2000 FIAT MAREA Heat
[x] Cancel search: HeatPage 97 of 330

Ma tea- Ma tea Weekend !@ ™
2000 range ©
Engine
Fuel feed system
10.
37 Not connected
38 Not connected
39 Not connected
40 Not connected
41 Not connected
42 Not connected
43 Not connected
44 Not connected
45 Not connected
46 Not connected
47 Engine rpm signal output
48 Diagnostic line k
49 Vehicle speed signal input
50 Not connected
51 Activation signal from 4-stage pressure switch
52 Activation signal from 3-stage pressure switch
53 Not connected
54 Not connected
55 Not connected
56 Not connected
57 Not connected
58 Key ON signal
59 Brake switch
60 Air conditioner activation request
61 Clutch switch
62 Glow plug diagnosis
63 Not connected
64 Not connected
65 Not connected
66 Not connected
67 Not connected
68 Not connected
69 Not connected
70 Not connected
71 Not connected
72 Not connected
73 Not connected
74 Not connected
75 Not connected
76 Accelerator pedal 1 earth
77 Accelerator pedal 1 signal
78 Accelerator pedal 1 power supply
79 Accelerator pedal 2 earth
80 Accelerator pedal 2 signal
81 Accelerator pedal 2 power supply
82 Diesel temperature sensor (pin 1)
83 Diesel temperature sensor (pin 2)
84 Coolant temperature sensor (pin 1)
85 Coolant temperature sensor (pin 2)
86 Air flow meter (pin 1)
87 Not connected
88 Air flow meter (pin 3)
89 Air flow meter (pin 5)
90 Fuel pressure sensor (pin 3)
91 Fuel pressure sensor (pin 2)
92 Fuel pressure sensor (pin 1)
93 Turbo pressure sensor (pin 1)
94 Turbo pressure sensor (pin 3)
95 Turbo pressure sensor (pin 2)
96 Not connected
97 Air flow meter (pin 4)
98 Not connected
99 RPM sensor (pin 1)
100 RPM sensor (pin 2)
101 RPM sensor (pin 3)
102 RPM sensor (pin 1)
103 Timing sensor (pin 2)
104 Timing sensor (pin 3)
105 Not connected
106 Not connected
107 Not connected
108 Fuel pressure regulator
109 Fuel pressure regulator
110 Not connected
111 Heater relay control Fuel filter
112 Not connected
113 Not connected
114 Cylinder 4 injector control
115 Not connected
116 Not connected
117 Cylinder 1 and 2 injector power supply
118 Cylinder 3 and 4 injector power supply
119 Cylinder 1 injector control
120 Cylinder 2 injector control
121 Cylinder 3 injector control
Copyright by Fiat Auto 11
Page 99 of 330

Marea- Marea Weekend 9"°
2000 range ©
Engine
Fuel feed system
10.
TIMING SENSOR
The Hall effect sensor is fitted to the cylinder head and faces the camshaft pulley.
An opening on the pulley allows the timing sensor to detect the engine timing position and indicate it to
the injection control unit.
The injection control unit uses the timing sensor signal to detect TDC at the end of compression.
Operation
A semi-condulator layer, through which a current passes, immersed in a magnetic field (lines of force per
pendicular to the direction of the current), produces a difference in power, known as Hall voltage.
If the intensity of the current remains constant, the voltage produced only depends on the intensity of the
magnetic field. The intensity of the field can simply be altered periodically to produce a modulated electri
cal signal. Signal frequency is proportional to the speed with which the magnetic field changes.
To achieve this change, the sensor is crossed by a metal ring (inner part of the pulley) with an opening.
When it moves, the metal part of the ring covers the sensor to magnetic field and the output signal is
therefore low; Conversely, the sensor generates a high signal at the opening when the magnetic field is
present.
This signal, together with the rpm and TDC signals, allows the injection control unit to identify piston po
sition and determine injection point.
AIR FLOW METER
(DEBIMETER)
The debimeter is located on the air intake
sleeve and is hot film type.
The debimeter contains an intake air tem
perature sensor.
Operation
The principle of operation is based on a
heated membrane fitted into a measurement
channel through which engine intake air
flows.
The hot film membrane is maintained at a
constant temperature (about 120 °C higher
than incoming air) by the heater coil.
The mass of air flowing through the measure
ment channel tends to take heat from the
membrane. To keep the membrane at constant
temperature, a certain current level must flow
through the resistance.
Because this current is proportional to the
mass of air that flows to the engine, it can be
measured with a Wheatstone bridge and the
resulting signal is sent to the injection control
unit.
