1998 HONDA CR-V Dash
[x] Cancel search: DashPage 405 of 1395
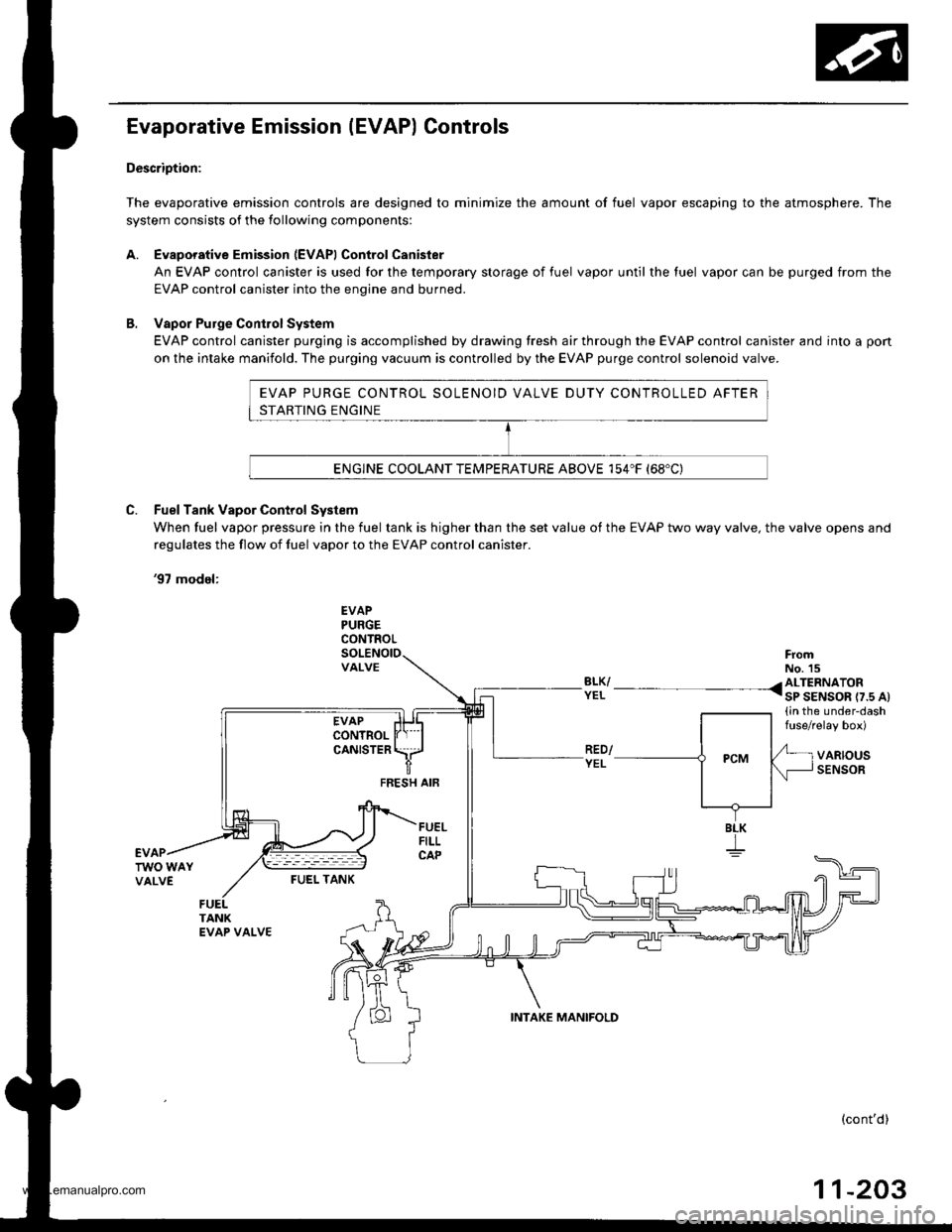
EVAP PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE DUTY CONTROLLED AFTER
STARTING ENGINE
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE ABOVE 154"F (68'C)
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Controls
Description:
The evaporative emission controls are designed to minimize the amount of fuel vapor escaping to the atmosphere. The
system consists of the following components:
A. Evaporative Emission (EVAPI Control Canister
An EVAP control canister is used for the temporary storage of fuel vapor until the luel vapor can be purged from the
EVAP control canister into the enqine and burned.
