1998 PONTIAC FIREBIRD traction control
[x] Cancel search: traction controlPage 183 of 406

Check your mirrors, glance over your shoulder, and start your
left lane change signal before moving out
of the right lane to pass. When you are far enough
ahead
of the passed vehicle to see its front in your
inside mirror, activate your right lane change signal
and move back into the right
lane. (Remember that
your right outside mirror
is convex. The vehicle YOU
just passed may seem to be farther away from YOU
than it really is.)
Try not to pass more than one vehicle at a time
on two-lane roads. Reconsider before passing the
next vehicle.
Don’t overtake a slowly moving vehicle too rapidly.
Even though the brake lamps are not flashing, it may
be slowing down or starting to turn,
If you’re being passed, make it easy for the
following driver to get ahead of you. Perhaps you
can ease a little to the right.
Loss of Control
Let’s review what driving experts say about what
happens when
the three control systems (brakes, steering
and acceleration) don’t have enough friction where the
tires meet the road to do what the driver has asked.
In any emergency, don’t give up. Keep tryins to steer and
constantly seek
an escape route or area of less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive
drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions, and by not “overdriving”
those conditions. But
skids are always possible.
The
three types of skids correspond to your vehicle’s
three control systems.
In the braking skid, your wheels
aren’t rolling.
In the steering or cornering skid, too
much speed or steering
in a curve causes tires to slip and
lose cornering force. And
in the acceleration skid, too
much throttle causes the driving wheels to spin.
A cornering skid is best handled by easing your foot off
the accelerator pedal.
If
you have the traction control system, remember: It
helps avoid only the acceleration skid.
4-14
Page 184 of 406

If you do not have traction control, or if the system is
off, then an acceleration skid is also best handled by
easing your foot
off the accelerator pedal.
If your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot
off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the
way you want the
vehicle to go. If you start steering quickly enough, your
vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready for a
second skid if it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when water, snow, ice,
gravel or other material
is on the road. For safety, you’ll
want to slow down and adjust your driving to these
conditions. It is important to slow down on slippery
surfaces because stopping distance will be longer and
vehicle control more limited.
While driving on
a surface with reduced traction, try
your best to avoid sudden steering, acceleration or
braking (including engine braking by shifting to a lower
gear). Any sudden changes could cause the tires to
slide. You may not realize
the surface is slippery until
your vehicle is skidding. Learn to recognize warning
clues
-- such as enough water, ice or packed snow on
the road to make a
“mirrored surface” -- and slow
down when you have any doubt.
Remember: Any anti-lock brake system (ABS) helps
avoid only the braking skid.
Driving at Night
Night driving is more dangerous than day driving.
One reason is that some drivers are likely to be
impaired
-- by alcohol or drugs, with night vision
problems,
or by fatigue.
4-15
Page 196 of 406

What’s the worst time for this? “Wet ice.” Very cold
snow or ice can be slick and hard to drive on. But wet
ice can be even more trouble because it may offer the
least traction of all. You can get wet ice when it’s about
freezing
(32°F; 0” C) and freezing rain begins to fall.
Try to avoid driving on wet ice until salt and sand crews
can get there.
Whatever the condition
-- smooth ice, packed, blowing
or loose snow
-- drive with caution.
If you have traction control, keep the system on. It will
improve your ability to accelerate when driving on a slippery road. Even though your vehicle has a traction
control system, you’ll want to slow down and adjust
your driving to the road conditions. See “Traction
Control System”
in the Index.
If you don’t have the traction control system, accelerate
gently. Try not to break the fragile traction. If you
accelerate too fast, the drive wheels
will spin and polish
the surface under the tires even more. Your
anti-lock brakes improve your vehicle’s stability
when you make a hard stop on a slippery road. Even
though you have the anti-lock braking system, you’ll
want to begin stopping sooner than you would
on dry
pavement. See “Anti-Lock” in the Index.
0 Allow greater following distance on any
slippery road.
Watch for slippery spots. The road might be fine
until you hit a spot that’s covered with ice. On
an
otherwise clear road, ice patches may appear in
shaded areas where the sun can’t reach: around
clumps of trees, behind buildings
or under bridges.
Sometimes the surface of a curve or an overpass may
remain icy when the surrounding roads are clear. If
you see a patch of ice ahead of you, brake before you
are on it. Try not to brake while you’re actually on
the ice, and avoid sudden steering maneuvers.
4-27
Page 251 of 406

