1999 LAND ROVER DEFENDER water pump
[x] Cancel search: water pumpPage 26 of 667

GENERAL SPECIFICATION DATA
3
INFORMATION FUEL SYSTEM - Td5
Type Direct injection from pressure regulated supply with.................................................................................
cooled return flow
Pressure regulator setting 4 bar (58 lbf.in
2) ................................................
Pump Electric two stage submersible................................................................................
Pump output
Low pressure 30 l/h (6.6 gal/h) at 0.5 bar (7.25 lbf.in
2) ..........................................................
High pressure 180 l/h (39.6 gal/h) at 4 bar (58 lbf.in2) ..........................................................
Max consumption 30 l/h (6.6 gal/h).............................................................
Injectors Electronic unit injectors...........................................................................
Injector normal operating pressure 1500 bar (21750 lbf.in
2) ..................................
Filter In-line canister filter/water separator with water.................................................................................
detection
COOLING SYSTEM - Td5
Type Pressurised spill return partial flow, thermostatically.................................................................................
controlled
Cooling fans 11 blade axial flow on viscous coupling and 11 blade.....................................................................
axial flow electric
Electric cooling fan switching points
On Vehicle speeds of 50 mph (80 km/h) and below while...........................................................................
ambient temperature is 28°C (82°F) or above
Off Vehicle speeds of 62.5 mph (100 km/h) and above or...........................................................................
ambient temperatures of 25°C (77°F) and below
Coolant pump Centrifugal impeller, belt driven from crankshaft...................................................................
Thermostat Waxstat with pressure relief valve.......................................................................
Thermostat opening temperature
Initial opening 82°C (179°F) ..........................................................
Fully open 96°C (204°F) ...............................................................
Expansion tank cap relief valve operating pressure 1.4 bar (20.3 lbf.in
2) .........
CLUTCH - Td5
Type Diaphragm spring, hydraulically operated with.................................................................................
self-centering pre-loaded release bearing
Drive plate diameter 267 mm.........................................................
Pressure plate diameter 270 mm...................................................
ProCarManuals.com
Page 110 of 667

ENGINE
25
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION CYLINDER HEAD COMPONENTS
The cylinder head components are described below:
Cylinder head
The cylinder head is of aluminium construction. It is not possible to reface the cylinder head if it becomes worn or
damaged. An alloy camshaft carrier is bolted directly to the upper surface of the cylinder head. Two dowels are
included in the cylinder head upper face for correct location of the camshaft carrier.
The EU3 cylinder head has a single internal fuel rail for delivering fuel to the injectors and an external fuel pipe for
returning spill fuel back to the fuel connector block. Therefore, pre EU3 and EU3 cylinder heads are not
interchangeable.
CAUTION: The cylinder head incorporates drillings for the fuel injection system, any
contamination which enters these drillings could cause engine running problems or injector
failure. It is therefore, essential that absolute cleanliness is maintained when carrying out work on
the cylinder head.
The camshaft carrier and cylinder head assembly is attached to the cylinder block by twelve cylinder head
retaining bolts which pass through the camshaft carrier and the cylinder head to secure the assembly to the
cylinder block.
CAUTION: The valve heads, tips of the injectors and glow plugs protrude below the face of the
cylinder head and will be damaged if the cylinder head is stored face down.
The camshaft is located between the cylinder head and the camshaft carrier, and the bearing journals are line
bored between the two components to form a matched pair.
CAUTION: Always fit plugs to open connections to prevent contamination.
The valve guides and valve seat inserts are sintered components which are an interference fit to the cylinder
head. The cylinder head machining also provide the locations for the electronic unit injectors, glow plugs, hydraulic
lash adjusters, finger followers and low pressure fuel rail.
Cooling to the cylinder head is provided by coolant flow through a water jacket machined into the cylinder head.
Drillings through the block provide lubrication channels for pressurised oil supply to cylinder head components
such as the lash adjusters, finger followers, rocker arms and camshaft bearings.
