1999 LAND ROVER DEFENDER fuel pump
[x] Cancel search: fuel pumpPage 259 of 667

19FUEL SYSTEM
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Fuel Pump
The fuel pump assembly comprises a top cover which locates the electrical connector, and four fuel pipe
couplings. The top cover is attached to a plastic cup shaped housing and retained on three sliding clips. Two coil
springs are located between the cover and the housing and ensure that the fuel pump remains seated positively at
the bottom of the tank when installed.
The housing locates the two stage fuel pump and also the fuel gauge sender unit. The lower part of the housing is
the swirl pot which maintains a constant level of fuel at the fuel pick-up. A coarse filter is located in the base of the
housing and prevents the ingress of contaminants into the pump and the fuel system from the fuel being drawn
into the pump. A fine filter is located in the intake to the low pressure stage to protect the pump from
contaminants. Flexible pipes connect the couplings on the top cover to the pump.
A non-return valve is located in the base of the housing. When the fuel tank is full, fuel pressure keeps the valve
lifted from its seat, allowing fuel to flow into the swirl pot. As the tank level reduces, the fuel pressure in the tank
reduces causing the valve to close. When the valve is closed, fuel is retained in the swirl pot, ensuring that the
swirl pot remains full and maintains a constant supply to the fuel pump.
The two stage pump comprises a high and low pressure stage. The low pressure stage draws fuel from the swirl
pot through a filter. The low pressure stage pumps fluid at a pressure of 0.75 bar (10.9 lbf.in) and a flow of 30
litres/hour (8 US Gallons/hour) to the fuel filter. A proportion of the fuel from the low pressure stage also passes,
via a restrictor, through a jet pump which keeps fuel circulating in the swirl pot. The high pressure stage draws the
low pressure fuel from the fuel filter and pressurises it to a pressure of 4.0 bar (58 lbf.in). The pressurised fuel is
then passed from the pump to the injectors at a flow of 180 litres/hour (47.6 US Gallons/hour). A fuel pressure
regulator is located at the rear of the engine and ensures that the delivery pressure remains at 4.0 bar (58 lbf.in)
by controlling the amount of fuel returning to the fuel tank.
The fuel pump has a maximum current draw of 15 Amps at 12 Volts and is supplied a feed (C0114-1) from the fuel
pump relay (C0730-2) on a white/purple wire.
Fuel Gauge Sender
The fuel gauge sender unit comprises a rotary potentiometer operated by a float. The float rises and falls with the
fuel level in the tank and moves the potentiometer accordingly.
A feed is supplied to the fuel gauge sender (C0114-1) by the fuel pump relay (C0730-2) on a purple/white then
white/purple wire. The sender is earthed (C0114-3) on a slate/black wire via header 287. The output voltage
(C0114-2) from the sender to the instrument pack (C1061-3) varies in relation to the fuel level. This output voltage
is connected to the fuel gauge C1054-2). The fuel gauge receives a battery voltage input (C1054-3) on a
white/green wire. This is compared with the output voltage from the potentiometer. The difference between the two
voltages determines the deflection of the fuel gauge pointer.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 260 of 667

FUEL SYSTEM
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
NOTE: Non EU3 Model illustrated.
1.Gasket
2.Housing
3.Bolt
4.Fuel feed union and pipe
5.Fuel return union and hose
6.Fuel temperature sensor
7.Bonded seal8.’O’ring
9.Circlip
10.Fuel pressure regulator
11.’O’ring
12.’O’ring
13.Gauze filter
The fuel pressure regulator is located in a cast alloy housing which is attached to the rear right hand corner of the
cylinder head with three flanged bolts and sealed with a metal gasket. Two ports in the housing connect with ports
in the cylinder head for fuel pressure feed and return. A gauze filter is located in the pressure feed port in the
cylinder head, and filters the fuel before it reaches the injectors. The filter is a fit for life item but can be changed if
required. An’O’ring is located in a recess in the cylinder head and provides additional sealing for the pressure
feed port between the gauze filter, the cylinder head, and the housing.
A union and pipe is attached to the feed port in the housing and connects with a quick release coupling to the fuel
pressure feed pipe from the fuel pump. A second union and hose is located in the return port and provides the fuel
return connection to the fuel cooler. A third port provides location for the fuel temperature sensor, which is sealed
to the housing with a bonded seal. The fuel temperature sensor is used by the ECM for engine management.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 261 of 667

