1999 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY catalytic converter
[x] Cancel search: catalytic converterPage 269 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-36 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Failure of the closed loop control of the exhaust emission system may be attributable to one of the failure modes
indicated below:
lMechanical fitting & integrity of the sensor.
lSensor open circuit / disconnected.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply or ground.
lLambda ratio outside operating band.
lCrossed sensors.
lContamination from leaded fuel or other sources.
lChange in sensor characteristic.
lHarness damage.
lAir leak into exhaust system (cracked pipe / weld or loose fixings).
System failure will be indicated by the following symptoms:
lMIL light on (NAS and EU-3 only).
lDefault to open-loop fuelling for the defective cylinder bank.
lIf sensors are crossed, engine will run normally after initial start and then become progressively unstable with
one bank going to its maximum rich clamp and the other bank going to its maximum lean clamp – the system will
then revert to open-loop fuelling.
lHigh CO reading
lStrong smell of H
2S (rotten eggs)
lExcessive emissions
Fuel Metering
When the engine is cold, additional fuel has to be provided to the air:fuel mixture to assist starting. This supplementary
fuel enrichment continues until the combustion chamber has heated up sufficiently during the warm-up phase.
Under normal part-throttle operating conditions the fuel mixture is adjusted to provide minimum fuel emissions and
the air:fuel mixture is held close to the optimum ratio (λ = 1). The engine management system monitors the changing
engine and environmental conditions and uses the data to determine the exact fuelling requirements necessary to
maintain the air:fuel ratio close to the optimum value that is needed to ensure effective exhaust emission treatment
through the three-way catalytic converters.
During full-throttle operation the air:fuel mixture needs to be made rich to provide maximum torque. During
acceleration, the mixture is enriched by an amount according to engine temperature, engine speed, change in throttle
position and change in manifold pressure, to provide good acceleration response.
When the vehicle is braking or travelling downhill the fuel supply can be interrupted to reduce fuel consumption and
eliminate exhaust emissions during this period of operation.
If the vehicle is being used at altitude, a decrease in the air density will be encountered which needs to be
compensated for to prevent a rich mixture being experienced. Without compensation for altitude, there would be an
increase in exhaust emissions and problems starting, poor driveability and black smoke from the exhaust pipe. For
open loop systems, higher fuel consumption may also occur.
Exhaust Emission System Diagnostics
The engine management ECM contains an on-board diagnostics (OBD) system which performs a number of
diagnostic routines for detecting problems associated with the closed loop emission control system. The diagnostic
unit monitors ECM commands and system responses and also checks the individual sensor signals for plausibility,
these include:
lLambda ratio outside of operating band
lLambda heater diagnostic
lLambda period diagnostic
lPost-catalytic converter lambda adaptation diagnostic (NAS only)
lCatalyst monitoring diagnostic
Lambda Ratio Outside Operating Band
The system checks to ensure that the system is operating in a defined range around the stoichiometric point. If the
system determines that the upper or lower limits for the air:fuel ratio are being exceeded, the error is stored as a fault
code in the ECM diagnostic memory (the MIL light is illuminated on NAS vehicles).
Page 270 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-37
Lambda Heater Diagnostic
The system determines the heater current and supply voltage so that the heater's resistance can be calculated. After
the engine has been started, the system waits for the heated oxygen sensors to warm up, then calculates the
resistance from the voltage and current measurements. If the value is found to be outside of the upper or lower
threshold values, then the fault is processed (the MIL light is illuminated on NAS vehicles).
Lambda Period Diagnostic
The pre-catalytic converter sensors are monitored. As the sensors age, the rich to lean and the lean to rich switching
delays increase, leading to increased emissions if the lambda control becomes inaccurate. If the switching period
exceeds a defined limit, the sensor fault is stored in the ECM diagnostic memory (the MIL light is illuminated on NAS
vehicles).
