1998 OPEL FRONTERA stop start
[x] Cancel search: stop startPage 4096 of 6000

4B2–13 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD)
Diagnosis
General Information Diagnosis
The troubles on TOD are classified into the group that can
be identified by the lighting status of the TOD indicator
lamps and those that can be recognized as abnormal
phenomena of the vehicle by the driver.
The troubles that can be identified by the lighting status of
the TOD indicator lamps are examined by the procedures
“Diagnosis from Trouble Codes” and “Trouble Diagnosis
Depending on The Status of TOD indicator”. The troubles
that can be recognized as abnormal phenomena of the
vehicle by the driver are examined by the procedure
“Diagnosis from symptom”.
Self-diagnosis
The control unit has a function of self-diagnosis. If a
trouble occurs in the course of system startup, the control
unit blinks the CHECK lamp and saves the trouble code.
C07RW021
NOTE: If an intermittent fault occurs, the control unit
stops blinking upon removal of the fault. The trouble code
is saved to the control unit.
Page 4098 of 6000

4B2–15 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD)
How to Clear The Trouble Code
The trouble codes saved to the control unit can be deleted
by the following procedure if the starter switch is being in
the OFF position.
1. Shift the transfer lever to the neutral position between
HIGH and 4L, and short-circuit the self-diagnostic
connector.
NOTE: The neutral position between HIGH and 4L refers
to the point that turns off the TOD indicator lamps.
(However, be sure to check the position before
short-circuiting the self-diagnostic connector.)
C07RW011
2. Turn on the starter switch while maintaining the state
of step 1, and step on the brake pedal five times within
five seconds from the first step on. (Note that “five
times” includes the first step on). (The TOD indicator
lamps display the 4L mode whenever the brake pedal
is stepped on.)
3. If the conditions shown in steps 1 and 2 are met, the
trouble codes saved to the control unit are cleared.
(After the codes are completely deleted, the code 12
that indicates the normal condition is continuously
displayed.)
Precautions on Diagnosis
Replacement of Control Unit
The control unit itself rarely fails. In most cases, the
harnesses have failed (i.e. short-circuit) to cause
secondary troubles. Other cases include that the cause
has been unknown due to intermittent occurrence of
troubles and the troubles are removed accidentally along
with replacement of control unit, resulting in misjudgment
of cause. Therefore, before replacing the control unit,
check the connector joints and whether the unspecified
current flows in the control unit due to short-circuit
between harnesses.Trouble Intermittently Observed
Troubles intermittently observed are mostly attributable
to temporary imperfect connection of harnesses and
connectors.
When such troubles are found, check the associated
circuit according to the following procedure.
1. Check whether improper connectors are plugged in
or connector terminals are completely engaged.
2. Check whether the terminals are deformed or
damaged. If yes, remove the deformation or damage
and connect the terminals securely.
3. It is likely that wires in the harness are falsely broken.
Therefore, in examination of failed harness circuit,
shake the harness for check to such extent that the
harness will not be damaged.
Test Run of Failed TOD Vehicle
If the TOD indicator lamps experienced faulty operation
even once in the past, the failed portion can be identified
by use of the procedure “Diagnosis from Trouble Codes”
or “Trouble Diagnosis Depending on The Status of TOD
Indicator”. If the troubles that are only recognized as
abnormal phenomena of the vehicle by the driver are
observed, conduct the test run in the following procedure
to reproduce the faulty phenomena and diagnose the fault
for each phenomenon.
1. Start the engine, and check that the TOD indicator
lamps are turned on for about two seconds for initial
check; the CHECK lamp goes off; and the TOD
indicator lamps display the specified drive mode. (If
the CHECK lamp starts blinking, read the trouble
codes and identify the failed portion.)
2. While keeping the vehicle standstill, operate the 4WD
switch and shift the transfer lever to change the
modes: 2H mode
TOD mode4L modeTOD
mode
2H mode. Check that the TOD indicator
lamps correctly display the status whenever the
mode is changed. If the transition status is displayed
during the shift operation, run the vehicle a little to
complete shifting.
3. Slowly start the vehicle in the TOD mode, and add the
power to accelerate to at least 40 km/h and maintain
the speed for about two minutes. Apply the brake to
completely stop the vehicle. Repeat this test pattern
at least three times.
4. Turn the steering to the right end (or left end) in the
TOD mode, and slowly start the vehicle and make a
c i r c l e f i v e t i m e s . N e x t , c o n d u c t t h e s a m e t e s t i n t h e 2 H
mode.
