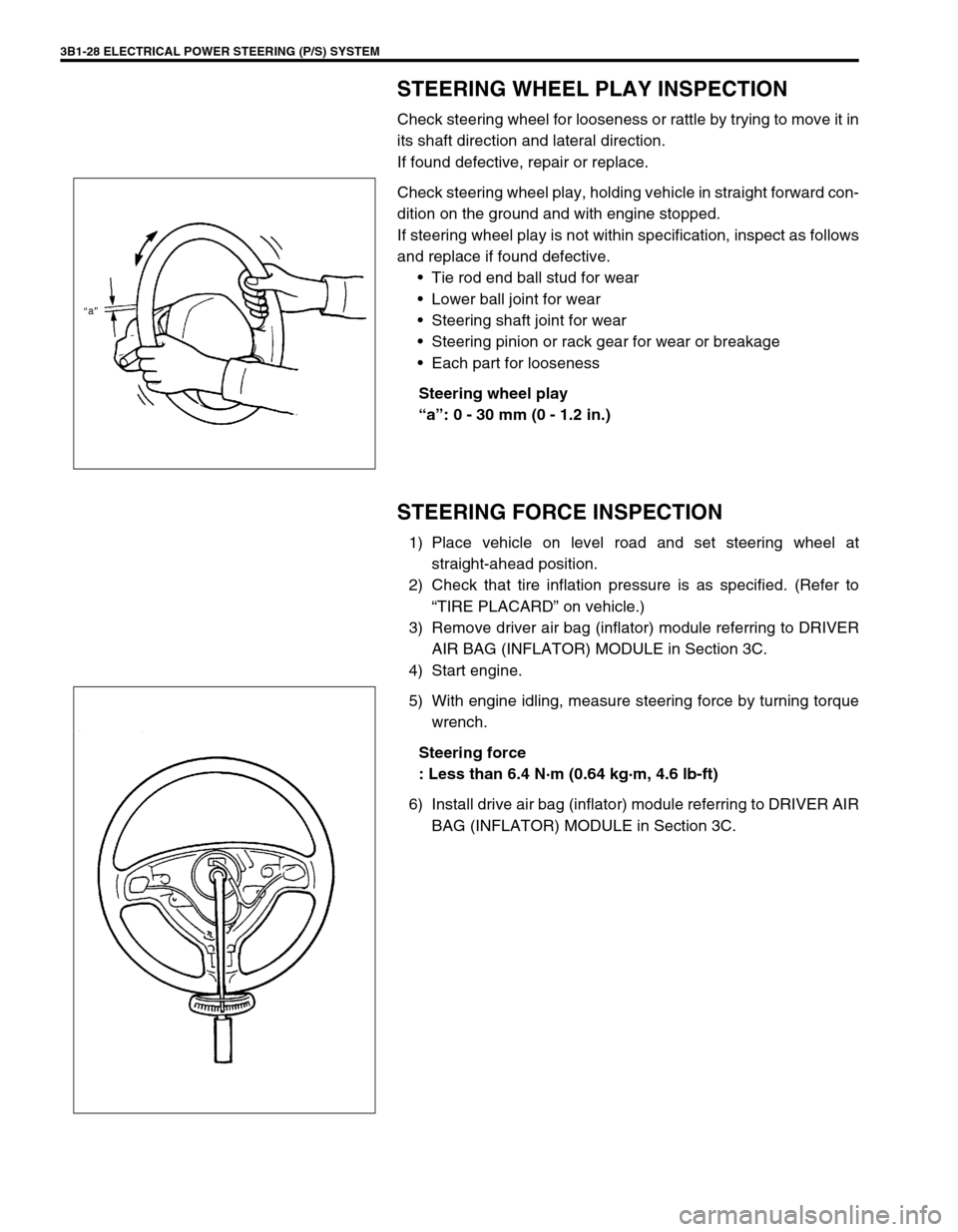
STEERING WHEEL PLAY INSPECTION
Check steering wheel for looseness or rattle by trying to move it in
its shaft direction and lateral direction.
