Page 147 of 280
1 (First)
Use 1 (Low) to provide maximum
engine braking on steep
downgrades. Upshifts can be made
by shifting to 2 (Second) or to
(Overdrive). Selecting 1 (Low) at
higher speeds causes the transmission to shift to a lower gear, and will
shift to 1 (Low) after vehicle decelerates to the proper speed.
Forced Downshifts
To gain acceleration in(Overdrive) or Drive (O/D OFF) when
passing another vehicle, push the accelerator to the floor. The
transmission will downshift to the appropriate gear: third, second or first
gear.
Shift strategy (4R100 automatic transmission)
To account for customer driving habits and conditions, your 4R100
automatic transmission electronically controls the shift quality by using
an adaptive learning strategy. The adaptive learning strategy is
maintained by power from the battery. When the battery is disconnected
or a new battery is installed, the transmission must relearn its adaptive
strategy. Optimal shifting will resume within a few hundred kilometers
(miles) of operation.
If the shift quality does not improve within a few hundred
kilometers (miles) of operation, or if the downshifts and other
throttle conditions do not function normally, see your dealer or a
qualified service technician as soon as possible.
MANUAL TRANSMISSION OPERATION (IF EQUIPPED)
Using the clutch
Vehicles equipped with a manual transmission have a starter interlock
that prevents cranking the engine unless the clutch pedal is fully
depressed.
Driving
147
Page 155 of 280
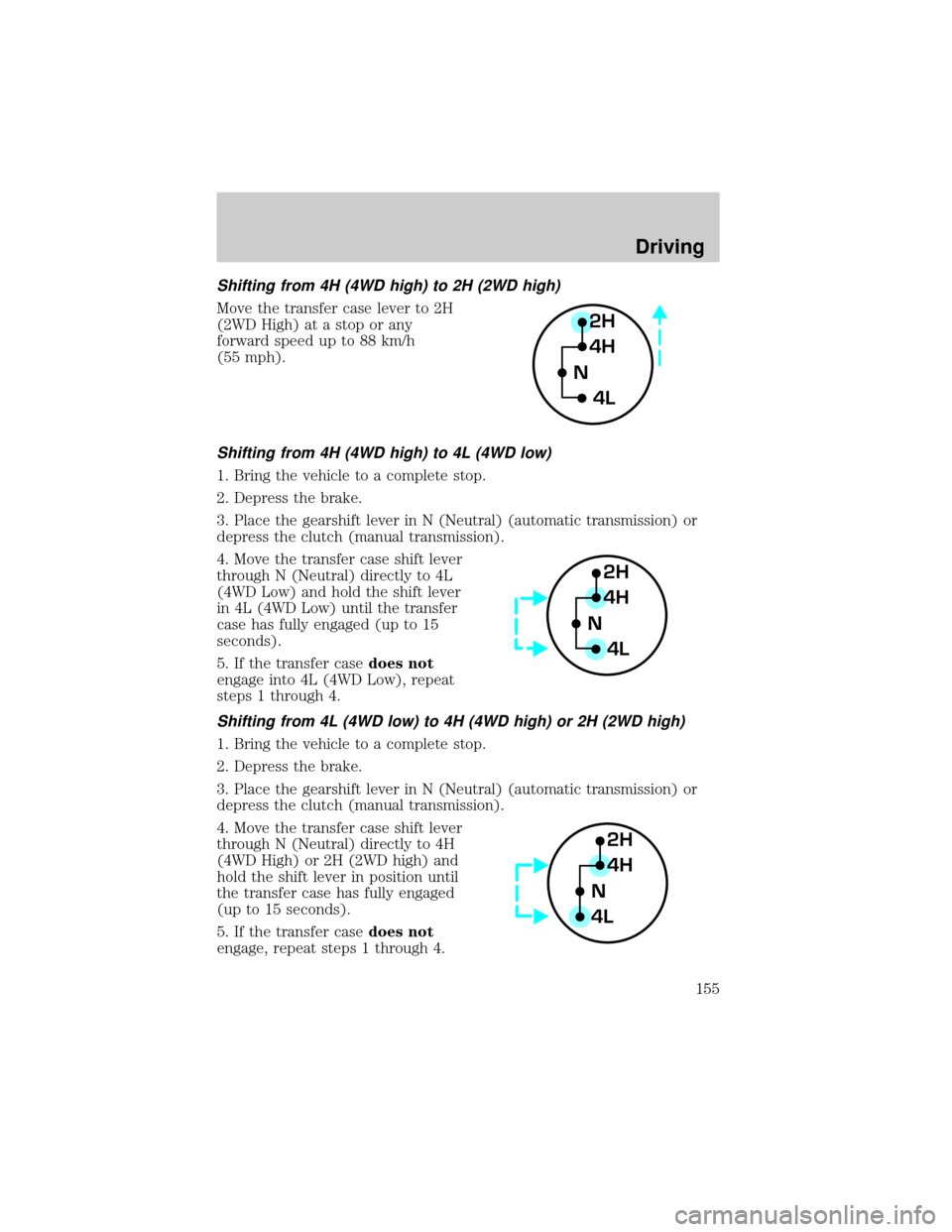
Shifting from 4H (4WD high) to 2H (2WD high)
Move the transfer case lever to 2H
(2WD High) at a stop or any
forward speed up to 88 km/h
(55 mph).
Shifting from 4H (4WD high) to 4L (4WD low)
1. Bring the vehicle to a complete stop.
2. Depress the brake.
3. Place the gearshift lever in N (Neutral) (automatic transmission) or
depress the clutch (manual transmission).
4. Move the transfer case shift lever
through N (Neutral) directly to 4L
(4WD Low) and hold the shift lever
in 4L (4WD Low) until the transfer
case has fully engaged (up to 15
seconds).
5. If the transfer casedoes not
engage into 4L (4WD Low), repeat