5. Slowly start the vehicle in the TOD mode, and
accelerate to at least 40 km/h. Keep the established
speed, carefully change the mode in the sequence
“TOD mode
2H mode TOD mode” while checking
that the shift is complete in each mode change. After
the test, apply the brake to completely stop the
vehicle.
6. Slowly start the vehicle in the TOD mode, and
accelerate to at least 40 km/h. Apply the brake
strongly so that the ABS works, and completely stop
the vehicle.
Page 4099 of 6000

DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD) 4B2–16
7. Slowly start the vehicle in the 4L mode, and
accelerate to at least 20 km/h. Apply the brake to
completely stop the vehicle.
If the CHECK lamp starts blinking during the test run, read
the trouble codes and give appropriate maintenance
according to the diagnostic procedure. If the TOD
indicator lamps are lit abnormally during the run, check
the lighting condition and give appropriate maintenance
according to the diagnostic procedure. Even if the
phenomena are not observed, try to reproduce the
abnormal state reported by the customer to the possible
extent.
Post-Repair Check
As long as the starter is not turned off, the TOD indicator
lamps continue blinking even after the failed portion
repaired. Therefore, upon completion of repair, be sure to
turn off the starter switch once and then turn on it to
conduct the test run sequence specified in steps 1
through 7 above and check that the TOD indicator lamps
no longer show any faulty status.
Page 4122 of 6000
4B2–39 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD)
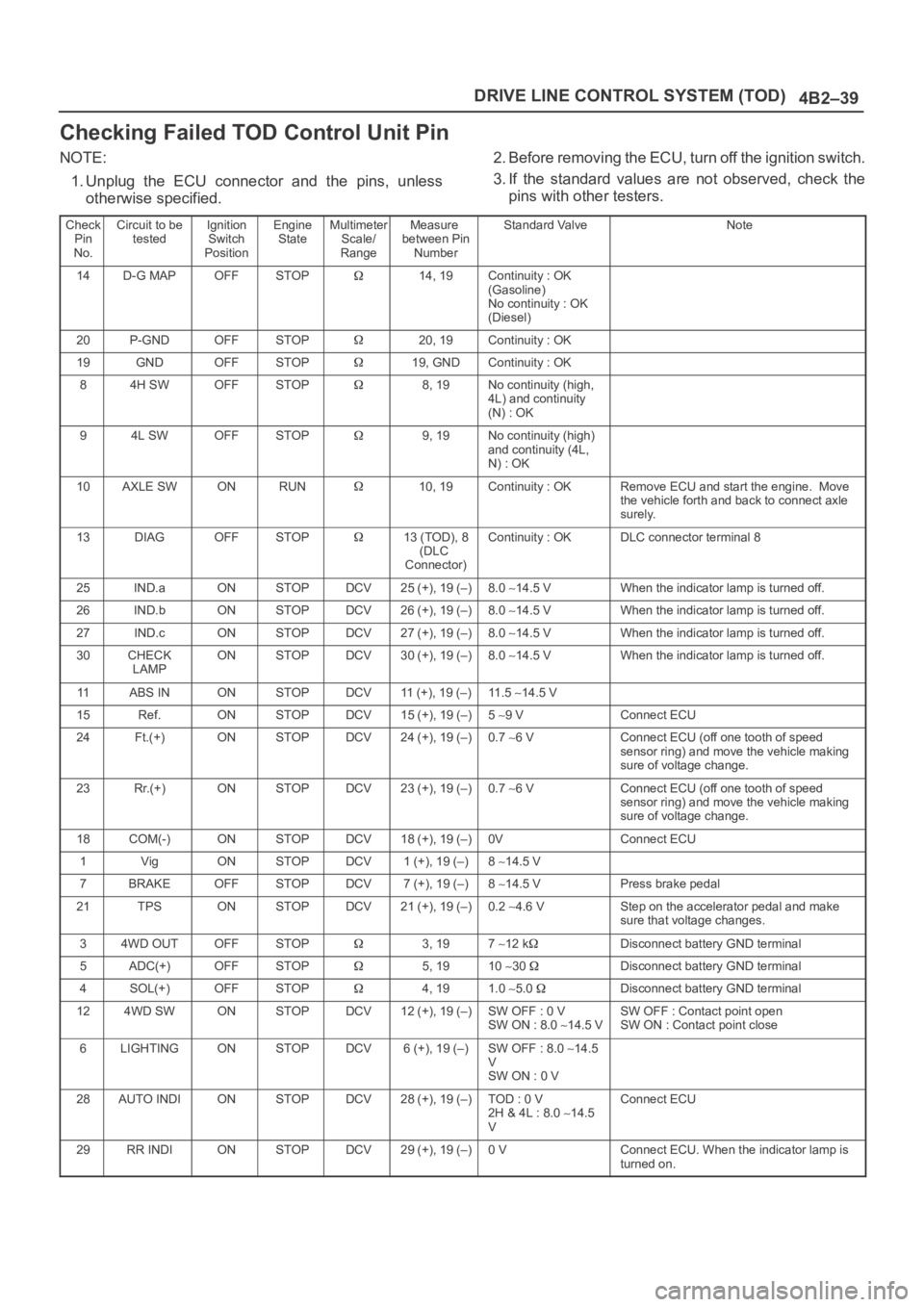
Checking Failed TOD Control Unit Pin
NOTE:
1. Unplug the ECU connector and the pins, unless
otherwise specified.2. Before removing the ECU, turn off the ignition switch.