I NOTICE:
Spinning your wheels can destroy parts of your
vehicle as
well as the tires. If you spin the wheels
too fast while shifting your transmission back and forth, you can destroy your transmission.
For information about using tire chains on your vehicle,
see “Tire Chains” in the Index.
~ Rocking Your Vehicle To Get It Out
~ First, turn your steering wheel left and right. That will
clear
the area around your front wheels. If your vehicle
has traction control, you should turn the system
off.
(See “Traction Control System’’ in the Index.) Then shift
back and
forth between REVERSE (R) and a forward
gear (or with a manual transmission, between
FIRST (1)
or SECOND (2) and REVERSE (R)), spinning the
wheels as little as possible. Release the accelerator pedal
while you shift, and press lightly on the accelerator
pedal when the transmission
is in gear. If that doesn’t
get
you out after a few tries, you may need to be towed
out. If you do need to be towed out, see “Towing Your
Vehicle” in the Index.
5-42
Page 302 of 406

Buying New Tires
To find out what kind and size of tires you need, look at
the Tire-Loading Information label.
The tires installed on your vehicle when it was new had
a Tire Performance Criteria Specification (TPC Spec) number on each tire’s sidewall. When you get new tires,
get ones with that same TPC Spec number. That way
your vehicle will continue to have tires that
are designed
to
give proper endurance, handling, speed rating,
traction, ride and other things during normal service on
your vehicle.
If your tires have an all-season tread
design, the TPC number will be followed by an
“MS”
(for mud and snow).
If you ever replace your tires with those not having a
TPC Spec number, make sure they are the same size,
load range, speed rating and construction type (bias,
bias-belted
or radial) as your original tires.
A CAUTION:
Mixing tires could cause you to lose control while
driving.
If you mix tires of different sizes or types
(radial and bias-belted tires), the vehicle may
not handle properly, and you could have a crash.
Using tires
of different sizes may also cause
damage to your vehicle. Be sure to use the same
size and type tires on all wheels.
It’s all right to drive with your compact spare,
though.
It was developed for use on your vehicle.
’ A, CAUTION:
If you use bias-ply tires on your vehicle, the
wheel rim flanges could develop cracks after
many miles of driving.
A tire and/or wheel could
fail suddenly, causing a crash. Use only radial-ply
tires
with the wheels on your vehicle.
6-49
Page 303 of 406

