1999 HONDA CIVIC PCM
[x] Cancel search: PCMPage 1961 of 2189

- How the Circuit Works
Radiator Fan
Voltage is provided at all times to the radiator fan
relay (contacts) through fuse 57. With the ignition
swilch in ON (ll), voltage is provided to the coil of
the relay through luse 17.
The radiator tan relay can be grounded through
either the engine coolant temperature switch or the
engine control module (ECM) or powertrain control
module (PCM).
The engine coolant temperature switch grounds
the radiator fan relay (coil) when the engine
coolant temperature exceeds 199'F (83'C). The
switch opens when coolanl temperature
decreases 3'- 8'C.
Condenser Fan
Voltage is provided at all times to the condenser fan
relay (contacts) through fuse 56. With the ignition
switch in ON (ll), voltage is provided to the coil of
the relay through fuse 17. When you push the A'lC
switch and put the heater fan switch in 1, 2,3, o( 4
position, the ly'C thermostat comes on, the
condenser fan relay energizes, and the condenser
fan motor runs.
A,/C Thermostat
The A,/C thermostat is located on the evaporator
housing. The A,/C thermostat tums off the A/C
compressor clutch if the temperature at the
evaporator goes below 3'C (37'F). This prevents
condensation from freezing on the evaporator fins
and blocking the air delivery into the passenger
compartment. lf the temperature goes below 3'C
(37"F) tuming off the Ay'C thermostat, ground will be
removed from the condenser fan relay. This will
deenergize the relay and remove voltage from the
condenser fan motor causing the fan to stop running.
Reter to the Service Manual (Section 23, Eleckical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
63-3
Page 1972 of 2189
![HONDA CIVIC 1999 6.G Workshop Manual Low Fuel Indicator Light
l
t
I
I
I
IJ
pag6 106.
,
-ls,T,*-*:lligff*,
l,;l:l?,
A3A
!-{ilril}-1 PowERTRAtNI Lowtuel I CONTROL
I i$grtor I MoD]LE (pcM)
i
S i18l7"*
UNDER.DASHFUSE/RELAYBOXPHOTO 5 HONDA CIVIC 1999 6.G Workshop Manual Low Fuel Indicator Light
l
t
I
I
I
IJ
pag6 106.
,
-ls,T,*-*:lligff*,
l,;l:l?,
A3A
!-{ilril}-1 PowERTRAtNI Lowtuel I CONTROL
I i$grtor I MoD]LE (pcM)
i
S i18l7"*
UNDER.DASHFUSE/RELAYBOXPHOTO 5](/manual-img/13/6068/w960_6068-1971.png)
Low Fuel Indicator Light
l
't
I
I
I
IJ
pag6 106.
,
-ls,T,*-*:lligff*,
l',;l:'l?,'
A3A
!'-{ilril}-1 PowERTRAtNI Lowtuel I CONTROL
I i$grtor I MoD]LE (pcM)
i
S' i18l7"*
UNDER.DASHFUSE/RELAYBOXPHOTO 58
!ra
or*+* i
TFI i
--l------i"I
I
A oxc€pt GX
c503PHO|O 61
AFN/GFI{
9FN/GBN
15
BLU/FEO
c410
vlEw 3s
c'131PHO|O A5vtEw 59
I TANK: UNITThan|tlrlor
So€qauges
L-----J- ----J
Sae GroundDistribution,pa$ 14-9.
74
Page 1973 of 2189

How the Gircuit Works
All Except GX
Do not smoke while working on the fuel system.
Keep open flame away trom the work area. Drain
fuel only into an approved container.
A thermistor is mounted in the fuel tank unit. When
the thermistor is cool, its resistance is very high.
When the thermistor's temperature increases, its
resistance decreases. Fuel in the fuel tank transters
heat away lrom the thermistor fast enough to keep it
cool so the thermistor's resistance stays high and
lhe low fuel indicator light does not come on. When
the fuel level drops below the thermistor, the
thermistor's temoerature increases. Without the fuel
to cool it, the thermistor's resislance decreases,
allowing current to llow through the low fuel
indicator light and the thermistor to ground, and the
low fuel indicator light comes on.
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
GX
The PCM turns on the low fuel indicator light when
the fuel level is low. The PCM will also blink the
indicator light when a problem is detected by the
fuel tank pressure sensor or the fuel tank
temperature sensor.
Refer to the Service Manual GX Supplement
(Section 11 , Fuel and Emissions) for specific tests
or troubleshooting procedures.