3. If the standard values are not observed, check the
pins with other testers.
Check
Pin
No.Circuit to be
testedIgnition
Switch
PositionEngine
StateMultimeter
Scale/
RangeMeasure
between Pin
NumberStandard ValveNote
14D-G MAPOFFSTOP14, 19Continuity : OK
(Gasoline)
No continuity : OK
(Diesel)
20P-GNDOFFSTOP20, 19Continuity : OK
19GNDOFFSTOP19, GNDContinuity : OK
84H SWOFFSTOP8, 19No continuity (high,
4L) and continuity
(N) : OK
94L SWOFFSTOP9, 19No continuity (high)
and continuity (4L,
N) : OK
10AXLE SWONRUN10, 19Continuity : OKRemove ECU and start the engine. Move
the vehicle forth and back to connect axle
surely.
13DIAGOFFSTOP13 (TOD), 8
(DLC
Connector)Continuity : OKDLC connector terminal 8
25IND.aONSTOPDCV25 (+), 19 (–)8.0 14.5 VWhen the indicator lamp is turned off.
26IND.bONSTOPDCV26 (+), 19 (–)8.0 14.5 VWhen the indicator lamp is turned off.
27IND.cONSTOPDCV27 (+), 19 (–)8.0 14.5 VWhen the indicator lamp is turned off.
30CHECK
LAMPONSTOPDCV30 (+), 19 (–)8.0 14.5 VWhen the indicator lamp is turned off.
11ABS INONSTOPDCV11 (+), 19 (–)11 . 5 14.5 V
15Ref.ONSTOPDCV15 (+), 19 (–)5 9 VConnect ECU
24Ft.(+)ONSTOPDCV24 (+), 19 (–)0.7 6 VConnect ECU (off one tooth of speed
sensor ring) and move the vehicle making
sure of voltage change.
23Rr.(+)ONSTOPDCV23 (+), 19 (–)0.7 6 VConnect ECU (off one tooth of speed
sensor ring) and move the vehicle making
sure of voltage change.
18COM(-)ONSTOPDCV18 (+), 19 (–)0VConnect ECU
1VigONSTOPDCV1 (+), 19 (–)8 14.5 V
7BRAKEOFFSTOPDCV7 (+), 19 (–)8 14.5 VPress brake pedal
21TPSONSTOPDCV21 (+), 19 (–)0.2 4.6 VStep on the accelerator pedal and make
sure that voltage changes.
34WD OUTOFFSTOP3, 197 12 kDisconnect battery GND terminal
5ADC(+)OFFSTOP5, 1910 30 Disconnect battery GND terminal
4SOL(+)OFFSTOP4, 191.0 5.0 Disconnect battery GND terminal
124WD SWONSTOPDCV12 (+), 19 (–)SW OFF : 0 V
SW ON : 8.0 14.5 VSW OFF : Contact point open
SW ON : Contact point close
6LIGHTINGONSTOPDCV6 (+), 19 (–)SW OFF : 8.0 14.5
V
SW ON : 0 V
28AUTO INDIONSTOPDCV28 (+), 19 (–)TOD : 0 V
2H & 4L : 8.0 14.5
VConnect ECU
29RR INDIONSTOPDCV29 (+), 19 (–)0 VConnect ECU. When the indicator lamp is
turned on.
