1998 HONDA CIVIC Brake master cylinder
[x] Cancel search: Brake master cylinderPage 1176 of 2189
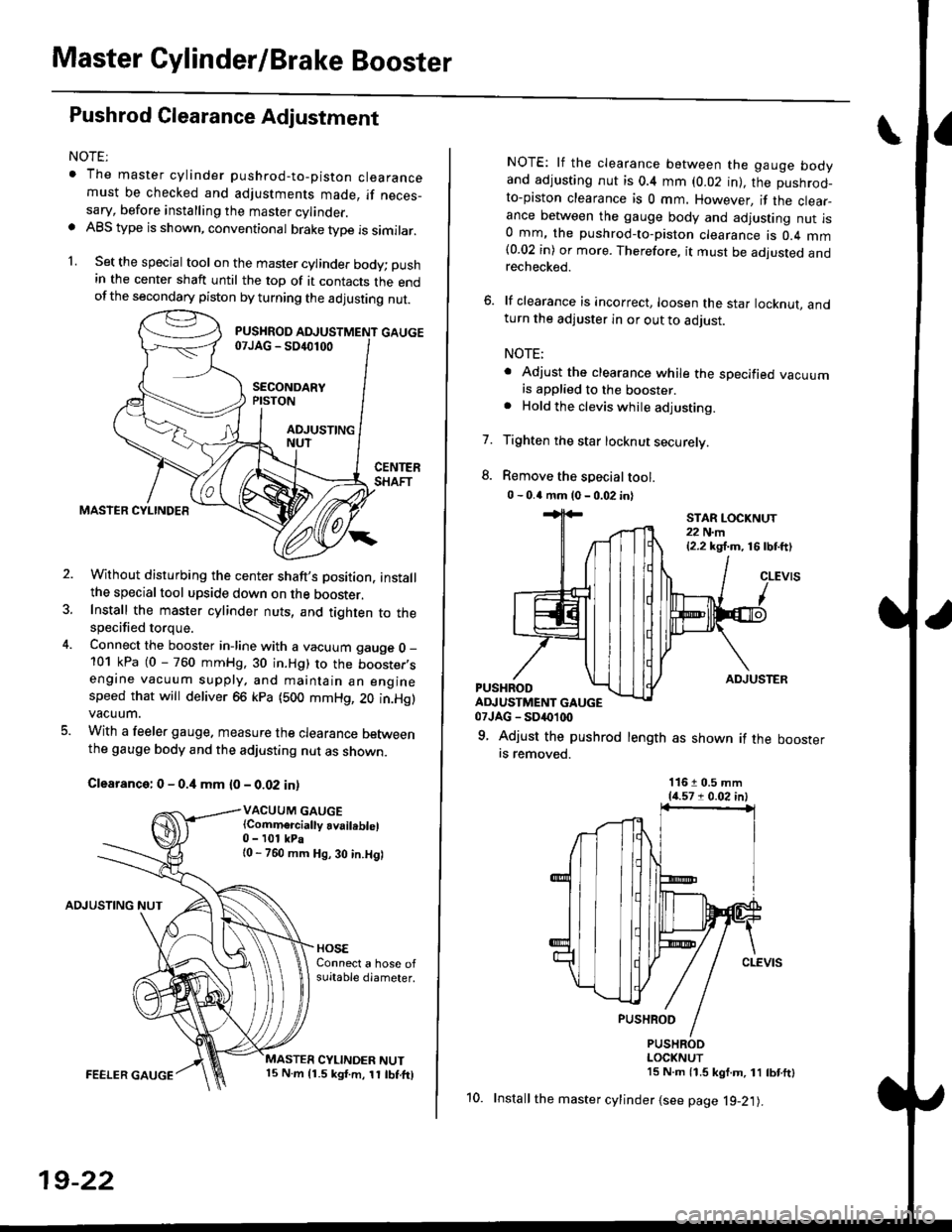
Master Cylinder/Brake Booster
Pushrod Glearance Adjustment
NOTEr
. The master cylinder pushrod-to-piston clearancemust be checked and adjustments made, if neces_sary, before installing the master cylinder.. ABS type is shown, conventional brake type is similar.