1. Covers
2. Electronic card
3. Sensor
4. Mounting plate
5. Mount
6. o-ring
7. Temperature sensor
Copyright by Fiat Auto 13
Page 102 of 330
![FIAT MAREA 2000 1.G Workshop Manual Engine
Fuel feed system
JTD Marea-Marea Weekend ©
2000 range ©
10.
iH
ft
B I 0 ] I D
[ 0 0 1 1
D
0 1 <fi=2 1 1 15J
GLOW PLUG PREHEATING CONTROL
UNIT
The glow plugs are controlled by mea FIAT MAREA 2000 1.G Workshop Manual Engine
Fuel feed system
JTD Marea-Marea Weekend ©
2000 range ©
10.
iH
ft
B I 0 ] I D
[ 0 0 1 1
D
0 1 <fi=2 1 1 15J
GLOW PLUG PREHEATING CONTROL
UNIT
The glow plugs are controlled by mea](/manual-img/10/4653/w960_4653-101.png)
Engine
Fuel feed system
JTD Marea-Marea Weekend ©
2000 range ©
10.
iH
ft
B I 0 ] I D
[ 0 0 1 1
D
0 1
UNIT
The glow plugs are controlled by means of a
preheating control unit under the direct con
trol of the injection control unit.
The preheating control unit contains a smart
relay that sends a return response (feedback)
to the injection control unit, which is thus in
formed of faults in the preheating control unit
or glow plug short-circuits to earth.
The figure shows the connectors on the base
of the preheating control unit and the pin-out
1. Earth
2. Injection control unit (pin 22)
3. Power supply from main injection relay
4. Not connected
5. Injection control unit (pin 62)
8. Positive from battery (+30)
G. Glow plugs (only four outputs are used)
ACCELERATOR
PEDAL POTENTIOMETER
Accelerator pedal position is converted to an
electrical voltage signal and send to the injec
tion control unit by a potentiometer connected
to the accelerator pedal.
Accelerator pedal position is processed to
gether with rpm information to provide injec
tion times and pressure.
The sensor consists of a case (1) secured to
the pedal by a flange, which contains an axi-
ally-positioned shaft (2) connected to two
potentiometers (3): main and safety potenti
ometers.
A coil spring on the shaft ensures the correct
resistance to pressure while a second spring
ensures return upon release.
16 Publication no. 506.763/24
Page 104 of 330
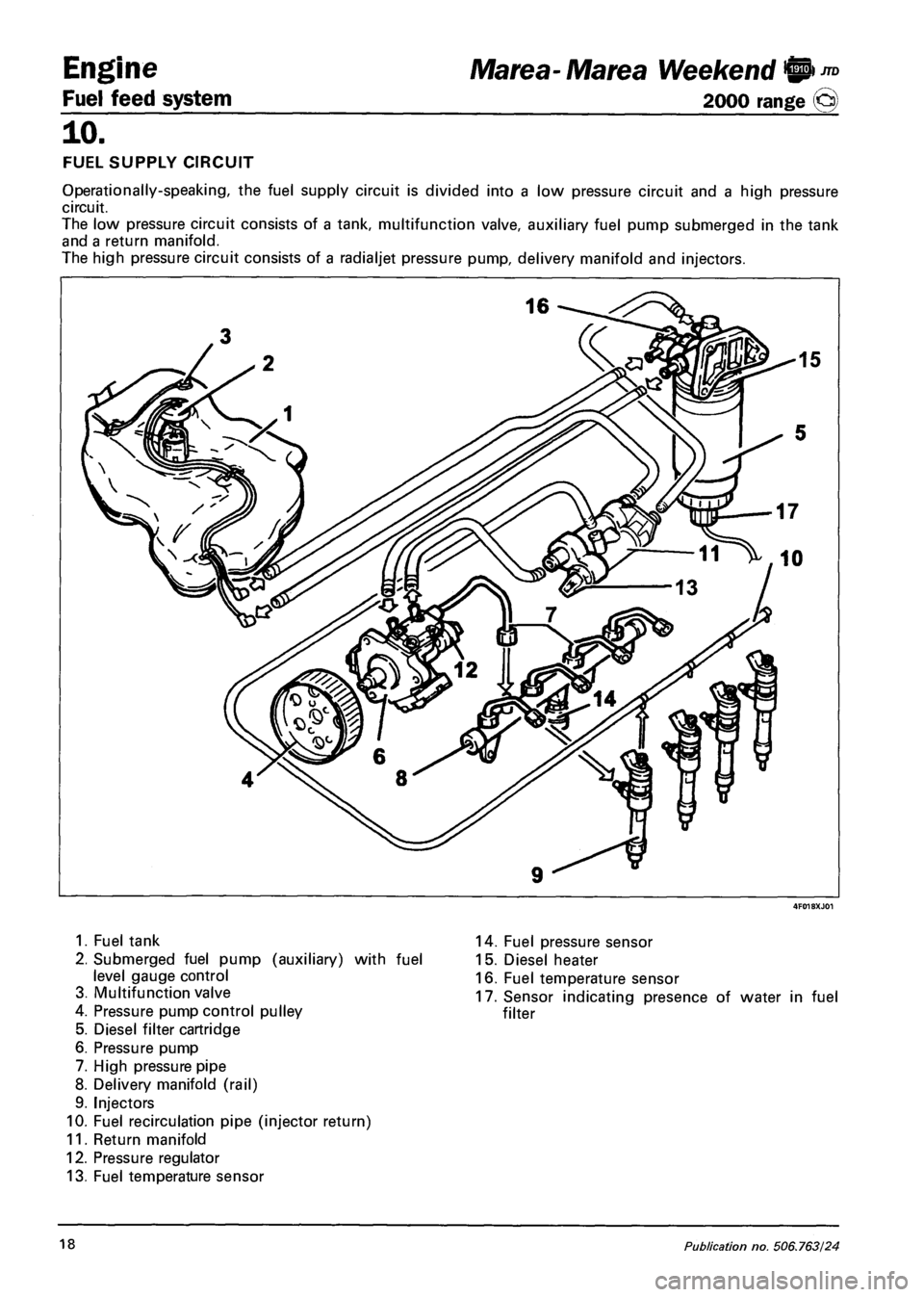
Engine
Fuel feed system
JTD Marea- Marea Weekend 0
2000 range ©
10.
FUEL SUPPLY CIRCUIT
Operationally-speaking, the fuel supply circuit is divided into a low pressure circuit and a high pressure
circuit.
The low pressure circuit consists of a tank, multifunction valve, auxiliary fuel pump submerged in the tank
and a return manifold.
The high pressure circuit consists of a radialjet pressure pump, delivery manifold and injectors.
