1999 BMW X5 steering
[x] Cancel search: steeringPage 70 of 80
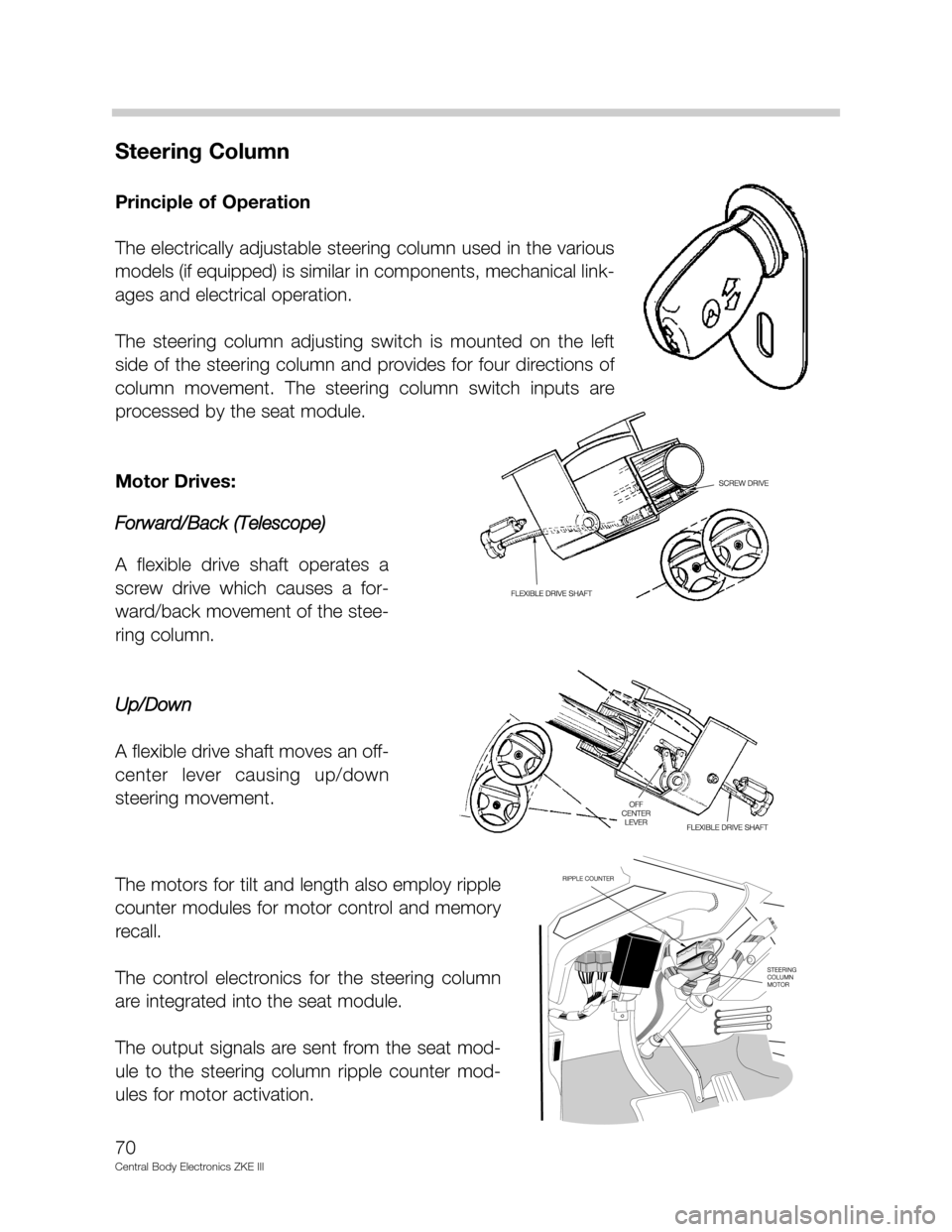
Steering Column
Principle of Operation
The electrically adjustable steering column used in the various
models (if equipped) is similar in components, mechanical link-
ages and electrical operation.
The steering column adjusting switch is mounted on the left
side of the steering column and provides for four directions of
column movement. The steering column switch inputs are
processed by the seat module.
Motor Drives:
Forward/Back (Telescope)
A flexible drive shaft operates a
screw drive which causes a for-
ward/back movement of the stee-
ring column.
Up/Down
A flexible drive shaft moves an off-
center lever causing up/down
steering movement.
The motors for tilt and length also employ ripple
counter modules for motor control and memory
recall.
The control electronics for the steering column
are integrated into the seat module.
The output signals are sent from the seat mod-
ule to the steering column ripple counter mod-
ules for motor activation.
70
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Page 71 of 80