steps 1 through 4.
Shifting from 4L (4WD low) to 4H (4WD high) or 2H (2WD high)
1. Bring the vehicle to a complete stop.
2. Depress the brake.
3. Place the gearshift lever in N (Neutral) (automatic transmission) or
depress the clutch (manual transmission).
4. Move the transfer case shift lever
through N (Neutral) directly to 4H
(4WD High) or 2H (2WD high) and
hold the shift lever in position until
the transfer case has fully engaged
(up to 15 seconds).
5. If the transfer casedoes not
engage, repeat steps 1 through 4.
2H
4H
4L N
2H
4H
4L N
2H
4H
4LN
Driving
155
Page 157 of 280
Shifting from 4H (4WD high) to 2H (2WD high)
Move the 4WD control to 2H at any
forward speed.
Shifting between 4H (4WD high) and 4L (4WD low)
1. Bring the vehicle to a stop.
2. Depress the brake.
3. Place the gearshift in N (Neutral) (automatic transmission) or depress
the clutch (manual transmission).
4. Move the 4WD control to the 4H
or 4L position.
Driving off-road with 4WD
Your vehicle is specially equipped for driving on sand, snow, mud and
rough terrain and has operating characteristics that are somewhat
different from conventional vehicles, both on and off the road.
Maintain steering wheel control at all times, especially in rough terrain.
Since sudden changes in terrain can result in abrupt steering wheel
motion, make sure you grip the steering wheel from the outside. Do not
grip the spokes.
Drive cautiously to avoid vehicle damage from concealed objects such as
rocks and stumps.
4H
2H
4L
4H
2H
4L
Driving
157
Page 159 of 280

Water intrusion into the transmission may damage the
transmission.
Replace rear axle lubricant any time the axle has been submerged in
water. The rear axle does not normally require a lubricant change for the
life of the vehicle. Rear axle lubricant quantities are not to be checked or
changed unless a leak is suspected or repair is required.
Driving on hilly or sloping terrain
When driving on a hill, avoid driving crosswise or turning on steep
slopes. You could lose traction and slip sideways. Drive straight up,
straight down or avoid the hill completely. Know the conditions on the
other side of a hill before driving over the crest.
