1999 DODGE DURANGO Idle
[x] Cancel search: IdlePage 109 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine spring seat in cylinder head to the bottom surface of
spring retainer. If spacers are installed, measure
from the top of spacer. If height is greater than 42.86
mm (1-11/16 inches), install a 1.587 mm (1/16 inch)
spacer in head counterbore. This should bring spring
height back to normal 41.27 to 42.86 mm (1-5/8 to
1-11/16 inch).
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the air cleaner assembly and air inlet
hose.
(2) Remove cylinder head cover, rocker assembly
and push rods. Identify push rods to ensure installa-
tion in original location.
(3) Remove intake manifold, yoke retainer and
aligning yokes.
(4) Slide Hydraulic Tappet Remover/Installer Tool
C-4129-A through opening in cylinder head and seat
tool firmly in the head of tappet.
(5) Pull tappet out of bore with a twisting motion.
If all tappets are to be removed, identify tappets to
ensure installation in original location.
INSTALLATION
(1) If the tappet or bore in cylinder block is scored,
scuffed, or shows signs of sticking, ream the bore to
next oversize. Replace with oversize tappet.
(2) Lubricate tappets.
(3) Install tappets and push rods in their original
positions. Ensure that the oil feed hole in the side of
the tappet body faces up (away from the crankshaft).
(4) Install aligning yokes with ARROW toward
camshaft.
(5) Install yoke retainer. Tighten the bolts to 23
N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque. Install intake manifold.
(6) Install push rods in original positions.
(7) Install rocker arm.
(8) Install cylinder head cover.
(9) Install air cleaner assembly and air inlet hose.
(10) Start and operate engine. Warm up to normal
operating temperature.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to valve mechanism,
engine must not be run above fast idle until all
hydraulic tappets have filled with oil and have
become quiet.
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Remove fan shroud retainer bolts and set
shroud back over engine.(3) Remove the cooling system fan.
(4) Remove the serpentine belt (refer to Group 7,
Cooling System).
(5) Remove the vibration damper pulley.
(6) Remove vibration damper bolt and washer from
end of crankshaft.
(7) Install bar and screw from Puller Tool Set
C-3688. Install 2 bolts with washers through the
puller tool and into the vibration damper (Fig. 46).
(8) Pull vibration damper off of the crankshaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the vibration damper onto the crank-
shaft.
(2) Place installing tool, part of Puller Tool Set
C-3688 in position and press the vibration damper
onto the crankshaft (Fig. 47).
(3) Install the crankshaft bolt and washer. Tighten
the bolt to 183 N´m (135 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install the crankshaft pulley. Tighten the pul-
ley bolts to 23 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install the serpentine belt (refer to Group 7,
Cooling System).
(6) Install the cooling system fan. Tighten the
bolts to 23 N´m (17 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 46 Vibration Damper Assembly
1 ± SPECIAL TOOL C-3688
Fig. 47 Installing Vibration Damper
1 ± SPECIAL TOOL C-3688
DN5.2L ENGINE 9 - 109
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 121 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine (6) To align the bearing cap, use cap slot, align-
ment dowel and cap bolts. DO NOT remove excess
material after assembly. DO NOT strike rear cap
more than 2 times for proper engagement.
(7) Install the rear main bearing cap with cleaned
and oiled cap bolts. Alternately tighten ALL cap bolts
to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install oil pump.
(9) Apply MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant, or equivalent, at bearing cap to block joint to
provide cap to block and oil pan sealing (Fig. 72).
Apply enough sealant until a small amount is
squeezed out. Withdraw nozzle and wipe excess seal-
ant off the oil pan seal groove.
(10) Immediately install the oil pan.
LOWER SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the oil pan.
(2) Remove the oil pump from the rear main bear-
ing cap.
(3) Remove the rear main bearing cap and discard
the old lower seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the rear main cap mating surfaces
including the oil pan gasket groove.
(2) Carefully install a new upper seal (refer to
Upper Seal Replacement - Crankshaft Installed pro-
cedure above).
(3) Lightly oil the new lower seal lips with engine
oil.
(4) Install a new lower seal in bearing cap with
the white paint facing the rear of engine.
(5) Apply 5 mm (0.20 in) drop of MopartGasket
Maker, or equivalent, on each side of the rear main
bearing cap (Fig. 71). DO NOT over apply sealant or
allow the sealant to contact the rubber seal. Assem-
ble bearing cap to cylinder block immediately after
sealant application.