B. Vapor Purge ConirolSystem
EVAP control canister purging is accomplished by drawing fresh air through the EVAP control canister and into a pon
on the intake manifold. The purging vacuum is controlled by the EVAP purge control solenoid valve.
C. Fuel Tank Vapor Control System
When fuel vapor pressure in the fuel tank is higher than the set value of the EVAP two way valve, the valve opens and
regulates the flow ot fuel vapor to the EVAP control canister.
'97 model:
EVAPPURGECONTROL
VALVEFromNo. 15BLK/ /ALTERNATORYEL I sP SENSOR r7.s At(in the under-dashfuse/relay box)
VARIOUSSENSORFEESH AIF
BLK
I
FUEI- TANK
(cont'd)
11-203
INTAKE MANIFOLD
www.emanualpro.com
Page 406 of 1395
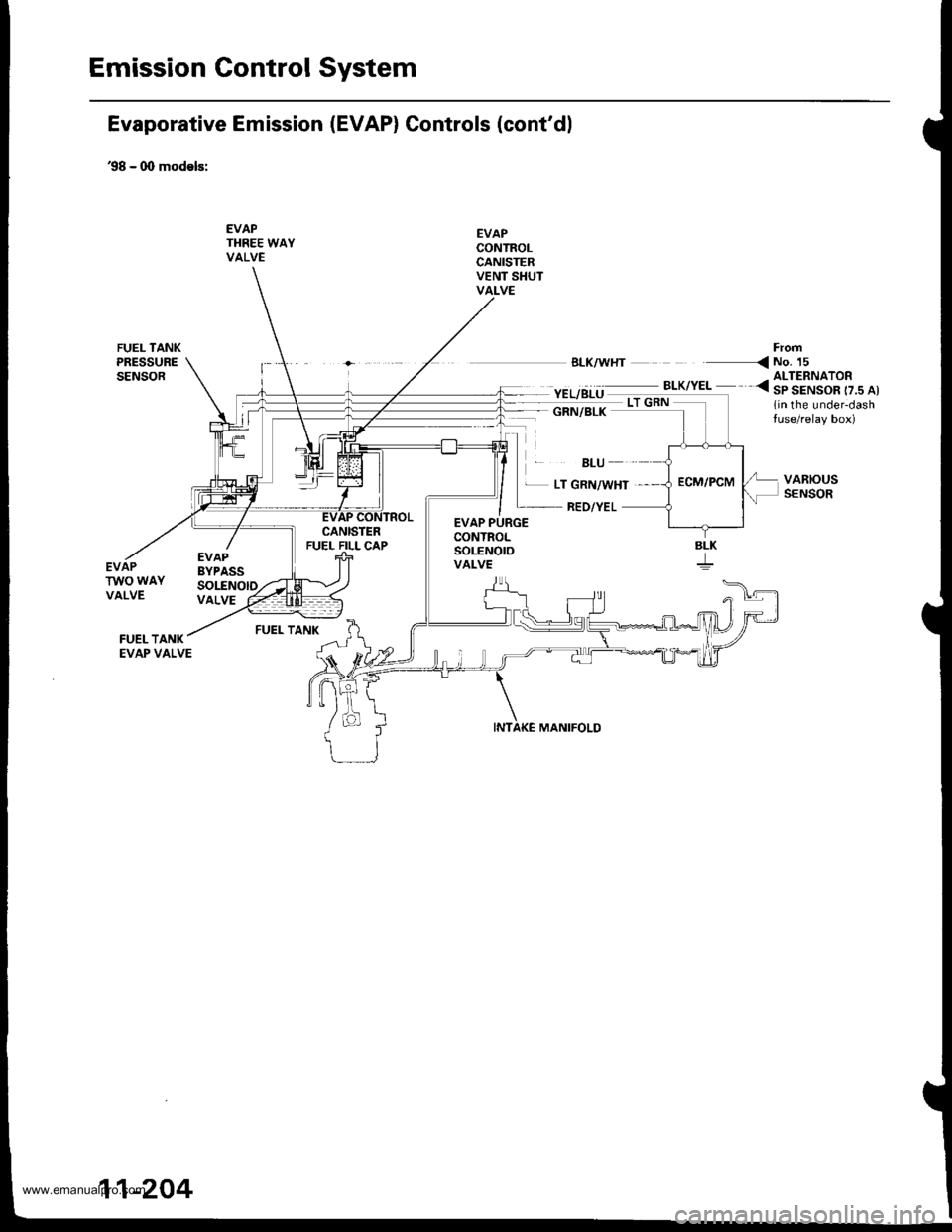
Emission Gontrol System
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Controls (cont'dl
'98 - 0O models:
EVAPTHREE WAYVALVE
EVAPCONTROLCANISTERVENT SHUTVALVE
'EL/BLU ._^_-:.*,".. <3|ltAIS"o[..^,
1in the under-dashtuse/relay box)
FrofiBLK/WHT < NO. 15
GRN/BLK
BLU
EVAPBYPASSSOLENOID
EVAP PURGECONTROLSoLENOtOVALVE
L LT GRN/WHT ,
RED/YEL
MANIFOLD
VARIOUSSENSOR
EVAPTWO WAYVALVEVALVE
FUEL TANK
SLK
11-204
www.emanualpro.com
Page 519 of 1395

Description
General Operation
The Automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and triple-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides 4
speeds forward and 1 reverse speed The unit is positioned in line with the engine'
There are two tvoes of automatic transmission on CR-V; the four-wheel drive (4WD) model ('97 - 00)' and the front-wheel
drive (2WD) model ('98 - 00).
Toroue Converter, G€ars, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump. turbine. and stator assembly in a single unit. The torque converter is connected to
the engine crankshatt. These parts turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is
a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is started. The torque converter assembly serves as a fly-
wheel while transmitting power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has three parallel shafts: the mainshaft. the countershaft, and the sub-shaft. The mainshaft is in line with
the engine crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd. and 4th clutches, and gears lor 3rd,2nd,4th. reverse and 1st
(3rd gear is integral with the mainshaft, while reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd
clutch and gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse, 1st, and park. Reverse and 4th gears can be locked to the countershaft at its cen-
ter, providing 4th gear or reverse, depending on which way the selector is moved. The sub-shaft includes the lst-hold
clutch and gears for lst and 4th.