When climbing a steep hill, start in a lower gear rather than downshifting
to a lower gear from a higher gear once the ascent has started. This
reduces strain on the engine and the possibility of stalling.
When descending a steep hill, avoid sudden braking. Shift to a lower gear
when added engine braking is desired.
When speed control is on and you are driving uphill, your vehicle speed
may drop considerably, especially if you are carrying a heavy load.
If vehicle speed drops more than 16 km/h (10 mph), the speed control
will cancel automatically. Resume speed with accelerator pedal.
If speed control cancels after climbing the hill, reset speed by pressing
and holding the SET ACCEL button (to resume speeds over 50 km/h [30
mph]).
Automatic transmissions may shift frequently while driving up steep
grades. Eliminate frequent shifting by shifting out of
(Overdrive) into
a lower gear.
Driving on snow and ice
A 4WD vehicle has advantages over 2WD vehicles in snow and ice but
can skid like any other vehicle.
Avoid sudden applications of power and quick changes of direction on
snow and ice. Apply the accelerator slowly and steadily when starting
from a full stop.
When braking, apply the brakes as you normally would. In order to allow
the anti-lock brake system (ABS) to operate properly, keep steady
pressure on the brake pedal.
Driving
159
Page 163 of 280

Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the
certification label.
Towing trailers beyond the maximum recommended gross trailer
weight could result in engine damage, transmission/axle damage,
structural damage, loss of control, and personal injury.
Engine Rear axle ratio Maximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
