1998 HONDA CIVIC PC box
[x] Cancel search: PC boxPage 1819 of 2189
How To Use This Manual
Circuit Schematics
oa
Each schematic represents one circult. A
circuit's wires and components are arranged
to show current flow, from power at the top of
the page, to ground, at the bottom.
Shared Circuits
Other circuits may share power or ground
terminals or wiring with the circuit shown. A
wire that connects one circuit to another, for
example, is cut short and has an arrowhead
at the end of it pointing in the direction of
current flow. Nelit to the anowhead is the
name o{ the circuil or comoonent which
shares that wiring. To quickly check shared
wiring, check the operation of a component it
serves. lf that component works, you know
the shared wiring is OK.
Connectors
All in-line and fuse box connectors are
numbered (C725, C416, etc.).
Component connectors are not numbered
but are identiJied by the name of the
component. lf a componenl has more than
one connector, each connector is assigned
a letter (A, B, C, etc.). Below most connector
numbers and comDonent names are
PHOTO and VIEW numbers. The PHOTO
number refers to a Dhoto in the back of the
book that shows lhe conneclor's location on
the car. The VIEW number refers to an
illustration in the back of the book that
shows the connector face, wire colors,
connector cavity numbers, and other details.
The connector cavity numbering sequence
begins at the top left corner oJ the connector
as seen from either of the viewooints shown
on page ffl . Disregard any numbers