The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the countershaft and sub-shaft. When certain combinations
of gears are engaged by the ctutches, power is transmitted from the mainshaft to the countershaft to provide E, D!, tr, tr,
and E position ('97 - 98 models). and E. E, E, and E position ('99 - 00 models)'
Electlonic Control
The electronic controt system consists of the Powenrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid, and four
solenoid valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the kick panel on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main valve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body, and
the lock up valve body. They are bolted to the torque converter housing. The main valve body contains the manual valve,
the 1-2 shift valve, the 2nd orifice control valve. the CPB {Clutch Pressure Back-up) valve, the modulator valve, the servo
control valve. the relief valve, and ATF pump gears. The secondary valve body contains the 2-3 shift valve, the 3-4 shift
valve, the 3,4 orifice control valve. the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch Pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve
bodv contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve, the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up con-
trol valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the reverse shift tork, and the accumulators
The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing valve. The linear solenoid and the shift con-
trol solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted to the outside of the transmission housing, and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is
bolted to the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid trom the regulator passes through the manual valve to the
various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective feed pipes or internal hydraulic circuit
ShiftControl Mechanism
input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will acti-
vate. Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes
a line to one of the clutches. engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear. The shift control solenoid valves A and B are
controlled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
tn E! position (,97 - 98 modets) and in E position ('99 - O0 models), in 3rd and 4th, and in Del position in 3rd ('97 - 98
models) and in El position with Over,Drive (O/D) is OFF (by pressing rhe O/D switchl in 3rd ('99 - 00 models), pressurized
fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held
against the torque converter cover, As this takes place, the mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshaft.
