Page 385 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Battery, Starter, Alternator
- Installation is reverse of removal, noting the following:
Replace alternator rubber sealing O-ring.
* Fill and bleed cooling system as described in 170 Radiator
and Cooling System.
Tightening torques
Fan clutch to coolant pump
with
BMW special tool 11 5 040 30 Nm (22 ft-lb)
without
BMW special tool 11 5 040 40 Nm (29 ft-lb)
Terminal 30 (Bc) wire to alternator (ME) 13 Nm (10 ft-lb)
STARTER
Starter troubleshooting
Typical starter wiring terminal identification is shown. Large
wire at terminal
30 (not shown in photo) is direct battery volt-
age. Smaller wire at terminal
50 operates starter solenoid via
ignition switch.
If starter turns engine slowly when ignition is in start position:
Check battery state of charge.
Inspect starter wires, terminals, and ground
connectlons
for good contact. In particular, make sure ground connec-
tions between battery, body and
englne are completely
clean and tight.
If no faults are found, starter may be faulty and should be
replaced.
- If starter fails to operate, check EWS (drive-away protection
system). Try another ignition key.
If no faults can be found,
have the EWS system checked using
BMW scan tool equip-
ment.
Checkclutch pedal operated
starter lock-out switch or gear
position switch (automatic).
NOTE-
* A factory-installed drive-away protection system, also re-
ferred to as
EWS, is used on E39 cars. This system pre-
vents operation of the starter if a specially coded ignition
key is not used.
On cars with automatic transmission, the transmission
gear position switch signals
EWS to prevent the engine
from starting in gear positions other than PARK or NEU-
TRAL.
On cars with manual transmissions, a starter immobiliza-
tion switch
at the clutch pedal is used to prevent the starter
from operating unless the clutch pedal is pushed fully to
the floor.
Page 414 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Fuel Injection
- Ignition:
Direct ignition
Knock control
4 Primary1 secondary ignition monitoring
- Emissions:
OBD II compliance
Secondary air injection
Pre- and post-catalyst oxygen sensors
0 Electrically heated DME-mapped thermostat
Misfire detection
Evaporative emission control and
leak detection
Malfunction indicator light (MIL)
Performance controls:
Dual VANOS control
Output of injection signal (TI) for fuel economy gauge
Output of engine rpm (TD) for tachometer
AIC compressor control
0 Electric radiator cooling fan
CAN-Bus communication
Stability and traction system
(ABSIASCIDSC) interlace
Electronic immobilizer (EWS)
Cruise control
ECM programming
Page 497 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
176 Radiator and Cooling System
General ........................... .I7 0.2
Special tools
........................ .I7 0.2
Cooling system overview
(M52 TU shown. others similar) ......... .I7 0.3
Coolant pump
....................... .I7 0.3
Thermostat
......................... .I7 0.3
Mechanical thermostat (M52 engine)
..... .I7 0.4
Electrically heated thermostat
.......... .I7 0.4
Radiator and expansion tank
........... .I7 0.4
Mechanical cooling fan with viscous clutch
.I7 0.4
Electric (auxiliary) cooling fan ........... .I7 0.4
Transmission fluid heat exchanger
....... .I7 0.5
Warnings and cautions
................ .I7 0.7
Troubleshooting ................... .I7 0.7
Cooling system inspection
............. .I7 0.8
Cooling system pressure test
........... .I7 0.9
Combustion chamber leak test
......... .I7 0.10
Thermostat
........................ .I7 0.1 0
Cooling System Service ........... 170-10
Coolant. draining and filling
(6-cylinder models)
.................. 170-1 0
Coolant. draining and filling (V-8 models)
. 170-12
Cooling system. bleeding
............. 170-14
Mechanical (viscous clutch) cooling fan.
removing and installing
............... 170-14
Electric cooling fan.
removing and installing
............... 170-15
Thermostat. removing and installing
(M52engine) ....................... 170-16
Thermostat. removing and installing
(M52 TU or M54 engine) .............. 170-17
Thermostat. removing and installing (V-8 models)
....................... 170-1 8
Coolant pump. replacing (6-cylinder models)
.................. 170-1 9
Coolant pump. replacing (V-8 models) ... 170-20
Radiator. removing and installing
....... 170-22
Expansion tank. removing and
installing . . 170-24
Page 498 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
I Radiator and Cooling System
This section covers component repair information for the en-
gine cooling system.
Heater core replacement is covered in
640 Heating and Air
Conditioning.
Special tools
Special tools are necessaryfor belt-driven fan clutch removal
and also for pressure testing the cooling system.