1. Set the special tool on the master cylinde. body; push
in the center shaft until the top of it contacts the endofthe secondary piston by turning the adjusting nut.
Without disturbing the center shaft's Dosition, installthe specialtool upside down on the booster.Install the master cylinder nuts, and tighten to thespecified torque.
Connect the booster in-line with a vacuum gauge O _
101 kPa (0 - 760 mmHg, 30 in.Hg) to the booster,sengine vacuum supply, and maintain an enginespeed that will deliver 66 kpa (500 mmHg, 20 in.Hg)vacuum.
With a feeler gauge. measure the clearance Detweenthe gauge body and the adjusting nut as shown.
Clearance: 0 - 0.4 mm {0 - 0.02 in)
VACUUM GAUGE(Comm€rcially availeblel0 - 101 kPa{0 - 760 mm Hg, 30 in.Hg)
AOJUSTING NUT
FEELER GAUGE
19-22
10.
NOTE: lf the clearance between the gauge bodyand adjusting nut is 0.4 mm (0.02 in), the pushrod-to-piston clearance is 0 mm. However, if the clear_ance between the gauge body and adjusting nut is0 mm, the pushrod-to-piston clearance is 0.4 mm(0.02 in) or more. Therefore, it must be adjusted andrechecked.
6. lf clearance is incorrect, loosen the star locknut, andturn the adjuster in or out to adjust.
NOTE;
. Adjust the clearance while the specified vacuumis applied to the booster.. Hold the clevis while adjusting.
Tighten the star locknut securely.
Remove the special tool.
0 - 0.4 mm (0 - 0.02 in)
7.
ADJUSTERPUSHRODADJUSTMENT GAUGE07JAG - SD('1(x)
9. Adjust the pushrod length as shown if the boosterrs removed.
STAR LOCKNUT22 N.m{2.2 kg,f.m, 16lbtft)
11610.5 mm{{.571 0.02 in)
PUSHRODLOCKNUT15 N.m 11.5 kgf.m, 11 tbtftl
Install the master cylinder {see page l9-21).
Page 1177 of 2189

Brake Booster InsPection
FunctionalTest
1. With the engine stopped, depress the brake pedal
several times to deplete the vacuum reservoir, then
depress the pedal hard and hold it for 15 seconds lf
the pedal sinks' either the master cYlinder is
bypassing internally, or the brake system (master
cylinder. lines. modulator, proportioning control
valve, or caliPer) is ieaking.
2. Start the engine with the pedal depressed lf the
pedal sinks slightly, the vacuum booster is operating
normally. lf the pedal height does not vary, the
booster or check valve is faultY.
3. With the engine running. depress the brake pedal
lightly. Apply just enough pressure to hold back
automatic transmission creep. lf the brake pedal
sinks more than 25 mm (1.0 in.) in three minutes,
the master cvlinder is faulty. A slight change in
pedal height when the A'lC compressor cycles on
and off if normal. (The A/C compressor load
changes the vacuum available to the booster')
Leak Test
1. Depress the brake pedal with the engine running.
then stop the engine. lf the pedal height does not
vary while depressed for 30 seconds, the vacuum
booster is OK. lf the pedal rises. the booster is
faulty.
2, With the engine stopped, depress the brake pedal
several times using normal pressure When the
Dedal is first depressed, it should be low On con-
secutive applications, the pedal height should grad-
uallv rise. lf the pedal position does not vary, checK
the booster check valve.
l./
19-23
Booster Check Valve Test
1. Disconnect the brake booster vacuum hose at the
booster.
2. Stan the engine and let it idle. There should be vac-
uum. lf no vacuum is available, the check valve is
not working properly. Replace the brake booster
vacuum hose and check valve, and retest.