(6) To align the bearing cap, use cap slot, align-
ment dowel and cap bolts. DO NOT remove excess
material after assembly. DO NOT strike rear cap
more than 2 times for proper engagement.
(7) Install the rear main bearing cap with cleaned
and oiled cap bolts. Alternately tighten the cap bolts
to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install oil pump.
(9) Apply MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant, or equivalent, at bearing cap to block joint to
provide cap to block and oil pan sealing (Fig. 72).
Apply enough sealant until a small amount is
squeezed out. Withdraw nozzle and wipe excess seal-
ant off the oil pan seal groove.
(10) Immediately install the oil pan.
ENGINE CORE OIL AND CAMSHAFT PLUGS
Engine core plugs have been pressed into the oil
galleries behind the camshaft thrust plate (Fig. 73).
This will reduce internal leakage and help maintain
higher oil pressure at idle.
REMOVAL
(1) Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screw-
driver and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the
cup plug (Fig. 74).
(2) With the cup plug rotated, grasp firmly with
pliers or other suitable tool and remove plug (Fig.
74).
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Be certain the new plug is cleaned of all oil or
grease.
(1) Coat edges of plug and core hole with Mopart
Gasket Maker, or equivalent.
CAUTION: DO NOT drive cup plug into the casting,
as restricted coolant flow can result and cause seri-
ous engine problems.
(2) Using proper plug drive, drive cup plug into
hole. The sharp edge of the plug should be at least
0.50 mm (0.020 in.) inside the lead-in chamfer.
(3) It is not necessary to wait for curing of the
sealant. The cooling system can be filled and the
vehicle placed in service immediately.
Fig. 73 Location of Cup Plugs in Oil Galleries
1 ± CUP PLUGS
9 - 120 5.2L ENGINEDN
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 131 of 193
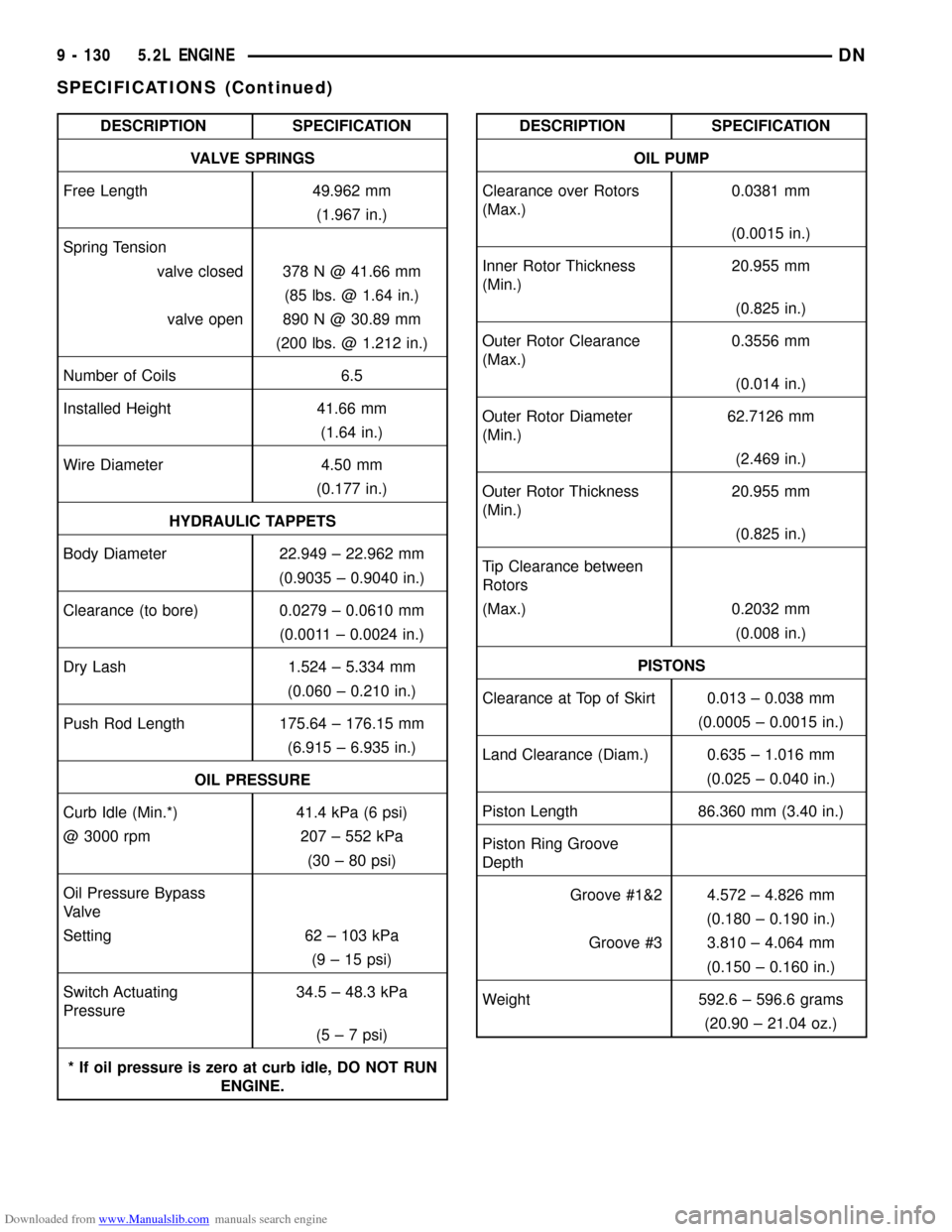
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
VALVE SPRINGS
Free Length 49.962 mm
(1.967 in.)