4 Cooling fan counterhold wrench
(Tool No. BMW
11 5 030)
4 Cooling fan wrench
(Tool No. BMW
11 5 040)
< Expansion tank cap test adaptor
(Tool No.
BMW 17 0 007)
17 0 002 4 Cooling system pressure tester set
1 17 o 005 (Tool No. BMW 17 0 OOZi17 0 005)
Page 499 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
- -
L- -
--
-. - - - Radiator and Cooling sYstelll/ --
Cooling system overview
(M52 TU shown, others similar)
Coolant pump
A centrifugal coolant pump is mounted to the front of the en-
gine. The belt-driven pump circulates coolant through the
system whenever the engine is running.
Thermostat
Two types of thermostats are used in the cars covered by this
manual. 6-cylinder models built up to
911 998 (M52 engine)
use a conventional mechanical thermostat. All
V-8 models
and 6-cylinder models from
911998 use an electrically heated
thermostat.
Page 500 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
-
I Radiator and Cooling System
Mechanical thermostat
(M52 engine)
4 The mechanical thermostat relies on coolant temperature to
operate. While coolant is cold, it remains closed, and circu-
lating coolant bypasses the radiator for rapid engine warm
up. At higher coolant temperature, the thermostat progres-
sively opens to allow coolant flow through the radiator, thus
controlling engine temperature. Port
A restricts coolant flow
from radiator, and port
B restricts coolant flow to radiator.
Electrically heated thermostat
4 The electrically heated thermostat is DME map-controlled.
The engine control module (ECM) activates the thermostat to
maintain engine coolant temperature within a narrow range.
In case of failure of the electronics, the mechanical function of
the thermostat acts as a fail-safe.
Radiator and expansion tank
The radiator is a crossflow design. An expansion tank pro-
vides for coolant expansion at higher temperatures and easy
monitoring of the coolant level.
On cars with automatic transmission, ATF is circulated
through an additional heat exchanger (ATF cooler).
Mechanical cooling fan with viscous clutch
The mechanical cooling fan is belt-driven via a viscous fluid
coupling (clutch) attached to the front of the coolant pump.
The fan clutch controls the speed of the fan based on the tem-
perature of the air flowing through the radiator core.
Electric (auxiliary) cooling fan
The electric cooling fan is mounted on the bumper side of the
radiator.
In models manufactured up to
911 998 (M52 or 1997 M62 en-
gine), the electric cooling fan is controlled by a dual tempera-
ture fan switch mounted in the side of the radiator.
Page 501 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
170-5
Radiator and Cooling System
Fan switch calibration (M52, M62 engine)
coniprairoi OUt rlgnal
Auto. ciimilte ~ontioi inpuls via CAN bus
Electric fan activation:
Low speed
91°C (196°F)
High speed 104' C (21 9' F)
< In models manufactured after 911998 (M52 TU engine, M54
engine.
M62 TU engine), the electric cooling fan is controlled
by the engine control module (ECM) via the output final
stage.
The output final stage is mounted on the fan housing, next to
the fan motor. The fan is operated using a pulse width modu-
lated signal. Fan circuit wiring is protected by a 50-amp fuse.
Electric fan activation is based on the following inputs to the
ECM:
Radiator outlet temperature
Calculated catalytic converter temperature
Vehicle speed
* Battery voltage
Calculated
A/C pressure
When the vehicle is first started, the ECM activates the elec-
tric fan briefly at 20% of its maximum speed, then switches
off. This is for diagnostic monitoring. The voltage generated
by the fan when it slows down (acting as a generator) must
match the stored rpm values in the fan output stage toconfirm
that the fan is operating correctly.
NOTE-
If the ECM fault memory indicates a cooling fan fault, check
that the fan is not seized and that it spins freely.
When
A/C is switched ON, the electric fan is not immedi-
ately turned on.
After the engine is switched
OFF the fan may continue to
run at varying speeds for up to 10 minutes, based on cal-
culated catalyst temperature.
Transmission fluid heat exchanger
Automatic transmission fluid lines circulate transmission fluid
(ATF) to and from a heat exchanger at the radiator.
All 6-cylinder
models andV-8 models produced to 911998 are
equipped with a transmission cooler located in a cooling cas-
sette in front of the radiator.