molded into the connector housino.
Wires
Wires are identilied by the abbreviated
names of their colors; the second color rs the
color of the stripe. Wires are also identified by
their location in a connector. The number '2"
next to the male and female wire terminals at
C416, for example, means those terminals
join in cavity 2 of connector C416.
Symbols
A complete description of schematic
symbols begins on page | 8
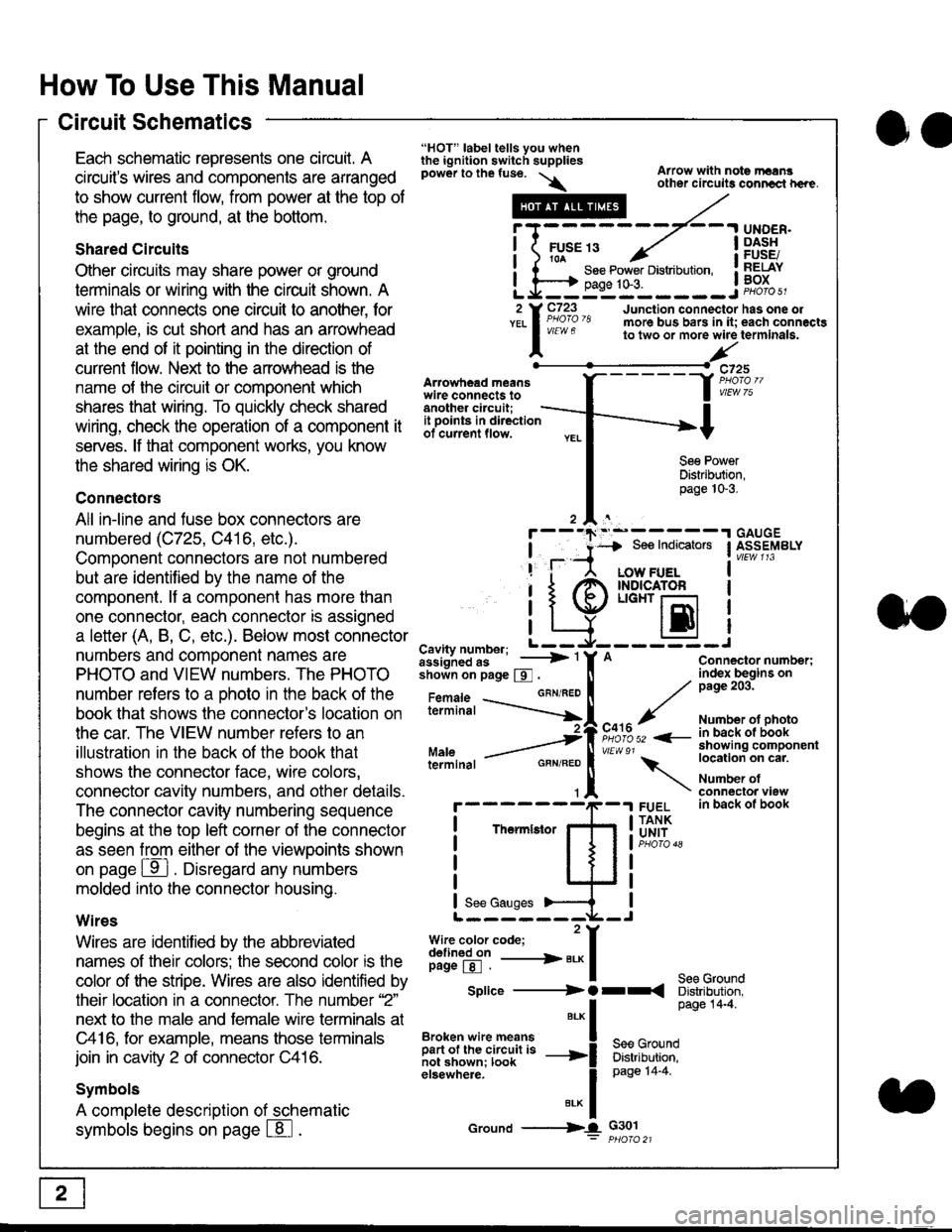
"HOT" label tells you whenthe ignition switch suppliespower to the fuse. \
Artowhead meanswire connects toanother circuit;
Arrow with note rErngother circuils conncct h€re.
it .a
llu":: ^,{ ii t See Power Distribution, .I t----t oaqe tO-3. IL*--:--------J2 Y C723 Junction connectorYEL I Pao'o'8 more bus bars in it;
I - " " to two or more wire
l,/
-t>?
See PowerDistribution,page 10-3.
UNDER.DASHFUSE/RELAYBOX
has one oleach connactgterminala.
it ooints in directionof current flow.
TheImletor
t_I
Cavity number; L ---
Jiili'iJi!--' -----> '
shoin on page S .
Maleterminal
L?*?l?,-
"'"'I
c725
vlEUt/ 75
Connector number;index begins onpage 203.
Number ot photoin back ol bookshowing componentlocation on cat.
Number ofconneclor viewin back of book
7
GBN/FEO
See Ground
Soe Indicators I ASSEMBLY
:-------J
LOW FUELINDICATOFLIGHT r-l
EI
A
"o'r"/PHOTO 52 <-
\
FUELTANKUNIT
Splice ---------) O rr
".* I Page 14'4'
IBroken wire means | --^ -
iar";J.'It,;,rJ;ii; -----i Bffi,Bili*l
elsewhere. I 0a0e tn-a
IBrK Icround --->lL c301: ptioro 21
Page 1821 of 2189
How To Use This Manual