Post-Catalytic Converter Lambda Adaptation Diagnostic (NAS only)
On NAS vehicles the ageing effects of the pre-catalytic converter sensors are compensated for by an adaptive value
derived from the post-catalytic converter sensors. This is a long term adaption which only changes slowly. For a rich
compensation the additive value is added to the rich delay time. For a lean compensation, the adaptive value is added
to the lean delay time. The adaptive time is monitored against a defined limit, and if the limit is exceeded, the fault is
stored in the ECM's diagnostic memory and the MIL light is illuminated on the instrument pack.
Catalyst Monitoring Diagnostic
On NAS specification vehicles the catalysts are monitored both individually and simultaneously for emission pollutant
conversion efficiency. The conversion efficiency of a catalyst is monitored by measuring the oxygen storage, since
there is a direct relationship between these two factors. The closed loop lambda control fuelling oscillations produce
pulses of oxygen upstream of the catalyst, as the catalyst efficiency deteriorates its ability to store oxygen is
decreased. The amplitudes of the signals from the pre-catalytic and post-catalytic converter heated oxygen sensors
are compared. As the oxygen storage decreases, the post-catalytic converter sensor begins to follow the oscillations
of the pre-catalytic converter heated oxygen sensors. Under steady state conditions the amplitude ratio is monitored
in different speed / load sites. There are three monitoring areas, and if the amplitude ratio exceeds a threshold in all
three areas the catalyst conversion limit is exceeded; the catalyst fault is stored in the diagnostic memory and the MIL
light is illuminated on the instrument pack. There is a reduced threshold value for both catalysts monitored as a pair.
In either case, a defective catalyst requires replacement of the downpipe assembly.
In the case of a catalytic converter failure the following failure symptoms may be apparent:
lMIL light on after 2 driving cycles (NAS market only).
lHigh exhaust back pressure if catalyst partly melted.
lExcessive emissions
lStrong smell of H
2S (rotten eggs).
Oxygen sensor voltages can be monitored using TestBook/T4, the approximate output voltage from the heated
oxygen sensors with a warm engine at idle and with closed loop fuelling active are shown in the table below:
Measurement Normal catalyst Defective catalyst
Pre-catalytic heated oxygen sensors ~ 100 to 900 mV switching @ ~ 0.5
Hz~ 100 to 900 mV switching @ ~ 0.5 Hz
Post-catalytic heated oxygen sensors ~ 200 to 650 mV, static or slowly
changing~ 200 to 850 mV, changing up to same
frequency as pre-catalytic heated oxygen
sensors
Amplitude ratio (LH HO
2 sensors & RH
HO
2 sensors)<0.3 seconds >0.6 seconds (needs to be approximately
0.75 seconds for single catalyst fault)
Number of speed/load monitoring areas
exceeded (LH & RH)0 >1 (needs to be 3 for fault storage)
Page 272 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-39
Evaporative Emission Control Operation
Fuel vapour is stored in the activated charcoal (EVAP) canister for retention when the vehicle is not operating. When
the vehicle is operating, fuel vapour is drawn from the canister into the engine via a purge control valve. The vapour
is then delivered to the intake plenum chamber to be supplied to the engine cylinders where it is burned in the
combustion process.
During fuel filling the fuel vapour displaced from the fuel tank is allowed to escape to atmosphere, valves within the
fuel filler prevent any vapour escaping through to the EVAP canister as this can adversely affect the fuel cut-off height.
Only fuel vapour generated whilst driving is prevented from escaping to atmosphere by absorption into the charcoal
canister. The fuel filler shuts off to leave the tank approximately 10% empty to ensure the ROVs are always above
the fuel level and so vapour can escape to the EVAP canister and the tank can breathe. The back pressures normally
generated during fuel filling are too low to open the pressure relief valve, but vapour pressures accumulated during
driving are higher and can open the pressure relief valve. Should the vehicle be overturned, the ROVs shut off to
prevent any fuel spillage.
Fuel vapour generated from within the fuel tank as the fuel heats up is stored in the tank until the pressure exceeds
the operating pressure of the two-way valve. When the two-way valve opens, the fuel vapour passes along the vent
line from the fuel tank (via the fuel tank vapour separator) to the evaporation inlet port of the EVAP canister. The fuel
tank vents between 5.17 and 6.9 kPa.
