1998 NISSAN PATROL Ac control
[x] Cancel search: Ac controlPage 4 of 47

+Clean all disassembled parts in the designated liquid or solvent
prior to inspection or assembly.
+Replace oil seals, gaskets, packings, O-rings, locking washers,
cotter pins, self-locking nuts, etc. with new ones.
+Replace inner and outer races of tapered roller bearings and
needle bearings as a set.
+Arrange the disassembled parts in accordance with their
assembled locations and sequence.
+Do not touch the terminals of electrical components which use
microcomputers (such as ECMs).
Static electricity may damage internal electronic components.
+After disconnecting vacuum or air hoses, attach a tag to indi-
cate the proper connection.
+Use only the ¯uids and lubricants speci®ed in this manual.
+Use approved bonding agent, sealants or their equivalents
when required.
+Use tools and recommended special tools where speci®ed for
safe and efficient service repairs.
+When repairing the fuel, oil, water, vacuum or exhaust systems,
check all affected lines for leaks.
+Dispose of drained oil or the solvent used for cleaning parts in
an appropriate manner.
WARNING:
To prevent ECM from storing the diagnostic trouble codes, do
not carelessly disconnect the harness connectors which are
related to the ECCS system and TCM (Transmission Control
Module) system. The connectors should be disconnected only
when working according to the WORK FLOW of TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES in EC and AT sections.
Precautions for Multiport Fuel Injection System
or ECCS Engine
+Before connecting or disconnecting any harness connector for
the multiport fuel injection system or ECM (Engine Control
Module):
Turn ignition switch to ``OFF'' position.
Disconnect negative battery terminal.
Otherwise, there may be damage to ECM.
+
Before disconnecting pressurized fuel line from fuel pump to
injectors, be sure to release fuel pressure.
+Be careful not to jar components such as ECM and mass air
¯ow sensor.SGI787
PRECAUTIONS
General Precautions (Cont'd)
GI-3
Page 15 of 47
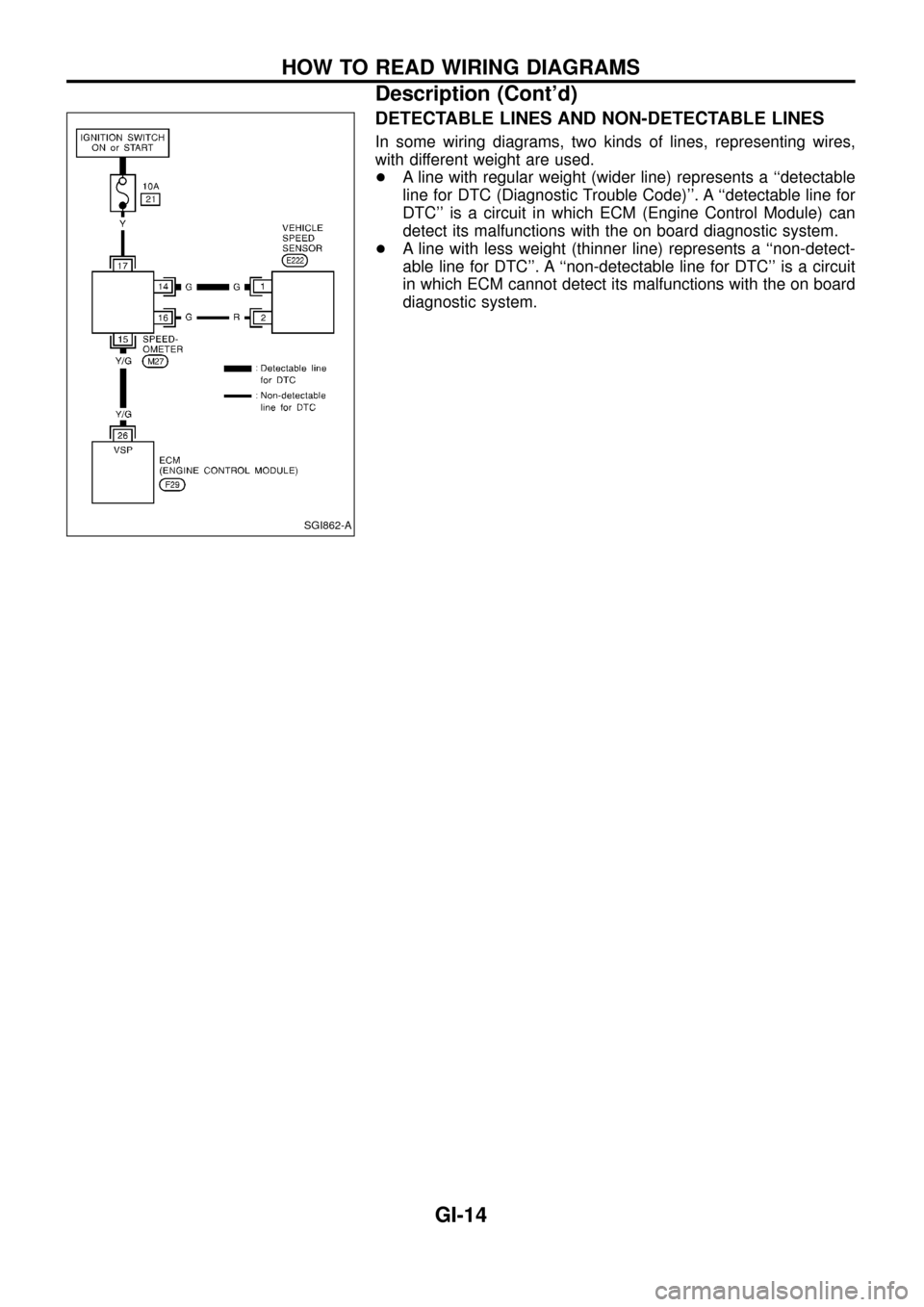
DETECTABLE LINES AND NON-DETECTABLE LINES