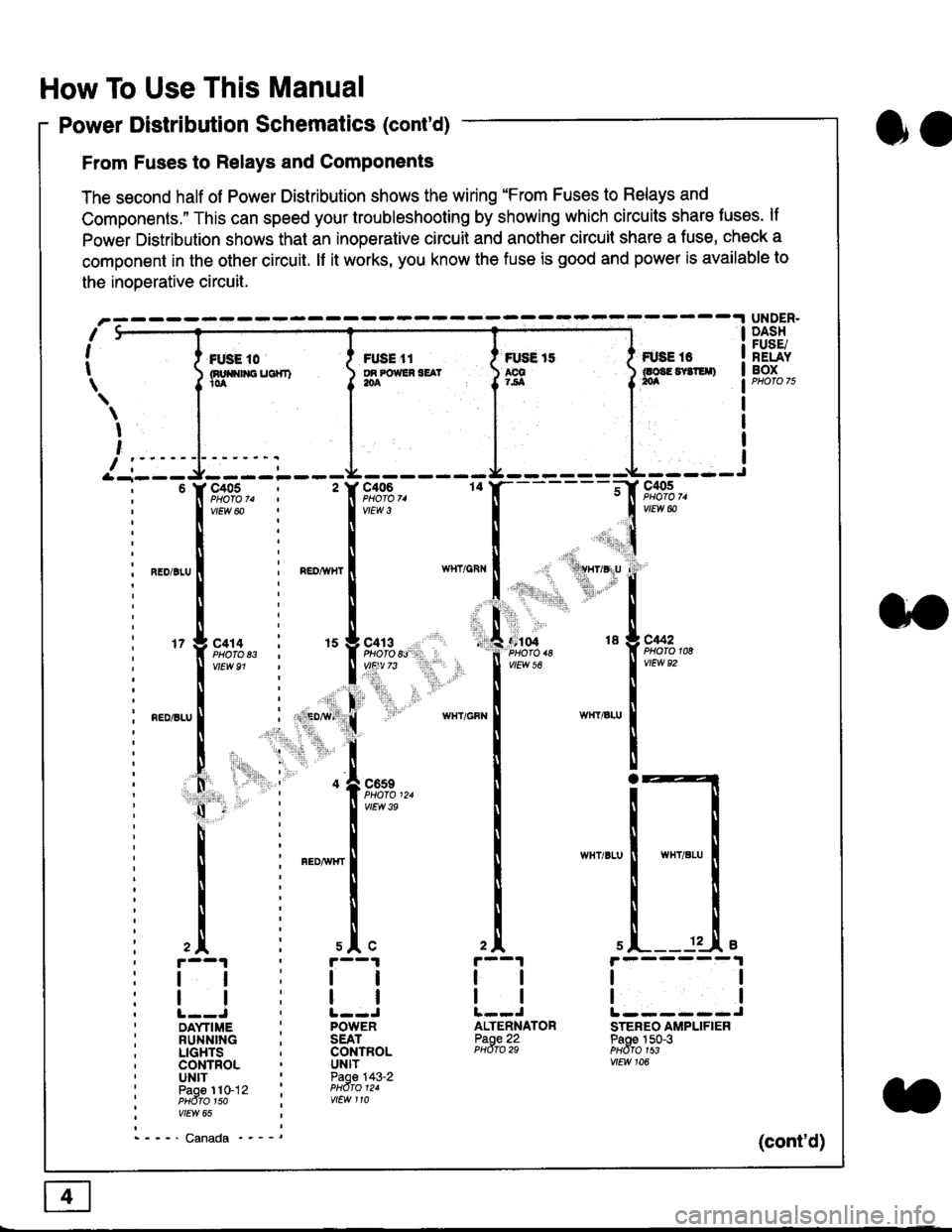
Power Distribution Schematics (cont'd)
From Fuses to Relays and Components
The second half of Power Distribution shows the wiring "From Fuses to Relays and
Components." This can speed your troubleshooting by showing which circuits share luses. lf
Power Distribution shows thal an inoperative circuit and another circuit share a fuse, check a
component in the other circuit. lf it works, you know the fuse is good and power is available to
the inoDerative circuit.
oa
UNDER.DASHFUSE/RELAYBOXI i *. to i ru..'.' l * tt I tust tt
){nuo$rouc}rr) }g*"""' }tS }ff***,
\
I
,
I-- - ----\&- -----J-------ir
9,s9:,.,
,.,'li"'"rr' ' 'rll$vryglu
:
]:l. ,' "'':r.,
,:ti. .:1,,.,
*_lu*'.
'71ffi"�
- -t**,-
vtEw &
04 18 g C442
2A
tl
12 .L e
tl
ALTENNATORPaoe 22PHdro 29
ll
tlL------JSTEREO AMPLIFIERPaoe 150-3PHdfo 1s3vtEw 106
121
'f,"c;93,. : '� f,t'ffi
lv'Ew6o ! 1,.",
l:lN'll
^.o,r.u I i ".o,*", I
l:t
l,l
u*,.11,2", i "l9*',g
11""" : l*'-
l:lnEDisLu
|
; . ED,w' (
I'lP:ll
! " : .1".,9t3
q - '
I v'Ew3e
h;ll
l:ll
I : FED^rir{r
i
l:i
tii
,.L i slc
r--1 : r--1
tt:ll
ltlllt--J ' l--JDAYTIME : POWERRUNNING ; SEATLIGHTS . CONTROLCONTROL . UNITUNIT ' Paoe 143-2paoe 1to-j2 t PHdro t2.PHdTo 1so i wEw 110vtEw 65
- - -' Canada '_ _ _(cont'd)
Page 1824 of 2189

Connector Views
To see the configuration of a connector's cavities, look up its view number in the Connector
View section in the back of the book. Each view includes the color of the connector, where it
is located, and what it connects to.