Page 502 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
.. - -
I Radiator and Cooling System
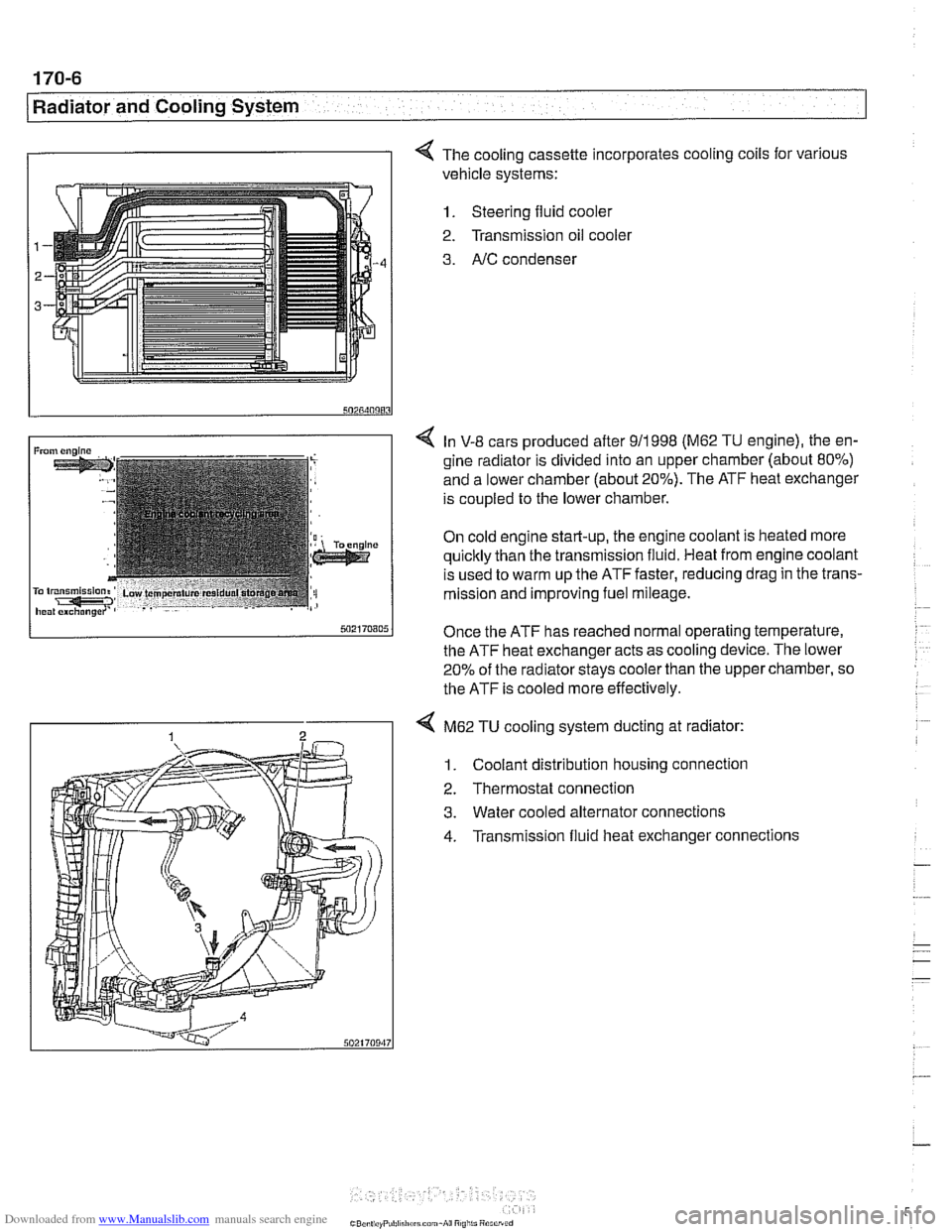
I I 4 The cooling cassette incorporates cooling coils for various
vehicle systems:
1. Steering fluid cooler
2. Transmission oil
coolel
3. AIC condenser
4 In V-8 cars produced after 911998 (M62 TU engine), the en-
gine radiator is divided into an upper chamber (about 80%)
and a lower chamber (about 20%). The ATF heat exchanger
is coupled to the lower chamber.
On cold engine start-up, the engine coolant is heated more
quicltly than the transmission fluid. Heat from engine coolant
is used to warm up the ATF faster, reducing drag in the trans-
mission and improving fuel mileage.
Once the ATF has reached normal operating temperature,
the ATF heat exchanger acts as cooling device. The lower
20% of the radiator
stays cooler than the upper chamber, so
the ATF is cooled more effectively.
4 M62 TU cooling system ducting at radiator:
1. Coolant distribution housing connection
2. Thermostat connection
3. Water cooled alternator connections
4. Transmission fluid heat exchanger connections