19FUEL SYSTEM
6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION The fuel pressure regulator is located in a machined port in the lower part of the housing. The regulator is sealed
in the housing with two’O’rings and secured with an internal clip.
The regulator maintains the fuel pump delivery pressure at 4 bar (58 lbf.in
2). When the fuel pressure exceeds 4
bar (58 lbf.in2), the regulator opens and allows fuel to return to the fuel tank via the fuel cooler. The fuel returned
from the regulator is directed back into the fuel filter before being drawn by the high pressure stage of the fuel
pump and directed back to the injectors. A special tool can be attached to the regulator housing fuel feed port and
allows for the fitment of a suitable gauge to measure fuel pump delivery pressure.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 262 of 667

FUEL SYSTEM
7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION INJECTORS
1.Solenoid housing
2.Electrical connector
3.Push rod socket
4.Push rod return spring
5.Housing
6.Fuel delivery port7.Fuel return port
8.Nozzle cap nut
9.Copper washer
10.Nozzle
11.’O’ring
12.Cap screw
The five injectors are located in the cylinder head adjacent the camshaft, with the nozzle of each injector
protruding directly into the cylinder. Each injector is sealed into the cylinder head with a’O’ring and copper
washer and secured with a clamp and bolt.
Each injector is operated mechanically by an overhead camshaft and rocker, and electrically by a solenoid
controlled by the ECM. Each injector is supplied with pressurised fuel from the pump via the regulator housing and
internal drillings in the cylinder head.
The solenoid housing is secured to the injector body with two cap screws and is a sealed unit. It has a two pin
electrical connector on its top face.
The injector body is machined from a forging. The body has a machined central bore which locates the push rod.
A thread on the outer diameter provides the attachment for the nozzle cap nut. The body also provides attachment
for the solenoid housing.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 263 of 667

