1998 SSANGYONG MUSSO transmission fluid
[x] Cancel search: transmission fluidPage 14 of 1463
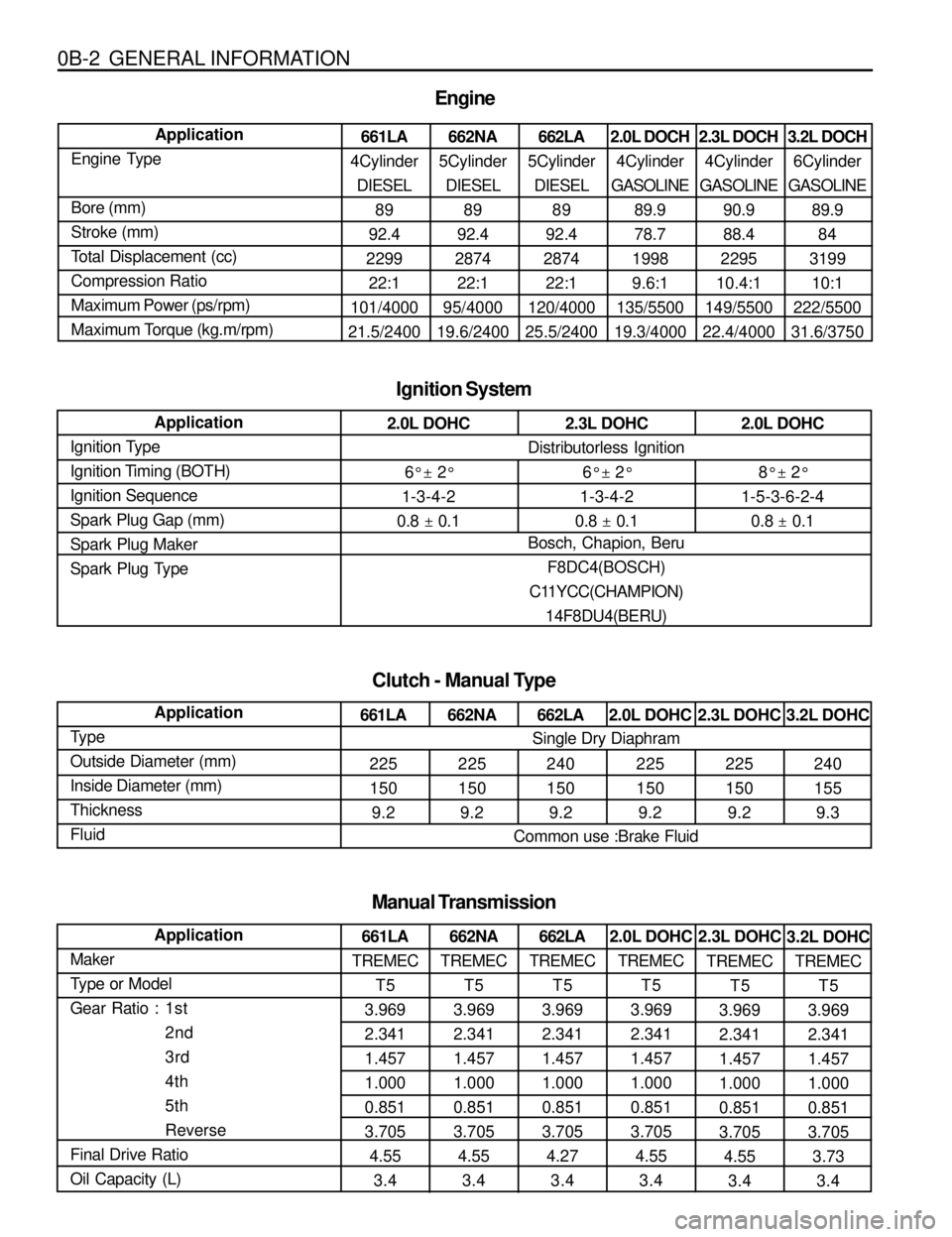
0B-2 GENERAL INFORMATION
661LA
4Cylinder
DIESEL
89
92.4
2299
22:1
101/4000
21.5/2400 Application
Engine Type
Bore (mm)
Stroke (mm)
Total Displacement (cc)
Compression Ratio
Maximum Power (ps/rpm)
Maximum Torque (kg.m/rpm)
Engine
662NA
5Cylinder
DIESEL
89
92.4
2874
22:1
95/4000
19.6/2400662LA
5Cylinder
DIESEL
89
92.4
2874
22:1
120/4000
25.5/24002.0L DOCH
4Cylinder
GASOLINE
89.9
78.7
1998
9.6:1
135/5500
19.3/40002.3L DOCH
4Cylinder
GASOLINE
90.9
88.4
2295
10.4:1
149/5500
22.4/40003.2L DOCH
6Cylinder
GASOLINE
89.9
84
3199
10:1
222/5500
31.6/3750
661LA
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
4.55
3.4 Application
Ignition Type
Ignition Timing (BOTH)
Ignition Sequence
Spark Plug Gap (mm)
Spark Plug Maker
Spark Plug Type
Ignition System
Clutch - Manual Type
2.0L DOHC
6° ± 2°
1-3-4-2
0.8 ± 0.12.3L DOHC
6° ± 2°
1-3-4-2
0.8 ± 0.12.0L DOHC
8° ± 2°
1-5-3-6-2-4
0.8 ± 0.1 Distributorless Ignition
Bosch, Chapion, Beru
F8DC4(BOSCH)
C11YCC(CHAMPION)
14F8DU4(BERU)
661LA
225
150
9.2
662NA
225
150
9.2662LA
240
150
9.22.0L DOHC
225
150
9.22.3L DOHC
225
150
9.23.2L DOHC
240
155
9.3 Application
Type
Outside Diameter (mm)
Inside Diameter (mm)
Thickness
Fluid
Single Dry Diaphram
Common use :Brake Fluid
Application
Maker
Type or Model
Gear Ratio : 1st
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
Reverse
Final Drive Ratio
Oil Capacity (L)
Manual Transmission
662NA
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
4.55
3.4662LA
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
4.27
3.42.0L DOHC
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
4.55
3.42.3L DOHC
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
4.55
3.43.2L DOHC
TREMEC
T5
3.969
2.341
1.457
1.000
0.851
3.705
3.73
3.4
Page 21 of 1463