In some wiring diagrams, two kinds of lines, representing wires,
with different weight are used.
+A line with regular weight (wider line) represents a ``detectable
line for DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code)''. A ``detectable line for
DTC'' is a circuit in which ECM (Engine Control Module) can
detect its malfunctions with the on board diagnostic system.
+A line with less weight (thinner line) represents a ``non-detect-
able line for DTC''. A ``non-detectable line for DTC'' is a circuit
in which ECM cannot detect its malfunctions with the on board
diagnostic system.
SGI862-A
HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS
Description (Cont'd)
GI-14
Page 27 of 47
Voltage check method
1. Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid discon-
nected) powered through the fuse.
2. Turn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify battery voltage at the B
+side of the fuse ter-
minal (one lead on the B
+terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
3. With SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
4. With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check
for voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
5. With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid
(point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
GROUND INSPECTION
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can become
an unwanted resistance. This unwanted resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can dras-
tically affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin ®lm of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
1. Remove the ground bolt screw or clip.
2. Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
3. Clean as required to assure good contact.
4. Reinstall bolt or screw securely.
5. Inspect for ``add-on'' accessories which may be interfering with the ground circuit.
6. If several wires are crimped into one ground eyelet terminal, check for proper crimps. Make sure all of the
wires are clean, securely fastened and providing a good ground path. If multiple wires are cased in one
eyelet make sure no ground wires have excess wire insulation.
