2000 MITSUBISHI MONTERO egr valve
[x] Cancel search: egr valvePage 399 of 1839

Page 410 of 1839

Page 415 of 1839
Page 420 of 1839
Page 493 of 1839

DIESEL FUEL <4M4> -General Information13C-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
The electronically-controlled fuel injection system consists of sensors which detect the condition of the
diesel engine, an engine-ECU which controls the system based on signals from these sensors, and actuators
which operate according to control commands from the engine-ECU.
The engine-ECU carries out operations such as fuel injection rate control, fuel injection timing control
and idle up control. In addition, the engine-ECU is equipped with several self-diagnosis functions which
make troubleshooting easier in the event that a problem develops.
FUEL INJECTION RATE CONTROL
The fuel injection completion timing is controlled by means of a solenoid-type spill valve to ensure that
the optimum amount of fuel is supplied to the engine in accordance with gradual changes in the engine
running condition.
Before fuel injection starts, the solenoid-type spill valve is on (energized), so that the valve is closed.
As the plunger turns and rises, fuel is sent out under pressure, and when the fuel flow rate reaches
the target value for fuel injection, the solenoid-type spill valve turns off. When the solenoid-type spill
valve turns off, the fuel under high pressure inside the plunger is leaked out into the pump chamber
and fuel injection is completed.
FUEL INJECTION TIMING CONTROL
The position of the injection pump timer piston is controlled so that fuel injection is carried out at the
optimum timing in accordance with the engine running condition.
The timer piston position is determined by duty control of the timing control solenoid valve which is located
in the line between the high-pressure chamber and the low-pressure chamber of the timer piston.
The fuel injection timing is advanced by increasing the control duty of the timing control solenoid valve.
IDLE SPEED CONTROL
Controlling the fuel injection rate in accordance with the engine running condition maintains the idle speed
at the optimum condition.
SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, the engine warning lamp illuminates
to warn the driver.
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, a diagnosis code number
corresponding to the problem which occurred is output.
DThe RAM data relating to the sensors and actuators which is stored in the engine-ECU can be read
using the MUT-II. In addition, the actuators can be force-driven under certain conditions.
OTHER CONTROL FUNCTIONS
1. Power Supply Control
When the ignition switch is turned to ON, the relay turns on and power is supplied to components
such as the timing control solenoid valve.
2. Intake Air Throttle Control
When the engine is idling after having warmed up, the throttle valve is half opened to restrict the
amount of intake air in order to reduce vibration and noise.
3. A/C Relay Control
Turns the compressor clutch of the A/C ON and OFF
4. Fan motor relay control
The radiator fan and condenser fan operating speeds are controlled in accordance with the engine
coolant temperature and the vehicle speed.
5. Glow Control
Refer to GROUP 16.
6. EGR Control
Refer to GROUP 17.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 497 of 1839
DIESEL FUEL <4M4> -Troubleshooting13C-6
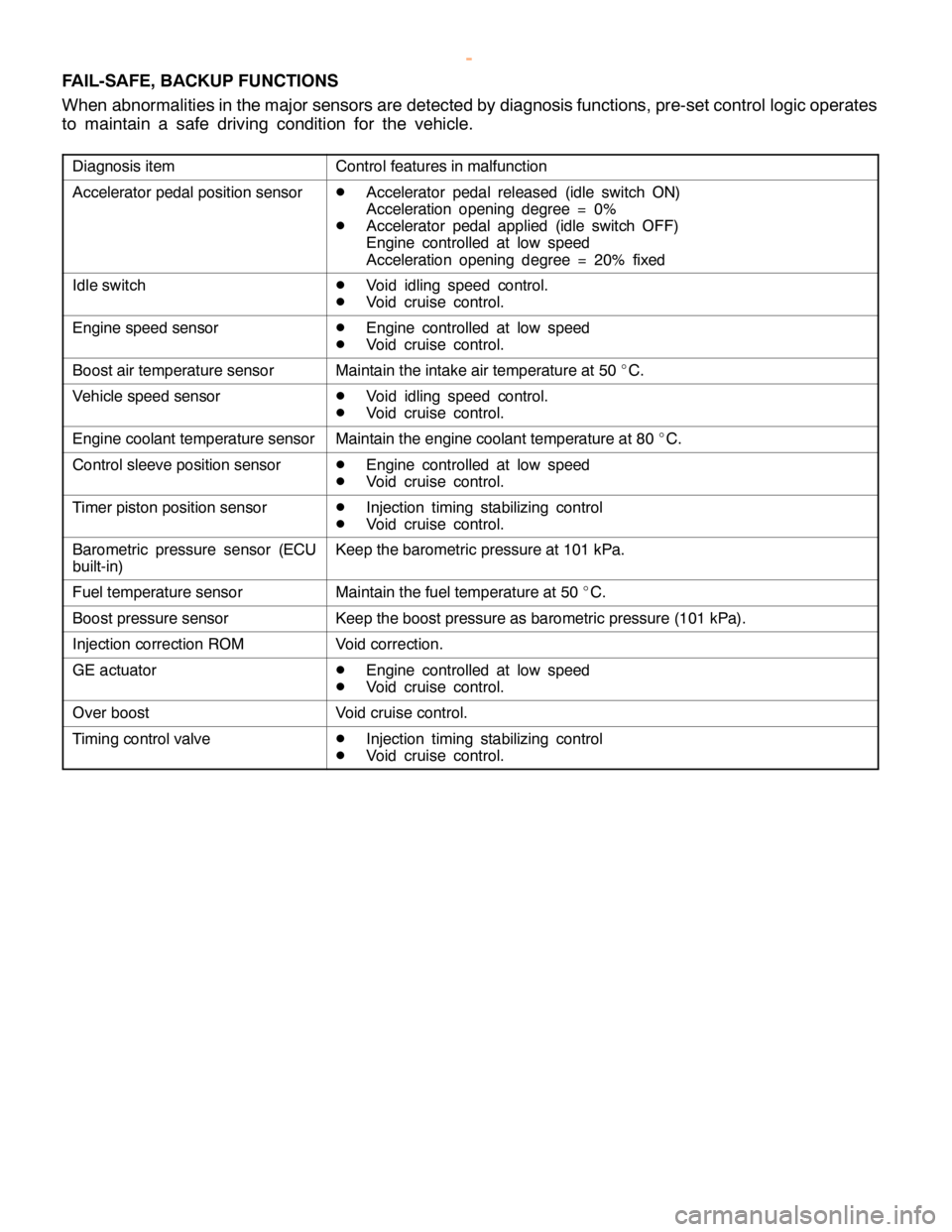
FAIL-SAFE, BACKUP FUNCTIONS
When abnormalities in the major sensors are detected by diagnosis functions, pre-set control logic operates
to maintain a safe driving condition for the vehicle.
Diagnosis itemControl features in malfunction
Accelerator pedal position sensorD
Accelerator pedal released (idle switch ON)
Acceleration opening degree = 0%
D
Accelerator pedal applied (idle switchOFF)
Engine controlled at low speed
Acceleration opening degree = 20% fixed
Idle switchD
Void idling speed control.
D
Void cruise control.
Engine speed sensorD
Engine controlled at low speed
D
Void cruise control.
Boost air temperature sensorMaintain the intake air temperature at 50_
C.
Vehicle speed sensorD
Void idling speed control.
D
Void cruise control.
Engine coolant temperature sensorMaintain the engine coolant temperature at 80_
C.
Control sleeve position sensorD
Engine controlled at low speed
D
Void cruise control.
Timer piston position sensorD
Injection timing stabilizing control
D
Void cruise control.
Barometric pressure sensor (ECU
built-in)Keep the barometric pressure at 101 kPa.
Fuel temperature sensorMaintain the fuel temperature at 50_
C.
Boost pressure sensorKeep the boost pressure as barometric pressure (101 kPa).
Injection correction ROMVoid correction.
GE actuatorD
Engine controlled at low speed
D
Void cruise control.
Over boostVoid cruise control.
Timing control valveD
Injection timing stabilizing control
D
Void cruise control.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 510 of 1839

