1999 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 440 of 1529

MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 30-2-5
Description
General
The inlet manifold on the V8 engine is located on the top of the engine, between the cylinders. The manifold directs
intake air into the cylinders. The intake air is mixed with fuel delivered by the injectors prior to ignition in the cylinders.
The inlet manifold comprises three separate aluminium castings.
Two exhaust manifolds are used, one for each bank of four cylinders. Each exhaust manifold allows combustion
gases from the cylinders to leave the engine and directs them into the exhaust system.
The exhaust system is connected to each exhaust manifold and merges into one pipe midway along the underside of
the vehicle. A catalytic converter (where fitted) is located in the front pipe from each manifold. A silencer is installed
midway along the system and a second tail silencer is located at the rear of the vehicle.
Inlet manifold
The inlet manifold comprises three aluminium castings; a lower manifold, an upper manifold and a plenum. The inlet
manifold is located on the top of the engine and feeds air into the cylinders.
Lower manifold
The lower manifold is a one piece machined aluminium casting which locates in the vee on the top of the engine and
is secured to each cylinder head with six bolts per head. A one piece coated metal gasket seals the lower manifold to
each cylinder head and also serves as a cover for the cylinder block.
Eight injectors are fitted into the lower manifold, four on each side. Each injector is sealed in the manifold with O-ring
seals and retained in position by the fuel rails. A fuel rail is attached to each side of the manifold and secured with two
bolts.
Eight air intake ports are cast and machined on the top of the manifold, each port directing intake air into one cylinder.
These ports mate with matching ports in the upper manifold and are sealed with a coated metal gasket between the
two manifolds.
A cavity at the front of the manifold collects coolant flow from the engine. A coolant outlet pipe is sealed and attached
to the front of the manifold and provides for coolant to flow through the cavity in the casting to the radiator top hose.
A smaller port in the manifold also allows coolant to flow from the cavity to the heater matrix. The lower manifold also
locates the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor in a port in the front of the manifold.
Upper manifold
The upper manifold is a one piece machined aluminium casting. The manifold has eight ports on its lower face which
mate with the eight ports on the lower manifold. The joint between the upper and lower manifolds is sealed with a
coated metal gasket and secured with six bolts.
The manifold divides from the eight ports into eight branches, four on each side. Each set of four branches merge into
one gallery on each side of the manifold. Each gallery has an opening at its forward end which mates with the intake
plenum.
The upper manifold provides attachment for the Idle Air Control (IAC) valve and for brackets which retain pipes, plug
leads and throttle cables.
Inlet plenum
The plenum is mounted transversely on the front of the upper manifold. The plenum divides into two galleries which
connect with the galleries on the upper manifold. The plenum is secured to the upper manifold with four bolts and
sealed with a coated metal gasket.
The plenum provides attachment for the throttle housing, which is secured with four bolts and sealed with a coated
metal gasket. The plenum also has vacuum connections for brake servo, rocker cover breather and fuel vapour from
the charcoal canister. A port on the top of the plenum connects via a hose to the IAC valve.
Page 486 of 1529

MANUAL GEARBOX - R380
REPAIRS 37-15
32.Remove 3 bolts securing oil cooling pipe
housing to gearbox, release housing and
discard 'O' rings.
33.Using a second jack support the weight of the
engine.
34.Remove 14 bolts securing gearbox to engine.
35.With assistance, remove gearbox from engine.
Refit
1.Clean gearbox to engine mating faces, dowels
and dowel holes.
2.Raise gear gearbox on jack and align to clutch
and engine.
3.Fit bolts securing gearbox to engine and
tighten to 45 Nm (33 lbf.ft).
4.Lubricate and fit new 'O' rings to oil cooling
pipe housing. 5.Position coolant pipe housing, fit bolts and
tighten to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
6. If fitted: Secure harness in retaining clips,
connect Lucars to differential lock warning
switch and multiplug to neutral sensor.
7.Position breather pipes and secure 'P' clip with
bolt.
8.Using new sealing washers fit breather pipe
banjo bolts and tighten to 15 Nm (11 lbf.ft).
9.Connect oil temperature sensor Lucars and
reverse lamp switch multiplug.
10.Position low ratio selector cable to housing and
secure with 'C' washer and clevis pin.
11.Secure cable to fuel pipes with new cable ties.
12.Raise gearbox, ensuring gear change lever is
located in grommet.
13.Fit gearbox mountings and tighten bolts to 85
Nm (63 lbf.ft).
14.Fit nuts to mountings and tighten to 48 Nm (37
lbf.ft).