Uniform Tire Quality Grading
The following information relates to the system
developed
by the United States National Highway
Traffic Safety Administration, which grades tires by
treadwear, traction and temperature performance.
(This
applies only to vehicles sold in the United States.) The
grades are molded on the sidewalls
of most passenger
car tires. The Uniform Tire Quality Grading system
does not apply to deep tread, winter-type snow tires,
space-saver or temporary
use spare tires, tires with
nominal
rim diameters of 10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm),
or
to some limited-production tires.
While the tires available on General Motors passenger
cars and light trucks may
vary with respect to these
grades,
they must also conform to Federal safety
requirements and additional General Motors Tire
Performance Criteria (TPC) standards.
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on
the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled
conditions on a specified government test course.
For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one and a
half (1 1/2) times as well on the government course
as a tire graded
100. The relative performance of tires
depends upon the actual conditions of their use,
however,
and may depart significantly from the norm
due to variations in driving habits, service practices and
differences in road characteristics and climate.
%action -- A, B, C
The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are A, B,
and C, and they represent the tire’s ability to stop
on wet pavement as measured under controlled
conditions on specified government test surfaces
of
asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have poor
traction performance.
Warning: The traction grade assigned to this tire is
based on braking (straight ahead) traction tests and
does not include cornering (turning) traction.
6-50
Page 317 of 406
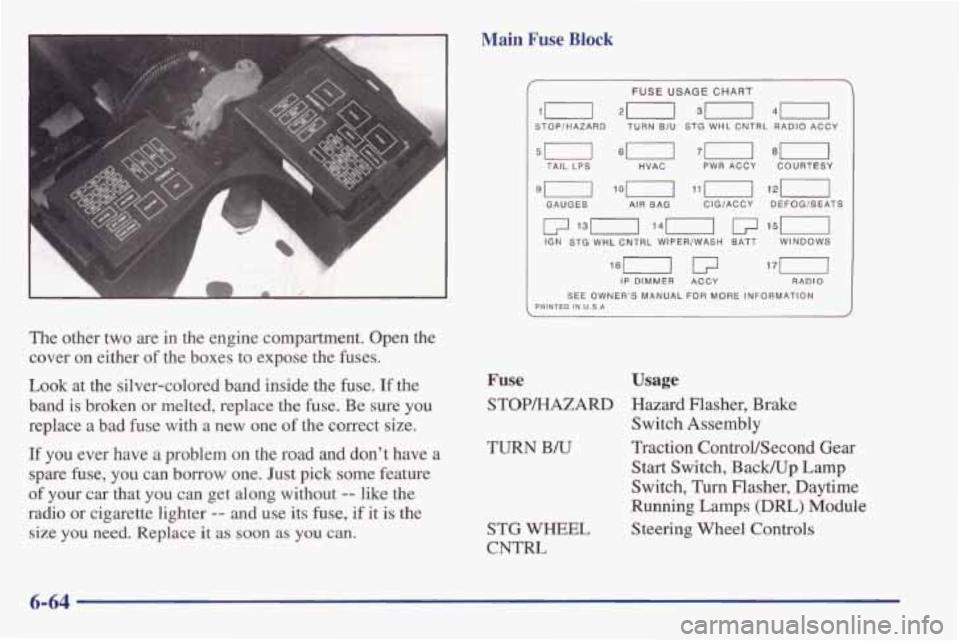
The other two are in the engine compartment. Open the
cover on either
of the boxes to expose the fuses.
Look at the silver-colored band inside the fuse. If the
band is broken or melted, replace
the fuse. Be sure you
replace a bad fuse with a new one of the correct size.
If you ever have a problem on the road and don't have a
spare fuse, you can borrow one. Just pick some feature
of your car that you
can get along without -- like the
radio or cigarette lighter
-- and use its fuse, if it is the
size
you need. Replace it as soon as you can.
Main Fuse Block
III 20 30 40
FUSE USAGE CHART
STOPIHAZARD TURN BIU STG WHL CNTRL RADIO ACCY
--
5u 4--l 7u 8U TAIL LPS HVAC PWR ACCY COURTESY
9-1 lin 121-1
GAUGES AIR BAG CIGIACCY DEFOGISEATS
IP DIMMER ACCY RADIO
SEE OWNER'S MANUAL FOR MORE INFORMATION PRINTED IN U.S.A
Fuse Usage
STOP/HAZARD Hazard Flasher, Brake
Switch Assembly
TURN B/U Traction ControVSecond Gear
Start Switch, Back/Up Lamp
Switch, Turn Flasher, Daytime
Running Lamps
(DRL) Module
Steering Wheel Controls
STG WHEEL
CNTFU
6-64
Page 318 of 406

TAIL LPS HVAC
PWR ACCY
COURTESY
GAUGES
Fuse Usage
RADIO ACCY Delco Monsoon Radio Amplifier, Power Antenna, Remote CD
Player (trunk)
Daytime Running Lamps (DRL)
Module, Headlamp Switch
HVAC Selector Switch, Rear
Defogger Switch/Timer
Park Lamp Relay, Hatch
Release Relay, Power Mirror Switch, Radio,
Shock Sensor,
Instrument Cluster
Body Control Module (BCM)
Body Control Module (BCM),
Brake Switch Assembly
(BTSI),
Instrument Cluster, Daytime
Running Lamps (DRL) Module
AIR BAG Air Bag, Dual Pole Arming Sensor
CIGAFUACCY Cigar Lighter, Data Link
Connector (DLC), Auxiliary
Accessory Wire
Defogger Timermelay, Power Seats
DEFOGBEATS Rear Defogger Switch/Timer, Rear WINDOWS
I/p DIMMER
RADIO
Usage
Steering Wheel Controls
Fuse
STG WHEEL
CNTRL
WIPEWASH Wiper Motor Assembly,
Wiper/Washer Switch
Power Windows Switch
(RH, LH),
Express-Down Module, Coolant
Level Latching Module, Convertible Top Switch
Door Illumination Lamp
(RH,
LH), Headlamp Switch, Fog Lamp
Switch, Instrument Cluster,
HVAC
Control Assembly, PRNDL
Illumination Lamp, Ashtray Lamp,
Radio, Steering Wheel
Controls-Radio, Rear Window
Defogger Switch/Timer, Traction
Control Switch
(TCS) and 2nd
Gear Start Switch
Body Control Module (BCM),
Radio, Amplifier, Steering
Wheel
Controls-Radio
6-65