1. Fuel tank
2. Submerged fuel pump (auxiliary) with fuel
level gauge control
3. Multifunction valve
4. Pressure pump control pulley
5. Diesel filter cartridge
6. Pressure pump
7. High pressure pipe
8. Delivery manifold (rail)
9. Injectors
10. Fuel recirculation pipe (injector return)
11. Return manifold
12. Pressure regulator
13. Fuel temperature sensor
14. Fuel pressure sensor
15. Diesel heater
16. Fuel temperature sensor
17. Sensor indicating presence of water in fuel
filter
18 Publication no. 506.763/24
Page 105 of 330

Marea- Marea Weekend 9 ™
2000 range (Q)
4F019XJ01
1. Impeller
2. Volumes
3. Intake port
4. Outlet port
5. Rollers
6. Outer race
7. Pressure relief valve
4F019XJ02
Engine
Fuel feed system
10.
SUBMERGED FUEL PUMP ASSEMBLY
(AUXILIARY) AND LEVEL GAUGE CON
TROL
The assembly consists mainly of:
- a roller-type fuel pump;
- a fuel level gauge;
- a fuel filter
The submerged fuel pump is volumetric type
with rollers and a motor with brushes and
permanent magnet excitation.
Impeller (1) is driven by the electric motor to
turn and create volumes (2) that move from
intake port (3) to outlet port (4).
These volumes are delimited by rollers (5) that
adhere to outer race(6) as the motor turns.
The pump is fitted with two valves: a check
valve to prevent the fuel circuit emptying
(with the pump off); a second pressure relief
valve (7) that short-circuits the outlet to the
inlet when pressures exceed 5 bars.
FUEL FILTER
The fuel filter is located in the engine bay.
The filter is cartridge type with a filter element
(1) made up of a pack of paper discs with a
filtering area of some 5300 cm 2 and a filter
gauge of 4 - 5 microns.
The filter is equipped with a fuel preheating
device (2) controlled by the engine control
unit via a relay.
The control unit activates or deactivates the
diesel filter on the basis of a diesel tempera
ture signal sent by sensor (3) on the filter.
A plug (4) screwed to the base of the fuel
filter cartridge is used to drai off the water.
The plug incorporates a sensor for the detec
tion of water in the diesel filter connected to a
warning light on the instrument panel.
1. Filter cartridge
2. Diesel preheating device
3. Diesel temperature sensor
4. Water drain plug with sensor to detect
presence of water in diesel filter
Copyright by Fiat Auto 19
Page 107 of 330

Marea- Marea Weekend <§l ™
2000 range ©
Engine
Fuel feed system
TZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZb
TZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ*
10.