74-1
Page 1980 of 2189

Gauges (cont'd)
- How the Gircuit Works
When the ignition switch is in ON (ll) or START (lll),
battery voltage is supplied through fuse 25 to the
gauges in the gauge assembly.
Speedometer and Odometer
The odometer and soeedometer drive circuits
receive pulses from the vehicle speed sensor
(VSS). The pulse rate increases as the car
accelerates. The frequency and duration of these
input pulses are measured and displayed by the
speedometer, odometer and tripmeter.
Tachometer
The tachometer drive circuit receives pulses from
the ignition control module (lCM) in the distributor
assembly or the ECM/PCM. The solid-state
lachometer then displays these pulses as engine
speed. For each 200 pulses per minute from the
ignition control modul€ (lCM) or the ECM/PCM, the
tachometer displays 100 RPM.
Engine Coolant Temperature Gauge
The engine coolant temperature gauge has two
intersecting coils wound around a permanent
magnet rotor. Voltage applied to the coils, through
fuse 25, generates a magnetic lield. The magnetic
field, controlled by the coolant temperature sending
unit, causes the rotor to rotate and the gauge
needle to move. As the resistance in the sending
unit varies, current through the gauge coils
changes. The gauge needle moves toward the coil
with the strongest magnetic field.
The 6ngine coolant temperature sending unit's
resistance varies from about 137 ohms at low
engine temperature to between 3H6 ohms at high
temperature (radiator fan running).
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
81-2
(
Fuel Gauge (All except cX)
The fuel gauge has two intersecting coils wound
around a permanent magnet rotor. Voltage applied
to the coils, through tuse 25, generates a magnetic
field. The magnetic field, controlled by the fuel
gauge sending unit, causes the rotor to rotate and
the gauge needle to move. As the resislance in the
sending unit varies, current through the gauge coils
changes. The gauge needle moves toward the coil
with the strongest magnetic field.
The fuel gauge sending unit's resistance varies
from about 2-5 ohms at full, to about 110 ohms at
empty. When you turn the ignition switch off, the
gauge remains at the last reading until you turn the
ignition switch to ON (ll) or START (lll) again,
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
Fuel Gauge (GX)
The fuel gauge has two intersecting coils wound
around a permanent magnet rotor. Voltage applied
to the coils, through fuse 25, generates a magnetic
field. The magnetic field, controlled by the PCM,
causes the rotor to rotate and the gauge needle to
move. The PCM calculates the gas quantity in the
fuel tank by using the fuel pressure value detected
by the tuel tank pressure sensor and the fuel
temperature value detected by the fuel tank
temperalure sensor, and outputs the signal to the
gauge assembly. The gauge needle moves toward
the coil with the strongest magnetic field.
When you turn the ignition switch off , the gauge
remains at the last reading until you turn the ignition
switch to ON (ll) or START (lll) again. When the
PCM detects a malfunction with the fuel pressure or
temperature, or detects a gas leak, the PCM
reduces the fuel meter to 0.
Refer to the Service Manual GX Supplement
(Section 11 , Fuel and Emissions) for specific tests
or troubleshooting procedures.
a
a
Page 1983 of 2189

A/T Gear Position Indicator (conrd)
- How the Circuit Works
With the ignition switch in ON (ll) or START (lll),
voltage is applied to the A,/T gear position indicator.
The A,/T gear position switch provides a ground for
each position. As an input is grounded, its indicator
light comes on. lf you select R, for example, ground
will be provided to the input of the A,/T gear position
indicato( and the R indicator will come on.
With the headlight switch in PARK or HEAD, voltage
is applied to the RED/BLK wire terminal. This
changes the indicator panel illumination from fixed
to controlled by the dash lights dimmer input
through the RED wire.
When the powertrain (all except '96-'98 CVT) or
transmission ('96198 CVT) control module (PCM or
TCM) detects an abnormality in the automatic
transmission control system, or when you request
diagnostic trouble codes through the service check
connector, the PCM or TCM will make the D4 (D for
CVT) indicator light blink.
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 14,
Automatic Transmission) for specific tests or
troubleshooting procedures.