Page 4320 of 6000
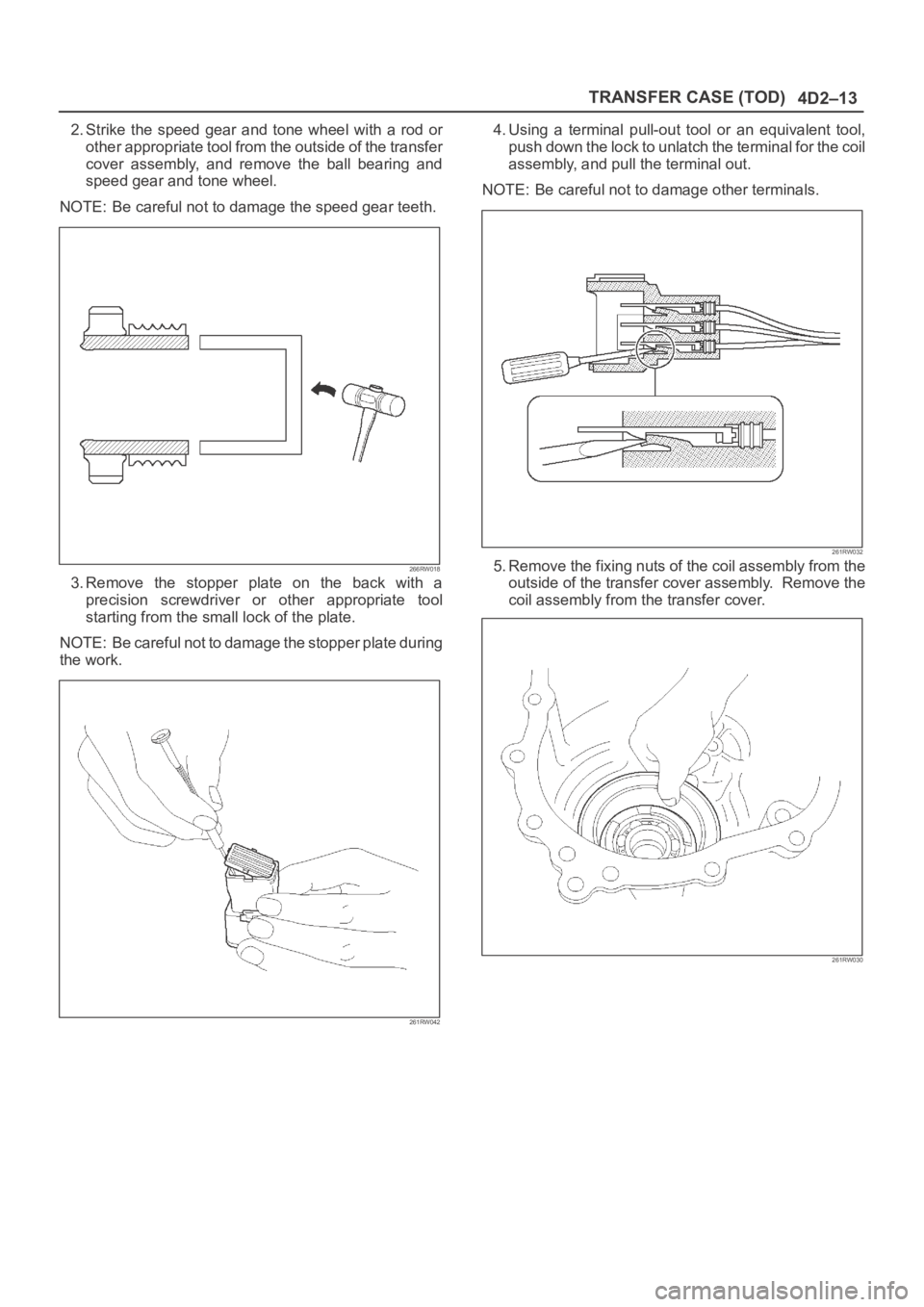
4D2–13 TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
2. Strike the speed gear and tone wheel with a rod or
other appropriate tool from the outside of the transfer
cover assembly, and remove the ball bearing and
speed gear and tone wheel.
NOTE: Be careful not to damage the speed gear teeth.
266RW018
3. Remove the stopper plate on the back with a
precision screwdriver or other appropriate tool
starting from the small lock of the plate.
NOTE: Be careful not to damage the stopper plate during
the work.