71
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
System Components: Inputs - Processing - Outputs
Entry/Exit Aid
The Steering Column Memory provides the feature of raising the steering column to ease
in exiting the vehicle and return it to the previous position after the vehicle is entered.
Raising the Steering Column:
Lowering the Steering Column:
• The ignition is switched “off”. • The ignition is switched to KL 15.
• The ignition is switched to KL R • The Handbrake is released or the door is closed.
and the driver’s door is opened.
• The ignition is switched to KL 15, The steering column recall movement can be inter-
driver’s door open with the hand- rupted at any time by tapping the adjusting lever.
brake applied.
Page 72 of 80
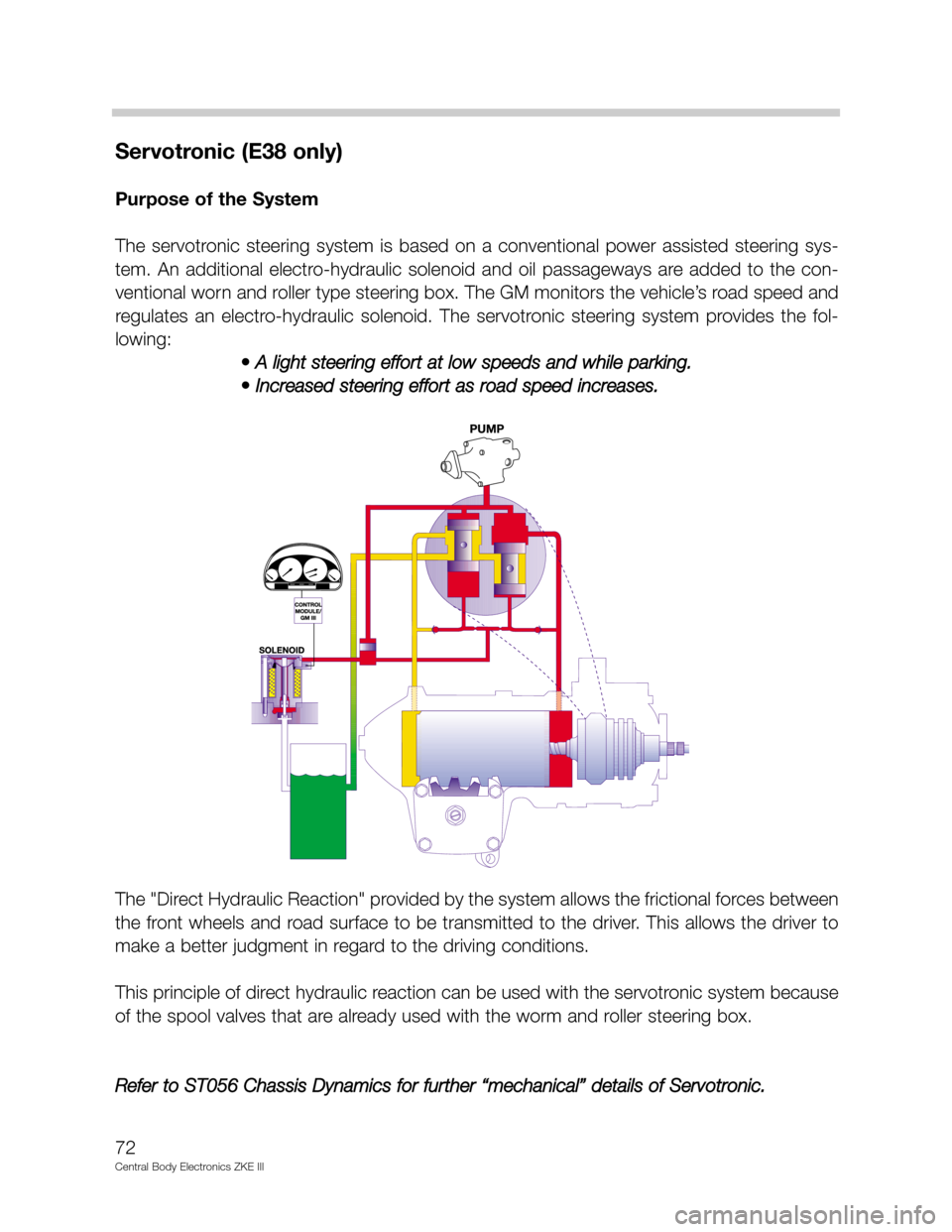
Servotronic (E38 only)
Purpose of the System
The servotronic steering system is based on a conventional power assisted steering sys-
tem. An additional electro-hydraulic solenoid and oil passageways are added to the con-
ventional worn and roller type steering box. The GM monitors the vehicle’s road speed and
regulates an electro-hydraulic solenoid. The servotronic steering system provides the fol-
lowing:
• A light steering effort at low speeds and while parking.
• Increased steering effort as road speed increases.
The "Direct Hydraulic Reaction" provided by the system allows the frictional forces between
the front wheels and road surface to be transmitted to the driver. This allows the driver to
make a better judgment in regard to the driving conditions.
This principle of direct hydraulic reaction can be used with the servotronic system because
of the spool valves that are already used with the worm and roller steering box.
Refer to ST056 Chassis Dynamics for further “mechanical” details of Servotronic.
72
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Page 73 of 80