If found defective, repair or replace.
Check steering wheel play, holding vehicle in straight forward con-
dition on the ground and with engine stopped.
If steering wheel play is not within specification, inspect as follows
and replace if found defective.
Tie rod end ball stud for wear
Lower ball joint for wear
Steering shaft joint for wear
Steering pinion or rack gear for wear or breakage
Each part for looseness
Steering wheel play
“a”: 0 - 30 mm (0 - 1.2 in.)
STEERING FORCE INSPECTION
1) Place vehicle on level road and set steering wheel at
straight-ahead position.
2) Check that tire inflation pressure is as specified. (Refer to
“TIRE PLACARD” on vehicle.)
3) Remove driver air bag (inflator) module referring to DRIVER
AIR BAG (INFLATOR) MODULE in Section 3C.
4) Start engine.
5) With engine idling, measure steering force by turning torque
wrench.
Steering force
: Less than 6.4 N·m (0.64 kg·m, 4.6 lb-ft)
6) Install drive air bag (inflator) module referring to DRIVER AIR
BAG (INFLATOR) MODULE in Section 3C.
Page 196 of 698

FRONT SUSPENSION 3D-3
DIAGNOSIS
STABILIZER BAR AND/OR BUSHING CHECK
Bar
Inspect for damage or deformation.
If defective, replace.
Bushing
Inspect for damage, wear or deterioration.
If defective, replace.
STRUT ASSEMBLY CHECK
Inspect strut for oil leakage, damage or deformation.
If strut is found faulty, replace it as an assembly unit,
because it can not be disassembled.
Inspect strut function refer to the following procedures.
1) Check and adjust tire pressures as specified.
2) Bounce vehicle body 3 or 4 times continuously by pushing
front end on the side with strut to be checked.
3) Apply the same amount of force at each push and note strut
resistance both when pushed and rebounding.
4) Also, note how many times vehicle body rebounds before
coming to stop after hands are off. Do the same for strut on
the other side.
5) Compare strut resistance and number of rebalance on the
right with those on the left. And they must be equal in both.
With proper strut, vehicle body should come to stop the
moments hands are off or after only one or two small rebal-
ances.
If conditions of struts are in doubt, compare them with known-
good vehicle or strut.
Inspect bearing for wear, abnormal noise or gripping.
If defective, replace.
Page 247 of 698

3F-2 WHEELS AND TIRES
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
TIRES
This vehicle is equipped with the following tire.
Tire size
: 165/70R14
The tire is of tubeless type. The tire is designed to operate satisfactorily with loads up to the full rated load
capacity when inflated to the recommended inflation pressures.
Correct tire pressures and driving habits have an important influence on tire life. Heavy cornering, excessively
rapid acceleration, and unnecessary sharp braking increase tire wear.
WHEELS
Standard equipment wheels are the following steel wheel.
Wheel size
: 14 x 4 1/2 J
REPLACEMENT TIRES
When replacement is necessary, the original equipment type tire should be used. Refer to the “Tire Placard”.
Replacement tires should be of the same size, load range and construction as those originally on the vehicle.
Use of any other size or type tire may affect ride, handling, speedometer/odometer calibration, vehicle ground
clearance and tire or snow chain clearance to the body and chassis.
It is recommended that new tires be installed in pairs on the same axle. If necessary to replace only one tire, it
should be paired with the tire having the most tread, to equalize braking traction.
The metric term for tire inflation pressure is the kilo pascal (kPa).
Tire pressures is usually printed in both kPa and psi on the “Tire
Placard”.
Metric tire gauges are available from tool suppliers.
The chart, shown the table, converts commonly used inflation
pressures from kPa to psi.