BRAKE BOOSTERVACUUM HOSE(Check valve
built-in)
Page 1179 of 2189
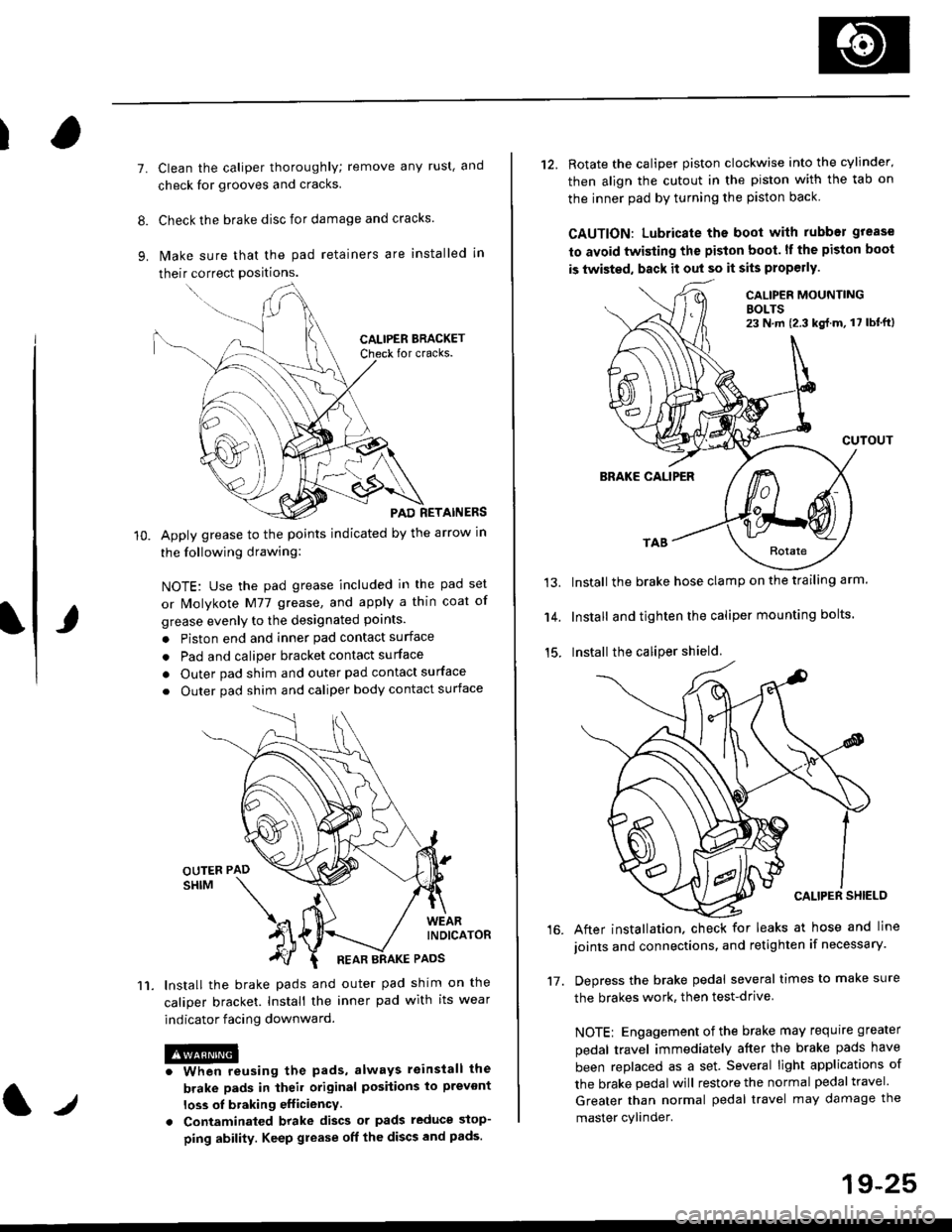
I
7.