Use the Connector Views to help locate the proper cavity when you need to probe a
connector. lt can be especially helpful if the connector has more than one wire of the same
cotor.
Connector views can also be used to help diagnose multiple symptoms in separate circuits
which could be caused by a single problem in a connector shared by those circuits. Here's
how:
1. Pick one of the multiple symptoms and look up the schematic for that circuit.
2. Make a list of all the in-line and fuse box connectors in that schematic (include page
numbers).
3. Then, in the Connector View section, look up each connector on your list to see il circuits
related to the other symptoms run through one of them. lf they do, inspect that connector
for the oroblem.
Example: The blower, rear window defogger, and the windshield wiper don't work. List all
in-line and fuse box connectors in the blower controls circuit and then check the Connector
View section (sample below). You find that C324 is common to the rear window defogger
circuit and wiper/washer circuit, so you inspect C324 and find the problem, bent terminals.
5.
6.
7.
1.
2.
WHT (Blower controls)
YEUBLU (Rear window
defogger)
BLK,ryVHT (Starting)
BLU/YEL(Wiper/washe0
8LU (Wiper/washed
BLfiEL (lgnition)
WHT/BLU (ABS)
Connector Views (cont'd)
21. C324
Brown
Behind left kick panel- Connects left engine compartry'ent wire harness to
main wire harness
ll,ll,
567
Page 1825 of 2189
How To Use This Manual
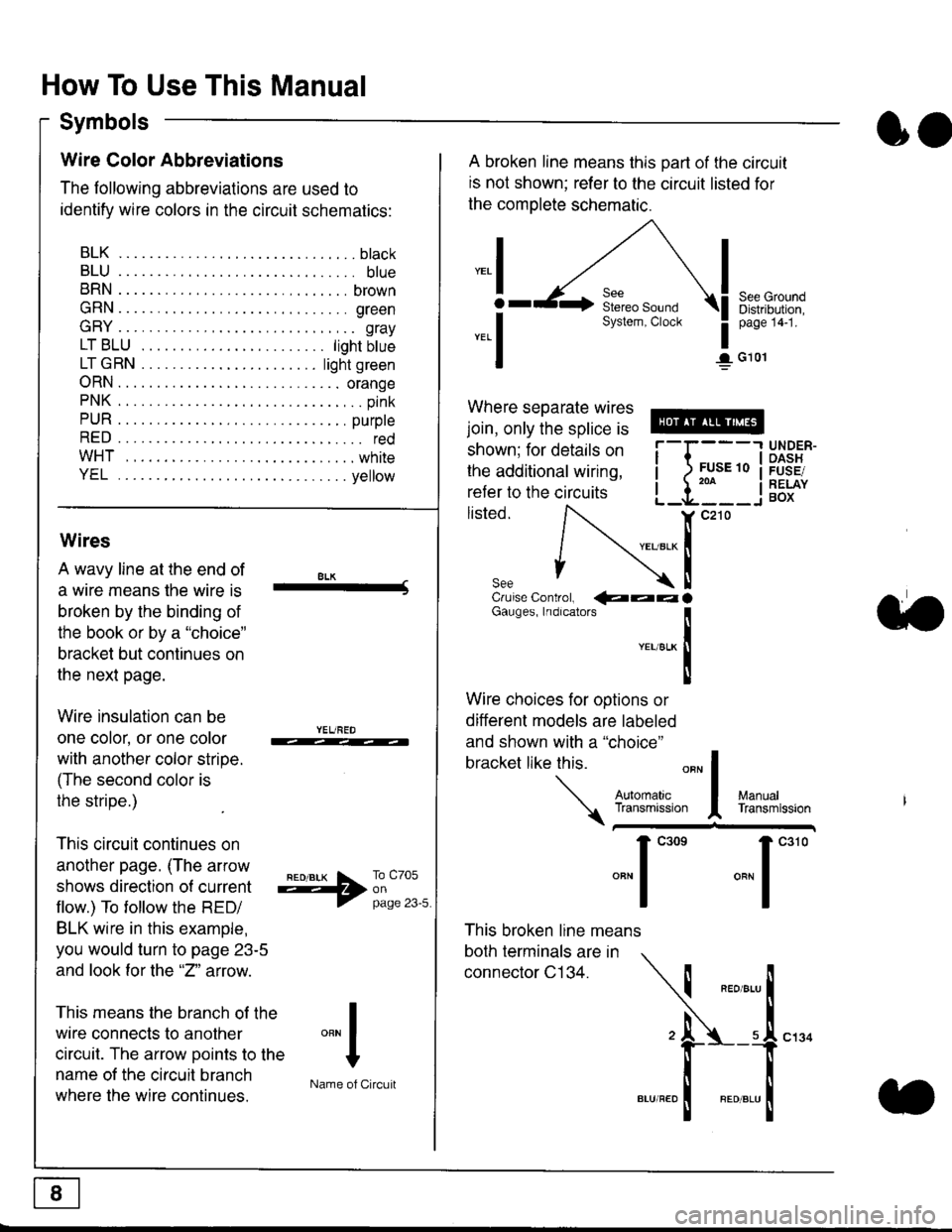
Symbols
oo
Wire Color Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used to
identify wire colors in the circuit schematics:
BLK.... .........b|ack
BLU.... ......... blue
BRN.... ,....... brown
GRN.... ........ green
GRY.... ......,.. gray
LTBLU . .....lightbtue
LTGRN. ....lightgreen
ORN.... ....... orange
PNK .... .......,.. pink
PUR .... ........ purple
RED .... .......... red
WHT... .........white
YEL .... ........ yellow
A broken line means this part of the circuit
is not shown; refer to the circuit listed for
the complete schematic.
"ral
o
-.1
See GroundDistribution,page 141.
I G101
Where separate wires