\ia
89-2
Page 2108 of 2189

-
Component Connector View Index (Views begin on page 202-21
Connector View
ABS Control Unit........ ......63
Audio Unit ('99-'00 models) ......74
Combination Light Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Combination Wiper Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Cruise Control Unit.... .....43
C\TTTransmission Solenoid ............. 25
Data Link Connector (DLC) ..... 48
Daytime Runnlng Lights Control Unit ..... 66
Engine control Module (ECM) ...........70
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve
and Lift Sensor (D16Y5 Mfl, D1685) . . . . 10
Gauge Assembly .............71
HazardWarnlngSwitch,,. .,,,...,,,,... 32
Heater Control Panel ('96-'98 models) .....44
Heater Control Panel ('99-'00 models) ...., 76
Heater Fan Switch ('96-'98 models) ,,,.... 11
fniector Control Module (GX) ............77
I/
202-1
Connector View
Integrated Control Unit .......,. 67
f nterfock Control Unit .... ...... 26
Keyfess Door Lock Control Unit . . . . , . . . . . 75
Mode Control Motor ... ........'17
Moonroof Close Relay .. .......13
Moonroof Open Relay ... .......15
PGM-FI Main Relay .. .......... 18
Power Door Lock Conlrol Unil ..... ...... 37
Power Mirror Switch .,... ...... 33
Power Window Master Switch .,.........36
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) .......70
Security Control Unit ..., ..,,... 58
Security Starter Cut Belay ... ...,,,....,, 12
SRS Unit ............. 51
Stereo Radio Tuner ('96-'98 models) ...... 68
Transmission Control Module CICM) .....69
Page 2133 of 2189
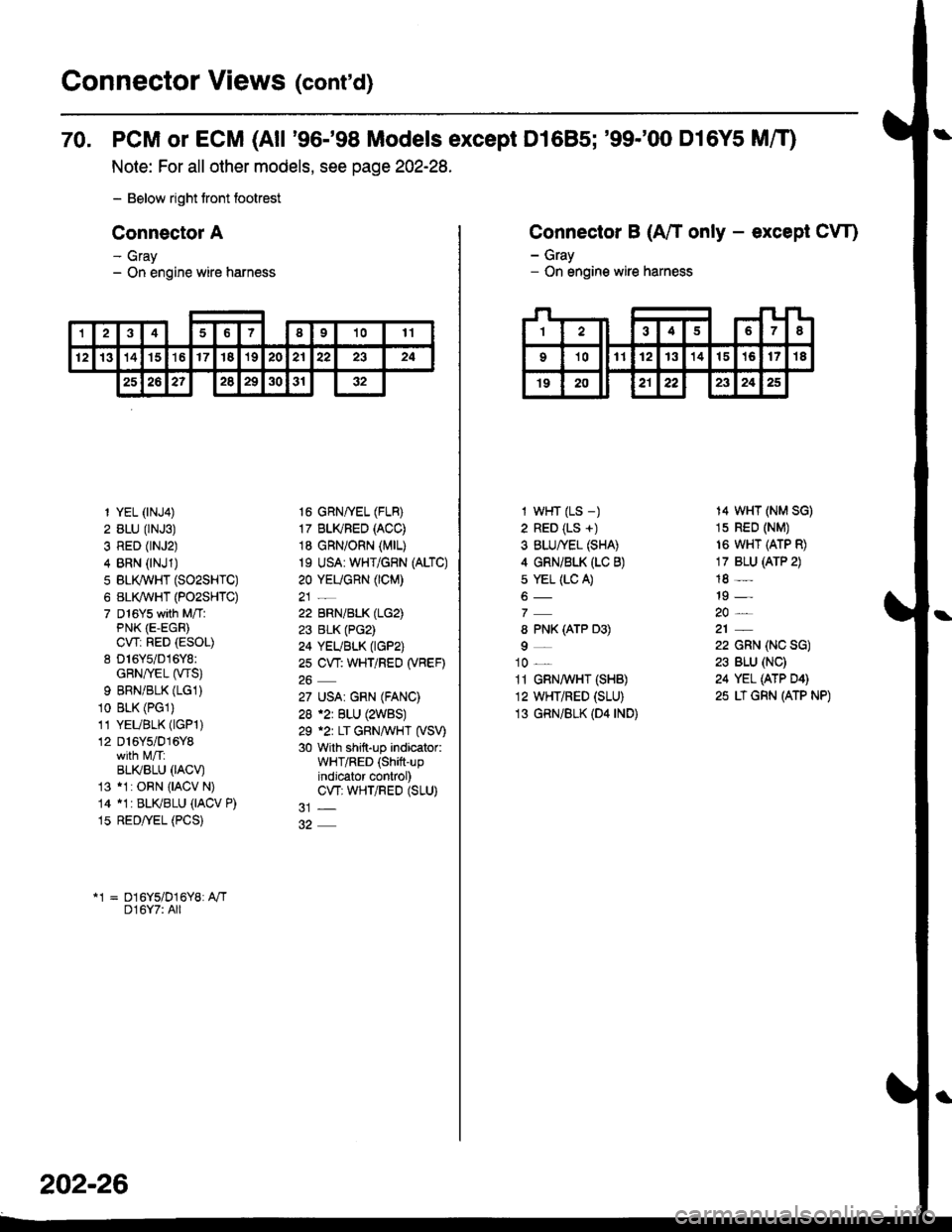
Connector Views (cont'd)
70. PCM or ECM (All '96-'98 Models except D1685; '99-'00 D16Y5 MfO
Note: For all other models, see page 202-28.