15.Remove 3 bolts securing support plate to
gearbox.
16.Position clutch slave cylinder and heat shield,
fit bolts and tighten to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
17.Clean handbrake back plate and mating face.
18.Position handbrake back plate, fit bolts and
tighten to 75 Nm (46 lbf.ft).
19.Clean handbrake drum.
20.Fit handbrake drum and tighten retaining
screw.
21.Clean propeller shafts and mating faces.
22.Position propeller shafts, align to marks and
tighten bolts to 47 Nm (35 lbf.ft).
23.Clean exhaust silencer and tail pipe mating
faces.
24.Position silencer and secure on mountings,
using a new gasket align to tail pipe, fit nuts
and tighten to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
25.Position rear cross member, fit bolts and
tighten to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
26.Refill gearbox with oil.
+ MAINTENANCE, PROCEDURES,
Manual gearbox.
27.Refill transfer gearbox oil.
+ MAINTENANCE, PROCEDURES,
Transfer box.
28.Fit front exhaust pipe.
+ MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST
SYSTEMS - V8, REPAIRS, Front pipe.
29.Fit gear lever extension, fit clamp bolt and
tighten to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
30.Fit gear lever trim and gear change knob.
31.Connect battery earth lead.
32. Fit battery cover and cooling fan cover and
secure fixings.
Page 1160 of 1529

HEATING AND VENTILATION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 80-3
Description
General
The heating and ventilation system controls the temperature and distribution of air supplied to the vehicle interior. The
system consists of an air inlet duct, heater assembly, distribution ducts and a control panel. An outlet vent is
incorporated at the rear of the cabin. Some diesel models also incorporate a fuel burning heater (FBH) system in the
engine coolant supply to the heater assembly.
Fresh or recirculated air flows into the heater assembly from the inlet duct. An electrical variable speed blower in the
inlet duct, and/or ram effect, forces the air through the system. Depending on the settings on the control panel, the air
is then heated and supplied through the distribution ducts to fascia and floor level outlets.
Page 1162 of 1529
HEATING AND VENTILATION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 80-5
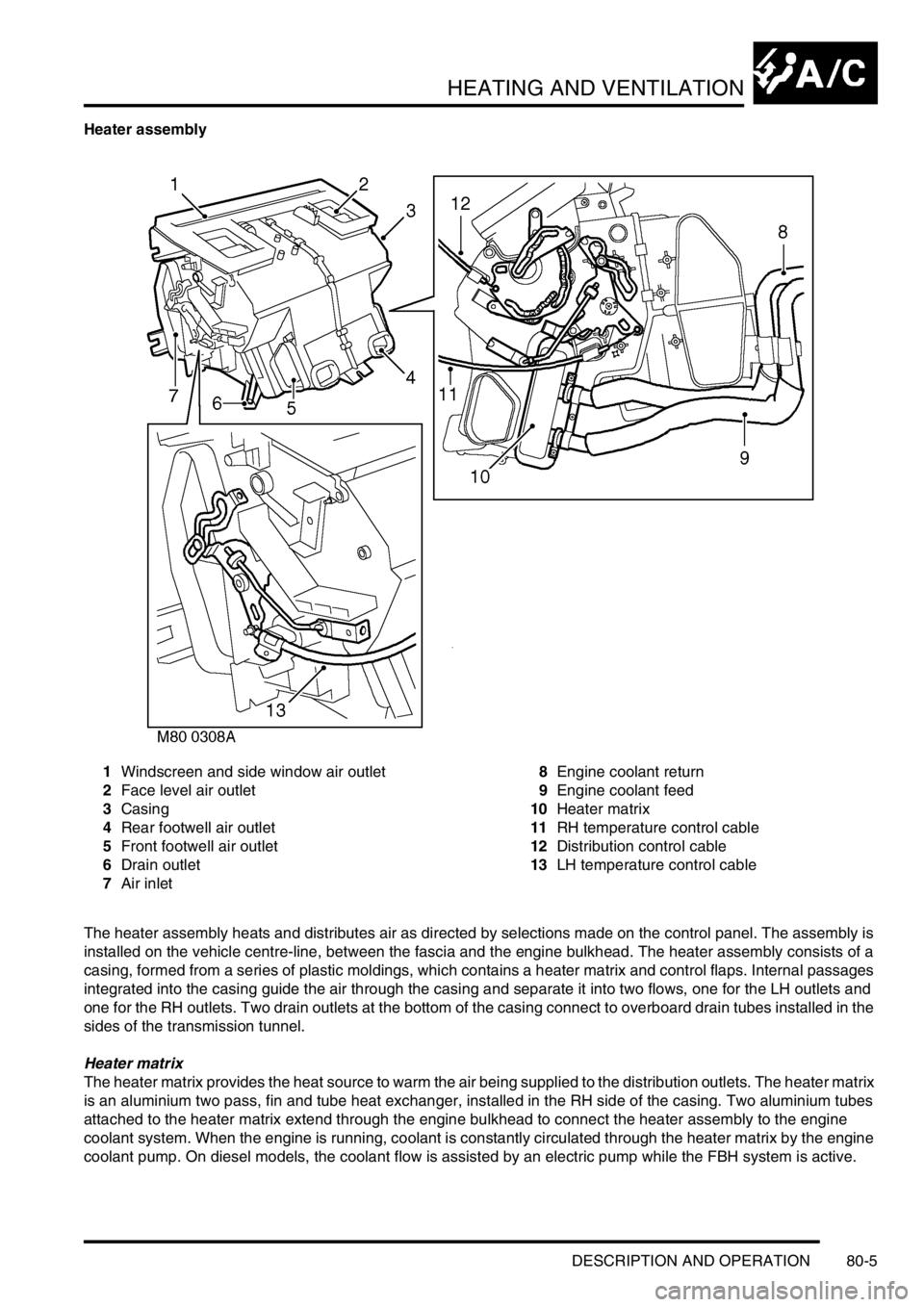
Heater assembly
1Windscreen and side window air outlet
2Face level air outlet
3Casing
4Rear footwell air outlet
5Front footwell air outlet
6Drain outlet
7Air inlet8Engine coolant return
9Engine coolant feed
10Heater matrix
11RH temperature control cable
12Distribution control cable
13LH temperature control cable
The heater assembly heats and distributes air as directed by selections made on the control panel. The assembly is
installed on the vehicle centre-line, between the fascia and the engine bulkhead. The heater assembly consists of a
casing, formed from a series of plastic moldings, which contains a heater matrix and control flaps. Internal passages
integrated into the casing guide the air through the casing and separate it into two flows, one for the LH outlets and
one for the RH outlets. Two drain outlets at the bottom of the casing connect to overboard drain tubes installed in the