join, only the splice is
shown; for details on
the additional wiring,
refer to the circuits
listed.ili::i
{[
UNDER-OASHFUSE/RELAYBOX
Wires
A wavy line at the end of
a wire means lhe wire is
broken by the binding of
the book or by a "choice"
bracket but continues on
the next page.
Wire insulation can be
one color, or one color
with another color stripe.
(The second color is
the stripe.)
This circuit continues on
another page. (The arrow
shows direction o{ current
flow.) To tollow the RED/
BLK wire in this example,
you would turn to page 23-5
and look for the "2" anow.
This means the branch of the
wire connects to another
circuit. The arrow Doints to the
name of the circuit branch
where the wire continues.
8LK-Cruise Control, €�aaaGauges, Indrcalors
!YEUsLK
Ttl
Wire choices for options or
different models are labeled
and shown with a "choice"
bracket like this.
This broken line means
both terminals are in
connector C134.
a.
+##l:i""lManuallransmission
ryil;::,
.""1
""'
"""1".'0
I
""^l
:-lName of Circuit
Page 1829 of 2189

In the "OHMS" range, the DVOM will measure
resistance between two points along a circuit.
Low resistance means good continuity.
Diodes and solid-state devices in a circuit can
make a DVOM give a false reading. To check
a reading, reverse the leads, and take a
second reading. lf the readings differ, the
component is affecting lhe measurement.
Jumper Wire
Use a jumper wire to bypass an open circuit.
A iumper wire is made up ot an in-line fuse
holder connected to a set of test leads. lt
should have a five amoere fuse. Never
connect a jumper wire across a short circuit.
The direct battery short will blow the fuse.
Short Finder (Short Circuit Locater)
Short finders are available to locale shorts to
ground. The short tinder creates a pulsing
magnetic field in the shorted circuit whlch you
can follow to the location of the short. lts use
is explained on page 15.
SHORT FINDER
To ordei any test equipment shown above,
contact your local tool supplier. For a list of
suppliers and tool numbers, refer to Honda
Required Special Tools and Equipment
Service Bulletin.