REPLACEMENT WHEELS
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented, have excessive lateral or radial runout, air leak through
welds, have elongated bolt holes, if lug nuts won’t stay tight, or if they are heavily rusted. Wheels with greater
runout than shown in figure below may cause objectional vibrations.
Replacement wheels must be equivalent to the original equipment wheels in load capacity, diameter, rim with
offset and mounting configuration. A wheel of improper size or type may affect wheel and bearing life, brake
cooling, speedometer/odometer calibration, vehicle ground clearance and tire clearance to body and chassis.WARNING:
Do not mix different types of tires on the same vehicle such as radial, bias and bias-belted tires except
in emergencies, because handling may be seriously affected and may result in loss of control.
kPa kgf/cm²pis
160 1.6 23
180 1.8 26
200 2.0 29
220 2.2 32
240 2.4 35
260 2.6 38
280 2.8 41
300 3.0 44
Page 250 of 698

WHEELS AND TIRES 3F-5
MAINTENANCE AND MINOR ADJUSTMENTS
WHEEL MAINTENANCE
Wheel repairs that use welding, heating, or peening are not approved. All damaged wheels should be replaced.
WHEEL ATTACHING STUDS
If a broken stud is found, see Section 3E (rear) or Section 3D (front) for Note and Replacement procedure.
MATCHED TIRES AND WHEELS
Tires and wheels are match mounted at the assembly plant.
This means that the radially stiffest part of the tire, or “high spot”,
is matched to the smallest radius or “low spot” of the wheel.
This is done to provide the smoothest possible ride.
The “high spot” of the tire is originally marked by paint dot (1) on
the outboard sidewall. This paint dot will eventually wash off the
tire.
The “ow spot” of the wheel is originally marked by paint dot (2) on
the wheel rim-flange. Properly assembled, the wheel rims’ paint
dot should be aligned with the tires’ paint dot as shown in left fig-
ure.
Whenever a tire is dismounted from its wheel, it should be
remounted so that the tire and wheel are matched. If the tire’s
paint dot cannot be located, a line should be scribed on the tire
and wheel before dismounting to assure that it is remounted in
the same position.
TIRE MAINTENANCE
TIRE PLACARD
The “Tire Placard” is located on the left door (right door for right-hand side steering vehicle) lock pillar and
should be referred to tire information.
The placard lists the maximum load, tire size and cold tire pressure where applicable.
NOTE:
Whether rim size and/or maximum load are listed or not depends on regulations of each country.
Page 251 of 698
3F-6 WHEELS AND TIRES
INFLATION OF TIRES
The pressure recommended for any model is carefully calculated to give a satisfactory ride, stability, steering,
tread wear, tire life and resistance to bruises.
Tire pressure, with tires cold, (after vehicle has set for 3 hours or more, or driven less than one mile) should be
checked monthly or before any extended trip. Set to the specifications on the “Tire Placard” located on the left
door (right door for right-hand side steering vehicle) lock pillar.
It is normal for tire pressure to increase when the tires become hot during driving.
Do not bleed or reduce tire pressure after driving. Bleeding reduces the “Cold Inflation Pressure”.