sides of the transmission tunnel.
Heater matrix
The heater matrix provides the heat source to warm the air being supplied to the distribution outlets. The heater matrix
is an aluminium two pass, fin and tube heat exchanger, installed in the RH side of the casing. Two aluminium tubes
attached to the heater matrix extend through the engine bulkhead to connect the heater assembly to the engine
coolant system. When the engine is running, coolant is constantly circulated through the heater matrix by the engine
coolant pump. On diesel models, the coolant flow is assisted by an electric pump while the FBH system is active.
Page 1165 of 1529
HEATING AND VENTILATION
80-8DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Control panel
The controls for heating and ventilation are installed on a control panel in the centre of the fascia, below the radio.
Three rotary knobs control the LH and RH outlet temperatures and distribution. A slider switch controls blower speed.
A latching pushswitch controls the selection of fresh/recirculated air; an amber LED in the switch illuminates when
recirculated air is selected.
Graphics on the panel and the controls indicate the function and operating positions of the controls.
Outlet vent
The outlet vent promotes the free flow of heating and ventilation air through the cabin. The outlet vent is installed in
the RH rear quarter body panel and vents cabin air into the sheltered area between the rear quarter body panel and
the outer body side panel. The vent consists of a grille covered by soft rubber flaps and is effectively a non-return
valve. The flap opens and closes automatically depending on the differential between cabin and outside air pressures.
FBH system (diesel models only)
The FBH system is an auxiliary heating system that compensates for the relatively low coolant temperatures inherent
in the diesel engine. At low ambient temperatures, the FBH system heats the coolant supply to the heater assembly,
and maintains it within the temperature range required for good in-car heating performance. Operation is fully
automatic, with no intervention required by the driver.
The system consists of an air temperature sensor, a FBH fuel pump and a FBH unit. Fuel for the FBH system is taken
from the fuel tank, through a line attached to the fuel tank's fuel pump, and supplied via the FBH fuel pump to the FBH
unit. The connection on the fuel tank's fuel pump incorporates a tube which extends down into the tank. At the FBH
unit connection, the fuel line incorporates a self-sealing, quick disconnect coupling. In the FBH unit, the fuel delivered
by the FBH fuel pump is burned and the resultant heat output is used to heat the coolant. An ECU integrated into the
FBH unit controls the operation of the system at one of two heat output levels, 2.5 kW at part load and 5 kW at full load
Ambient temperature sensor
The ambient temperature sensor controls a power supply from the alternator to the FBH unit. The sensor is installed
on the RH support strut of the bonnet closing panel and contains a temperature sensitive switch that is closed at
temperatures below 5 °C (41 °F) and open at temperatures of 5 °C (41 °F) and above.