How To Use This Manual
Test Equipment (cont'd)
oa
Troubleshooting Precautions
Before Troubleshooting
1. Check the main fuse and the fuse box.
2. Check the battery for damage, state of
charge, and clean and tight connections.
CAUTION:
. Do not quick-charge a battery unlers
the battery ground cable has been
disconnected, or you will damage the
alternator diodes.
. Do not attempt to crank the engine wlth
the ground cable disconnected or you
will severely damage the wiring.
While You're Working
1. Make sure connectors are clean, and have
no loose terminals or receptacles.
2. Make sure lhat connectors without wire
seals are packed with dielectric (silicone)
grease. Part Number: 08798-9001 .
Pack wllh dlelectrlc (sillcons) greass
When connecting a connector, push it until it"clicks" into place.
Do not pull on the wires when
disconnecting a connector. Pull
only on the connector houslngs.
Most circuits Include solid-state
devlces. Test the voltages In these
circuits only with a lo-megaohm or
higher impedance digital multlm6ter.
Never use a test light or analog meter
on chcuits that contain solld-state
devices. Damage to the devices
may result.
oo
Page 1831 of 2189
How To Use This Manual
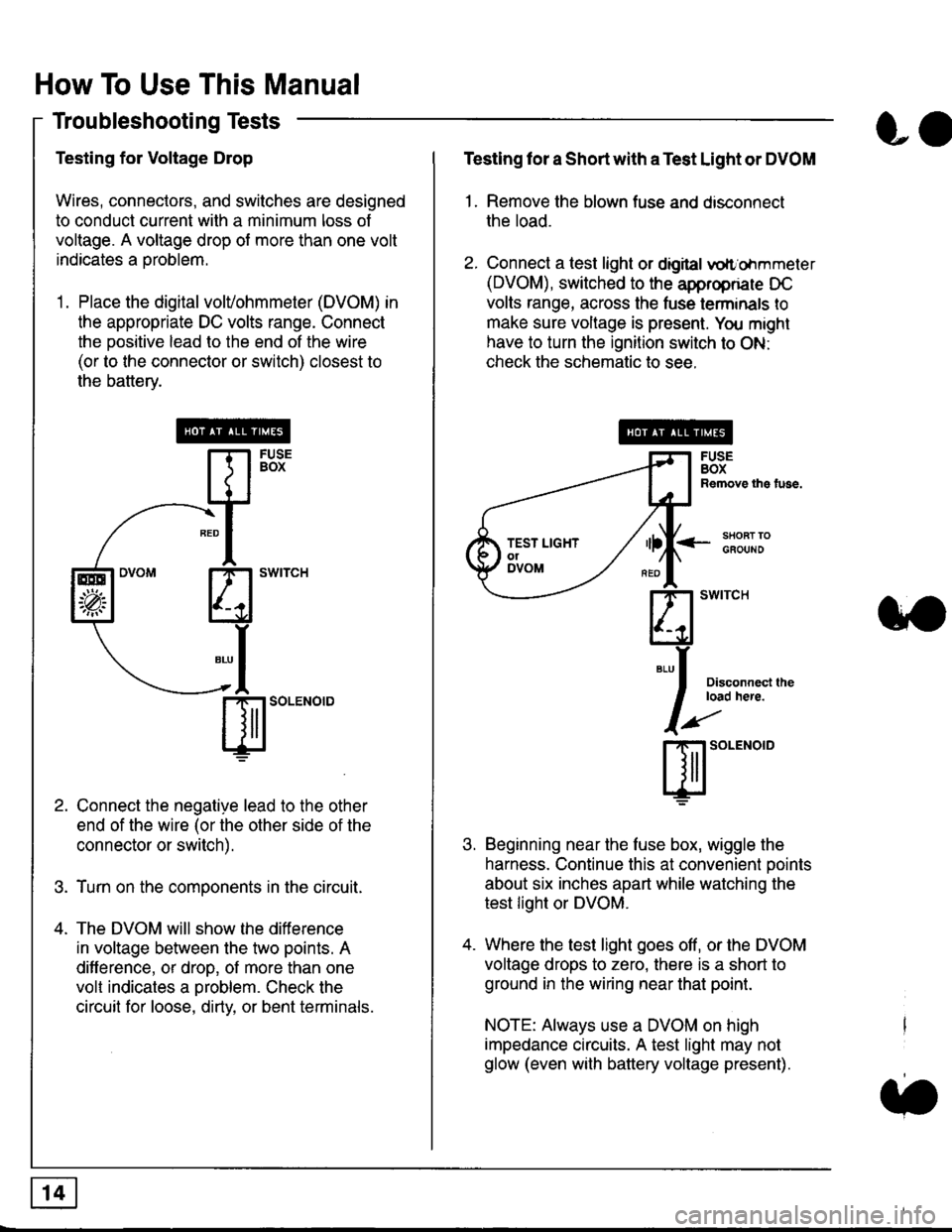
Troubleshooting Tests
Testing for Voltage Drop
Wires, connectors, and switches are designed
to conduct current wilh a minimum loss of
voltage. A voltage drop of more than one volt
indicates a Droblem.