A coolant outlet elbow is fitted to the front LH side of the cylinder head to allow flow of coolant from the cylinder
head back to the radiator. A metal gasket is used to seal the joint between the water outlet elbow and the cylinder
head. A coolant temperature sensor is located in a port in the side of the water outlet elbow for monitoring coolant
temperature.
A stub pipe is connected at the front RH side of the cylinder block above the timing cover which connects a pipe to
supply oil to the vacuum pump. The timing chain tensioner adjuster is screwed in a thread in the cylinder head at a
location on the front RH side of the engine below the oil feed port for the vacuum pump.
An access hole for the camshaft gear is included at the front of the cylinder head which is sealed with a plastic
plug and rubber’O’ring. A press-fit core plug for the chain chest is located on the front face of the cylinder head.
A press-fit core plug for the cylinder head water jacket is located at the rear of the cylinder head and a threaded
brass plug for the water jacket is located on the LH side of the cylinder head beneath the exhaust manifold
assembly.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 254 of 667

19 - FUEL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
Page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COMPONENT LOCATION 1...................................................................................
DESCRIPTION 2.....................................................................................................
FUEL PUMP AND FUEL GAUGE SENDER 3........................................................
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR 5........................................................................
INJECTORS 7.........................................................................................................
FUEL FILTER 9.......................................................................................................
WATER SENSOR 10..............................................................................................
OPERATION 11......................................................................................................
ADJUSTMENT
HEATER PLUG TEST 1..........................................................................................
FUEL SYSTEM - BLEED 1.....................................................................................
FUEL TANK - DRAIN 2...........................................................................................
REPAIR
ELEMENT - AIR FILTER 1......................................................................................
SENSOR - FUEL TEMPERATURE 1......................................................................
SWITCH - INERTIA - FUEL CUT OFF 2.................................................................
SENSOR - MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) 2....................................................................
SENSOR - COMBINED MAP AND IAT 3................................................................
SENSOR - AMBIENT AIR PRESSURE (AAP) 3.....................................................
ELEMENT - FUEL FILTER 4...................................................................................
COOLER - FUEL 4..................................................................................................
TURBOCHARGER 5...............................................................................................
FILTER ASSEMBLY - AIR 6...................................................................................
INJECTOR - SET 7.................................................................................................
HEATER PLUGS - SET 9.......................................................................................
INTERCOOLER 9...................................................................................................
POTENTIOMETER - THROTTLE 10......................................................................
PUMP - FUEL 10.....................................................................................................
REGULATOR - FUEL PRESSURE 11....................................................................
FUEL TANK 12.......................................................................................................
NECK - FUEL TANK FILLER 14.............................................................................
ProCarManuals.com
Page 256 of 667

FUEL SYSTEM
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION COMPONENT LOCATION
1.HP stage
2.LP stage
3.Filters
4.Jet pump
5.Fuel pump and fuel gauge sender unit
6.LP return connection
7.LP feed connection8.HP feed connection
9.Air bleed connection
10.Fuel filter
11.Water sensor
12.Fuel cooler
13.Fuel pressure regulator
14.Electronic Unit Injectors
ProCarManuals.com
Page 257 of 667

19FUEL SYSTEM
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
General
The fuel delivery system comprises a fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, five injectors and a fuel filter.
The system is controlled by the ECM, which energises the fuel pump relay and controls the operation and timing
of each injector solenoid.
Unlike other Diesel engines, the Td5 has no injection pump. The diesel direct injection system receives fuel at
pressure from a two stage fuel pump located in the fuel tank. The system incorporates a fuel return to the fuel
pump, via a fuel cooler attached to the inlet manifold, and a fuel filter. A fuel pressure regulator is located in a
housing on the rear of the cylinder head. The regulator maintains the fuel delivered to the injectors at a constant
pressure and returns excess fuel back to the fuel filter and pump via the fuel cooler.
A fuel filter is positioned on the chassis longitudinal, below the RH rear wheel arch. The fuel feed and return to and
from the engine passes through the filter. The filter also incorporates a water sensor, which illuminates a warning
lamp in the instrument pack.