SGI853
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-26
Page 28 of 47
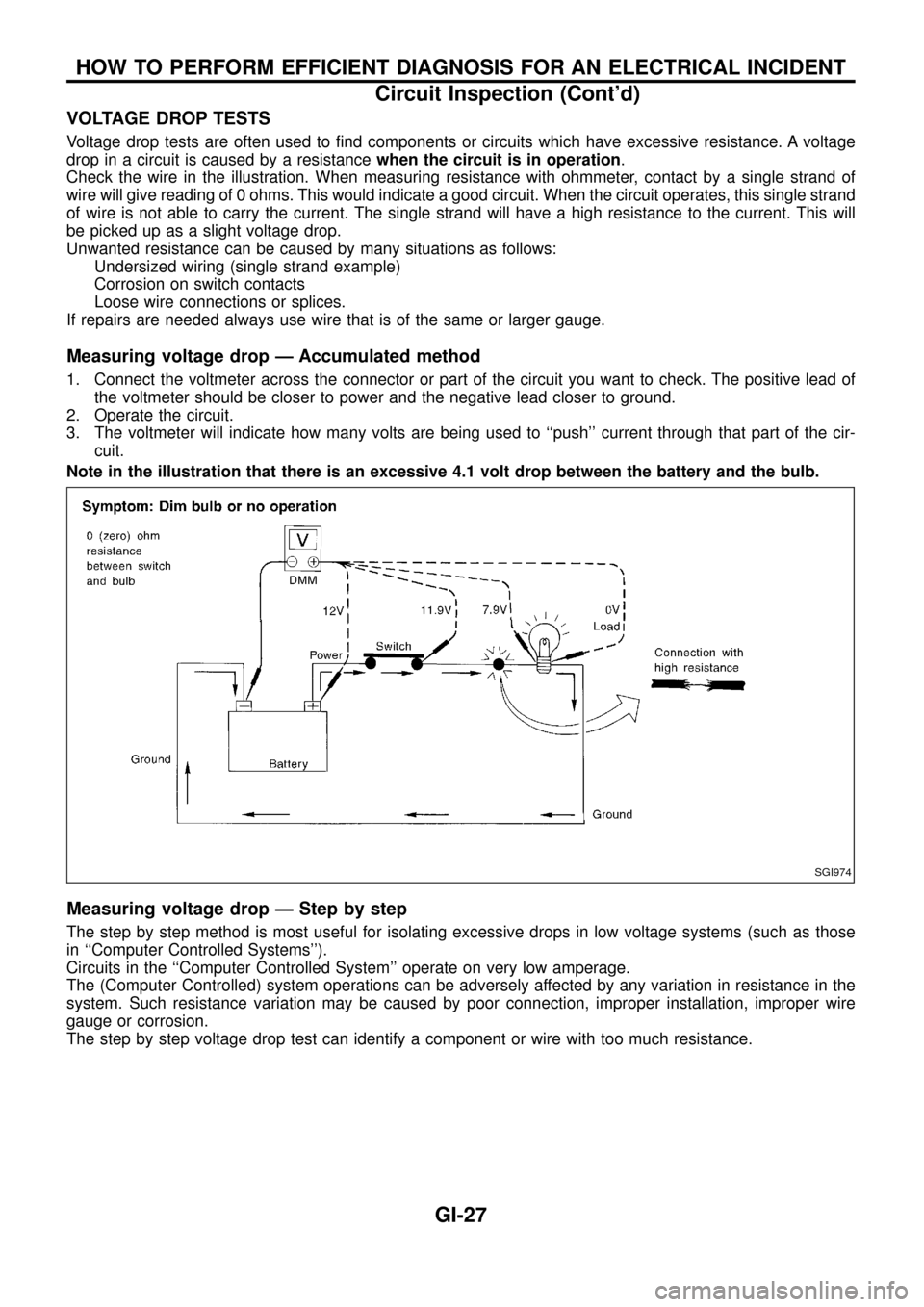
VOLTAGE DROP TESTS
Voltage drop tests are often used to ®nd components or circuits which have excessive resistance. A voltage
drop in a circuit is caused by a resistancewhen the circuit is in operation.
Check the wire in the illustration. When measuring resistance with ohmmeter, contact by a single strand of
wire will give reading of 0 ohms. This would indicate a good circuit. When the circuit operates, this single strand
of wire is not able to carry the current. The single strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will
be picked up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
Undersized wiring (single strand example)
Corrosion on switch contacts
Loose wire connections or splices.
If repairs are needed always use wire that is of the same or larger gauge.
Measuring voltage drop Ð Accumulated method
1. Connect the voltmeter across the connector or part of the circuit you want to check. The positive lead of
the voltmeter should be closer to power and the negative lead closer to ground.
2. Operate the circuit.
3. The voltmeter will indicate how many volts are being used to ``push'' current through that part of the cir-
cuit.
Note in the illustration that there is an excessive 4.1 volt drop between the battery and the bulb.
Measuring voltage drop Ð Step by step
The step by step method is most useful for isolating excessive drops in low voltage systems (such as those
in ``Computer Controlled Systems'').
Circuits in the ``Computer Controlled System'' operate on very low amperage.
The (Computer Controlled) system operations can be adversely affected by any variation in resistance in the
system. Such resistance variation may be caused by poor connection, improper installation, improper wire
gauge or corrosion.
The step by step voltage drop test can identify a component or wire with too much resistance.