'1. Place the digital volVohmmeter (DVOM) in
the appropriate DC volts range. Connect
the positive lead to the end of the wire
(or to the connector or switch) closest to
the bafterv.
Connect the negative lead to the other
end of the wire (or the other side of the
connector or switch).
Turn on the components in the circuit.
The DVOM will show the difference
in voltage between the two points. A
difference, or drop, of more than one
volt indicates a oroblem. Check the
circuit for loose, dirty, or bent terminals.
co
Testing lor a Short with a Test Light or DVOM
1. Remove the blown fuse and disconnect
the load.
2. Connect a test light or digital
oltr'ohmmeter
(DVOM), switched to the appropnare DC
volts range, across the tuse lerminals to
make sure voltage is present. You might
have to turn the ignition switch to ON:
check the schematic to see.
<-s80RT TOGFOUNO
Disconnecl lheload here.
Beginning near the luse box, wiggle the
harness. Continue this at convenient ooints
about six inches apart while watching the
test light or DVOM.
Where the test light goes off, or the DVOM
voltage drops to zero, there is a short to
ground in the wiring near that point.
NOTE: Always use a DVOM on high
impedance circuits. A test light may not
glow (even with battery voltage present).
3'�'
ffito.'"o'o
.t.
TEST LIGHTolDVOM
Page 1832 of 2189
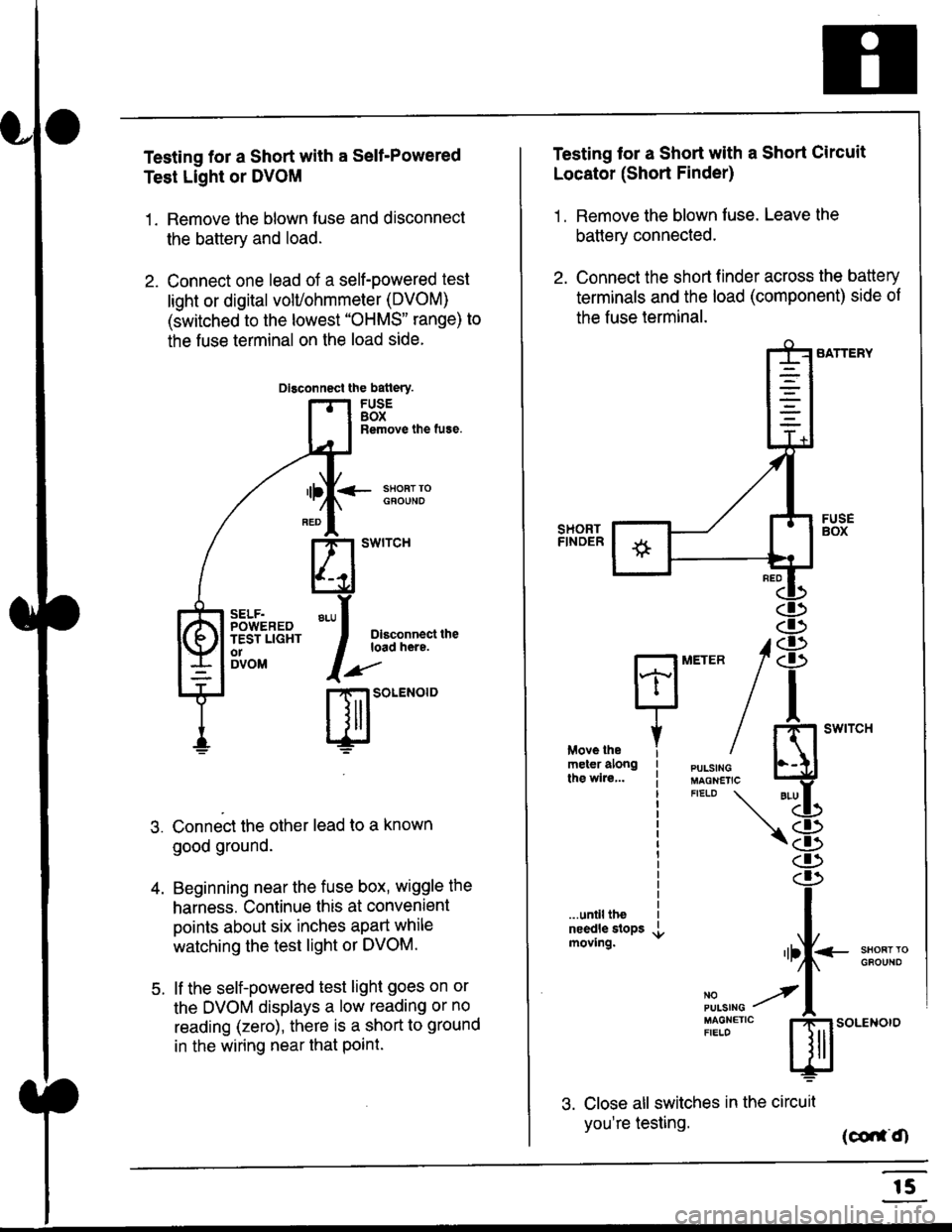
Testing for a Short with a Sell-Powered
Test Light or DVOM
1. Remove the blown fuse and disconnect
the battery and load.
2. Connect one lead of a self-powered test
light or digital volUohmmeter (DVOM)
(switched to the lowest "OHMS" range) to