11.
Clean the caliper thoroughly; remove any rust, and
check for grooves and cracks.
Check the brake disc for damage and cracks.
lvlake sure that the pad retainers are installed in
their correct positions.
PAD RETAINERS
Apply grease to the points indicated by the arrow in
the following drawing:
NOTE: Use the pad grease included in the pad set
or lMolykote M77 grease, and apply a thin coat of
grease evenly to the designated points.
. Piston end and inner pad contact surface
. Pad and caliper bracket contact surface
. Outer pad shim and outer pad contact surface
. Outer pad shim and caliper body contact surface
lnstall the brake pads and outer pad shim on the
caliper bracket. Install the inner pad with its wear
indicator facing downward.
@iwhen reusing the pads, always reinstall the
brake pads in iheil original posiiions lo prevont
loss ol braking efficiency
. Contaminaled brake discs or pads reduce stop-
ping ability. Keep grease off the discs and pads.
t./
19-25
12. Rotate the caliper piston clockwise into the cylinder'
then align the cutout in the piston with the tab on
the inner pad by turning the piston back
CAUTION: Lubricate ths boot with rubber grease
to avoid twisting the piston boot. lf the piston boot
is twisted, back it out so it sits properly.
CALIP€R MOUNTINGBOLTS23 N,m {2.3 kg{.m, 17 lbt'ft)
13.
14.
15.
CUTOUT
BRAKE CALIPER
Install the brake hose clamp on the trailing arm.
Install and tighten the caliper mounting bolts.
Install the caliper shield.
After installation. check for leaks at hose and line
joints and connections, and retighten if necessary.
Depress the brake pedal several times to make sure
the brakes work, then test-drive
NOTE: Engagement of the brake may requrre greater
pedal travel immediately after the brake pads have
been replaced as a set. Several light applications of
the brake pedal will restore the normal pedal travel.
Greater than normal pedal travel may damage the
master cylinder.
16.
17.
Page 1193 of 2189
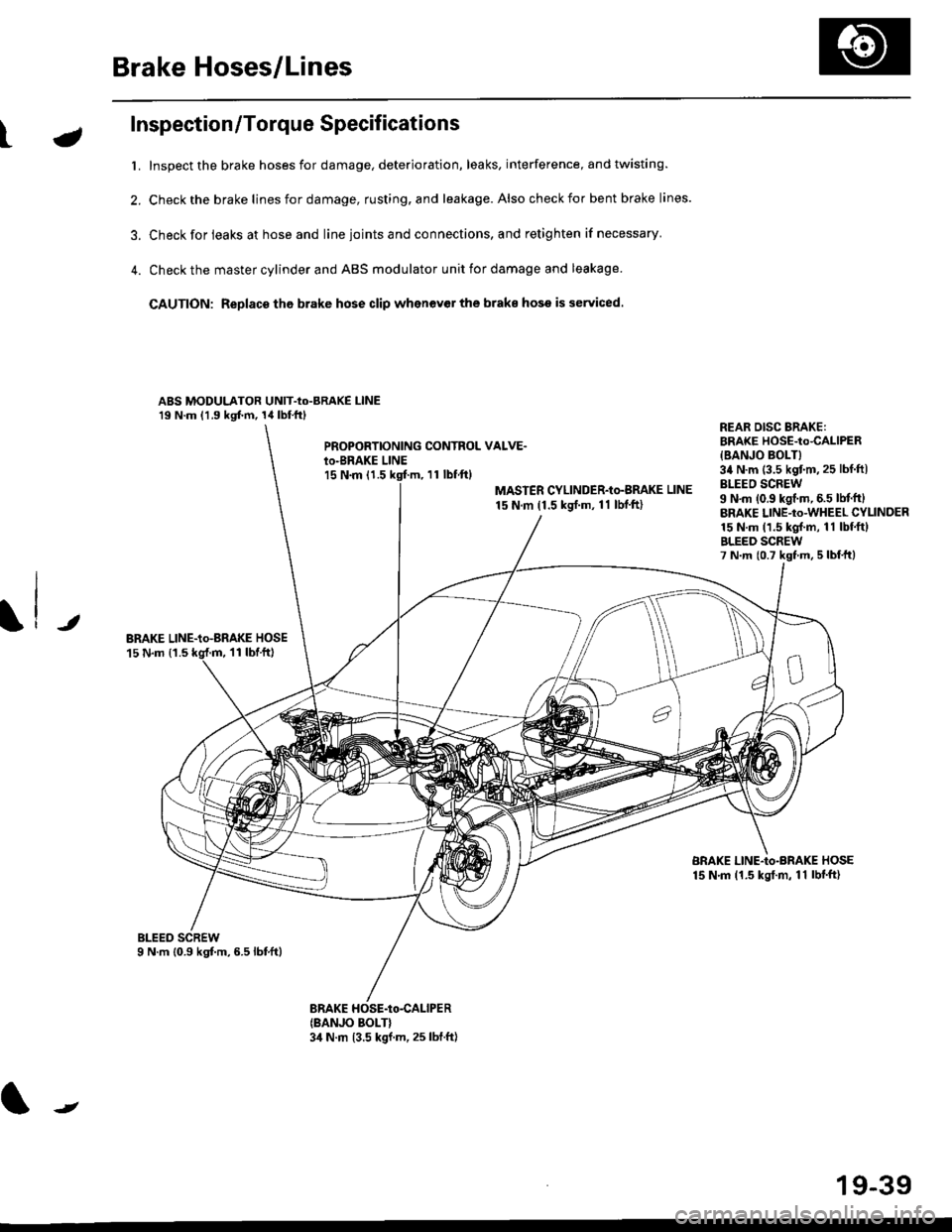
Brake Hoses/Lines
LJ
Inspection/Torque Specifications
t. Inspect the brake hoses for damage, deterioration, leaks, interference, and twisting.
2. Check the brake lines for damage, rusting. and leakage. Also check for bent brake lines.
3. Check for ieaks at hose and line ioints and connections, and retighten if necessary'
4. Check the master cylinder and ABS modulator unit for damage and leakage