SGI974
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-27
Page 30 of 47
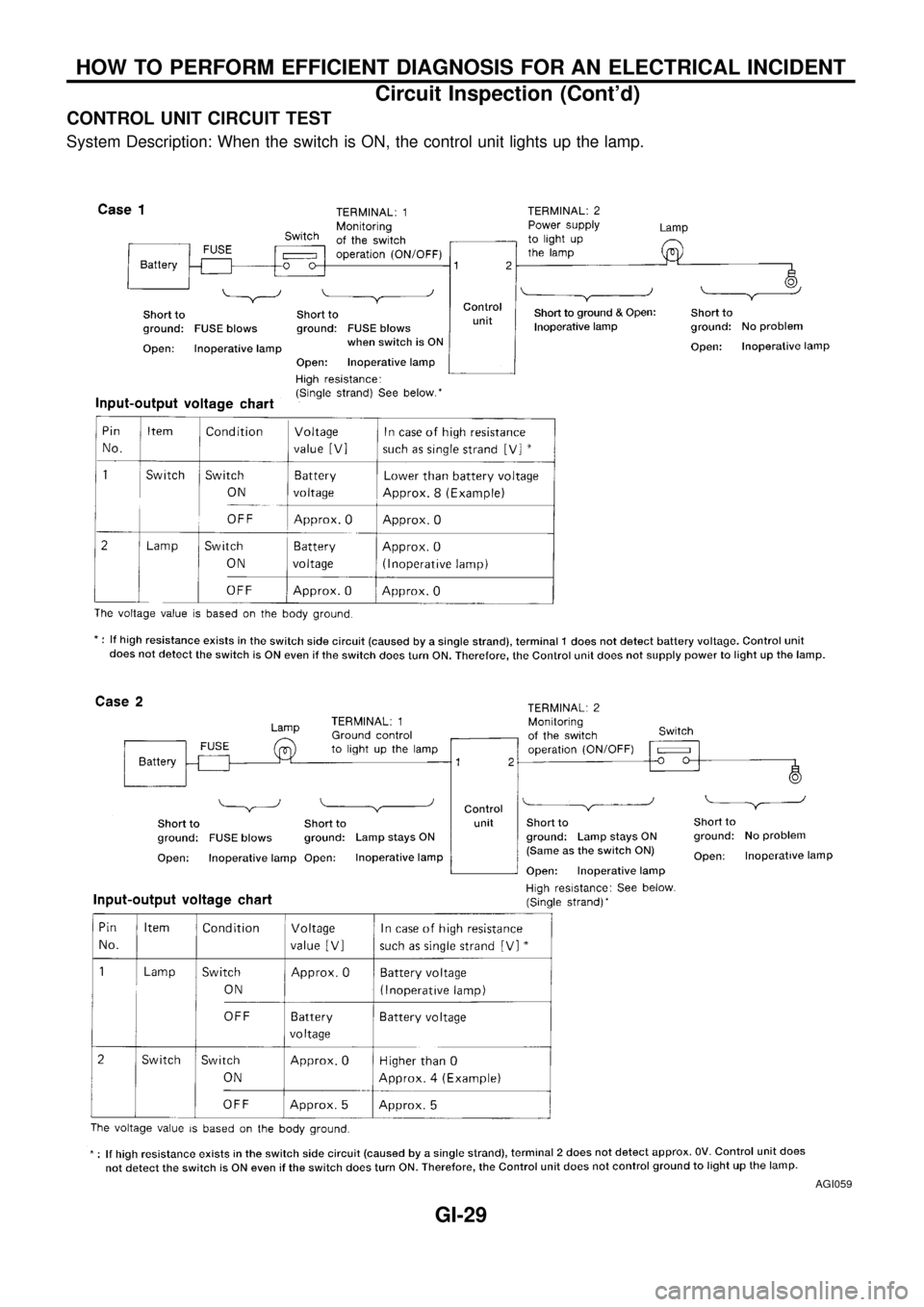
CONTROL UNIT CIRCUIT TEST
System Description: When the switch is ON, the control unit lights up the lamp.
AGI059
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-29
Page 35 of 47

Loading Procedure
CONSULT Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
If the CONSULT cannot diagnose the system properly, check the following items.