Together with hydraulic control, the PcM optimizes the timing of the lock-up mechanism The lock-up valves control the
range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B, and the linear solenoid. When lock-up control
solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes. The lock-up control solenoid valves A and B and the
linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
{cont'd)
14-3
www.emanualpro.com
Page 531 of 1395

Electronic Control System
The electronic control svstem consists of a Powertrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid, and four solenoid
valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions. The PCM is located
below the dashboard, under the kick panel on the passenger's side.
'97 - 98 Mod€ls
PGM.FIControl Sy3t6m
Throttl€ Poshion SensorSignalVehicle Sp.ed SensorSignal
Engino Coolant TamperetureService Check connectorSonsor Signrl
A/T Control Sy3tem
INTERLOCK
Shift Cont.ol
Shift ControlSolenoid valve ACONTROL UNITr
RShift ControlSolenoid Valve B
N
Linear SolenoidDr
Lock-up Control
Ds
Lock-up ControlSolenoid Valve A2
Lock-up ConirolSol6noid valvo B1
M.inshaft Spoed SensorSignel-D! Indicator Light
Count€rahaft Speedsensor SignelSelt-Oiagnosb signel
I
Sell-DiagnosisFunction
l-
{cont'd)
14-15
www.emanualpro.com
Page 566 of 1395
![HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Workshop Manual
PCM Circuit Diagram (A/T Gontrol System)
98 Model
UNOEF-HOOO FUSAFELAY sox
_YEL_
09 lD0 lDl,l lDl5
PNK BLU
F rronr
f-r------}-er
F_ cRN _______]_f- PN(
F_ GFNTBLX
F_ gnN
*,,,,)83HfL
f *-> 311 HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Workshop Manual
PCM Circuit Diagram (A/T Gontrol System)
98 Model
UNOEF-HOOO FUSAFELAY sox
_YEL_
09 lD0 lDl,l lDl5
PNK BLU
F rronr
f-r------}-er
F_ cRN _______]_f- PN(
F_ GFNTBLX
F_ gnN
*,,,,)83HfL
f *-> 311](/manual-img/13/5778/w960_5778-565.png)
PCM Circuit Diagram (A/T Gontrol System)
'98 Model
UNOEF-HOOO FUSAFELAY sox
_YEL_
09 lD0 lDl,l lDl5
PNK BLU
F rronr
f-'r'------}-'er'
F_ cRN _______]_f- PN(
F_ GFNTBLX
F_ gnN
*,',,,)83Hf'L
f *'-> 3111"?"
I
1*[-lll-,I I Gro]
UNOEF-DASHFUSE/BELAYBOX
I
rGD2 I ocr I oG2 | V8 S0. I SIOP SW I CAs
ATP IDl ,ATP , ATP , A-P , ATP , A_PNP lrND lR lD4 lD3 12 ll
sr{rTat
14-50
www.emanualpro.com
Page 572 of 1395

Troubleshooting Procedures
Checking ths Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
with an O8D ll Scan tool or Honda PGM Tsster
When the PCM senses an abnormality in the input or output systems, the El ('97 - 98) or E ('99 - O0) indicator light in thegauge ass€mbly will blink. When the 16P Data Link Connector (DLC) {located under the dash on the passenger's side) is
connected to the OBD ll Scan Tool or Honda PGM Tester as shown, the scan tool or tester will indicate the Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) when the ignition switch is turned ON(ll).