Regular Cab 4x2 w/automatic transmission
4.2L 3.31 4 077 (9 000) 2 177 (4 800)
4.2L 3.55 4 530 (10 000) 2 582 (5 800)
4.6L 3.08 4 530 (10 000) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31 4 763 (10 500) 2 812 (6 200)
4.6L 3.55 5 209 (11 500) 3 261 (7 200)
5.4L 3.31 5 443 (12 000) 3 402 (7 500)
5.4L 3.55 5 897 (13 000) 3 856 (8 500)
5.4L 3.73 6 124 (13 500) 3 992 (8 800)
SuperCab 4x2 w/automatic transmission
4.2L 3.55 4 530 (10 000) 2 495 (5 500)
4.6L 3.08 4 530 (10 000) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31 4 763 (10 500) 2 676 (5 900)
4.6L 3.55 5 216 (11 500) 3 130 (6 900)
5.4L 3.31 5 443 (12 000) 3 311 (7 300)
5.4L 3.55 5 897 (13 000) 3 765 (8 300)
5.4L 3.73 6 124 (13 500) 3 946 (8 700)
Harley-Davidson F-150 4x2 w/automatic transmission
Engine Rear axle ratio Maximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
5.4L 3.73 4 500 (10 000) 1 825 (4 000)
Driving
163
Page 164 of 280
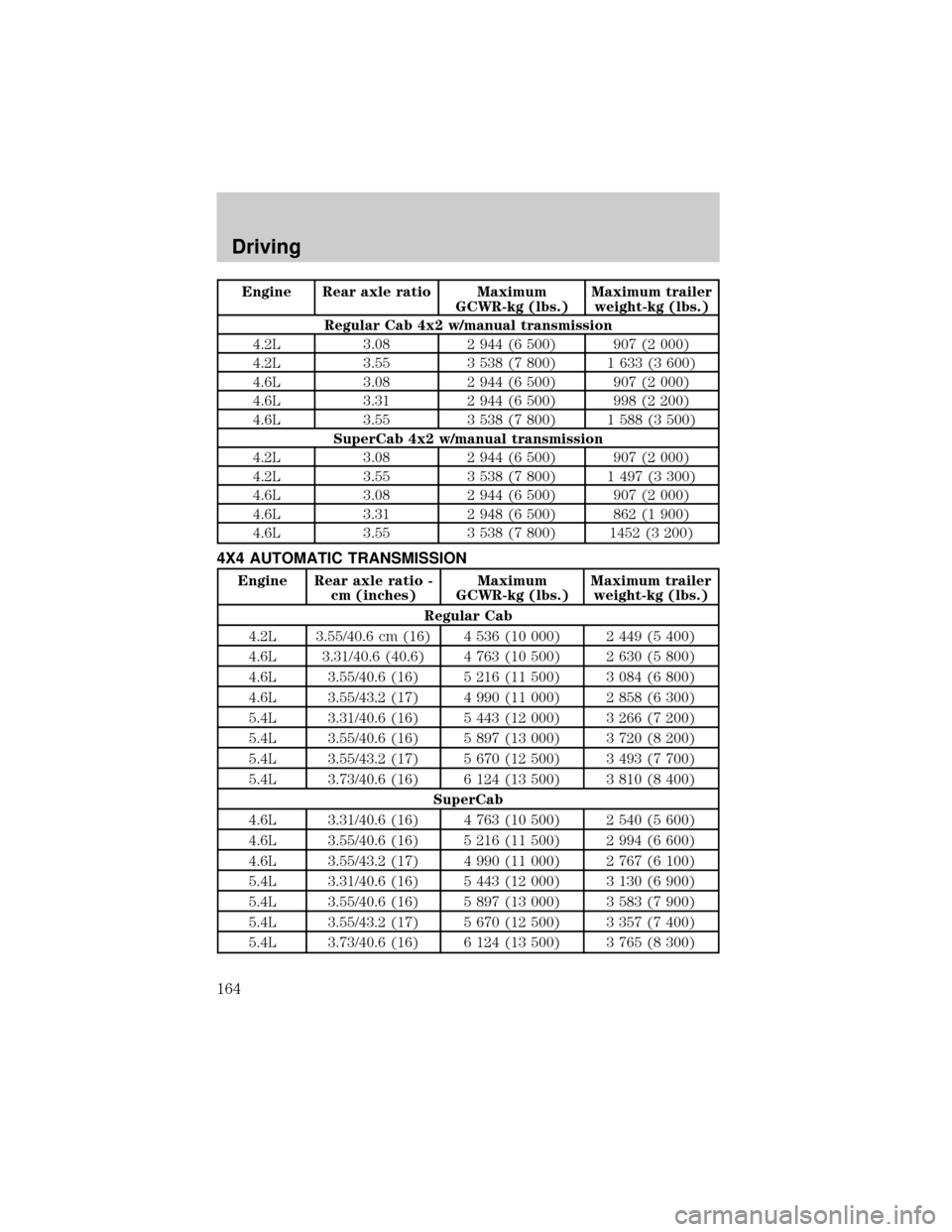
Engine Rear axle ratio Maximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
Regular Cab 4x2 w/manual transmission
4.2L 3.08 2 944 (6 500) 907 (2 000)
4.2L 3.55 3 538 (7 800) 1 633 (3 600)
4.6L 3.08 2 944 (6 500) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31 2 944 (6 500) 998 (2 200)
4.6L 3.55 3 538 (7 800) 1 588 (3 500)
SuperCab 4x2 w/manual transmission
4.2L 3.08 2 944 (6 500) 907 (2 000)
4.2L 3.55 3 538 (7 800) 1 497 (3 300)
4.6L 3.08 2 944 (6 500) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31 2 948 (6 500) 862 (1 900)
4.6L 3.55 3 538 (7 800) 1452 (3 200)
4X4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Engine Rear axle ratio -