Symptom Check item
CONSULT cannot access
any system.+CONSULT DLC power supply circuit (Terminal 7) and ground circuit (Terminal 8)
(For detailed circuit, refer to ``MIL & Data Link Connectors Wiring Diagram'' in EC section.)
+CONSULT DDL cable
CONSULT cannot access
individual system. (Other sys-
tems can be accessed.)+CONSULT program card (Check the appropriate CONSULT program card for the system. Refer
to GI-33.)
+Power supply and ground circuit for the control unit of the system
(For detailed circuit, refer to wiring diagram for each system.)
+Open or short circuit between the system and CONSULT DLC
(For detailed circuit, refer to wiring diagram for each system.)
SGI983
SGI984
CONSULT CHECKING SYSTEM
GI-34
Page 44 of 47
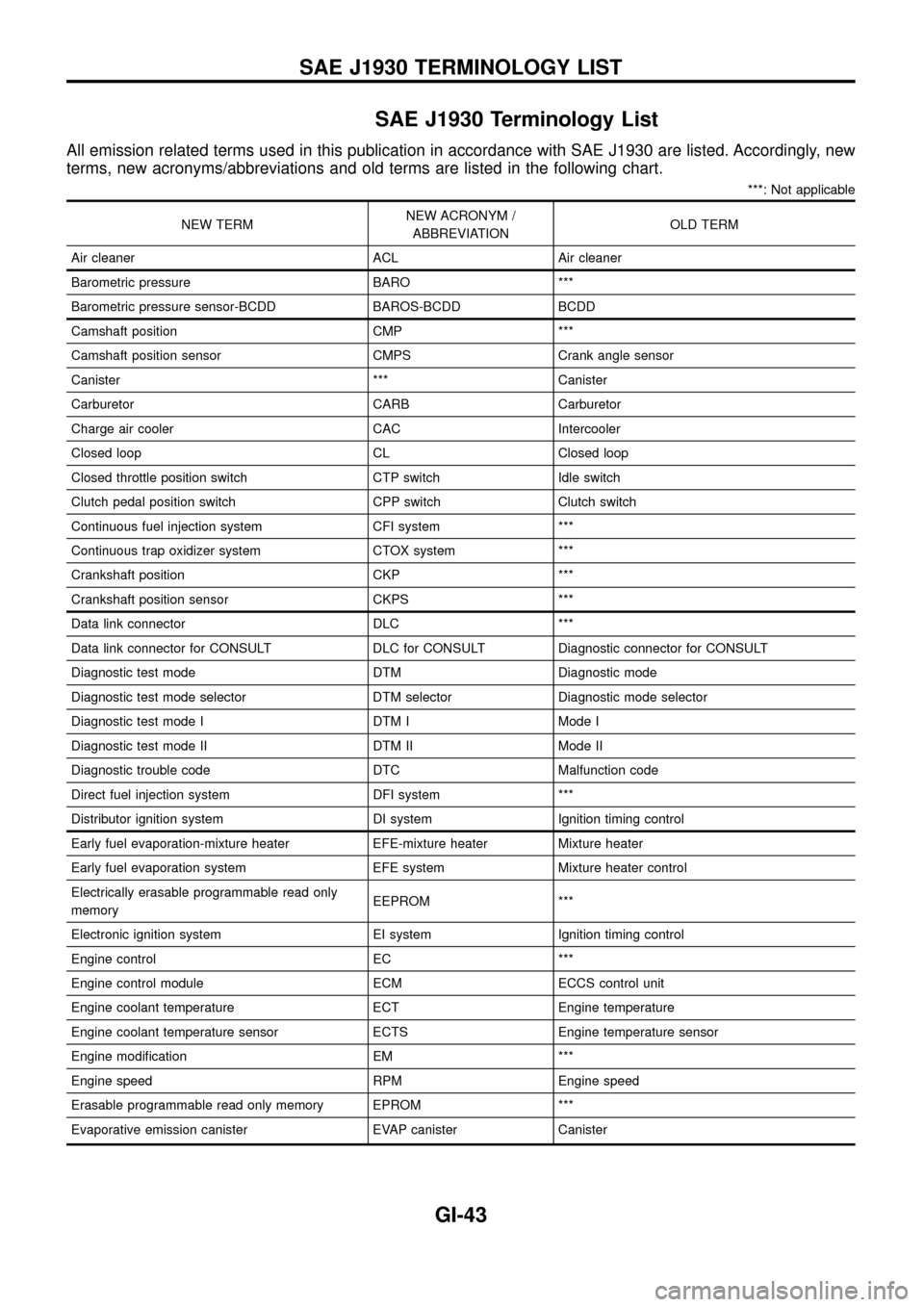
SAE J1930 Terminology List
All emission related terms used in this publication in accordance with SAE J1930 are listed. Accordingly, new
terms, new acronyms/abbreviations and old terms are listed in the following chart.