HONDA PGM TESTER olOBD II SCAN TOOL
lf the E or E indicator light or the MIL has been reported on, or if a driveability problem is suspected, follow this proce-
dure:
1. Connect the OBD ll Scan Tool (conforming to SAE J1978) or Honda PGM Tester to the 16P DLC. (See the OBD ll ScanTool or Honda PGM Tester user's manual for specific instructions. lf you are using the Honda PGM Tester, make sureit is set to the SAE DTC Wpe).2. Turn the ignition switch ON (ll), and observe the DTC on the screen
3. Record allfuel and emission DTCS, A,,/T DTCS, and freeze data.
4. lf there is a fuel and emissions DTC, first check the fuel and emissions system as indicated by the DTC (except for DTCP0700). DTC P0700 means there is one or more Ay'T DTC, and no Droblems were detected in the fuel and emissionscircuit of the PCM.
5. Wire down the radio station presets.
6. Reset the memory with the PGM Tester o. by removing the BACK UP fuse in the under-hood fuse/relay box for morethan 10 seconds.
7. Drive the vehicle for several minutes at speeds over 30 mph (50 km/hr), and then recheck for DTCS. lf the A/T DTCreturns, 9o to the Symptom-to Component Chart on pages 14-60 and 14-61 for the '97 models, and pages 14-62 and14-63 for '98 - 00 models. lf the OTC does not return, there was an intermittent problem within the circuit. Make sureall pins and terminals in the circuit are tight, and then go to step 8.8. Reset the radio Dreset stations, and set the clock.