cm (inches)Maximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
Regular Cab
4.2L 3.55/40.6 cm (16) 4 536 (10 000) 2 449 (5 400)
4.6L 3.31/40.6 (40.6) 4 763 (10 500) 2 630 (5 800)
4.6L 3.55/40.6 (16) 5 216 (11 500) 3 084 (6 800)
4.6L 3.55/43.2 (17) 4 990 (11 000) 2 858 (6 300)
5.4L 3.31/40.6 (16) 5 443 (12 000) 3 266 (7 200)
5.4L 3.55/40.6 (16) 5 897 (13 000) 3 720 (8 200)
5.4L 3.55/43.2 (17) 5 670 (12 500) 3 493 (7 700)
5.4L 3.73/40.6 (16) 6 124 (13 500) 3 810 (8 400)
SuperCab
4.6L 3.31/40.6 (16) 4 763 (10 500) 2 540 (5 600)
4.6L 3.55/40.6 (16) 5 216 (11 500) 2 994 (6 600)
4.6L 3.55/43.2 (17) 4 990 (11 000) 2 767 (6 100)
5.4L 3.31/40.6 (16) 5 443 (12 000) 3 130 (6 900)
5.4L 3.55/40.6 (16) 5 897 (13 000) 3 583 (7 900)
5.4L 3.55/43.2 (17) 5 670 (12 500) 3 357 (7 400)
5.4L 3.73/40.6 (16) 6 124 (13 500) 3 765 (8 300)
Driving
164
Page 165 of 280

Trailer frontal area considerations:
²Not to exceed towing vehicle front area without Class III trailer towing
package
²Not to exceed 5.52 square meters (60 square feet) with Class III
trailer towing package
Trailer towing tables
4x2 with automatic transmission
Engine Rear axle
ratio/Tire sizeMaximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
Regular Cab
4.2L 3.31/16 in 4 077 (9 000) 2 177 (4 800)
4.2L 3.55/16 in 4 530 (10 000) 2 582 (5 800)
4.6L 3.08/16 in 4 530 (10 000) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31/16 in 4 763 (10 500) 2 812 (6 200)
4.6L 3.55/16 in 5 209 (11 500) 3 261 (7 200)
5.4L 3.31/16 in 5 443 (12 000) 3 402 (7 500)
5.4L 3.55/16 in 5 897 (13 000) 3 856 (8 500)
5.4L 3.73/16 in 6 124 (13 500) 3 992 (8 800)
SuperCab
4.2L 3.55/16 in 4 530 (10 000) 2 495 (5 500)