Spring Tension
valve closed 378 N @ 41.66 mm
(85 lbs. @ 1.64 in.)
valve open 890 N @ 30.89 mm
(200 lbs. @ 1.212 in.)
Number of Coils 6.5
Installed Height 41.66 mm
(1.64 in.)
Wire Diameter 4.50 mm
(0.177 in.)
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
Body Diameter 22.949 ± 22.962 mm
(0.9035 ± 0.9040 in.)
Clearance (to bore) 0.0279 ± 0.0610 mm
(0.0011 ± 0.0024 in.)
Dry Lash 1.524 ± 5.334 mm
(0.060 ± 0.210 in.)
Push Rod Length 175.64 ± 176.15 mm
(6.915 ± 6.935 in.)
OIL PRESSURE
Curb Idle (Min.*) 41.4 kPa (6 psi)
@ 3000 rpm 207 ± 552 kPa
(30 ± 80 psi)
Oil Pressure Bypass
Valve
Setting 62 ± 103 kPa
(9 ± 15 psi)
Switch Actuating
Pressure34.5 ± 48.3 kPa
(5 ± 7 psi)
* If oil pressure is zero at curb idle, DO NOT RUN
ENGINE.DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
OIL PUMP
Clearance over Rotors
(Max.)0.0381 mm
(0.0015 in.)
Inner Rotor Thickness
(Min.)20.955 mm
(0.825 in.)
Outer Rotor Clearance
(Max.)0.3556 mm
(0.014 in.)
Outer Rotor Diameter
(Min.)62.7126 mm
(2.469 in.)
Outer Rotor Thickness
(Min.)20.955 mm
(0.825 in.)
Tip Clearance between
Rotors
(Max.) 0.2032 mm
(0.008 in.)
PISTONS
Clearance at Top of Skirt 0.013 ± 0.038 mm
(0.0005 ± 0.0015 in.)
Land Clearance (Diam.) 0.635 ± 1.016 mm
(0.025 ± 0.040 in.)
Piston Length 86.360 mm (3.40 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth
Groove #1&2 4.572 ± 4.826 mm
(0.180 ± 0.190 in.)
Groove #3 3.810 ± 4.064 mm
(0.150 ± 0.160 in.)
Weight 592.6 ± 596.6 grams
(20.90 ± 21.04 oz.)
9 - 130 5.2L ENGINEDN
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 137 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE
DESCRIPTION
The 5.9 Liter (360 CID) eight-cylinder engine is a
V-Type lightweight, single cam, overhead valve
engine with hydraulic roller tappets. This engine is
designed for unleaded fuel.
The engine lubrication system consists of a rotor
type oil pump and a full flow oil filter.
The cylinders are numbered from front to rear; 1,
3, 5, 7 on the left bank and 2, 4, 6, 8 on the right
bank. The firing order is 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2 (Fig. 1).
The engine serial number is stamped into a
machined pad located on the left, front corner of the
cylinder block. When component part replacement is
necessary, use the engine type and serial number for
reference (Fig. 2).
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
A gear-type positive displacement pump (Fig. 3) is
mounted at the underside of the rear main bearing
cap. The pump uses a pick-up tube and screen
assembly to gather engine oil from the oil pan.