***: Not applicable
NEW TERMNEW ACRONYM /
ABBREVIATIONOLD TERM
Air cleaner ACL Air cleaner
Barometric pressure BARO ***
Barometric pressure sensor-BCDD BAROS-BCDD BCDD
Camshaft position CMP ***
Camshaft position sensor CMPS Crank angle sensor
Canister *** Canister
Carburetor CARB Carburetor
Charge air cooler CAC Intercooler
Closed loop CL Closed loop
Closed throttle position switch CTP switch Idle switch
Clutch pedal position switch CPP switch Clutch switch
Continuous fuel injection system CFI system ***
Continuous trap oxidizer system CTOX system ***
Crankshaft position CKP ***
Crankshaft position sensor CKPS ***
Data link connector DLC ***
Data link connector for CONSULT DLC for CONSULT Diagnostic connector for CONSULT
Diagnostic test mode DTM Diagnostic mode
Diagnostic test mode selector DTM selector Diagnostic mode selector
Diagnostic test mode I DTM I Mode I
Diagnostic test mode II DTM II Mode II
Diagnostic trouble code DTC Malfunction code
Direct fuel injection system DFI system ***
Distributor ignition system DI system Ignition timing control
Early fuel evaporation-mixture heater EFE-mixture heater Mixture heater
Early fuel evaporation system EFE system Mixture heater control
Electrically erasable programmable read only
memoryEEPROM ***
Electronic ignition system EI system Ignition timing control
Engine control EC ***
Engine control module ECM ECCS control unit
Engine coolant temperature ECT Engine temperature
Engine coolant temperature sensor ECTS Engine temperature sensor
Engine modi®cation EM ***
Engine speed RPM Engine speed
Erasable programmable read only memory EPROM ***
Evaporative emission canister EVAP canister Canister
SAE J1930 TERMINOLOGY LIST
GI-43
Page 45 of 47
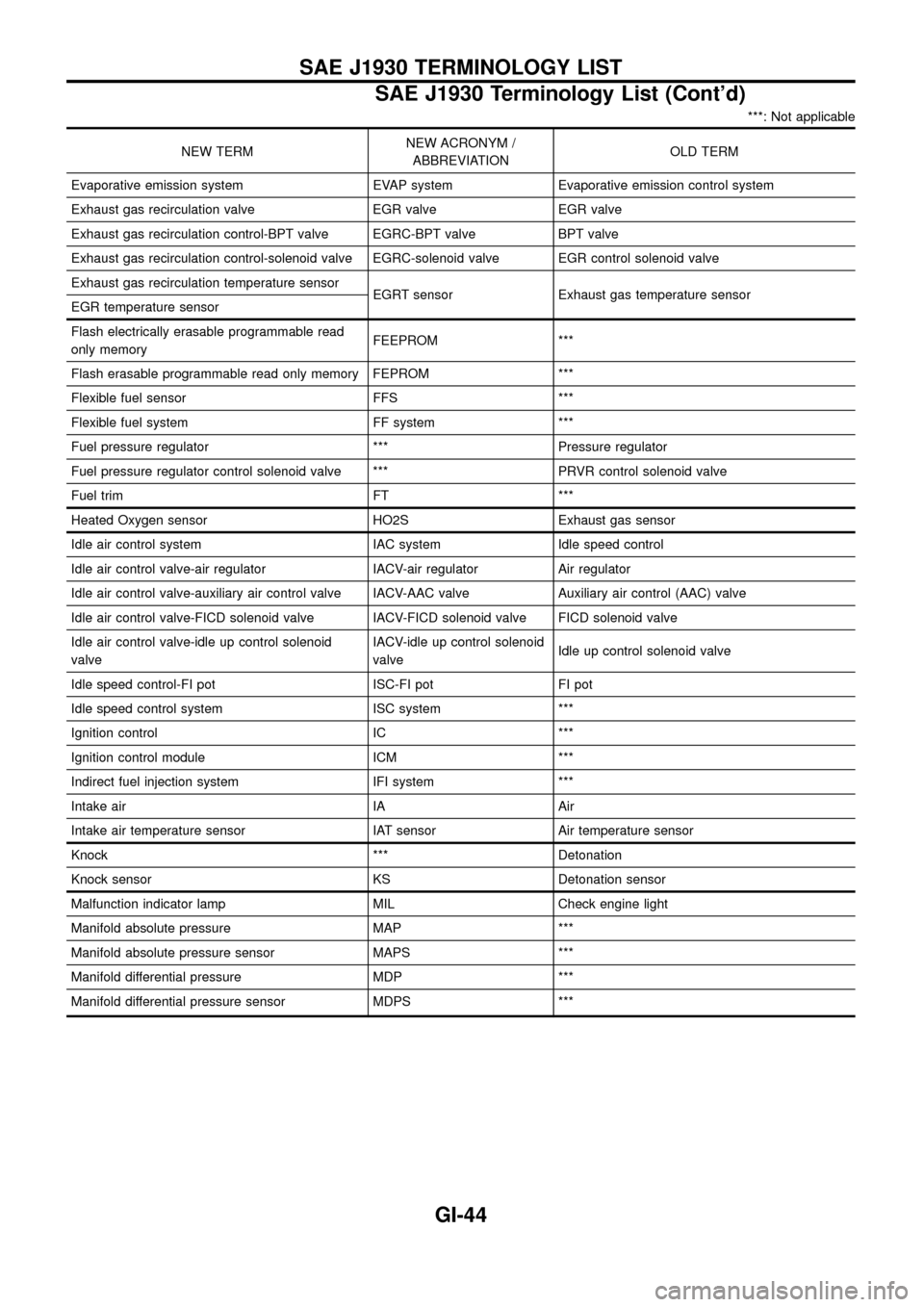
***: Not applicable
NEW TERMNEW ACRONYM /
ABBREVIATIONOLD TERM