A moulded fuel tank is located at the rear underside of the vehicle between the chassis longitudinals. The tank
provides the attachment for the fuel pump and the fuel gauge sender unit, which is located inside the tank.
Fuel Tank and Breather
The fuel tank and breather system is a major part of the fuel delivery system. The fuel tank and breathers are
located at the rear of the vehicle between the chassis longitudinals.
Fuel Tank
The moulded fuel tank is made from High Molecular Weight (HMW) High Density Polyethylene (HDPE), and is
manufactured using a proportion of recycled plastic.
The tank is held in position by a metal cradle which is secured to the chassis cross members by four bolts, two
holding the front of the cradle in position, two holding the rear. The fuel tank has a useable capacity of 75 litres
(16.5 gallons).
An aperture in the top surface of the tank allows for the fitment of the fuel pump and fuel gauge sender unit, which
is retained with a locking ring. A reflective metallic covering is attached to the tank with three scrivets to shield the
tank from heat generated by the exhaust system.
Fuel Tank Breather System
The fuel tank filler tube incorporates a tank vent which allows air and fuel vapour displaced from the tank when
filling to vent to atmosphere via the filler neck.
A breather spout within the tank controls the tank’Full’height. When fuel covers the spout it prevents fuel vapour
and air from escaping from the tank. This causes the fuel to’back-up’in the filler tube and shuts off the filler gun.
The position of the spout ensures that when the filler gun shuts off, a vapour space of approximately 10% of the
tanks total capacity remains. The vapour space ensures that the Roll Over Value (ROV) is always above the fuel
level and vapour can escape and allow the tank to breathe.
The ROV is welded to the top surface of the tank. It is connected by a tube to the filler tube, which in turn is
connected to the atmospheric vent pipe. The ROV allows fuel vapour to pass through it during normal vehicle
operation. In the event of the vehicle being overturned the valve shuts off, sealing the tank and preventing fuel
from spilling from the atmospheric vent pipe.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 264 of 667
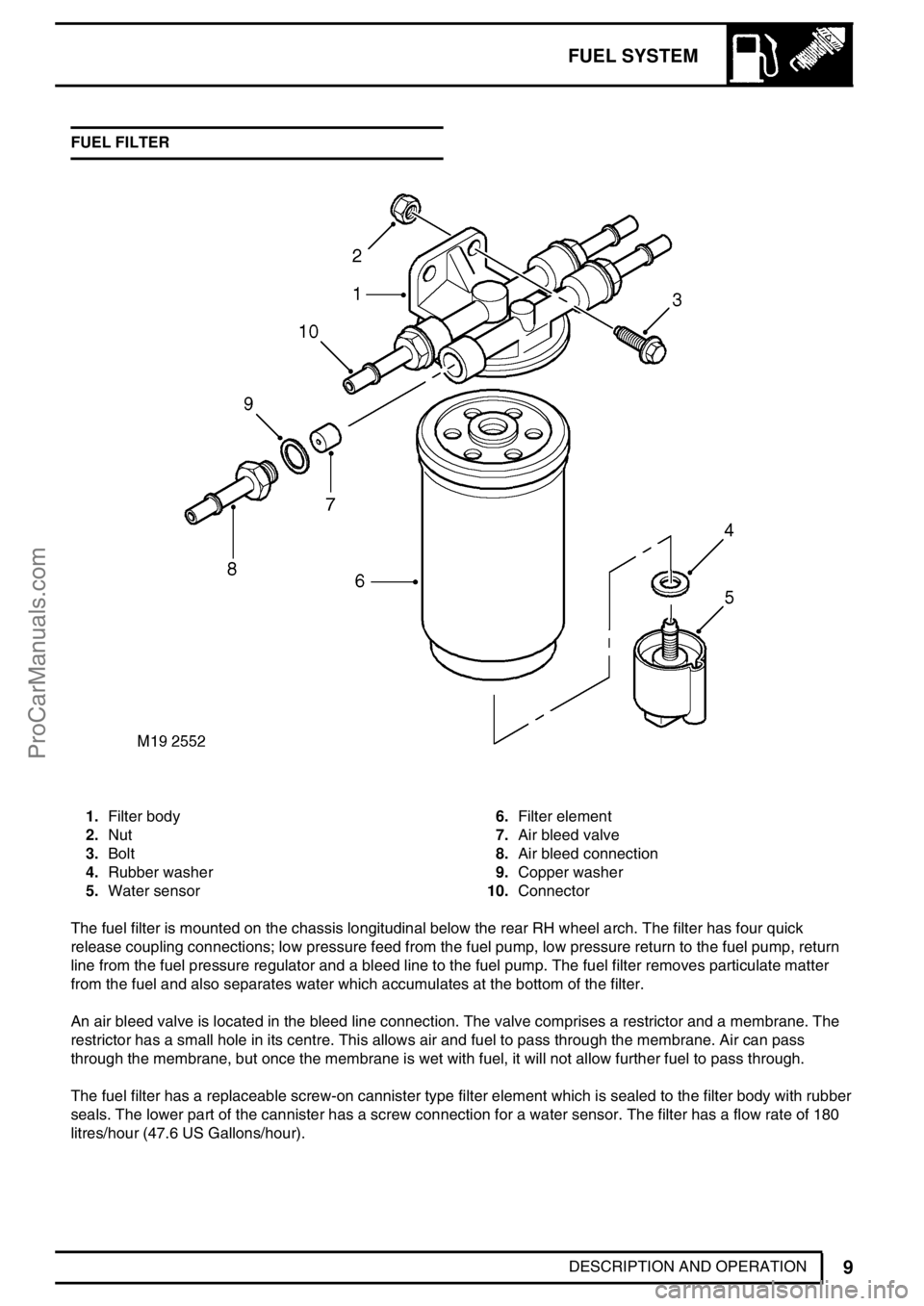
FUEL SYSTEM
9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION FUEL FILTER
1.Filter body
2.Nut
3.Bolt
4.Rubber washer
5.Water sensor6.Filter element
7.Air bleed valve
8.Air bleed connection