OPERATION
The pump draws oil through the screen and inlet
tube from the sump at the rear of the oil pan. The oil
is driven between the drive and idler gears and
pump body, then forced through the outlet to the
block. An oil gallery in the block channels the oil to
the inlet side of the full flow oil filter. After passing
through the filter element, the oil passes from the
center outlet of the filter through an oil gallery that
channels the oil up to the main gallery, which
extends the entire length on the right side of the
block. The oil then goes down to the No. 1 main bear-
ing, back up to the left side of the block, and into the
oil gallery on the left side of the engine.
Galleries extend downward from the main oil gal-
lery to the upper shell of each main bearing. The
crankshaft is drilled internally to pass oil from the
main bearing journals to the connecting rod journals.
Each connecting rod bearing has half a hole in it, oil
passes through the hole when the rods rotate and the
hole lines up, oil is then thrown off as the rod
rotates. This oil throwoff lubricates the camshaft
lobes, distributor drive gear, cylinder walls, and pis-
ton pins.
Fig. 1 Firing Order
Fig. 2 Engine Identification Number
Fig. 3 Positive Displacement Oil PumpÐTypical
1 ± INNER ROTOR AND SHAFT
2 ± BODY
3 ± DISTRIBUTOR DRIVESHAFT (REFERENCE)
4 ± COTTER PIN
5 ± RETAINER CAP
6 ± SPRING
7 ± RELIEF VALVE
8 ± LARGE CHAMFERED EDGE
9 ± BOLT
10 ± COVER
11 ± OUTER ROTOR
9 - 136 5.9L ENGINEDN
Page 142 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
DESCRIPTION
Main bearings are located in the cylinder block.
One half of the main bearing is located in the crank-
shaft main bore the other half of the matching bear-
ing is located in the main bearing cap (Fig. 9). There
are five main bearings. Number three main bearing
is flanged, this flange controls crankshaft thrust.
OPERATION
The main bearings encircle the crankshaft main
bearing journals, this aligns the crankshaft to the
centerline of the engine and allows the crankshaft to
turn without wobbling or shaking therefore eliminat-
ing vibration. The main bearings are available in
standard and undersizes.
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft is of a cast nodular steel splayed
type design, with five main bearing journals. The
crankshaft is located at the bottom of the engine
block and is held in place with five main bearing
caps. The number 3 counterweight is the location for
journal size identification (Fig. 10).
OPERATION
The crankshaft transfers force generated by com-
bustion within the cylinder bores to the flywheel or
flexplate.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐINTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
Refer to the Service DiagnosisÐMechanical Chart
and the Service DiagnosisÐPerformance Chart, for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions. Refer
to FUEL SYSTEM for the fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
²Lash Adjuster (Tappet) Noise Diagnosis
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection
Fig. 9 Main Bearing Orientation
Fig. 10 Crankshaft with Journal Size Identification
DN5.9L ENGINE 9 - 141
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 143 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐGASOLINE ENGINES
PERFORMANCE DIAGNOSIS CHARTÐGASOLINE ENGINES
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL
NOT CRANK1. Weak or dead battery 1. Charge/Replace Battery. Refer to Group 8A,
Battery, for correct procedures. Check charging
system. Refer to Group 8C, Charging Systems, for
correct procedures.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections2. Clean/tighten suspect battery/starter connections
3. Faulty starter or related circuit(s) 3. Check starting system. Refer to Group 8B,
Starting Systems, for correct diagnostics/procedures
4. Seized accessory drive
component4. Remove accessory drive belt and attempt to start
engine. If engine starts, repair/replace seized
component.
5. Engine internal mechanical
failure or hydro-static lock5. Refer to Group 9, Engine, for correct diagnostics/
procedures
ENGINE CRANKS
BUT WILL NOT
START1. No spark 1. Check for spark. Refer to Group 8D, Ignition
System, for correct procedures.
2. No fuel 2. Perform fuel pressure test, and if necessary,
inspect fuel injector(s) and driver circuits. Refer to
Group 14, Fuel System, for correct procedures.
3. Low or no engine compression 3. Perform cylinder compression pressure test. Refer
to Group 9, Engine, for correct procedures.