Fuel vapour evaporating from the fuel tank is routed to the EVAP canister through the fuel vapour separator and vent
line. Liquid fuel must not be allowed to contaminate the charcoal in the EVAP canister. To prevent this, the fuel vapour
separator fitted to the fuel neck allows fuel to drain back into the tank. As the fuel vapour cools, it condenses and is
allowed to flow back into the fuel tank from the vent line by way of the two-way valve.
The EVAP canister contains charcoal which absorbs and stores fuel vapour from the fuel tank while the engine is not
running. When the canister is not being purged, the fuel vapour remains in the canister and clean air exits the canister
via the air inlet port.
The engine management ECM controls the electrical output signal to the purge valve. The system will not work
properly if there is leakage or clogging within the system or if the purge valve cannot be controlled.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
When the engine is running, the ECM decides when conditions are correct for vapour to be purged from the EVAP
canister and opens the canister purge valve. This connects a manifold vacuum line to the canister and fuel vapour
containing the hydrocarbons is drawn from the canister's charcoal element to be burned in the engine. Clean air is
drawn into the canister through the atmosphere vent port to fill the displaced volume of vapour.
The purge valve remains closed below preset coolant and engine speed values to protect the engine tune and
catalytic converter performance. If the EVAP canister was purged during cold running or at idling speed, the additional
enrichment in the fuel mixture would delay the catalytic converter light off time and cause erratic idle. When the purge
valve is opened, fuel vapour from the EVAP canister is drawn into the plenum chamber downside of the throttle
housing, to be delivered to the combustion chambers for burning.
The purge valve is opened and closed in accordance with a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal supplied from the
engine management ECM. The system will not work properly if the purge valve cannot be controlled. Possible failure
modes associated with the purge valve are listed below:
lValve drive open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply or ground.
lPurge valve or pipework blocked or restricted.
lPurge valve stuck open.
lPipework joints leaking or disconnected.
Possible symptoms associated with a purge valve or associated pipework failure is listed below:
lEngine may stall on return to idle if purge valve is stuck open.
lPoor idling quality if the purge valve is stuck open
lFuelling adaptions forced excessively lean if the EVAP canister is clear and the purge valve is stuck open.
lFuelling adaptions forced excessively rich if the EVAP canister is saturated and the purge valve is stuck open.
lSaturation of the EVAP canister if the purge valve is stuck closed.
Page 289 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-56 REPAIRS
Sensor - heated oxygen (HO2S) - pre-
catalytic converter
$% 19.22.16
Remove
1.Raise vehicle on a ramp.
2.Release HO
2S multiplug from support bracket.
3.Release HO
2S harness from clip and
disconnect multiplug from HO
2S .
4.Using a 22 mm crow's-foot spanner, remove
HO
2S.
CAUTION: HO
2 sensors are easily damaged
by dropping, excessive heat or
contamination. Care must be taken not to
damage the sensor housing or tip.Refit
1.Clean sensor and exhaust pipe mating
surfaces.
2.If refitting existing sensor, apply anti-seize
compound to sensor threads.
WARNING: Some types of anti-seize
compound used in service are a health
hazard. Avoid skin contact.
NOTE: A new HO
2 sensor is supplied pre-
treated with anti-seize compound.
3.Fit a new sealing washer to HO
2S
4.Fit HO
2S and tighten to 45 Nm (33 lbf.ft).
5. Connect multiplug to HO
2S, and secure to
support bracket and harness clip.
6.Lower vehicle.
Page 290 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
REPAIRS 17-2-57
Sensor - heated oxygen (HO2S) - post-
catalytic converter
$% 19.22.17
Remove
1.Raise vehicle on ramp.
2.Release HO
2S multiplug from support bracket.
3.Disconnect HO
2S multiplug from harness.
4.Using a 22 mm crowsfoot spanner, remove
HO
2S.