9.Copper washer
10.Connector
The fuel filter is mounted on the chassis longitudinal below the rear RH wheel arch. The filter has four quick
release coupling connections; low pressure feed from the fuel pump, low pressure return to the fuel pump, return
line from the fuel pressure regulator and a bleed line to the fuel pump. The fuel filter removes particulate matter
from the fuel and also separates water which accumulates at the bottom of the filter.
An air bleed valve is located in the bleed line connection. The valve comprises a restrictor and a membrane. The
restrictor has a small hole in its centre. This allows air and fuel to pass through the membrane. Air can pass
through the membrane, but once the membrane is wet with fuel, it will not allow further fuel to pass through.
The fuel filter has a replaceable screw-on cannister type filter element which is sealed to the filter body with rubber
seals. The lower part of the cannister has a screw connection for a water sensor. The filter has a flow rate of 180
litres/hour (47.6 US Gallons/hour).
ProCarManuals.com
Page 292 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION A - EU 3 Models
B- Pre EU3 Models
GENERAL
The cooling system used on the Diesel engine is a pressure relief by-pass type system which allows coolant to
circulate around the engine block and heater circuit when the thermostat is closed. With coolant not passing
through the by-pass or the radiator promotes faster heater warm-up which in turn improves passenger comfort.
A coolant pump is mounted on a casting behind the PAS pump and is driven from the PAS pump at crankshaft
speed by the auxiliary drive belt. The pump mounting casting connects with passages in the cylinder block and
pumps coolant from the radiator through the cylinder block.
A viscous fan is attached to an idler pulley at the front of the engine. The fan is attached to a threaded spigot on
the pulley with a right hand threaded nut. The fan draws air through the radiator to assist in cooling when the
vehicle is stationary. The fan rotational speed is controlled relative to the running temperature of the engine by a
thermostatic valve regulated by a bi-metallic coil.
The cooling system uses a 50/50 mix of anti-freeze and water.
Thermostat Housing
A plastic thermostat housing is located behind the radiator. The housing has three connections which locate the
radiator bottom hose, top hose and coolant pump feed pipe. The housing contains a wax element thermostat and
a spring loaded by-pass flow valve.