Higher than recommended pressure can cause :
Hard ride
Tire bruising or carcass damage
Rapid tread wear at center of tire
Unequal pressure on same axle can cause :
Uneven braking
Steering lead
Reduced handling
Swerve on acceleration
Lower than recommended pressure can cause :
Tire squeal on turns
Hard Steering
Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread
Tire rim bruises and rupture
Tire cord breakage
High tire temperature
Reduced handling
High fuel consumption
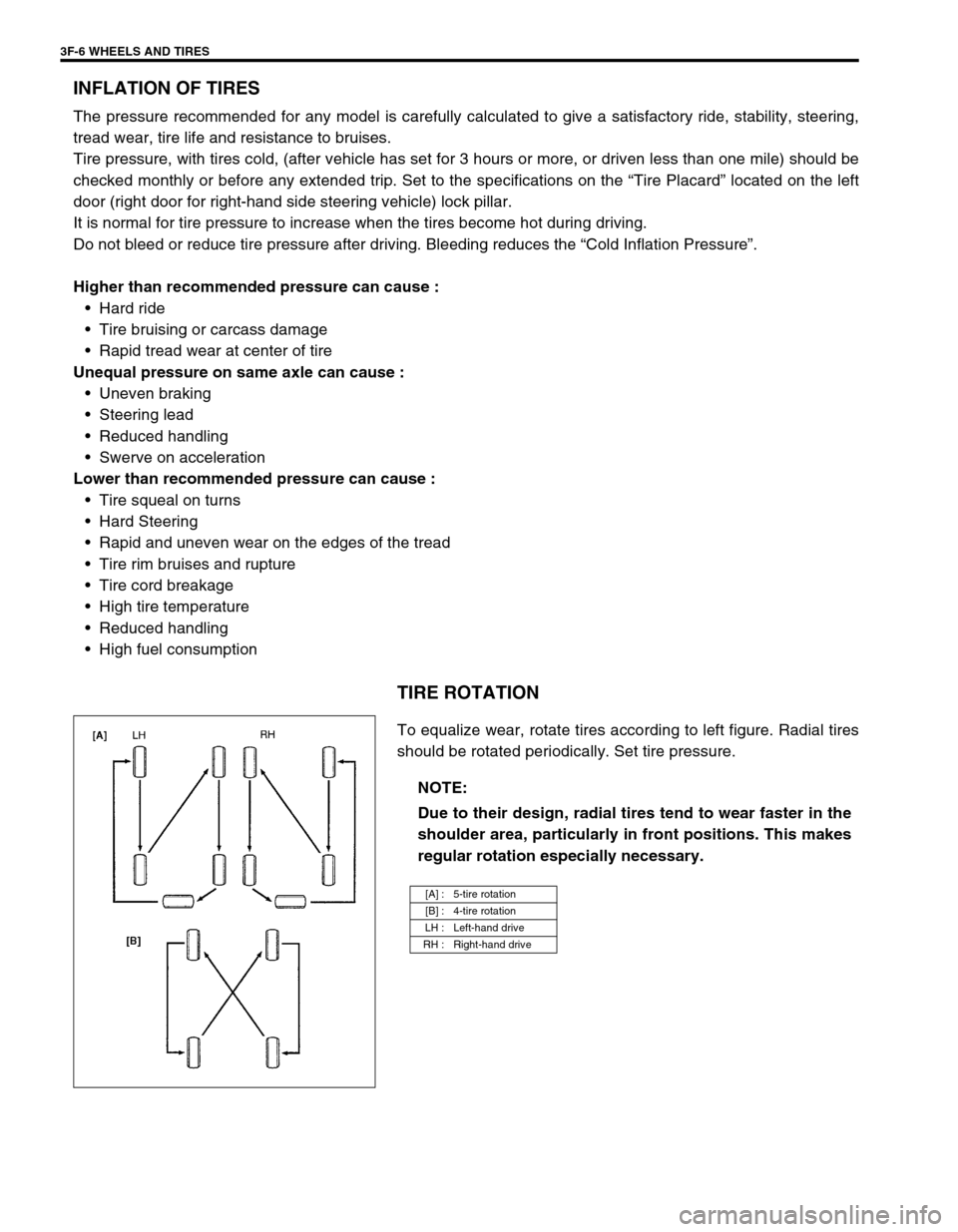
TIRE ROTATION
To equalize wear, rotate tires according to left figure. Radial tires
should be rotated periodically. Set tire pressure.
NOTE:
Due to their design, radial tires tend to wear faster in the
shoulder area, particularly in front positions. This makes
regular rotation especially necessary.