CAUTION: HO2 sensors are easily damaged
by dropping, excessive heat or
contamination. Care must be taken not to
damage the sensor housing or tip.Refit
1.Clean sensor and exhaust pipe mating
surfaces.
2.If refitting existing sensor, apply anti-seize
compound to sensor threads.
WARNING: Some types of anti-seize
compound used in service are a health
hazard. Avoid skin contact.
NOTE: A new HO2 sensor is supplied pre-
treated with anti-seize compound.
3.Fit a new sealing washer to HO
2S
4.Fit HO
2S and tighten to 45 Nm (33 lbf.ft).
5. Connect HO
2S multiplug to harness and fit
harness to bracket.
6.Secure harness to clip.
7.Lower vehicle.
Page 329 of 1529
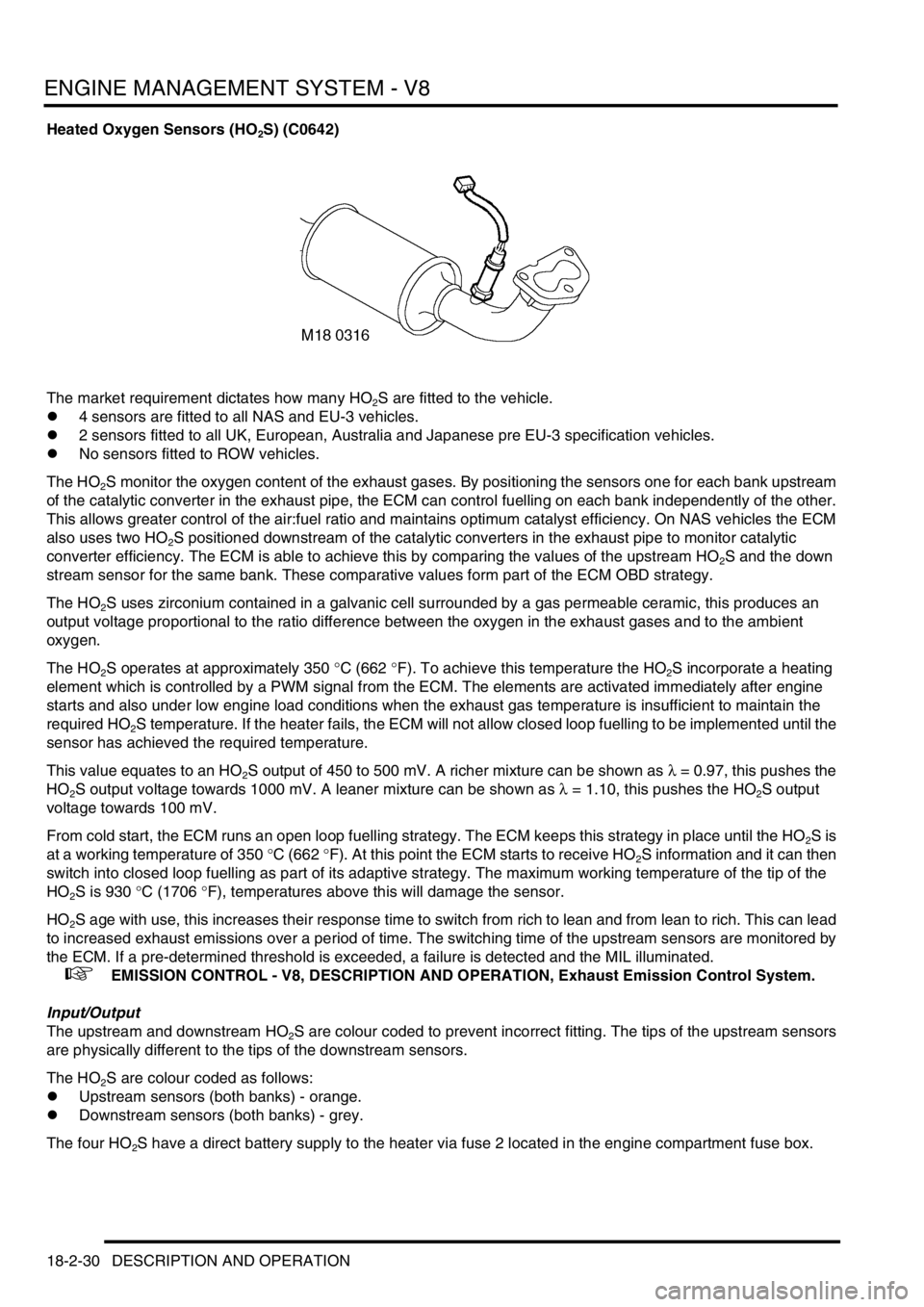
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-30 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Heated Oxygen Sensors (HO2S) (C0642)
The market requirement dictates how many HO
2S are fitted to the vehicle.