- Below right tront footrest
Connector A
- Gray- On engine wire harness
12346I91011
12131415't617'182021222324
25262?2829303'r32
1 YEL (rNJ4)
2 BLU (rNJ3)
3 RED (rNJ2)
4 BRN (NJ1)
5 BLI(WHT (SO2SHTC)
6 BL(WHT (PO2SHTC)
7 D16Ys with M/TlPNK (E-EGR)
CWi RED (ESOL)
8 D16Y5/016Y8:GRN/rEL (wS)
9 BRNiBLK (LG1)
10 BLK (PGl)
11 YEUBLK (lGPl)
12 D16Y5/016Y8
BLI(BLU 0ACV)13 11: ORN {IACV N)
14 11r BLKBLU (IACV P)
15 RED/yEL (PCS)
16 GRNffEL (FLB)
17 BLI(FED (ACC)
18 GRN/ORN (MrL)
19 USA: WHT/GRN (ALTC)
20 YEUGnN (CM)
22 BRN/BLK (LG2)
23 BLK (PG2)
24 YEUBLK (tGP2)
2s CW: WHT/REO (VBEF)
27 USA| GRN (FANC)
28 .2r BLU (2WBS)
29 .2r LT GRNAVHT (VSV)
30 with shift-up indicator:WHT/RED (Shift-upindjcator control)CW; WHTiRED (SLU)
*1 = D16Y5/D16Y8: A"/TD16Y7: All
202-26
Connector B (A/T only - except CW)
- Gray- On engine wire harness
I wHT (LS -)
2 RED (LS +)
3 BLU/YEL (SHA)
4 GRNi BLK (LC B)
s YEL (LC A)
8 PNK (ATP D3)
9_
10 _
11 GRN,4 HT (SHB)
12 WHT/RED (SLU)
13 GRN/BLK (D4 rND)
14 WHT (NM SG)
1s RED (NM)
16 WHT (ATP R)
17 BLU (ATP 2)
18 -
19 -
22 GRN (NC SG)
23 BLU (NC)
24 YEL (ATP D4)
25 LT GRN (ATP NP)
Page 2135 of 2189
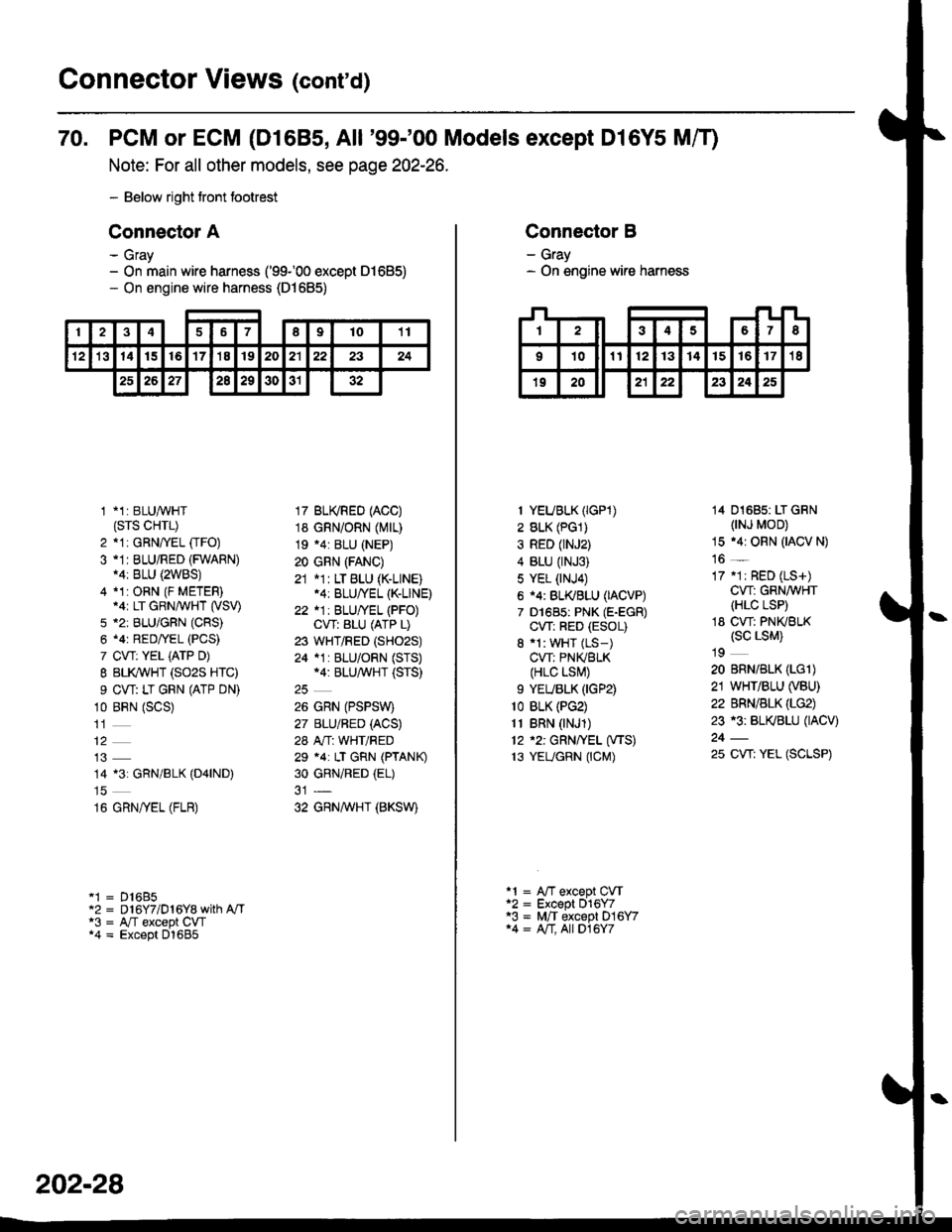
Connector Views (conrd)
70. PCM or ECM (D1685, All '99-'00 Models except Dl6Y5 Mff)
Note: For all other models, see page 202-26.
- Below right tront footrest
Connector A