CAUTION: Replace tho brake hose clip whenev€r the brake hose is serviced.
ABS MODULATOR UNIT-Io-BRAKE l-lNE19 N.m (1.9 kgf.m, 14lbl.ftl
PROPOBTIONING CONTROL VALVE.io-BRAKE LINEl5 N.m (1.511 tbf.ftl
MASTER CYLINDER-Io-BMKE LINE
15 N.m (1.5 ksrf.m, 11 lbf'ft)
REAR DISG BRAKE:BRAKE HOSE-to4ALlPER
{BANJO BOLT}34 N.m (3.5 kgtm,25 lbf ftlBLEEO SCREW9 N'm (0.9 kgf.m, 6.5 lM.ftlBRAKE LINE-to-WHEEL CYLINDER15 N.m (1.5 kgl.m, 11 lbf.ftlBLEED SCREW7 N.m {0.7 kst m, 5 lbf,ttl
JBRAKE LINE-io-aRAKE HOSE15 N.m {1.511 tbtft)
BRAKE LINE-Io-BRAKE HOSE15 N.m (1.5 kgt.m, 11 lbf'ft)
(BANJO BOLT}3,1 N.m 13.5 kgf.m, 25 lbf.ft)
J
19-39
Page 1201 of 2189
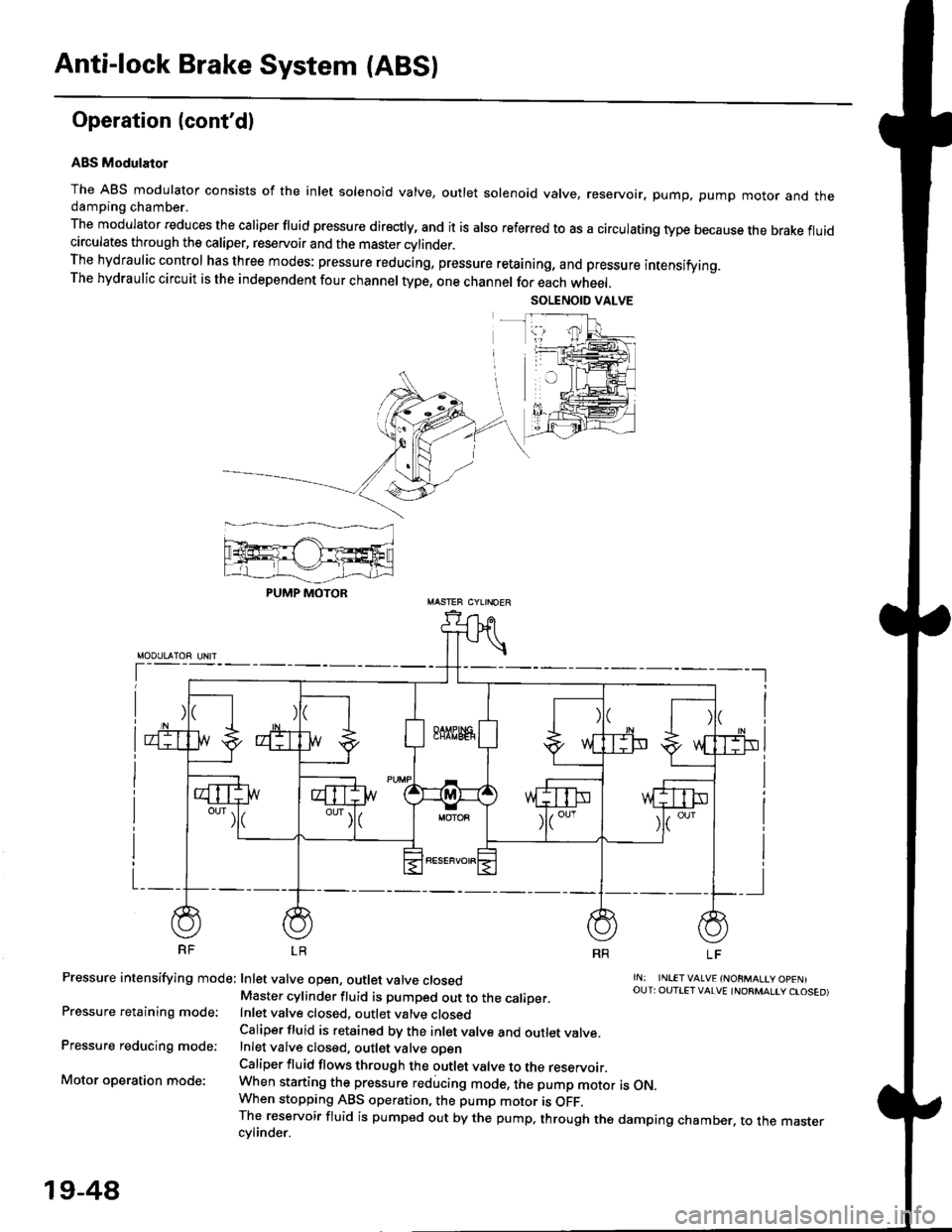
Anti-lock Brake System {ABS)
Operation (cont'dl
ABS Modulator
The ABS modulator consists of the inlet solenoid valve, outlet solenoid valve, reservoir, pump, pump motor and thedamping chamber.
The modulator reduces the caliper fluid pressure directly, and it is also referred to as a circulating type because the brake fluidcirculates through the caliper, reservoir and the master cylinder.The hydraulic control has three modes: pressure reducing, pressure retaining, and pressure intensifying.The hydraulic circuit is the independent four channel type, one channel for each wheel.
