Page 28 of 349

V07268
VIBRATION METHOD: When vibration seems to be the major cause.
CONNECTORS
WIRE HARNESS
PARTS AND SENSOR1
Slightly shake the connector vertically and horizontally.
Slightly shake the wire harness vertically and horizontally.
The connector joint, fulcrum of the vibration, and body
through portion are the major areas to be checked thorough-
ly.
Apply slight vibration with a finger to the part of the sensor
considered to be the problem cause and check that the mal-
function occurs.Shake Slightly
Swing Slightly
Vibrate Slightly
HINT:
Applying strong vibration to relays may result in open relays.
– INTRODUCTIONHOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED
SYSTEMSIN–23
3. SYMPTOM SIMULATION
The most difficult case in troubleshooting is when there are no problem symptoms occurring. In such cases,
a thorough customer problem analysis must be carried out, then simulate the same or similar conditions and
environment in which the problem occurred in the customer’s vehicle. No matter how much experience a
technician has, or how skilled he or she may be, if he or she proceeds to troubleshoot without confirming
the problem symptoms he or she will tend to overlook something important in the repair operation and make
a wrong guess somewhere, which will only lead to a standstill. For example, for a problem which only occurs
when the engine is cold, or for a problem which occurs due to vibration caused by the road during driving,
etc., the problem can never be determined so long as the symptoms are confirmed with the engine hot condi-
tion or the vehicle at a standstill. Since vibration, heat or water penetration (moisture) is likely cause for prob-
lem which is difficult to reproduce, the symptom simulation tests introduced here are effective measures in
that the external causes are applied to the vehicle in a stopped condition.
Important Points in the Symptom Simulation Test:
In the symptom simulation test, the problem symptoms should of course be confirmed, but the problem area
or parts must also be found out. To do this, narrow down the possible problem circuits according to the symp-
toms before starting this test and connect a tester beforehand. After that, carry out the symptom simulation
test, judging whether the circuit being tested is defective or normal and also confirming the problem symp-
toms at the same time. Refer to the problem symptoms table for each system to narrow down the possible
causes of the symptom.
Page 29 of 349

������
B02390
HEAT METHOD: When the problem seems to occur when the suspect area is heated. 2
NOTICE:3 WATER SPRINKLING METHOD:
(1)
(2)
4 OTHER: When a malfunction seems to occur when electrical load is excessive.When the malfunction seems to occur on a rainy day or in a
high–humidity condition. Heat the component that is the likely cause of the malfunction
with a hair dryer or similar object. Check to see if the malfunction
occurs.
Sprinkle water onto the vehicle and check to see if the malfunc-
tion occurs.
Turn on all electrical loads including the heater blower, head
lights, rear window defogger, etc. and check to see if the mal-
function occurs.ON HINT:
If a vehicle is subject to water leakage, the leaked water may
contaminate the ECU. When testing a vehicle with a water leak-
age problem, special caution must be taken.
Malfunc-
tion
Do not heat to more than 60 C (140 F). (Temperature
is limited not to damage the components.)
Do not apply heat directly to parts in the ECU. (1)
(2)
Never sprinkle water directly into the engine compart-
ment, but indirectly change the temperature and hu-
midity by applying water spray onto the radiator front
surface.
Never apply water directly onto the electronic compo-
nents. NOTICE: IN–24
– INTRODUCTIONHOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED
SYSTEMS
Page 265 of 349
I04818
SPEEDOMETER
TACHOMETER
WATER TEMP.
FUEL
OIL LEVEL
ODO / TRIP
METER
OUTSIDE TEMP.
CLOCK
RHEOSTATLCD
DISPLAY
LCD
DISPLAY S
T
W
FA18
B7
B20 A5
A15
A3
A6
A7
A8
A12
A11
A19
A10
A9
B11
B24
B5
A22
B4
A23
B14
A23
A25
B16
B14
B21
A22
A14VOLTAGE
STABILIZER
B17
B22
B9
B26
A24 Brake Warning
Fuel filter Warning
Discharge Waring
Economy Indicator
Turbo / Glow Plug Indicator
Glow Plug Indicator
ABS Warning
Low Oil Pressure Warning
Check Engine Warning
O / D OFF Indicator
ECT SNOW Indicator
ECT PWR Indicator
Rear Fog Light Indicator
High Beam Indicator
Right Turn Indicator
Left Turn Indicator
Open Door Warning
SRS Warning
Front Fog light Indicator A1
B15
B18A26
B2
A17
B1
B13
B6
B3 B19
BE–4
– BODY ELECTRICALCOMBINATION METER
Page 268 of 349
I01275
Ignition
Switch
BatterySender
Gauge Receiver
Gauge
I01276
Ignition
Switch
BatteryReceiver
Gauge
Test Bulb
(3.4 W)
I01277
Battery Ignition
SwitchWarning Light
Wire Harness Side
1
– BODY ELECTRICALCOMBINATION METER
BE–7
(b) Compare the tester and tachometer indications.