DIESEL FUEL <4M4> -Troubleshooting13C-19
Code No. 41 Main throttle solenoid valve systemProbable cause
Range of Check
DEngine speed is 1600 r/min or higher and the accelerationopening degree is
60% or more.
Set Conditions
DBoost pressure is lower than barometric pressure + 30 kPa for two seconds.
Range of Check
DWith the idlingspeed controlled, theengine warmed up, and no failure found
Set Conditions
DBoost pressure is higher than barometric pressure - 2.7 kPa for 3 seconds.DMain throttle solenoidvalve inoperative
DMain throttle solenoidvalveopencircuit, short
circuit, or connector contact inoperative
DEngine-ECU inoperative
OK
Check the following connector:
B-45NG
Repair
OK
OK
Check and repair the harness between the
control relay and the solenoid valve
connector.
Main throttle solenoidvalve check (Refer to
P.13C-48.)
Check the trouble symptoms.
Replace the engine-ECU.
NG
OK
RepairCheck the following connector:
D-110
Check the trouble symptoms.NGReplace
NG NG
Check the following connectors:
B-45, B-45-2NG
Repair
OK
Check and repair the harness between the
control relay and the solenoid valve
connector.
Check the trouble symptoms.
NG
NGMeasure at D-110 engine-ECU connector
DDisconnect the connector and measure at
the harness side.
DVoltage between 14 and the earth
(Ignition switch: ON)
OK:
System voltageOK
Measure at B-45-2 main throttle solenoid
valve connector
DDisconnect the connector and measure at
the harness side.
DVoltage between 1 and the earth
(Ignition switch: ON)
OK:
System voltage
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 519 of 1839

DIESEL FUEL <4M4> -Troubleshooting13C-28
Inspection procedure 11
Idling instable (rough idling, hunting)
Probable cause
Probable causes can be found in troubles with control system, injectionpump,
fuel system, glow system, intake system, and EGR system.DControl system inoperative
DInjection pump inoperative
DFuel system inoperative
DIntake system inoperative
DGlow system inoperative
DEGR system inoperative
DEngine-ECU inoperative
NG
Repair
MUT-
IISelf-Diag code
Is a diagnosis code output?YESInspection chart for diagnosis codes (Refer to P.13C-7.)
NO
Conduct MUT-IIData list check and an actuator test. (Refer
to P.13C-32, 37.)OKInspect the following items in order:
DGlow plug, glowplugrelay
DEGR system
DInjection nozzle
DCompression pressure
DValve clearance
DThrottle body assembly
DInjection timing
DFuel line bleeding
DInjection pump
Inspection procedure 12
The engine stalls after running for a while.
Probable cause
Probable causes can be found in troubles with control system, injectionpump,
fuel system, and intake system.DControl system inoperative
DInjection pump inoperative
DFuel system inoperative
DIntake system inoperative
DEngine-ECU inoperative
NG
Repair
MUT-
IISelf-Diag code
Is a diagnosis code output?YESInspection chart for diagnosis codes (Refer to P.13C-7.)
NO
Conduct MUT-IIData list check and an actuator test. (Refer
to P.13C-32, 37.)OKInspect the following items in order:
DThrottle body assembly
DFuel filter
DInjection pump
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk