2000 FORD F150 tow
[x] Cancel search: towPage 146 of 280
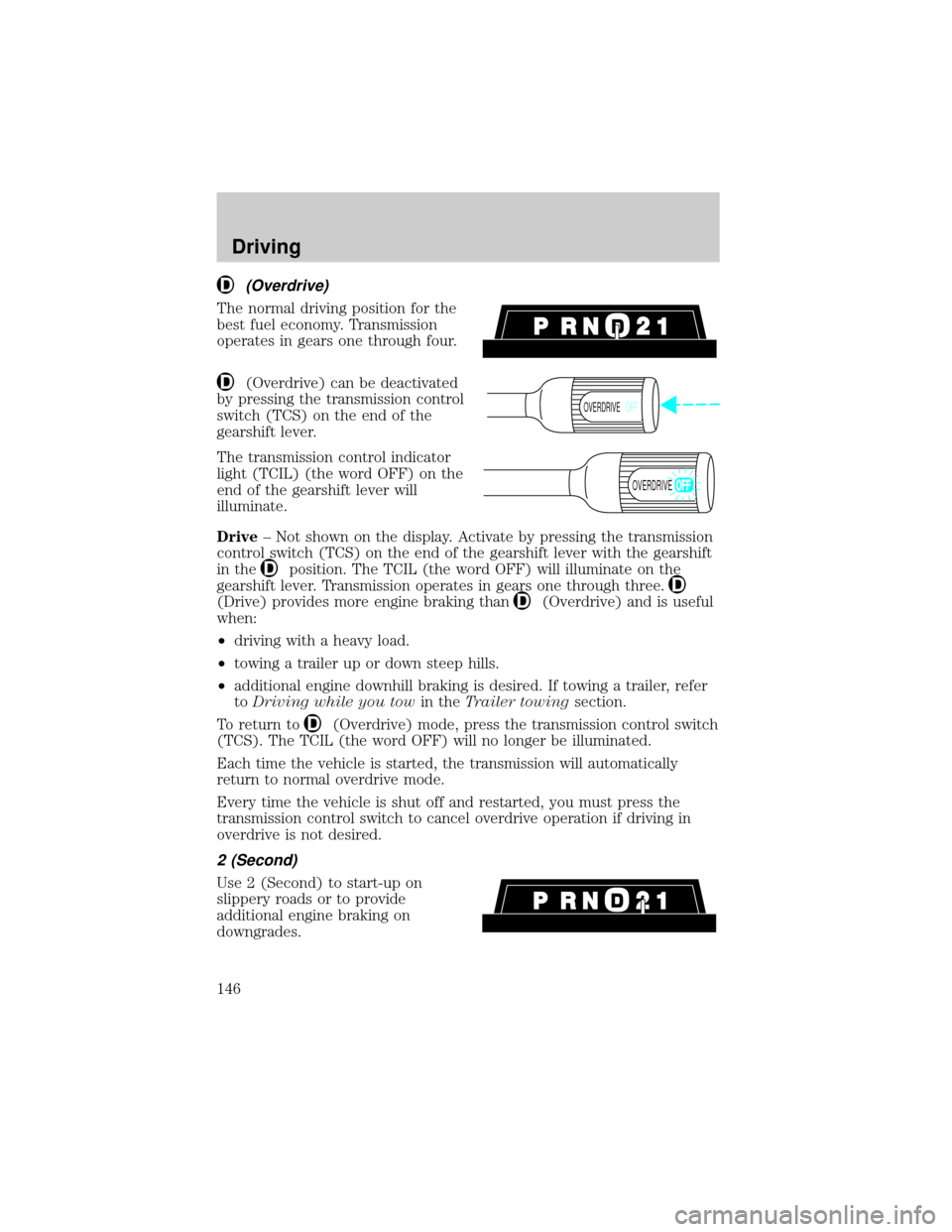
(Overdrive)
The normal driving position for the
best fuel economy. Transmission
operates in gears one through four.
(Overdrive) can be deactivated
by pressing the transmission control
switch (TCS) on the end of the
gearshift lever.
The transmission control indicator
light (TCIL) (the word OFF) on the
end of the gearshift lever will
illuminate.
Drive± Not shown on the display. Activate by pressing the transmission
control switch (TCS) on the end of the gearshift lever with the gearshift
in the
position. The TCIL (the word OFF) will illuminate on the
gearshift lever. Transmission operates in gears one through three.
(Drive) provides more engine braking than(Overdrive) and is useful
when:
²driving with a heavy load.
²towing a trailer up or down steep hills.
²additional engine downhill braking is desired. If towing a trailer, refer
toDriving while you towin theTrailer towingsection.
To return to
(Overdrive) mode, press the transmission control switch
(TCS). The TCIL (the word OFF) will no longer be illuminated.
Each time the vehicle is started, the transmission will automatically
return to normal overdrive mode.
Every time the vehicle is shut off and restarted, you must press the
transmission control switch to cancel overdrive operation if driving in
overdrive is not desired.
2 (Second)
Use 2 (Second) to start-up on
slippery roads or to provide
additional engine braking on
downgrades.
OVERDRIVEOFF
OVERDRIVE
Driving
146
Page 153 of 280

Removing key from ignition
²Turn the ignition key to position 2.
²Push the release lever forward
and rotate the key towards you
and remove.
FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE (4WD) OPERATION (IF EQUIPPED)
For important information regarding safe operation of this type
of vehicle, seePreparing to drive your vehiclein this chapter.
When Four±wheel drive (4WD) is engaged, power is supplied to all four
wheels through a transfer case. 4WD power can be selected when
additional driving power is desired.
If equipped with the Electronic Shift 4WD System, and the
instrument panel control is moved to 4WD Low while the vehicle
is moving, the system will not engage and no damage will occur to
the 4WD system. Before 4WD Low can be engaged, the vehicle
must be brought to a complete stop with the brake pedal
depressed and the transmission placed in neutral (or the clutch
pedal depressed on manual transmissions).
4WD operation is not recommended on dry pavement. Doing so could
result in difficult disengagement of the transfer case, increased tire wear
and decreased fuel economy.
Driving
153
Page 156 of 280

Using the N (Neutral) position
The transfer case neutral position overrides the transmission and
puts the vehicle in neutral regardless of transmission gearshift
lever position. The vehicle can move forward or backwards.
This position should only be used
when towing the vehicle.
Do not leave the vehicle unattended with the transfer case in the
N (Neutral) position. Always set the parking brake fully and turn
off the ignition when leaving the vehicle.
Using the electronic shift 4WD system (if equipped)
Positions of the electronic shift system
2H (2WD High)± Power to rear axle only.
4H (4WD High)± Power delivered to front and rear axles for increased
traction.
4L (4WD Low)± Power to front and rear axles at low speeds.
Shifting from 2H (2WD high) to 4H (4WD high)
Move the 4WD control to the 4H at
a stop or up to 88 km/h (55 mph).
²At temperatures below 0ÉC
(32ÉF), shifts from 2H to 4H
should not be performed above
72 km/h (45 mph).
Do not shift into 4H with the
rear wheels slipping.
2H
4H
4L N
4H
2H
4L
Driving
156
Page 160 of 280

Allow more stopping distance and drive slower than usual. Consider
using one of the lower gears.
VEHICLE LOADING
Before loading a vehicle, familiarize yourself with the following terms:
²Base Curb Weight:Weight of the vehicle including any standard
equipment, fluids, lubricants, etc. It does not include passengers or
aftermarket equipment.
²Payload:Combined maximum allowable weight of cargo, passengers
and optional equipment. The payload equals the gross vehicle weight
rating minus base curb weight.
²GVW (Gross Vehicle Weight):Base curb weight plus payload
weight. The GVW is not a limit or a specification.
²GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating):Maximum total weight of
the base vehicle, passengers, optional equipment and cargo. The
GVWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the Safety
Certification Label on the driver's door pillar.
²GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating):Carrying capacity for each axle
system. The GAWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the
Safety Certification Label on the driver's door pillar.
²GCW (Gross Combined Weight):The combined weight of the
towing vehicle (including passengers and cargo) and the trailer.
²GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating):Maximum combined
weight of towing vehicle (including passengers and cargo) and the
trailer. The GCWR indicates the maximum loaded weight that the
vehicle is designed to tow.
²Maximum Trailer Weight Rating:Maximum weight of a trailer the
vehicle is permitted to tow. The maximum trailer weight rating is
determined by subtracting the vehicle curb weight for each
engine/transmission combination, any required option weight for trailer
towing and the weight of the driver from the GCWR for the towing
vehicle.
²Maximum Trailer Weight:Maximum weight of a trailer the loaded
vehicle (including passengers and cargo) is permitted to tow. It is
determined by subtracting the weight of the loaded trailer towing
vehicle from the GCWR for the towing vehicle.
²Trailer Weight Range:Specified weight range that the trailer must
fall within that ranges from zero to the maximum trailer weight rating.
Driving
160
Page 162 of 280

Calculating the load your vehicle can carry/tow
1. Use the appropriate maximum gross combined weight rating (GCWR)
chart to find the maximum GCWR for your type engine and rear axle
ratio.
2. Weigh your vehicle as you customarily operate the vehicle without
cargo. To obtain correct weights, try taking your vehicle to a shipping
company or an inspection station for trucks.
3. Subtract your loaded vehicle weight from the maximum GCWR on the
following charts. This is the maximum trailer weight your vehicle can tow
and must fall below the maximum shown under maximum trailer weight
on the chart.
DRIVING THROUGH WATER
Do not drive quickly through standing water, especially if the depth is
unknown. Traction or brake capability may be limited and if the ignition
system gets wet, your engine may stall. Water may also enter your
engine's air intake and severely damage your engine.
If driving through deep or standing water is unavoidable, proceed very
slowly. Never drive through water that is higher than the bottom of the
hubs (for trucks) or the bottom of the wheel rims (for cars).
Once through the water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop
the vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by
moving your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake
pedal.
Driving through deep water where the transmission vent tube is
submerged may allow water into the transmission and cause
internal transmission damage.
Your vehicle may tow a class I, II or III trailer provided the maximum
trailer weight is less than or equal to the maximum trailer weight listed
for your engine and rear axle ratio on the following charts.
Your vehicle's load capacity is designated by weight, not by volume, so
you cannot necessarily use all available space when loading a vehicle.
Towing a trailer places an additional load on your vehicle's engine,
transmission, axle, brakes, tires and suspension. Inspect these
components carefully after any towing operation.
Exceeding the maximum GCWR could result in extensive damage
to your vehicle and personal injury.
Driving
162
Page 163 of 280

Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the
certification label.
Towing trailers beyond the maximum recommended gross trailer
weight could result in engine damage, transmission/axle damage,
structural damage, loss of control, and personal injury.