Evaporative emission system EVAP system Evaporative emission control system
Exhaust gas recirculation valve EGR valve EGR valve
Exhaust gas recirculation control-BPT valve EGRC-BPT valve BPT valve
Exhaust gas recirculation control-solenoid valve EGRC-solenoid valve EGR control solenoid valve
Exhaust gas recirculation temperature sensor
EGRT sensor Exhaust gas temperature sensor
EGR temperature sensor
Flash electrically erasable programmable read
only memoryFEEPROM ***
Flash erasable programmable read only memory FEPROM ***
Flexible fuel sensor FFS ***
Flexible fuel system FF system ***
Fuel pressure regulator *** Pressure regulator
Fuel pressure regulator control solenoid valve *** PRVR control solenoid valve
Fuel trim FT ***
Heated Oxygen sensor HO2S Exhaust gas sensor
Idle air control system IAC system Idle speed control
Idle air control valve-air regulator IACV-air regulator Air regulator
Idle air control valve-auxiliary air control valve IACV-AAC valve Auxiliary air control (AAC) valve
Idle air control valve-FICD solenoid valve IACV-FICD solenoid valve FICD solenoid valve
Idle air control valve-idle up control solenoid
valveIACV-idle up control solenoid
valveIdle up control solenoid valve
Idle speed control-FI pot ISC-FI pot FI pot
Idle speed control system ISC system ***
Ignition control IC ***
Ignition control module ICM ***
Indirect fuel injection system IFI system ***
Intake air IA Air
Intake air temperature sensor IAT sensor Air temperature sensor
Knock *** Detonation
Knock sensor KS Detonation sensor
Malfunction indicator lamp MIL Check engine light
Manifold absolute pressure MAP ***
Manifold absolute pressure sensor MAPS ***
Manifold differential pressure MDP ***
Manifold differential pressure sensor MDPS ***
SAE J1930 TERMINOLOGY LIST
SAE J1930 Terminology List (Cont'd)
GI-44