Page 1169 of 1529

HEATING AND VENTILATION
80-12DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Burner housing. The burner housing contains the burner insert and also incorporates connections for the exhaust
pipe, the coolant inlet from the circulation pump and the coolant outlet to the heater assembly. The exhaust pipe
directs exhaust combustion gases to atmosphere at the bottom of the engine compartment.
The burner insert incorporates the fuel combustion chamber, an evaporator and a glow plug/flame sensor. Fuel from
the FBH fuel pump is supplied to the evaporator, where it evaporates and enters the combustion chamber to mix with
air from the combustion air fan. The glow plug/flame sensor provides the ignition source of the fuel:air mixture and,
once combustion is established, monitors the flame.
ECU/heat exchanger. The ECU controls and monitors operation of the FBH system. Ventilation of the ECU is
provided by an internal flow of air from the combustion air fan. The heat exchanger transfers heat generated by
combustion to the coolant. A sensor in the heat exchanger provides the ECU with an input of heat exchanger casing
temperature, which the ECU relates to coolant temperature and uses to control system operation. The temperature
settings in the ECU are calibrated to compensate for the difference between coolant temperature and the heat
exchanger casing temperature detected by the sensor. Typically: as the coolant temperature increases, the coolant
will be approximately 7 °C (12.6 °F) hotter than the temperature detected by the sensor; as the coolant temperature
decreases, the coolant will be approximately 2 °C (3.6 °F) cooler than the temperature detected by the sensor.
Page 1170 of 1529

HEATING AND VENTILATION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 80-13
Operation
Air distribution
Turning the distribution knob on the control panel turns the control flaps in the heater assembly to direct air to the
corresponding fascia and footwell outlets.
Air temperature
Turning the LH or RH temperature knob on the control panel turns the related blend flaps in the heater assembly. The
blend flaps vary the proportion of air going through the cold air bypass and the heater matrix. The proportion varies,
between full bypass no heat and no bypass full heat, to correspond with the position of the temperature knob.
Blower speed
The blower can be selected off or to run at one of four speeds. While the ignition is on, when the blower switch is set
to positions 1, 2, 3, or 4, ignition power energises the blower relay, which supplies battery power to the blower. At
switch positions 1, 2 and 3, the blower switch also connects the blower to different earth paths through the resistor
pack, to produce corresponding differences of blower operating voltage and speed. At position 4, the blower switch
connects an earth direct to the blower, bypassing the resistor pack, and full battery voltage drives the blower at
maximum speed.
Fresh/Recirculated inlet air
When the recirculated air switch is latched in, the amber indicator LED in the switch illuminates and an earth is
connected to the recirculated air side of the fresh/recirculated air servo motor. The fresh/recirculated air servo motor
then turns the control flaps in the air inlet duct to close the fresh air inlet and open the recirculated air inlets.
When the latch of the recirculated air switch is released, the amber indicator LED in the switch extinguishes and the
earth is switched from the recirculated air side to the fresh air side of the fresh/recirculated air servo motor. The fresh/
recirculated air servo motor then turns the control flaps in the air inlet duct to open the fresh air inlet and close the
recirculated air inlets.
FBH system (where fitted)
The FBH system operates only while the engine is running and the ambient temperature is less than 5 °C (41 °F).
With the engine running and the ambient temperature below 5 °C (41 °F), the air temperature sensor connects the
alternator power supply to the ECU in the FBH unit. On receipt of the alternator power supply, the ECU starts the
circulation pump and, depending on the input from the temperature sensor in the heat exchanger, enters either a
standby or active mode of operation. If the heat exchanger casing temperature is 65 °C (149 °F) or above, the ECU
enters a standby mode of operation. If the heat exchanger casing temperature is below 65 °C (149 °F), the ECU enters
an active mode of operation. In the standby mode, the ECU monitors the heat exchanger casing temperature and
enters the active mode if it drops below 65 °C (149 °F). In the active mode, the ECU initiates a start sequence and
then operates the system at full or part load combustion to provide the required heat input to the coolant.