261RW042
4. Using a terminal pull-out tool or an equivalent tool,
push down the lock to unlatch the terminal for the coil
assembly, and pull the terminal out.
NOTE: Be careful not to damage other terminals.
261RW032
5. Remove the fixing nuts of the coil assembly from the
outside of the transfer cover assembly. Remove the
coil assembly from the transfer cover.
261RW030
Page 4355 of 6000

5A–5 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
FR
Front Right
GEN
Generator
MV
Millivolts
RL
Rear Left
RR
Rear RightRPS
Revolution per Second
VDC
Vo l t s D C
VA C
Vo l t s A C
W/L
Warning Light
WSS
Wheel Speed Sensor
General Diagnosis
General Information
ABS malfunction can be classified into two types, those
which can be detected by the ABS warning light and those
which can be detected as a vehicle abnormality by the
driver.
In either case, locate the fault in accordance with the
“BASIC DIAGNOSTIC FLOWCHART” and repair.
Please refer to Section 5C for the diagnosis of
mechanical troubles such as brake noise, brake judder
(brake pedal or vehicle vibration felt when braking),
uneven braking, and parking brake trouble.
ABS Service Precautions
Required Tools and Items:
Box Wrench
Brake Fluid
Special Tool
Some diagnosis procedures in this section require the
installation of a special tool.
J-39200 High Impedance Multimeter
When circuit measurements are requested, use a circuit
tester with high impedance.
Computer System Service Precautions
The Anti-lock Brake System interfaces directly with the
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU) which is a
control computer that is similar in some regards to the
Powertrain Control Module. These modules are designed
to withstand normal current draws associated with
vehicle operation. However, care must be taken to avoid
overloading any of the EHCU circuits. In testing for opens
or shorts, do not ground or apply voltage to any of the
circuits unless instructed to do so by the appropriate
diagnostic procedure. These circuits should only be
tested with a high impedance multimeter (J-39200) or
special tools as described in this section. Power should
never be removed or applied to any control module with
the ignition in the “ON” position.
Before removing or connecting battery cables, fuses or
connectors, always turn the ignition switch to the “OFF”
position.
General Service Precautions
The following are general precautions which should be
observed when servicing and diagnosing the Anti-lock
Brake System and/or other vehicle systems. Failure toobserve these precautions may result in Anti-lock Brake
System damage.
If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle using
an electric arc welder, the EHCU and valve block
connectors should be disconnected before the
welding operation begins.
The EHCU and valve block connectors should never
be connected or disconnected with the ignition “ON” .
EHCU of the Anti-lock Brake System are not
separately serviceable and must be replaced as
assemblies. Do not disassemble any component
which is designated as non-serviceable in this
Section.
If only rear wheels are rotated using jacks or drum
tester, the system will diagnose a speed sensor
malfunction and the “ABS” warning light will
illuminate. But actually no trouble exists. After
inspection stop the engine once and re-start it, then
make sure that the “ABS” warning light does not
illuminate.
If the battery has been discharged
The engine may stall if the battery has been completely
discharged and the engine is started via jumper cables.
This is because the Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
requires a large quantity of electricity. In this case, wait
until the battery is recharged, or set the ABS to a
non-operative state by removing the fuse for the ABS
(40A). After the battery has been recharged, stop the
engine and install the ABS fuse. Start the engine again,
and confirm that the ABS warning light does not light.
Note on Intermittents
As with virtually any electronic system, it is difficult to
identify an intermittent failure. In such a case duplicating
the system malfunction during a test drive or a good
description of vehicle behavior from the customer may be
helpful in locating a “most likely” failed component or
circuit. The symptom diagnosis chart may also be useful
in isolating the failure. Most intermittent problems are
caused by faulty electrical connections or wiring. When
an intermittent failure is encountered, check suspect
circuits for:
Suspected harness damage.
Poor mating of connector halves or terminals not fully
seated in the connector body (backed out).
Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Page 4356 of 6000

5A–6
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Test Driving ABS Complaint Vehicles
In case that there has been an malfunction in the lighting
pattern of “ABS” warning light, the fault can be located in
accordance with the “DIAGNOSIS BY “ABS” WARNING
LIGHT ILLUMINATION PATTERN” . In case of such
trouble as can be detected by the driver as a vehicle
symptom, however, it is necessary to give a test drive
following the test procedure mentioned below, thereby
reproducing the symptom for trouble diagnosis on a
symptom basis:
1. Start the engine and make sure that the “ABS” W/L
goes OFF. If the W/L remains ON, it means that the
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored. Therefore,
read the code and locate the fault.