- Gray- On main wire harness ('99100 except 01685)- On engine wire harness (D1685)
246789t011
't21314t516'17'18192021222324
2526272a29303132
1 *1: BLUAVHT(srs cHrL)
2 *1: GRNffEL [rFO)3 -1I BLU/RED (FWARN)14: BLU {2WBS)4 *1:ORN (F METER).ar LT GRN/WHT (VSV)
5 *2: BLU/GFN (CRS)
6 .4r RED/YEL (PCS)
7 CVT: YEL iATP D)
I BLI(WHT (SO2S HTC)
9 CW: LT GRN (ATP DN)
10 BRN (SCS)
14 13: GRN/BLK (D4|ND)
16 GRN/yEL (FLR)
'1 = D16B5"2 = D 16Y7/D 1 6Y8 with A"/Ta3 = A,/T except CW*4 = Except D1685
17 BU(RED (ACC)
18 GRN/ORN (Mrr)
19 .4: BLU (NEP)
20 GRN (FANC)
21 *1: LT BLU (K-LINE).4: BLU/YEL (K-LINE)
22 *1: BLU/YEL (PFO)CVT: ALU (ATP L)
23 WHT/RED (SHO2S)
24 *1 : BLU/ORN (STS)*4: BLU/^,iVHT (STS)
26 GRN (PSPSW)
27 BLU/BED (ACS)
28 A"/T: WHT/RED
29 *4: LT GRN (PTANK)
30 GRNiRED (EL)
32 GRNAVHT (BKSW)
202-28
Connector B
- Gray- On engine wire harness
I YEUBLK (IGP1)
2 BLK (PG1)
3 RED (rNJ2)
4 BLU (rNJ3)
5 YEL (NJ4)
6 i4: BL(BLU (IACVP)
7 D1685: PNK (E-EGR)
CW: RED (ESOL)
8 'l: WHT (LS-)
CVT: PNIVBLK(HLC LSI\,!)
9 YEUBLK (IGP2)
1o BLK (PG2)
11 BRN (NJ1)
12 '2: GRN/YEL (VTS)
13 YEUGRN (CM)
14 01685: LT GRN(NJ MOD)
15 .4r ORN (IACV N)
16 _
17 .1r RED (LS+)
CW: GRN/WHT(HLC LSP)
18 CW: PNKBLK(sc LsM)
19
20 BRN/BLK (LGl)
21 WHT/BLU (VBU)
22 BRN/BLK (LG2)
23 r3: BL(BLU (IACV)
25 CW: YEL (SCLSP)
a1 = A"fT except CVTa2 = Except 016Y7'3 = M,/T except D16Y714 = A/T, All D16Y7