Engine Rear axle ratio Maximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
Regular Cab 4x2 w/automatic transmission
4.2L 3.31 4 077 (9 000) 2 177 (4 800)
4.2L 3.55 4 530 (10 000) 2 582 (5 800)
4.6L 3.08 4 530 (10 000) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31 4 763 (10 500) 2 812 (6 200)
4.6L 3.55 5 209 (11 500) 3 261 (7 200)
5.4L 3.31 5 443 (12 000) 3 402 (7 500)
5.4L 3.55 5 897 (13 000) 3 856 (8 500)
5.4L 3.73 6 124 (13 500) 3 992 (8 800)
SuperCab 4x2 w/automatic transmission
4.2L 3.55 4 530 (10 000) 2 495 (5 500)
4.6L 3.08 4 530 (10 000) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31 4 763 (10 500) 2 676 (5 900)
4.6L 3.55 5 216 (11 500) 3 130 (6 900)
5.4L 3.31 5 443 (12 000) 3 311 (7 300)
5.4L 3.55 5 897 (13 000) 3 765 (8 300)
5.4L 3.73 6 124 (13 500) 3 946 (8 700)
Harley-Davidson F-150 4x2 w/automatic transmission
Engine Rear axle ratio Maximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
5.4L 3.73 4 500 (10 000) 1 825 (4 000)
Driving
163
Page 165 of 280

Trailer frontal area considerations:
²Not to exceed towing vehicle front area without Class III trailer towing
package
²Not to exceed 5.52 square meters (60 square feet) with Class III
trailer towing package
Trailer towing tables
4x2 with automatic transmission
Engine Rear axle
ratio/Tire sizeMaximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
Regular Cab
4.2L 3.31/16 in 4 077 (9 000) 2 177 (4 800)
4.2L 3.55/16 in 4 530 (10 000) 2 582 (5 800)
4.6L 3.08/16 in 4 530 (10 000) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31/16 in 4 763 (10 500) 2 812 (6 200)
4.6L 3.55/16 in 5 209 (11 500) 3 261 (7 200)
5.4L 3.31/16 in 5 443 (12 000) 3 402 (7 500)
5.4L 3.55/16 in 5 897 (13 000) 3 856 (8 500)
5.4L 3.73/16 in 6 124 (13 500) 3 992 (8 800)
SuperCab
4.2L 3.55/16 in 4 530 (10 000) 2 495 (5 500)