Start sequence
At the beginning of the start sequence the ECU energises the glow plug function of the glow plug/flame sensor, to
preheat the combustion chamber, and starts the combustion air fan at slow speed. After 30 seconds, the ECU
energises the FBH fuel pump at the starting sequence speed. The fuel delivered by the FBH fuel pump evaporates in
the combustion chamber, mixes with air from the combustion air fan and is ignited by the glow plug/flame sensor. The
ECU then progressively increases the speed of the FBH fuel pump and the combustion air fan to either part or full
load speed, as required by the system. Once full or part load speed is achieved, the ECU switches the glow plug/flame
sensor from the glow plug function to the flame sensing function to monitor combustion. From the beginning of the
start sequence to stable combustion takes approximately 90 seconds for a start to part load combustion and 150
seconds for a start to full load combustion.
Page 1171 of 1529

HEATING AND VENTILATION
80-14DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Coolant temperature control
When the ECU first enters the active mode, it initiates a start to full load combustion. Full load combustion continues
until the heat exchanger casing temperature reaches 60 °C (140 °F), when the ECU decreases the speed of the FBH
fuel pump and the combustion air fan to half speed, to produce part load combustion. The ECU maintains part load
combustion while the heat exchanger casing temperature remains between 54 and 65 °C (129 and 149 °F). If the heat
exchanger casing temperature decreases to 54 °C (129 °F), the ECU switches the system to full load combustion
again. If the heat exchanger casing temperature increases to 65 °C (149 °F), the ECU enters a control idle phase of
operation.
On entering the control idle phase, the ECU immediately switches the FBH fuel pump off, to stop combustion, and
starts a timer for the combustion air fan. After a 2 minute cooldown period, the ECU switches the combustion air fan
off and then remains in the control idle phase while the heat exchanger casing temperature remains above 59 °C (138
°F). If the heat exchanger casing temperature decreases to 59 °C (138 °F), within 15 minutes of the ECU entering the
control idle phase, the ECU initiates a start to part load combustion. If more than 15 minutes elapse before the heat
exchanger casing temperature decreases to 59 °C (138 °F), the ECU initiates a start to full load combustion.
In order to limit the build-up of carbon deposits on the glow plug/flame sensor, the ECU also enters the control idle
phase if the continuous part and/or full load combustion time exceeds 72 minutes. After the cooldown period, if the
heat exchanger casing is still in the temperature range that requires additional heat, the ECU initiates an immediate
restart to part or full load combustion, as appropriate.
Shutdown
The FBH system is de-activated when the alternator power supply to the FBH unit is disconnected, either by the
engine stopping or, if the ambient temperature increases to 5 °C (41 °F) or above, by the contacts in the air
temperature sensor opening. If the system is active when the alternator power supply is disconnected, the ECU de-
energises the FBH fuel pump to stop combustion, but continues operation of the combustion air fan and the circulation
pump to cool down the FBH unit. The cool down time depends on the combustion load at the time the alternator power
input is disconnected.
Cool down times
Diagnostics
The ECU in the FBH unit monitors the system for faults. Any faults detected are stored in a volatile memory in the the
ECU, which can be interrogated by Testbook. A maximum of three faults and associated freeze frame data can be
stored at any one time. If a further fault is detected, the oldest fault is overwritten by the new fault.
The ECU also incorporates an error lockout mode of operation that inhibits system operation to prevent serious faults
from causing further damage to the system. In the error lockout mode, the ECU immediately stops the FBH fuel pump,
and stops the combustion air fan and circulation pump after a cool down time of approximately 2 minutes. Error lockout
occurs for start sequence failures and/or combustion flameouts, heat exchanger casing overheat and out of limit input
voltage. The error lockout mode can be cleared using Testbook, or by disconnecting the battery power supply for a
minimum of 10 seconds.
Start failure/flameout. If a start sequence fails to establish combustion, or a flameout occurs after combustion is
established, the ECU immediately initiates another start sequence. The start failure or flameout is also recorded by
an event timer in the ECU. The event timer is increased by one after each start failure or flameout, and decreased by
one if a subsequent start is successful. If the event timer increases to three (over any number of drive cycles), the
ECU enters the error lockout mode.
Heat exchanger casing overheat. To protect the system from excessive temperatures, the ECU enters the error
lockout mode if the heat exchanger casing temperature exceeds 105 °C (221 °F).
Out of limit voltage. The ECU enters the error lockout mode if the battery or alternator power input is less than 10.5 ±
0.3 V for more than 20 seconds, or more than 15.5 ± 0.5 V for more than 6 seconds.
Combustion load Cool down time, seconds
Part 100
Full 175