DATA LINK CONNECTOR {16PI
[ -=.r,
ili,i /i,
v,., i
14-56
www.emanualpro.com
Page 573 of 1395
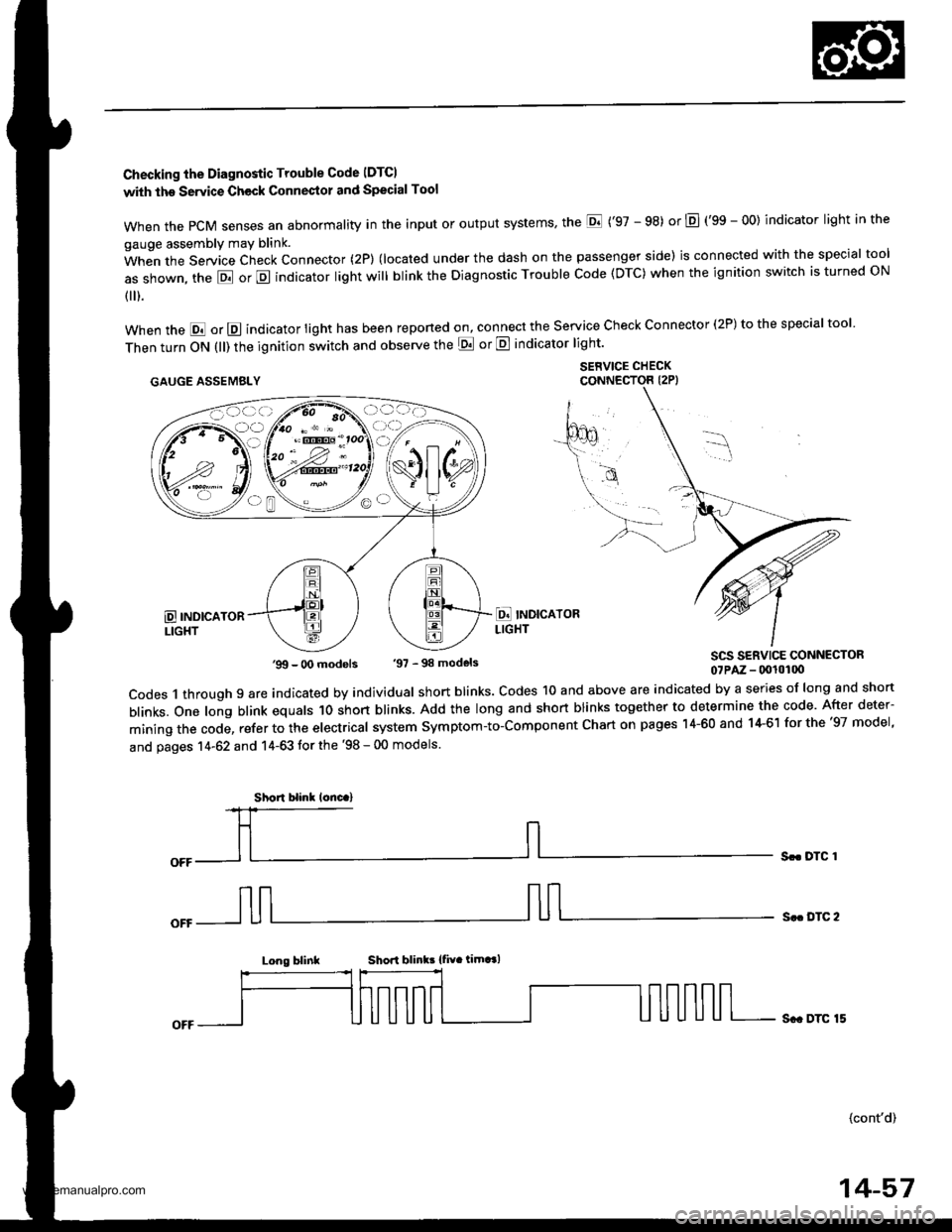
Checking the Diagnostic Trouble Code IDTCI
with the Servic€ Check Connestol and Special Tool
when the PcM senses an abnormality in the input or output systems' the E ('97 - 98) or E (gS - OO) indicator light in the
gauge assembly may blink.
When the Service Check Connector (2P) (located under the dash on the passenger side) is connected with the special tool
as shown, the E or E indicator light will blink the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) when the ignition switch is turned ON
{ ).
when the E or E indicator light has been reponed on, connect the service check connector (2P) to the special tool
Then turn ON (ll) the ignition switch and observe the E or E indicator light'
.AUGE AssEMaLY $1,"^f:tT"'ff,
SCS SERVICE CONNECTOR07PAz - (x!l0100
codes 1 through 9 are indicated by individual short blinks. codes 1o and above are indicated by a series of long and short
blinks. one long blink equals 1o short blinks. Add the long and short blinks together to determine the code. After deter-
mining the code, refer to the electrical system symptom-to-component chart on pages 14-60 and 14-61 for the '97 model,
and pages 14-62 and 14-63 tor the '98 - 00 models.
Sr. DTC 1
S.. DTC 2
Long blinkShori blink! {fiv. timt l
Sc. DTC 15
(cont'd)
'99 - O0 models '97 - 98 models
Short blinl lonc.)