19FUEL SYSTEM
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION The injector push rod is operated from the rocker and cam assembly by a sprocket. The push rod is located in the
housing bore and retained in its extended position by a push rod return spring. The powerful spring ensures that
the push rod socket is always in contact with the rocking lever and the cam.
The lower part of the injector housing locates the spring loaded nozzle. The nozzle is retained in the housing by a
nozzle cap nut which is screwed onto the housing. The nozzle cap nut has four holes around its circumference
which connect to the fuel pump drilling in the cylinder head. The injector housing has ports located above the
nozzle cap nut which connect with the fuel delivery drilling in the cylinder head. An’O’ring seals the injector in the
machined location in the cylinder head and a copper washer seals the injector from the combustion chamber.
The injectors are supplied with pressurised fuel from the fuel pump via the pressure regulator housing and internal
drillings in the cylinder head. Each injector sprays fuel directly into the cylinder at approximately 1500 bar (22000
lbf.in) atomising the fuel and mixing it with intake air prior to combustion.
The camshaft and rocker arrangement depresses the push rod which pressurises the fuel within the injector.
When the injector is required to inject fuel into the cylinder, the ECM energises the solenoid which closes a valve
within the solenoid housing. The closure of the valve stops the fuel entering the return line to the pump, trapping it
in the injector. The compression of the fuel by the push rod causes rapid pressurisation of the fuel which lifts the
injector nozzle, forcing the fuel into the cylinder at high pressure. The ECM controls the injection timing by altering
the time at which the solenoid is energised and the injection period by controlling the period for which the solenoid
is energised.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 264 of 667
FUEL SYSTEM
9
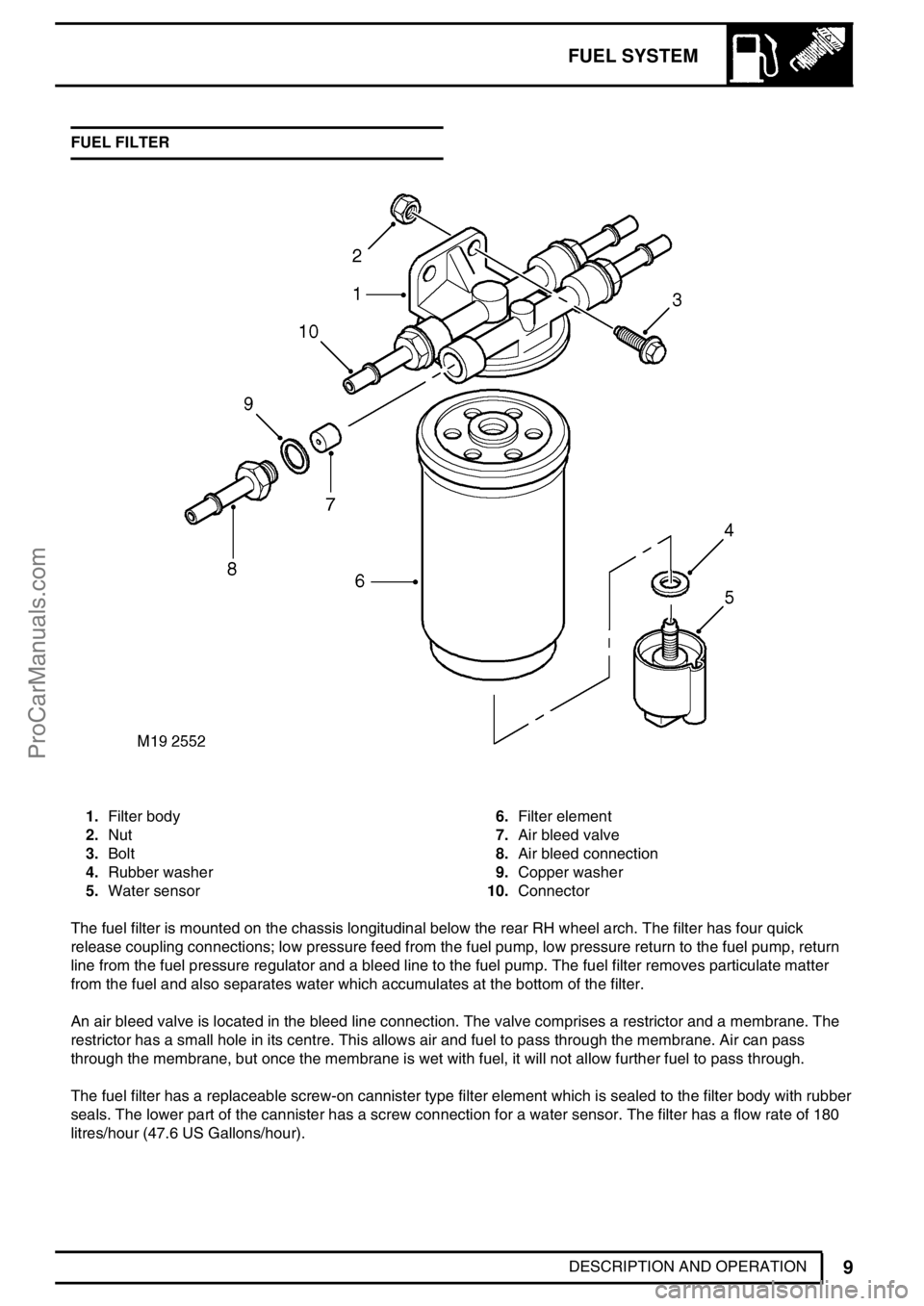
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION FUEL FILTER
1.Filter body
2.Nut
3.Bolt
4.Rubber washer
5.Water sensor6.Filter element
7.Air bleed valve
8.Air bleed connection
9.Copper washer
10.Connector
The fuel filter is mounted on the chassis longitudinal below the rear RH wheel arch. The filter has four quick
release coupling connections; low pressure feed from the fuel pump, low pressure return to the fuel pump, return
line from the fuel pressure regulator and a bleed line to the fuel pump. The fuel filter removes particulate matter
from the fuel and also separates water which accumulates at the bottom of the filter.
An air bleed valve is located in the bleed line connection. The valve comprises a restrictor and a membrane. The
restrictor has a small hole in its centre. This allows air and fuel to pass through the membrane. Air can pass
through the membrane, but once the membrane is wet with fuel, it will not allow further fuel to pass through.
The fuel filter has a replaceable screw-on cannister type filter element which is sealed to the filter body with rubber
seals. The lower part of the cannister has a screw connection for a water sensor. The filter has a flow rate of 180
litres/hour (47.6 US Gallons/hour).
ProCarManuals.com
Page 266 of 667