[A] : 5-tire rotation
[B] : 4-tire rotation
LH : Left-hand drive
RH : Right-hand drive
Page 253 of 698

3F-8 WHEELS AND TIRES
TIRE
MOUNTING AND DISMOUNTING
Use a tire changing machine to mount or dismount tires. Follow equipment manufacturer’s instructions. Do not
use hand tools or tire irons alone to change tires as they may damage tire beads or wheel rim.
Rim bead seats should be cleaned with a wire brush or coarse steel wool to remove lubricants, old rubber and
light rust. Before mounting or dismounting a tire, bead area should be well lubricated with approved tire lubri-
cant.
After mounting, inflate to specified pressure shown on tire placard so that beads are completely seated.
Install valve core and inflate to proper pressure.
REPAIR
There are many different materials and techniques on the market to repair tires. As not all of these work on all
types of tires, tire manufacturers have published detailed instructions on how and when to repair tires. These
instructions can be obtained from each tire manufacturer.WARNING:
Do not stand over tire when inflating. Bead may break when bead snaps over rim’s safety hump and
cause serious personal injury.
Do not exceed specified pressure when inflating. If specified pressure will not seat beads, deflate, re-
lubricate and reinflate.
Over inflation may cause bead to break and cause serious personal injury.
Page 265 of 698

4A-12 FRONT DRIVE SHAFT
7) Driver in the cage (1) by using a pipe (2).
Drive shaft joint cage installing pipe diameter
“a” : 22.5 mm (0.886 in.) or more
“b” : 30.0 mm (1.181 in.) or less
8) Install circlip (1) by using special tool (A).
Special tool
(A) : 09900-06107
9) Apply grease to entire surface of cage.
Use specified grease in tube included in spare parts.
10) Insert cage into outer race and fit snap ring (1) into groove of
outer race (2).
11) Apply grease to inside of outer race, and fit boot to outer
race. After fitting boot, insert screwdriver into boot on outer
race side and allow air to enter boot so that air pressure in
boot becomes the same as atmospheric pressure. CAUTION:
Install cage directing smaller outside diameter side to
wheel side.
CAUTION:
Position opening of snap ring “c” so that it will not be
lined up with a ball.
Page 277 of 698

5-4 BRAKES
DIAGNOSIS
ROAD TESTING BRAKES
Brakes should be tested on dry, clean, smooth and reasonably level roadway which is not crowned. Road test
brakes by making brake applications with both light and heavy pedal forces at various speeds to determine if the
vehicle stops evenly and effectively. Also drive vehicle to see if it leads to one side or the other without brake
application. If it does, check the tire pressure, front end alignment and front suspension attachments for loose-
ness. See diagnosis table for other causes.
BRAKE FLUID LEAKS
Check the master cylinder fluid levels. While a slight drop in reservoir level does result from normal lining wear,
an abnormally low level indicates a leak in the system. In such a case, check the entire brake system for leak-
age. If even a slight evidence of leakage is noted, the cause should be corrected or defective parts should be
replaced.
SUBSTANDARD OR CONTAMINATED BRAKE FLUID
Improper brake fluid, mineral oil or water in the fluid may cause the brake fluid to boil or the rubber components
in the hydraulic system to deteriorate.
If primary piston cups are swollen, then rubber parts have deteriorated. This deterioration may also be evi-
denced by swollen wheel cylinder piston cups on the drum brake wheels.
If deterioration of rubber is evident, disassemble all hydraulic parts and wash with alcohol. Dry these parts with
compressed air before assembly to keep alcohol out of the system. Replace all rubber parts in the system,
including hoses. Also, when working on the brake mechanisms, check for fluid on the linings.
If excessive fluid is found, replace the pads.
If master cylinder piston seals are satisfactory, check for leakage or excessive heat conditions. If leakage is not
found, drain fluid, flush with brake fluid, refill and bleed system.
The system must be flushed if there is any doubt as to the grade of fluid in the system or if fluid has been used
which contained parts that have been subjected to contaminated fluid.