RF LR
Pressure intensifying mode: Inlet valve open, outlet valve closed
Pressure retaining mode:
Pressure reducing mode:
Motor operation mode:
rN: INLETVALVE {NORMALtY OpENIOUT: OUTIET VALVE {NORMALIY CTOSED)Master cylinder fluid is pumped out to the caliDer.Inlet valve closed, outlet valve closedCaliper fluid is retained by the inlet valve and outlet valve.Inlet valve closed, outlet valve oDenCaliper fluid flows through the outlet valve to the reservoir.When starting the pressure reducing mode, the pump motor is ON.When stopping ABS operation, the pump motor is OFF.The reservoir fluid is pumped out by the pump, through the damping chamber, to the mastercvlinder.
PUMP MOTOR
19-48
Page 1208 of 2189

tJ
t\
Kickback
1. The motor operates when the ABS is functioning, and the fluid in the reservoir is forced out to the master cylinder
causing kickback at the brake pedal.
2. TheABScontrol unit operates the solenoid valve when the brake pedal is released afterthe initial diagnosis Youmay
hear the faint solenoid valve operation sound at this time. but it is normal.
Pump Motor
1. The pump motor operates when the ABS is functioning
2. The ABS control unit checks the pump motor operation during acceleration. You may hear the faint operation sound
at this time. but it is normal.
Brake Fluid Replacament/Air Blsading
1. Brake fluid replacement and air bleeding procedures are the same as for conventional brakes
Troubleshooting
1. The troubleshooting flowcharts explain the procedures on the assumption that the cause of the problem is still pre-
sent and the ABS indicator light is still on.
Note that troubleshooting following the flowchart when the ABS indicator light does not come on can result in incor-
rect judgment.
2. Ouestion the customer about the conditions when the problem occurred, and try to reproduce the same conditions
for troubleshooting.
self,diagnosis is made at various times such as the initial diagnosis, except ABS control. during ABS control, during
acceleraiion, during the specified vehicle speed, etc. Therefore, the symptom cannot be checked unless the check
conditions match with the problem conditions
3. When the ABS indicator light does not come on during the test drive, but the troubleshooting is performed based on
the DTC, check for the loose connectors. poor contact of the terminals, etc, before troubleshooting.
4. After troubleshooting, erase the DTC and test-drive the car. Be sure that the ABS indicator light does not come on.
5. The connector illustrations show the female connectors with a single outline and the male connectors with a double
ouflrne.
6. The connector terminal cavities containing female terminals are always numbered by looking at the connector from
the wire side. and the cavities containing male terminals are always numbered by looking at the connector from the
terminal side.
r'
19-55
Page 1969 of 2189

Brake System Indicator Light (cont'd)
- How the Circuit Works
The brake system indicator light comes on to alert
the driver that the parking brake is applied, or that
the brake fluid level is low. lt also comes on as a
bulb test when the engine is cranked.
Parking Brake
With the ignition switch in ON (ll) or START (lll),
voltage is applied through fuse 25 to the brake
system light. When you apply the parking brake, the
switch closes and provides a ground for the light.
The light then comes on to remind you that the
parking brake is applied.
Brake Fluid Level
With the ignition switch in ON (ll) or START (lll),
voltage is applied through fuse 25 to the brake
system light. lf the brake fluid level is low, the brake
fluid level switch closes, providing ground to the
circuit. The brake system light then comes on,
alerting the d verto a low brake fluid level in the
brake master cylinder. (Check brake pad wear
before you add fluid).
Bulb Check
With the ignition switch in START (lll) and clutch
pedal depressed or A'lT gear selector in PARK (P)
or NEUTRAL (N), voltage is applied through fuse 31
to the brake bulb check circuit. The brake bulb
check circuit closes, allowing current to flow through
the brake system light and bulb check circuit to
ground. The brake system light then comes on to
test the bulb.
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
71-2
a
\fa