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B-9
Chassis and Body
Months
MAINTENANCE
ITEMMAINTENANCE INTERVALKilometers or time in months, whichever comes first
120 105 90 75 60 45 30 15 1
96 84 72 60 48 36 24 12
- x1,000 km
Exhaust pipes & mountings
Brake/Clutch fluid(3)(4)
Parking brake/Brake pads F & R (5)
Brake line & connections (including booster)
Manual transmission oil (3)
Clutch & brake pedal free play
Front & Rear Differential Fluid (3)I
R
I
I
I
I
I-
-
-
I
I
-
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
R
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
R
I
RI
I
I
I
I
I
II
R
I
I
R
I
RI
I
I
I
I
I
II
R
I
I
I
I
I
Automatic transmission fluid (MB W4A040) (6)
Automatic transmission fluid (BTRA M74)
Chassis & underbody bolts & nuts tight/secure
Tire condition & inflation pressure
Wheel alignment (7)
Steering wheel & linkage
Power steering fluid & lines* (3)
Drive shaft boots
Seat belts, buckles & anchors
Lubricate locks, hinges & bonnet latchI
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
IR
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
IR
R
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
Transfer case fluidRIII
Inspect & ADJUST when abnormal condition is noted
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
Chart Symbols :
I - Inspect these items and their related parts. If necessary, correct, clean, replenish, adjust or replace.
R - Replace or change.
(3) Refer to “Recommended fluids and lubricants”.
(4) Change the brake / clutch fluid every 15,000 km if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe conditions:
- Driving in hilly or mountainous terrain, or
- Towing a trailer frequently
(5) More frequent maintenance is required if under severe condition : short distance driving, extensive idling, frequent low -
speed operation in stop-and-go traffic or driving in dusty condition.
(6) Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter every 75,000 km if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe conditions.
- In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly reaches 32°C (90°F) or higher, or
- In hilly or mountainous terrain, or
- When doing frequent trailer towing, or
- Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service.
(7) If necessary, rotate and balance wheels.
Page 23 of 1463