FUEL SYSTEM
11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OPERATION
The low pressure stage of the fuel pump draws fuel from the swirl pot and pumps it into the fuel filter. The high
pressure stage of the fuel pump draws the fuel from the fuel filter and pumps it along the fuel feed pipe to the
cylinder head.
The fuel enters the cylinder head through a connection on the fuel pressure regulator housing and supplies each
injector with pressurised fuel. The fuel pressure regulator maintains the fuel pressure at the injectors at 4 bar (58
lbf.in) by returning excess fuel back to the fuel filter. The returned fuel passes through the fuel cooler in the engine
compartment before it passes to the fuel filter.
When the engine is running, each injector is operated by an overhead camshaft which depresses a push rod in
each injector at a timed interval. When the cam has depressed the push rod and the push rod is returning to its
extended position, fuel is drawn from the fuel supply drilling in the injector.
When the ECM determines that injection is required, the ECM transmits an electrical pulse which energises the
fast acting solenoid, closing the spill valve on the injector and locking fuel in the injector body. As the cam begins
to depress the push rod, the fuel in the injector is rapidly pressurised. When the pressure exceeds the nozzle
spring pressure, the nozzle opens and injects fuel at very high pressure into the cylinder.
When the ECM determines that the injection period should end, the solenoid is rapidly de-energised, opening the
spill valve on the injector and allowing fuel to pass into the return circuit.
The ECM controls the injection timing by altering the time at which the solenoid is energised, and the injection
period by controlling the period for which the solenoid is energised.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 279 of 667

19FUEL SYSTEM
10
REPAIR POTENTIOMETER - THROTTLE
Service repair no - 19.30.14
Remove
NOTE: The throttle potentiometer is an
integral part of the throttle pedal assembly
and must not be dismantled.
1.With assistance remove 2 nuts and bolts
securing throttle pedal to body.
2.Disconnect multiplug from throttle potentiometer
and remove throttle pedal.
Refit
NOTE: From Vin 607225 a three track
throttle potentiometer was fitted in place
of a two track potentiometer. Three track
potentiometers cannot be fitted to vehicles
previously fitted with two track potentiometers.
Two track potentiometers can be fitted to vehicles
previously fitted with three track potentiometers,
but TestBook must be used to configure the ECM.
3.Connect multiplug to throttle potentiometer.
4.Position throttle pedal assembly, tighten nuts
and bolts to25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).PUMP - FUEL
Service repair no - 19.45.08
Remove
1.Remove fuel tank.See this Section.
2.UsingLRT-19-009remove locking ring from fuel
pump housing.
3.Remove fuel pump from tank and discard
sealing ring.
Refit
4.Clean pump housing and mating face on fuel
tank.
5.Fit seal to pump housing.
6.Fit pump to fuel tank and secure with locking
ring.
7.Fit fuel tank.See this Section.
ProCarManuals.com