l4 sensors are fitted to all NAS and EU-3 vehicles.
l2 sensors fitted to all UK, European, Australia and Japanese pre EU-3 specification vehicles.
lNo sensors fitted to ROW vehicles.
The HO
2S monitor the oxygen content of the exhaust gases. By positioning the sensors one for each bank upstream
of the catalytic converter in the exhaust pipe, the ECM can control fuelling on each bank independently of the other.
This allows greater control of the air:fuel ratio and maintains optimum catalyst efficiency. On NAS vehicles the ECM
also uses two HO
2S positioned downstream of the catalytic converters in the exhaust pipe to monitor catalytic
converter efficiency. The ECM is able to achieve this by comparing the values of the upstream HO
2S and the down
stream sensor for the same bank. These comparative values form part of the ECM OBD strategy.
The HO
2S uses zirconium contained in a galvanic cell surrounded by a gas permeable ceramic, this produces an
output voltage proportional to the ratio difference between the oxygen in the exhaust gases and to the ambient
oxygen.
The HO
2S operates at approximately 350 °C (662 °F). To achieve this temperature the HO2S incorporate a heating
element which is controlled by a PWM signal from the ECM. The elements are activated immediately after engine
starts and also under low engine load conditions when the exhaust gas temperature is insufficient to maintain the
required HO
2S temperature. If the heater fails, the ECM will not allow closed loop fuelling to be implemented until the
sensor has achieved the required temperature.
This value equates to an HO
2S output of 450 to 500 mV. A richer mixture can be shown as λ = 0.97, this pushes the
HO
2S output voltage towards 1000 mV. A leaner mixture can be shown as λ = 1.10, this pushes the HO2S output
voltage towards 100 mV.
From cold start, the ECM runs an open loop fuelling strategy. The ECM keeps this strategy in place until the HO
2S is
at a working temperature of 350 °C (662 °F). At this point the ECM starts to receive HO
2S information and it can then
switch into closed loop fuelling as part of its adaptive strategy. The maximum working temperature of the tip of the
HO
2S is 930 °C (1706 °F), temperatures above this will damage the sensor.
HO
2S age with use, this increases their response time to switch from rich to lean and from lean to rich. This can lead
to increased exhaust emissions over a period of time. The switching time of the upstream sensors are monitored by
the ECM. If a pre-determined threshold is exceeded, a failure is detected and the MIL illuminated.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Exhaust Emission Control System.
Input/Output
The upstream and downstream HO
2S are colour coded to prevent incorrect fitting. The tips of the upstream sensors
are physically different to the tips of the downstream sensors.
The HO
2S are colour coded as follows:
lUpstream sensors (both banks) - orange.
lDownstream sensors (both banks) - grey.
The four HO
2S have a direct battery supply to the heater via fuse 2 located in the engine compartment fuse box.
Page 348 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-49
Operation - engine management
Fuel quantity
The ECM controls engine fuel quantity by providing sequential injection to the cylinders. Sequential injection allows
each injector to deliver fuel to the cylinders in the required firing order.
To achieve optimum fuel quantity under all driving conditions, the ECM provides an adaptive fuel strategy.
Conditions
Adaptive fuel strategy must be maintained under all throttle positions except:
lCold starting.
lHot starting.
lWide open throttle.
lAcceleration.