4.6L 3.08/16 in 4 530 (10 000) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31/16 in 4 763 (10 500) 2 676 (5 900)
4.6L 3.55/16 in 5 216 (11 500) 3 130 (6 900)
5.4L 3.31/16 in 5 443 (12 000) 3 311 (7 300)
5.4L 3.55/16 in 5 897 (13 000) 3 765 (8 300)
5.4L 3.73/16 in 6 124 (13 500) 3 946 (8 700)
Harley-Davidson F-150
4x2 with automatic transmission
Engine Rear axle ratio/
Tire size (wheel
diameter)Maximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
5.4L 3.73/20 in 4 500 (10 000) 1 825 (4 000)
Driving
165
Page 166 of 280
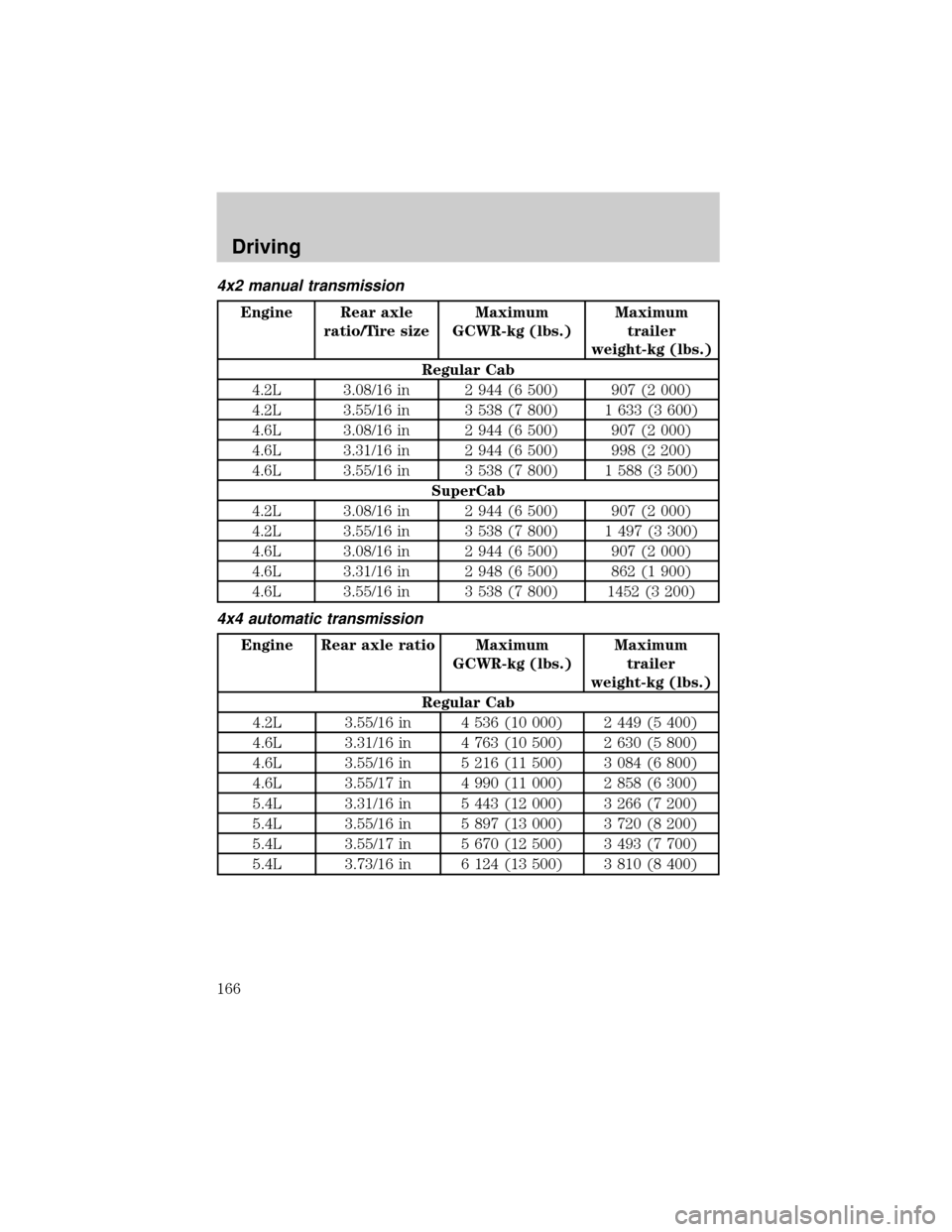
4x2 manual transmission
Engine Rear axle
ratio/Tire sizeMaximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum
trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
Regular Cab
4.2L 3.08/16 in 2 944 (6 500) 907 (2 000)
4.2L 3.55/16 in 3 538 (7 800) 1 633 (3 600)
4.6L 3.08/16 in 2 944 (6 500) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31/16 in 2 944 (6 500) 998 (2 200)
4.6L 3.55/16 in 3 538 (7 800) 1 588 (3 500)
SuperCab
4.2L 3.08/16 in 2 944 (6 500) 907 (2 000)
4.2L 3.55/16 in 3 538 (7 800) 1 497 (3 300)
4.6L 3.08/16 in 2 944 (6 500) 907 (2 000)
4.6L 3.31/16 in 2 948 (6 500) 862 (1 900)
4.6L 3.55/16 in 3 538 (7 800) 1452 (3 200)
4x4 automatic transmission
Engine Rear axle ratio Maximum
GCWR-kg (lbs.)Maximum
trailer
weight-kg (lbs.)
Regular Cab
4.2L 3.55/16 in 4 536 (10 000) 2 449 (5 400)
4.6L 3.31/16 in 4 763 (10 500) 2 630 (5 800)
4.6L 3.55/16 in 5 216 (11 500) 3 084 (6 800)
4.6L 3.55/17 in 4 990 (11 000) 2 858 (6 300)
5.4L 3.31/16 in 5 443 (12 000) 3 266 (7 200)
5.4L 3.55/16 in 5 897 (13 000) 3 720 (8 200)
5.4L 3.55/17 in 5 670 (12 500) 3 493 (7 700)
5.4L 3.73/16 in 6 124 (13 500) 3 810 (8 400)
Driving
166