ENGINE LOSS OF
POWER1. Worn or burned distributor rotor 1. Install new distributor rotor
2. Worn distributor shaft 2. Remove and repair distributor (Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System
3. Worn or incorrect gapped spark
plugs3. Clean plugs and set gap. (Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System)
4. Dirt or water in fuel system 4. Clean system and replace fuel filter
5. Faulty fuel pump 5. Install new fuel pump
6. Incorrect valve timing 6. Correct valve timing
7. Blown cylinder head gasket 7. Install new cylinder head gasket
8. Low compression 8. Test cylinder compression
9. Burned, warped, or pitted valves 9. Install/Reface valves as necessary
10. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system10. Install new parts as necessary
11. Faulty ignition cables 11. Replace any cracked or shorted cables
12. Faulty ignition coil 12. Test and replace, as necessary (Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System)
ENGINE STALLS
OR ROUGH IDLE1. Carbon build-up on throttle plate 1. Remove throttle body and de-carbon. (Refer to
Group 14 for correct procedures)
2. Engine idle speed too low 2. Check Idle Air Control circuit. (Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System)
9 - 142 5.9L ENGINEDN
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 148 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
Refer to the Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leak-
age Test Diagnosis chart.
INSPECTION (ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil-soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
be sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light source.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat previous step.
(5) If the oil leak source is not positively identified
at this time, proceed with the air leak detection test
method as follows:
(6) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(7) Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve grommet.
(8) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(9) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
(10) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
(11) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air sup-
ply and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the PCV valve and breather cap hose. Proceed
to next step.(12) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area
using a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
REAR SEAL AREA LEAKSÐINSPECTION
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs, oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces. See Group 9, Engines, for
proper repair procedures of these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crank-
case as outlined in the section, Inspection (Engine oil
Leaks in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks or
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is specially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled. Refer to the service DiagnosisÐMechani-
cal, under the Oil Leak row, for components
inspections on possible causes and corrections.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, Refer to Group
9, EnginesÐCrankshaft Rear Oil Seals, for proper
replacement procedures.
DN5.9L ENGINE 9 - 147
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 149 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at
the pressure sending-unit. The pressure should be
between 207-552 kPa (30-80 psi) at 3,000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the FULL mark or below the
ADD OIL mark on dipstick. Either of these two con-
ditions could be responsible for noisy tappets.
OIL LEVEL
HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the
engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the
hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
lose length and allow valves to seat noisily.
LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air.
When air is fed to the tappets, they lose length,
which allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on
intake side of oil pump through which air can be
drawn will create the same tappet action. Check the
lubrication system from the intake strainer to the
pump cover, including the relief valve retainer cap.
When tappet noise is due to aeration, it may be
intermittent or constant, and usually more than one
tappet will be noisy. When oil level and leaks have
been corrected, operate the engine at fast idle. Run
engine for a sufficient time to allow all of the air
inside the tappets to be bled out.
TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed.
(2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
(3) Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger, or by theplunger partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder.
The tappet should be replaced. A heavy click is
caused by a tappet check valve not seating, or by for-
eign particles wedged between the plunger and the
tappet body. This will cause the plunger to stick in
the down position. This heavy click will be accompa-
nied by excessive clearance between the valve stem
and rocker arm as valve closes. In either case, tappet
assembly should be removed for inspection and clean-
ing.
(4) The valve train generates a noise very much
like a light tappet noise during normal operation.
Care must be taken to ensure that tappets are mak-
ing the noise. If more than one tappet seems to be
noisy, it's probably not the tappets.
LEAK-DOWN TEST
After cleaning and inspection, test each tappet for
specified leak-down rate tolerance to ensure zero-lash
operation (Fig. 11).
Swing the weighted arm of the hydraulic valve tap-
pet tester away from the ram of the Universal Leak-
Down Tester.
(1) Place a 7.925-7.950 mm (0.312-0.313 inch)
diameter ball bearing on the plunger cap of the tap-
pet.
(2) Lift the ram and position the tappet (with the
ball bearing) inside the tester cup.
(3) Lower the ram, then adjust the nose of the ram
until it contacts the ball bearing. DO NOT tighten
the hex nut on the ram.
(4) Fill the tester cup with hydraulic valve tappet
test oil until the tappet is completely submerged.
(5) Swing the weighted arm onto the push rod and
pump the tappet plunger up and down to remove air.
When the air bubbles cease, swing the weighted arm
away and allow the plunger to rise to the normal
position.
(6) Adjust the nose of the ram to align the pointer
with the SET mark on the scale of the tester and
tighten the hex nut.
(7) Slowly swing the weighted arm onto the push
rod.
(8) Rotate the cup by turning the handle at the
base of the tester clockwise one revolution every 2
seconds.
(9) Observe the leak-down time interval from the
instant the pointer aligns with the START mark on
the scale until the pointer aligns with the 0.125
mark. A normally functioning tappet will require
20-110 seconds to leak-down. Discard tappets with
leak-down time interval not within this specification.
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit.
9 - 148 5.9L ENGINEDN
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)