2. Start the vehicle and accelerate to about 30 km/h (19
mph) or more.
3. Slowly brake and stop the vehicle completely.
4. Then restart the vehicle and accelerate to about 40
km/h (25 mph) or more.
5. Brake at a time so as to actuate the ABS and stop the
vehicle.
6. Be cautious of abnormality during the test. If the W/L
is actuated while driving, read the DTC and locate the
fault.
7. If the abnormality is not reproduced by the test, make
best efforts to reproduce the situation reported by the
customer.
8. If the abnormality has been detected, repair in
accordance with the “SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS” .NOTE:Be sure to give a test drive on a wide, even road with
little traffic.
If an abnormality is detected, be sure to suspend the
test and start trouble diagnosis at once.
“ABS” Warning Light
When ABS trouble occurs and actuates when possible
the “ABS” warning light, the trouble code corresponding
to the trouble is stored in the EHCU. Only the ordinary
brake system is available when the ABS is turned off.
When the “ABS” warning light is actuated, if the starter
switch is set ON after setting it OFF once, the EHCU
checks up on the entire system and, if there is no
abnormality, judges ABS to work currently and the
warning light works normally even though the trouble
code is stored.
NOTE: Illumination of the “ABS” warning light indicates
that anti-lock braking is no longer available. Power
assisted braking without anti-lock control is still available.
Normal Operation
“ABS” Warning Light
W h e n t h e i g n i t i o n i s f i r s t m o v e d f r o m “ O F F ” t o “ R U N ” , t h e
amber “ABS” warning light will turn “ON” . The “ABS”
warning light will turn “ON” during engine starting and will
usually stay “ON” for approximately three seconds after
the ignition switch is returned to the “ON” position. The
warning light should remain “OFF” at all other times.
Basic Diagnostic Flow Chart
StepActionYe sNo
11. Customer complaint.
2. Questioning to customer.
3. Basic inspection (Refer to “Basic inspection procedure”)
Using TECH 2?
Go to Step 2Go to Step 4
2Make sure of DTC by mode “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Codes”.
Is EHCU including DTC?
Go to Step 3Go to Step 5
31. Repair of faulty part.
2. Elimination of DTC.
3. Inspection of “ABS” W/L Illumination pattern with ignition SW
“ON”.
4. Test drive.
Does repeat trouble?
Repeat the
diagnosis it the
symptom or DTC
appears again Go
to Step 1
Go to Step 5
4Check if the DTC is stored.
Is EHCU including DTC?
Go to Step 3
Trouble diagnosis
based on
symptom (Refer
to “SYMPTOM
DIAGNOSIS”) Go
to Step 3
51. Reconnect all components and ensure all component are
properly mounted.
2. Clear diagnostic trouble code.
Was this step finished?
FinishedGo to Step 5
Page 4361 of 6000

5A–11 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Data List
DisplayContentOK/NG Criteria for Data
Battery VoltageVo l t a g eBetween 10-16.9V
Brake Light SwitchOpen/CloseOpen(0V) when pedal is released
Closed(12V) when pedal is depressed.
Front Left Wheel Speed
Front Right Wheel Speed
Rear Left Wheel Speed
Rear Right Wheel SpeedMPH(km/h)Start the vehicle and make sure of linear change in each
wheel speed.
Turn each wheel by hand and make sure that each
speed data change.
Wheel Sensor StatusOK/NGTo be OK usually
G-sensorLow/HighTo be Low usually
Transfer Monitor(TOD)2 Wheel Drive
4 Wheel DriveWhen 2WD: 2 Wheel Drive
When 4WD: 4 Wheel Drive
Off-Road Switch
(Transmission Input)
Active/InactiveWhen shift lever position is 1, 2 and R: Active (M/T)
(Transmission Input)When shift lever position is L and R: Active (A/T)
Valve RelayActive/InactiveTo be Active usually
ABS StateON/OFFTo be OFF usually
ABS RelayActive/InactiveTo be Active usually
Return Pump RelayActive/InactiveTo be Inactive usually
Front Left Isolation ValveActive/InactiveTo be Inactive usually
Front Left Dump Valve
Front Right Isolation Valve
Front Right Dump Valve
Rear Isolation Valve
Rear Dump Valve
ABS Warning LampON/OFFTo be ON usually (while engine stopped)