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B-11
Chassis and Body
Months
-
MAINTENANCE
ITEMMAINTENANCE INTERVAL
Kilometers or time in months, whichever comes first
100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 1
60 54 48 42 36 30 24 18 12 6 x1,000 km
Exhaust pipes & mountings
Brake/clutch fluid(3) (4)
Parking brake/Brake pads (F & R) (5)
Brake line & connections (including booster)
Manual transmission fluid (3)
Clutch & brake pedal free play
F & R Differential fluid (3)
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
R
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
R
I
RI
R
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
R
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
R
I
R
Automatic transmission fluid (BTRA M74) (6)
Chassis & underbody bolts & nuts tight/secure
Tire condition & inflation pressure
Wheel alignment (7)
Steering wheel & linkage
Power steering fluid & lines* (3)
Drive shaft boots
Seat belts, buckles & anchors
Lubricate locks, hinges & bonnet latchI
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
Transfer case fluid (3)R
IR
I II
I
I
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
Inspect & ADJUST when abnormal condition is noted
II
I
Chart Symbols :
I - Inspect these items and their related parts. If necessary, correct, clean, replenish, adjust or replace.
R - Replace or change.
(3) Refer to “Recommended fluids and lubricants”.
(4) Change the brake / clutch fluid more regularly if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe conditions :
- Driving in hilly or mountainous terrain, or
- Towing a trailer frequently
(5) More frequent maintenance is required if under severe condition : short distance driving, extensive idling, frequent low -
speed operation in stop-and-go traffic or driving in dusty condition.
(6) Change automatic transmission fluid every 70,000 km if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe conditions.
- In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly reaches 32°C (90°F) or higher, or
- In hilly or mountainous terrain, or
- When doing frequent trailer towing, or
- Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service.
(7) If necessary, rotate and balance wheels.
Page 38 of 1463

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A1-7
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. On some occasions a fluid leak may
be difficult to locate or repair. The following procedures
may help you in locating and repairing most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine oil,
automatic transmission fluid, power steering fluid, etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large sheet
of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate
location of the leak by the drippings on the
paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas that
are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be necessary
to clean the suspected area with a degreaser, steam
or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at normal
operating temperature and varying speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol-type powder (such as foot powder)
to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating
conditoins.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer to
the manufacturer's directions when using the kit.
1. Pour the specified amount of dye into the engine oil
fill tube.2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions as
directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The dyed
fluid will appear as a yellow path leading to the
source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpointed and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determined n order for it to be repaired properly. If a
gasket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the
new gasket will not repair the leak. The bent flange must
be repaired also. Before attempting to repair a leak,
check for the following conditions and correct them as
they may cause a leak.
Gaskets
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe fasteners are tightened improperly or the threads
are dirty or damaged.
lThe flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
lThere are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
lThe gasket is damaged or worn.
lThere is cracking or porosity of the component.
lAn improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
lThe seal is damaged or worn.
lImproper installation is evident.
lThere are cracks in the components.
lThe shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
lA loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal wear.
DIAGNOSIS
Page 52 of 1463

1A2-8 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. On some occasions a fluid leak may
be difficult to locate or repair. The following procedures
may help you in locating and repairing most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine oil,
automatic transmission fluid, power steering fluid, etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large sheet
of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate
location of the leak by the drippings on the
paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas that
are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be necessary
to clean the suspected area with a degreaser, steam
or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at normal
operating temperature and varying speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol-type powder (such as foot powder)
to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating
conditoins.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer to
the manufacturer's directions when using the kit.
1. Pour the specified amount of dye into the engine oil
fill tube.
2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions as
directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The dyed
fluid will appear as a yellow path leading to the
source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpointed and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determined n order for it to be repaired properly. If a
gasket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the
new gasket will not repair the leak. The bent flange must
be repaired also. Before attempting to repair a leak,
check for the following conditions and correct them as
they may cause a leak.
Gaskets
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe fasteners are tightened improperly or the threads
are dirty or damaged.
lThe flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
lThere are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
lThe gasket is damaged or worn.
lThere is cracking or porosity of the component.
lAn improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
lThe seal is damaged or worn.
lImproper installation is evident.
lThere are cracks in the components.
lThe shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
lA loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal wear.
DIAGNOSIS
Page 68 of 1463