System Components
Electro-Hydraulic Solenoid: The solenoid regulates the
amount of power steering assist for the servotronic system. It
contains a needle valve that can restrict oil flow. When current
is applied, the needle valve closes against spring pressure to
restrict the oil flow.
With maximum current applied, the valve is closed. This is the
condition of the valve for slow speed driving and parking.
Without current applied, the needle valve is held open by
spring pressure. This is the condition of the solenoid during
higher driving speeds.
Electro-Hydraulic Solenoid Control: The GM monitors the road speed input and sup-
plies the electro-hydraulic solenoid with power. The road speed signal “A” is supplied from
the IKE (and K-Bus) on E38 vehicles and from the DSC Control Module on E39/E53 vehi-
cles.
The solenoid is pulse width modulated for control and varies the amount of assist based
on the road speed. The maximum assist is available while parking and driving at slow
speeds.
73
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Page 74 of 80

Principle of Operation
Control logic (example E38) includes:
• Servotronic control electronics active with KL R being switched "ON" - ensure no delay
in operation if engine is started and vehicle is immediately driven.
• Plausibility check for speed signal - the control electronics monitor both the Speed sig-
nal "A" from the IKE and the vehicle speed signal on the K-Bus.
• The ability to detect both acceleration and deceleration from the two speed signals - the
speed signal from the IKE is updated every two seconds.
• The servotronic assist is reduced gradually when the vehicle is under acceleration.
• The servotronic assist is adopted to the lower direct reading during decel or braking.
Electric/electronic failures with the servotronic system will result in the following:
• Power/electronic failure of the control module or solenoid - steering assist the same as
high speed driving (increased effort).
• Vehicle speed signal missing - control module retains the assist mode in effect when the
speed signal was lost.
• Speed signal implausible - steering assist the same as high speed driving (increased
effort).
The GM also provides the diagnostic “gateway” to the Servotronic status and Component
Activation via the DISplus/MoDiC.
74
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Page 75 of 80

General Functions of ZKE III
Consumer Cut Off
The Consumer Cut Off function interrupts battery voltage to circuits preventing inadvertent
battery drain if one of these consumers were to remain activated. Circuits controlled by
consumer cut off will be switched off as the GM enters into the sleep mode.
For example, the interior lights are connected to the consumer cut out circuit (KL 30) and
can remain on if one of the control switches are left on. The consumer cut off will deacti-
vate KL 30 to the interior lighting after 16 minutes (or with the DISplus/MoDIC).
The following circuits are con-
trolled by consumer cut off:
• Map/Reading Lights
• Glove Box/Luggage Compart-
ment Lights
• Transmission Range Indicator
Light
• Overload Protection Relay for
- Power Seat Motors
- Steering Column Motors
Overload Protection
The seat and steering column motors receive
operating power through the consumer cutoff/
overload protection relay module. The consumer
cutoff signal from the GM signals the relay to
maintain operating power to the consumers.
If the relay module detects an increase in amper-
age (overload) the relay will open. The relay mod-
ule (K-72) is located in the electrical carrier
behind the glove box. The relay is reset by
switching the ignition “off” for 16 minutes, dis-
connecting the relay or the DISplus/ MoDIC.
75
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
E38 Shown
Overload
Protection Relay
Module
Page 80 of 80

9. What type of sensor is used to detect the position of a seat with Memory? What type
of signal does it produce?__________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
10. How does the Seat Module communicate a request for a stored memory position with
the mirror modules?_______________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
11. On an E38 with Servotronic, why is the speed signal provided to the GM from both
the IKE “A” signal and the K-Bus?___________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
12. An E38 customer complains that when exiting the vehicle the steering wheel moves
up. What is the cause of this?______________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
13. How does the SZM monitor the Seat Heating temperature?_____________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
14. What circuits are controlled by Consumer Cut Off? ____________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
15. If a technician double locked a 2000 MY E39 while still inside the vehicle, how could
he/she exit the vehicle?____________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
16. How is the MY 2000 key charged?__________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
17. How is the DWA Disarmed (emergency)?_____________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
18. What functions will deactivate the exterior door handle lighting? _________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
80
Central Body Electronics ZKE III