DC 13.5 V 25 �C at (77�F)
Standard indicationAllowable range
700630 – 770
1,000900 – 1,100
2,0001,850 – 2,150
3,0002,800 – 3,200
4,0003,800 – 4,200
5,0004,800 – 5,200
6,0005,750 – 6,250
7,0006,700 – 7,300
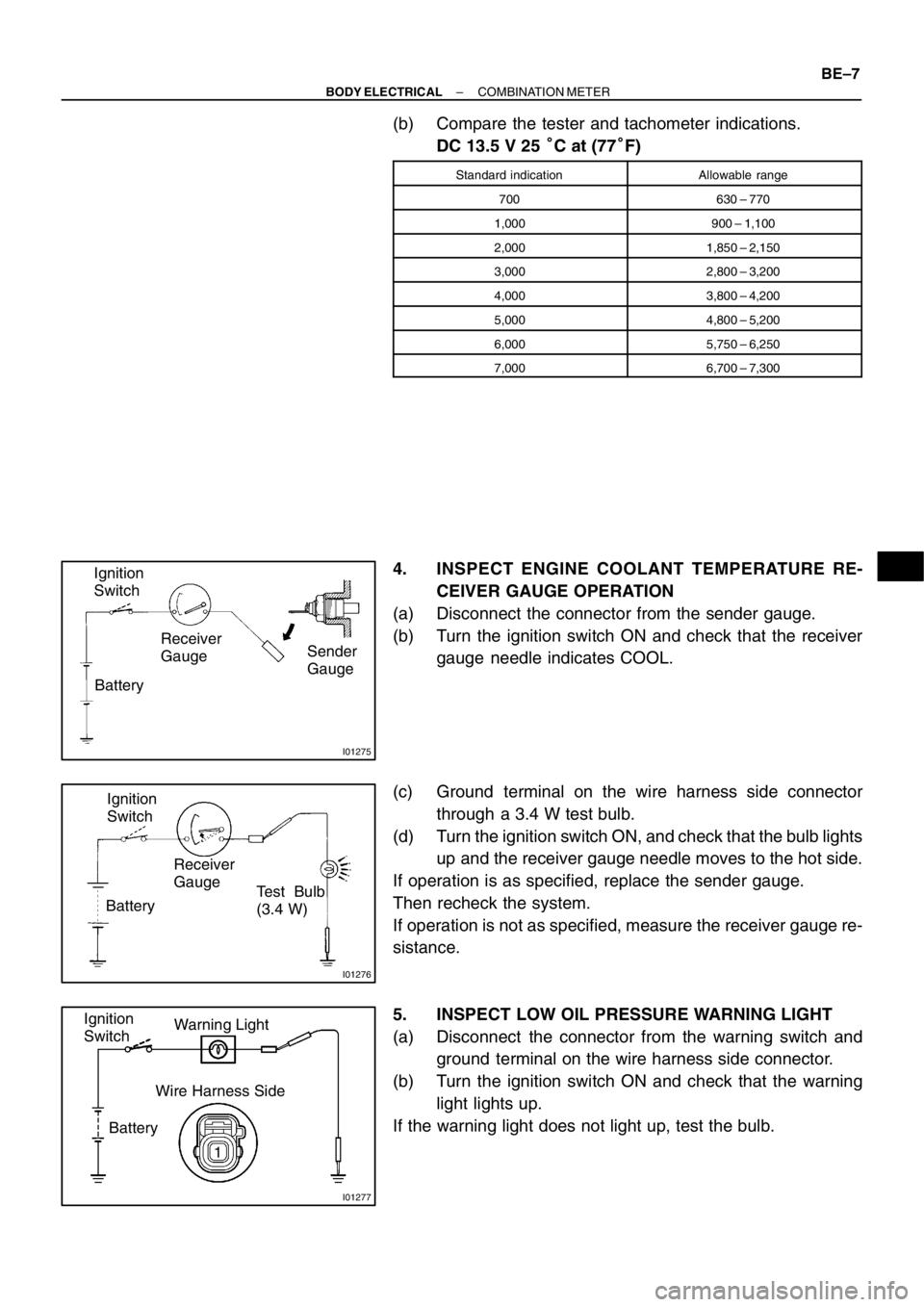
4. INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE RE-
CEIVER GAUGE OPERATION
(a) Disconnect the connector from the sender gauge.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON and check that the receiver
gauge needle indicates COOL.
(c) Ground terminal on the wire harness side connector
through a 3.4 W test bulb.
(d) Turn the ignition switch ON, and check that the bulb lights
up and the receiver gauge needle moves to the hot side.
If operation is as specified, replace the sender gauge.
Then recheck the system.
If operation is not as specified, measure the receiver gauge re-
sistance.
5. INSPECT LOW OIL PRESSURE WARNING LIGHT
(a) Disconnect the connector from the warning switch and
ground terminal on the wire harness side connector.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON and check that the warning
light lights up.
If the warning light does not light up, test the bulb.