4.6L 3.08/16 in 4 530 (10 000) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31/16 in 4 763 (10 500) 2 676 (5 900)
4.6L 3.55/16 in 5 216 (11 500) 3 130 (6 900)
5.4L 3.31/16 in 5 443 (12 000) 3 311 (7 300)
5.4L 3.55/16 in 5 897 (13 000) 3 765 (8 300)
5.4L 3.73/16 in 6 124 (13 500) 3 946 (8 700)
Harley-Davidson F-150
4x2 with automatic transmission
Engine Rear axle ratio/
Tire size (wheel
diameter)Maximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
5.4L 3.73/20 in 4 500 (10 000) 1 825 (4 000)
Driving
165
Page 167 of 280
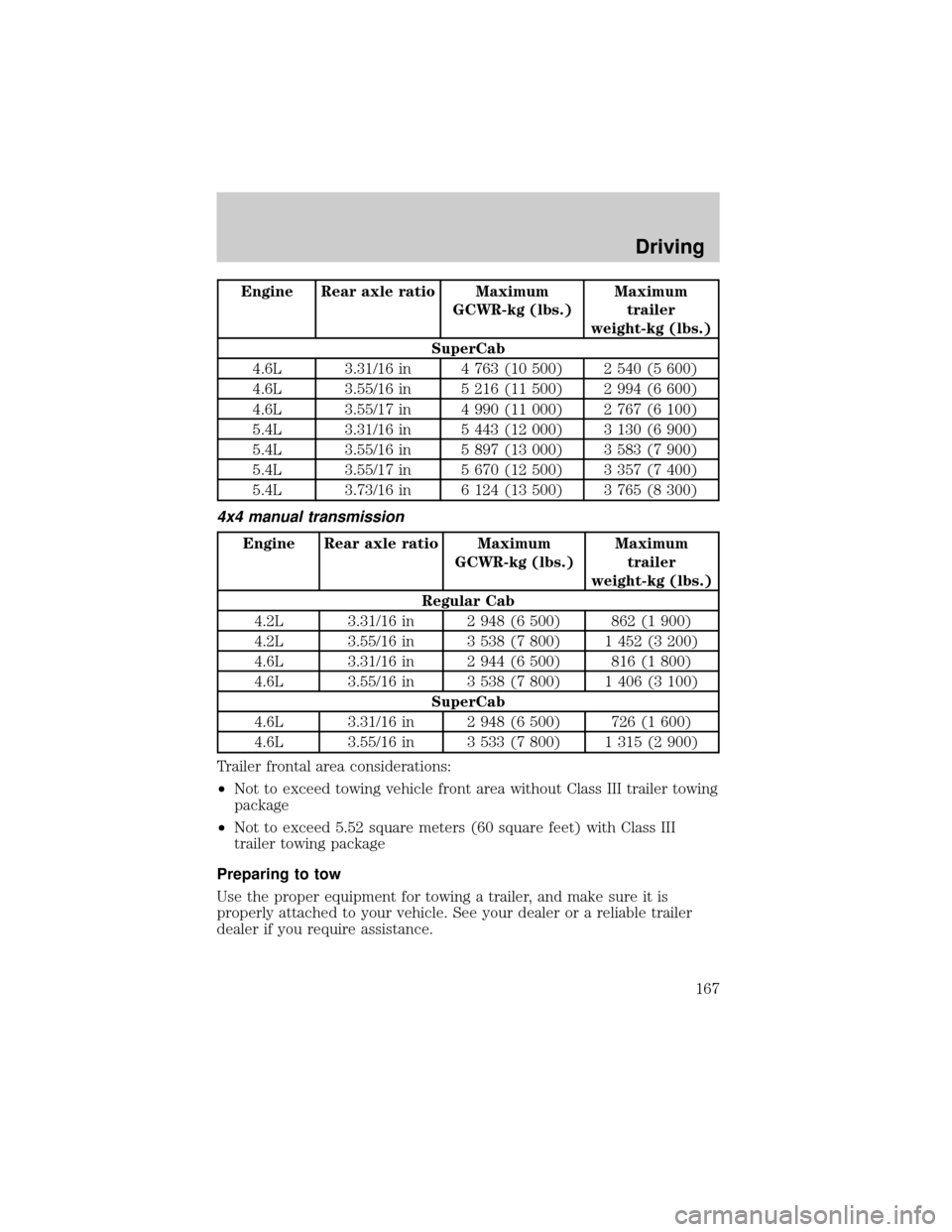
Engine Rear axle ratio Maximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum
trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
SuperCab
4.6L 3.31/16 in 4 763 (10 500) 2 540 (5 600)
4.6L 3.55/16 in 5 216 (11 500) 2 994 (6 600)
4.6L 3.55/17 in 4 990 (11 000) 2 767 (6 100)
5.4L 3.31/16 in 5 443 (12 000) 3 130 (6 900)
5.4L 3.55/16 in 5 897 (13 000) 3 583 (7 900)
5.4L 3.55/17 in 5 670 (12 500) 3 357 (7 400)
5.4L 3.73/16 in 6 124 (13 500) 3 765 (8 300)
4x4 manual transmission
Engine Rear axle ratio Maximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum
trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
Regular Cab
4.2L 3.31/16 in 2 948 (6 500) 862 (1 900)
4.2L 3.55/16 in 3 538 (7 800) 1 452 (3 200)
4.6L 3.31/16 in 2 944 (6 500) 816 (1 800)
4.6L 3.55/16 in 3 538 (7 800) 1 406 (3 100)
SuperCab
4.6L 3.31/16 in 2 948 (6 500) 726 (1 600)
4.6L 3.55/16 in 3 533 (7 800) 1 315 (2 900)
Trailer frontal area considerations:
²Not to exceed towing vehicle front area without Class III trailer towing
package
²Not to exceed 5.52 square meters (60 square feet) with Class III
trailer towing package
Preparing to tow
Use the proper equipment for towing a trailer, and make sure it is
properly attached to your vehicle. See your dealer or a reliable trailer
dealer if you require assistance.
Driving
167