All of the throttle positions mentioned above are deemed to be 'open loop'. Open loop fuelling does not rely on
information from the HO
2 sensors, but the air/ fuel ratio is set directly by the ECM. During cold start conditions the
ECM uses ECT information to allow more fuel to be injected into the cylinders to facilitate cold starting. This strategy
is maintained until the HO
2 sensors are at working temperature and can pass exhaust gas information to the ECM.
Because of the specific nature of the other functions e.g. hot starting, idle, wide open throttle, and acceleration they
also require an 'open loop' strategy. For NAS vehicles with secondary air injection for cold start conditions, refer to
the Emissions section.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Secondary Air Injection System.
Adaptive fuel strategy also allows for wear in the engine and components, as well as slight differences in component
signals, as no two components will give exactly the same readings.
Function
To be able to calculate the amount of fuel to be injected into each cylinder, the ECM needs to determine the amount
of air mass drawn into each cylinder. To perform this calculation, the ECM processes information from the following
sensors:
lMass air flow (MAF) sensor.
lCrank speed and position (CKP) sensor.
lEngine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
lThrottle position (TP) sensor.
During one engine revolution, 4 of the 8 cylinders draw in air. The ECM uses CKP sensor information to determine
that one engine revolution has taken place, and the MAF sensor information to determine how much air has been
drawn into engine. The amount of air drawn into each cylinder is therefore 1/4 of the total amount measured by the
ECM via the MAF sensor.
The ECM refers the measured air mass against a fuel quantity map in its memory and then supplies an earth path to
the relevant fuel injector for a period corresponding to the exact amount of fuel to be injected into the lower inlet
manifold. This fuel quantity is in direct relation to the air mass drawn into each cylinder to provide the optimum ratio.
During adaptive fuelling conditions, information from the heated oxygen sensors (HO
2S) is used by the ECM to correct
the fuel quantity to keep the air/ fuel ratio as close to the stoichiometric ideal as possible.
Closed loop fuelling
The ECM uses a closed loop fuelling system as part of its fuelling strategy. The operation of the three-way catalytic
converter relies on the ECM being able to optimise the air/ fuel mixture, switching between rich and lean either side
of lambda one. Closed loop fuelling is not standard for all markets, vehicles that are not fitted with HO
2S do not have
closed loop fuelling.
The ideal stoichiometric ratio is represented by λ =1. The ratio can be explained as 14.7 parts of air to every 1 part of
fuel.
Page 358 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-59
⇒ Drive cycle C:
1Switch ignition on for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 60°C (140°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph (0 to 60 km/h) with light pedal pressure).
5Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph (0 to 70 km/h) with moderate pedal pressure).
6Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph (0 to 90 km/h) with heavy pedal pressure).
7Cruise at 60 mph (100 km/h) for 8 minutes.
8Cruise at 50 mph (80 km/h) for 3 minutes.
9Allow engine to idle for 3 minutes.
10Connect TestBook and with the engine still running, check for fault codes.
NOTE: The following areas have an associated readiness test which must be flagged as complete, before a problem
resolution can be verified:
lcatalytic converter fault;
lEvaporative loss system fault;
lHO
2 sensor fault;
lHO
2 sensor heater fault.
When carrying out a drive cycle C to determine a fault in any of the above areas, select the readiness test icon to
verify that the test has been flagged as complete.
⇒ Drive cycle D:
1Switch ignition on for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 35°C (95°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph (0 to 60 km/h) with light pedal pressure).
5Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph (0 to 70 km/h) with moderate pedal pressure).
6Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph (0 to 90 km/h) with heavy pedal pressure).
7Cruise at 60 mph (100 km/h) for 5 minutes.
8Cruise at 50 mph (80 km/h) for 5 minutes.
9Cruise at 35 mph (60 km/h) for 5 minutes.
10Allow engine to idle for 2 minutes.
11Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.
⇒ Drive cycle E:
1Ensure fuel tank is at least a quarter full.
2Carry out Drive Cycle A.
3Switch off ignition.
4Leave vehicle undisturbed for 20 minutes.
5Switch on ignition.
6Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.