Thermostat - Main valve
The thermostat is used to maintain the coolant at the optimum temperature for efficient combustion and to aid
engine warm-up. The thermostat is closed at temperatures below approximately 82°C (179°F). When the coolant
temperature reaches approximately 82°C the thermostat starts to open and is fully open at approximately 96°C
(204°F). In this condition the full flow of coolant is directed through the radiator.
The thermostat is exposed to 90% hot coolant from the engine on one side and 10% cold coolant returning from
the radiator bottom hose on the other side.
Hot coolant from the engine passes from the by-pass pipe through four sensing holes in the flow valve into a tube
surrounding 90% of the thermostat sensitive area. Cold coolant returning from the radiator, cooled by the ambient
air, conducts through 10% of the thermostat sensitive area.
In cold ambient temperatures, the engine temperature is raised approximately 10°C (50°F) to compensate for the
heat loss of 10% exposure to the cold coolant returning from the radiator bottom hose.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 294 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Radiator
The 44 row radiator is located at the front of the vehicle in the engine compartment. The cross flow type radiator is
manufactured from aluminium with moulded plastic end tanks interconnected with tubes. The bottom four rows are
separate from the upper radiator and form the lower radiator for the fuel cooler. Aluminium fins are located
between the tubes and conduct heat from the hot coolant flowing through the tubes, reducing the coolant
temperature as it flows through the radiator. Air intake from the front of the vehicle when moving carries the heat
away from the fins. When the vehicle is stationary, the viscous fan draws air through the radiator fins to prevent
the engine from overheating.
Two connections at the top of the radiator provide for the attachment of the top hose from the outlet housing and
bleed pipe to the expansion tank. Three connections at the bottom of the radiator allow for the attachment of the
bottom hose to the thermostat housing and the return hose from the oil cooler and the feed hose to the fuel cooler.
The bottom four rows of the lower radiator are dedicated to the fuel cooler. The upper of the two connections at
the bottom of the radiator receives coolant from the oil cooler. This is fed through the four rows of the lower
radiator in a dual pass and emerges at the lower connection. The dual pass lowers the coolant temperature by up
to 24°C before being passed to the fuel cooler. Two smaller radiators are located in front of the cooling radiator.
The upper radiator is the intercooler for the air intake system and the lower radiator provides cooling of the
gearbox oil.
Pipes and Hoses
The coolant circuit comprises flexible hoses and metal formed pipes which direct the coolant into and out of the
engine, radiator and heater matrix. Plastic pipes are used for the bleed and overflow pipes to the expansion tank.
A bleed screw is installed in the radiator top hose and is used to bleed air during system filling. A drain plug to
drain the heater and cylinder block circuit of coolant is located on the underside of the coolant pump feed pipe.
Oil Cooler
The oil cooler is located on the left hand side of the engine block behind the oil centrifuge and oil filter. Oil from the
oil pump is passed through a heat exchanger which is surrounded by coolant in a housing on the side of the
engine.
Full water pump flow is directed along the cooler housing which also distributes the flow evenly along the block
into three core holes for cylinder cooling. This cools the engine oil before it is passed into the engine. A small
percentage of the coolant from the oil cooler passes into a metal pipe behind the engine. It then flows into the
lower radiator via a hose.
Fuel Cooler
The fuel cooler is located on the right hand side of the engine and is attached to the inlet manifold. The cooler is
cylindrical in design and has a coolant feed connection at its forward end. A’T’connection at the rear of the cooler
provides a connection for the coolant return from the heater matrix and coolant return from the fuel cooler.
The’T’connection houses a thermostat which opens at approximately 82°C. This prevents the cooler operating in
cold climates. Two quick release couplings on the cooler allow for the connection of the fuel feed from the
pressure regulator and return to the fuel tank. A counter flow system is used within the cooler.
Fuel flows around a coolant jacket within the cooler and flows from the back to the front of the cooler. As the hot
fuel cools travelling slowly forwards it meets progressively colder coolant travelling in the opposite direction
maintaining a differential cooling effect.
ProCarManuals.com