1A3-10 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. On some occasions a fluid leak may
be difficult to locate or repair. The following
procedures may help you in locating and repairing
most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine
oil, automatic transmission fluid, power steering
fluid, etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large
sheet of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate
location of the leak by the drippings on the
paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas
that are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be
necessary to clean the suspected area with a
degreaser, steam or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at
normal operating temperature and varying
speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol-type powder (such as foot
powder) to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating
conditions.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer
to the manufacturer's directions when using the kit.1. Pour the specified amount of dye into the engine
oil fill tube.
2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions
as directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The
dyed fluid will appear as a yellow path leading to
the source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpointed and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must
be determined n order for it to be repaired properly. If
a gasket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent,
the new gasket will not repair the leak. The bent flange
must be repaired also. Before attempting to repair a
leak, check for the following conditions and correct
them as they may cause a leak.
Gaskets
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe fasteners are tightened improperly or the
threads are dirty or damaged.
lThe flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
lThere are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
lThe gasket is damaged or worn.
lThere is cracking or porosity of the component.
lAn improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
lThe fluid level/pressure is too high.
lThe crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
lThe seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
lThe seal is damaged or worn.
lImproper installation is evident.
lThere are cracks in the components.
lThe shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
lA loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal
wear.
DIAGNOSIS
Page 318 of 1463

1B3-16 OM600 ENGINE MECHANICAL
16. Remove the power steering pump lines.
Notice
Completely drain the fluid.
17. Disconnect the fuel feed line with prefilter from the feed
pump on injection pump.
18. Vehicle with automatic transmission.
Remove the hydraulic lines (19, 20) from oil cooler (2).
19. Disconnect the engine harness.
20. Disconnect the preheating time relay cable.
Page 978 of 1463

SECTION 5A
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-2
Model Part Numbers and Applications . . . . . . 5A-2
Model Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-2
Clutch Pack Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-3
Special Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-4
Special Tools Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-4
Schematic and Routing Diagrams . . . . . . . . 5A-5
TCU Circuit (Diesel) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-5
TCU Circuit (Gasoline) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-6
Shift Pattern Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-7
661LA Normal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-7
661LA Power Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-8
662LA Normal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-9
662LA Power Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-10
662LA Low Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-11
E32 Power Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-12
E32 Normal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-13
E32 Low Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-14
E23 Power Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-15
E23 Normal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-16
E23 Low Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-17
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-18
Operator Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-20
Gear Select Lever Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-20
Driving Mode Selector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-21
Control Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-22
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-22
Electronic Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-22
Hydraulic Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-31
Power Train System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-42
Torque Converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-43
Clutch Packs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-44Bands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-45
One Way Clutches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-45
Planetary Gear Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-45
Parking Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-46
Power Flows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-47
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-47
Power Flow - Park and Neutral . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-48
Power Flow - Reverse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-49
Power Flow - Manual 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-50
Power Flow - Drive 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-51
Power Flow - Drive 2 and Manual 2 . . . . . . . 5A-52
Power Flow - Drive 3 and Manual 3 . . . . . . . 5A-54
Power Flow - Drive 3 Lock Up and Manual
3 Lock Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-56
Power Flow - Drive 4 (Overdrive) . . . . . . . . . 5A-57
Power Flow - Drive 4 Lock Up . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-59
Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-60
Diagnostic System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-60
Mechanical Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-69
Self Diagnosis Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-75
Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-79
Hydraulic System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-79
Transmission Fluid Test Procedure . . . . . . . . 5A-79
Electronic Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-80
Maintenance and Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-82
On-Vehicle Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-82
Removal and Installation of Transmission . . . 5A-82
Unit Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-85
Rebuild Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-85
Disassembly Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-85
Assembly Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-94
Front and Rear Band Adjustment . . . . . . . . 5A-128