MULTIFUNCTION VALVE
The multifunction valve is located on the fuel
tank and performs the following functions:
- tank pressurisation
- ventilation
- seal if the car rolls over
Tank pressurisation
Tank pressurisation is maintained at a level be
tween 55 and 75 mbars by means of a valve
mounted on a sealing rim.
The valve is supported by a steel plate and held in place by a spring.
When tank pressure exceeds a specified level, it overcomes spring resistance and allows the valve to rise
so that vapours can flow out.
When the pressure returns to within specified limits, the valve closes again
Ventilation
Under certain car service conditions, a vacuum may build up in the tank due to the effect of:
- heat changes;
- fuel consumption
in this case, the valve's function is to make up pressure inside the tank by letting air into the tank.
If this function is not performed correctly, the car may judder or stall due to difficulties in supplying the
pump.
Seal if the car rolls over
The roll-over function prevents fuel emerging from the tank if the car rolls over or tilts to a great extent.
During normal car operation (bends, acceleration, braking etc.), the fuel slops about and may emerge.
The highly-sensitive roll-over valve prevents this happening.
DELIVERY MANIFOLD (RAIL)
The delivery manifold (rail) is fitted to the cylinder head on the intake side.
Its volume damps fuel pressure fluctuations due mainly to:
- operation of the pressure pump;
- injector opening.
A fuel pressure sensor is fitted in the middle of the delivery manifold.
Hydraulic connections (high pressure) are via special steel pipes.
Copyright by Fiat Auto 21
Page 108 of 330

Engine
Fuel feed system
Marea- Marea Weekend W)JTD
2000 range ©
INERTIA SAFETY SWITCH
To increase car occupant safety in the case of
impact, the car is fitted with an inertia switch
located inside the passenger compartment se
cured to the inside of the left panel.
This sensor reduces the possibility of fire (due
to emerging fuel) by deactivating the auxiliary
fuel pump that supplies the injection circuit.
The switch consists of a steel ball, fitted in a
tapered housing, kept in place by the attrac
tion force of a permanent magnet.
In the case of violent impact, the ball is released from the magnetic detent and opens the normally closed
(NC) electrical circuit to cut off the auxiliary fuel pump connection to earth, and as a consequence the
supply to the injection system.
To restore the auxiliary pump earth connection, move back the seat and press the switch until a click is
heard.
Even after an apparently slight impact, if there is a smell of fuel or there are leaks from the fuel
system, do not turn the switch back on, but search for the fault and remedy it to prevent the risk
of fire.
'N.C. N.A. C
Inertia switch components
1. Inertia switch assembly
2. Sheath
3. Button
4. Upper side
5. Engagement side
6. Permanent magnet
7. Permanent magnet seat
8. Steel ball
C Common terminal
N.C. Normally closed contact
N.A. Normally open contact
22 Publication no. 506.763/24
Page 112 of 330

Engine
Fuel feed system
JTD Marea- Marea Weekend 9
2000 range @
10.
Operation at high rotation speeds
When the engine speed is increased, the ki
netic energy of the exhaust gases increases
gradually.
As a result, the speed of the turbine (5) in
creases and consequently the supercharging
pressure.
The VGT solenoid valve (2) operated by the
injection control unit (1), through the actuator
(4) causes the moving vanes to change posi
tion until the maximum opening position is
reached.
1. Injection control unit
2. VGT solenoid valve
3. Vacuum reservoir
4. Pneumatic actuator
5. Turbine
There is therefore an increase in the passage
sections and consequently a slowing down in
the flow of exhaust gases which pass through
the turbine (1) at the same speed or slower
than the low speed conditions.
The speed of the turbine (1) decreases and
settles down at a suitable vaule for the correct
operation of the engine at high speeds.
1. Turbine
2. Moving vanes
3. Pneumatic actuator
4. Rotary seal
TURBOCHARGER (1910 JTD 100 CV)
It basically consists of two impellers (1) on
one shaft (2) which rotates on floating bear
ings lubricated by a duct (3) from the engine
lubrication circuit.
The oil used dissipates some of the large
amount of heat given off by the exhaust gases
at the turbine.
There is a waste gate valve (4) fitted on the
turbocharger, operated by a pneumatic actua
tor (5), that makes it possible to shutter the
flow of exhaust gases to the turbine, accord
ing to the engine power/torque requirements.
The pneumatic actuator is controlled by the en
gine management control unit via a solenoid
valve.
* The turbocharger used on the 1910 JTD 100 CV version is the fixed geometry type.
26 VI 0^ Cam.frtfi and ri!plact<& Print n° 506.763/25