14-57
www.emanualpro.com
Page 614 of 1395
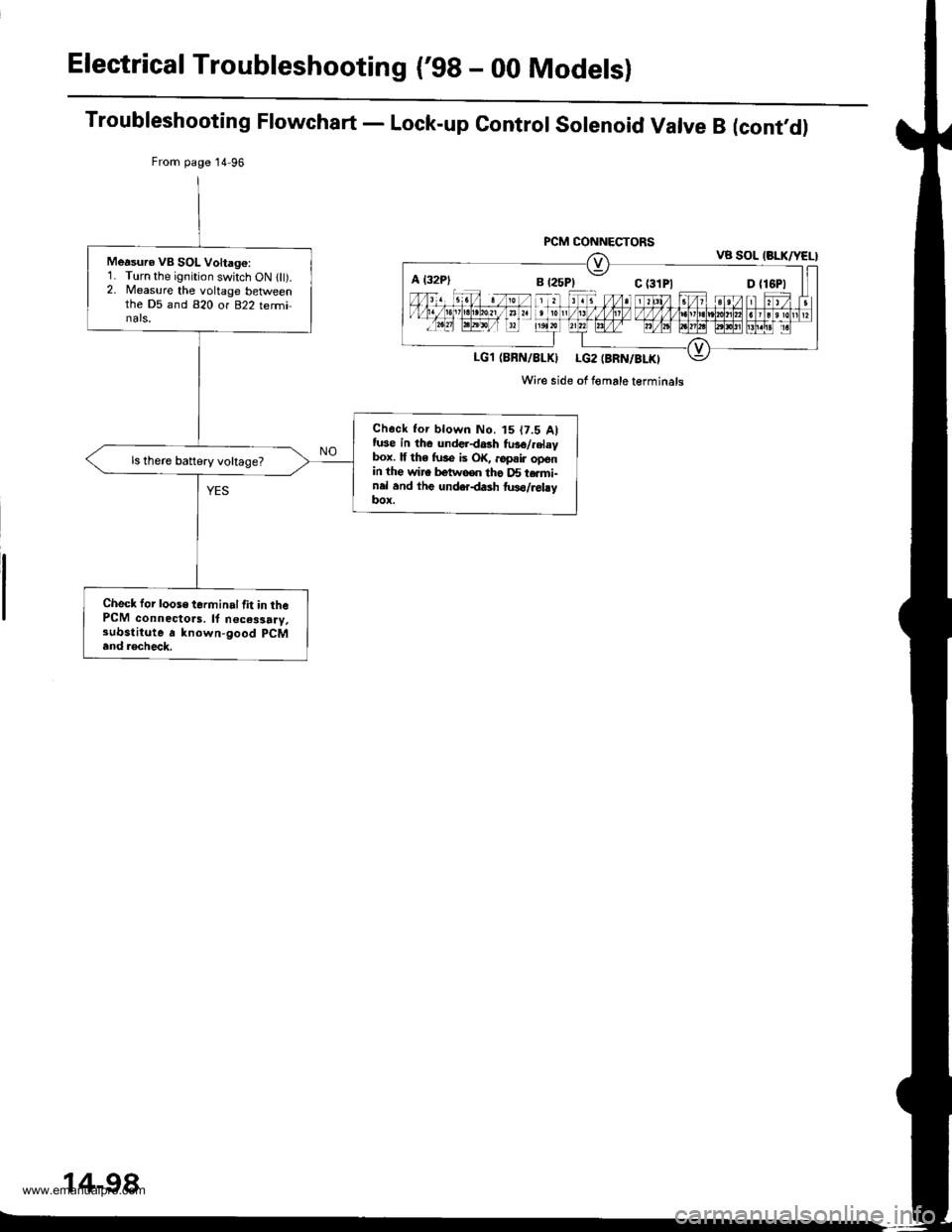
Electrical Troubleshooting ('98 - 00 Modelsl
Troubleshooting Flowchart - Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve B (cont,d)
From page 14 96
PCM CONNECTORSVB SOL (BLK/YEL}
LG1 (BBN/8LKI LG2 (BRN/BLKI
Wire side of Iomale terminals
Measuro VB SOL Voltago:1. Turn the ignition switch ON llt).2. Measure the voltage betlveenthe D5 and 820 or 822 terminals,
Check tor blown No. t5 (7.5 Alfuse in the underdash fu36/.elaybox. lf th6 fuse is OK, ..pair openin the wire betwooo tho D5 t.rmi-nel and thg underdash two/relayItox.
ls there battery voltage?
Check for loose terminal lit in thePCM connectors. ll n€ces3a.y,substitute a known-good pCM
and .€check.
A l32P)
14-98
www.emanualpro.com