the fuse terminal on the load side.
Dlsconnect the batlery.
FUSEBOXRemove the fuse.
<- ssoRr rociouNo
Dlsconnect theload here.
.)"'
r| SOLENOID
Connect the other lead to a known
good ground.
Beginning near the fuse box, wiggle the
harness. Continue this at convenient
points about six inches apart while
watching the test light or DVOM.
lf the self-powered test light goes on or
the DVOM displays a low reading or no
reading (zero), there is a short to ground
in the wiring near that Point.
SELF.POWEREDTEST LIGHTo1DVOM
4.
5.
Testing tor a Short with a Short Circuit
Locator (Short Finder)
1 . Remove the blown fuse. Leave the
battery connected.
2. Connect the short finder across the battery
terminals and the load (component) side of
the fuse terminal.
SATTERY
SHORTFINOER
FUSEBOX
PULSINGMAGNETICFIELD \
NOPUISING
\
I swtrcH
I
<- stl
Kl"I- -.T.1
"'at
\8
.r.
rlll<
,l
m
...unilltheneedle slopsmoving.SHOFTTGFOUNO'llt
No --tPULS|NG z
MAGNETTC IFIELD ISoLENOTO
3. Close all switches in the circuil
you're testing. (co,f,O
r5
Page 1833 of 2189

How To Use This Manual
Troubleshooting Tests (cont'd)
4. Turn on the short finder. This creates a
pulsing magnetic field around the wiring
between the fuse box and the short.
5. Beginning at the fuse box, slowly move
the short finder along the circuit wiring.
The meter will show current Dulses
through sheet metal and body trim. As
long as the meter is between the fuse and
lhe short, the needle will move with each
current pulse. Once you move the meter
past the point of the short, the needle will
stop moving. Check the wiring and
connectors in this area to locate the cause
of the short.
co